Exploring the Effects of a Mediterranean Diet and Weight Loss on the Gut Microbiome and Cognitive Performance in Older, African American Obese Adults: A Post Hoc Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
Intervention Description
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Stool and Blood Collection
2.2.2. DNA Extraction, Library Prep, and Sequencing
2.2.3. Basic Data Processing with DADA2
2.2.4. Differential Analysis of Microbial Taxa
2.2.5. Alpha Diversity Analyses
2.2.6. Beta Diversity/Dissimilarity Analyses
2.2.7. Butyryl-CoA CoA-Transferase Gene (BcoA)
2.2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.2.9. Mediation Analysis
3. Results
Mediation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2022 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 18, 700–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespa, J.; Armstrong, D.M.; Medina, L. Demographic Turning Points for the United States: Population Projections for 2020 to 2060; U.S. Department of Commerce, Economics and Statistics Administration, U.S. Census Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. Available online: https://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2020/demo/p25-1144.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Rajan, K.B.; Weuve, J.; Barnes, L.L.; McAninch, E.A.; Wilson, R.S.; Evans, D.A. Population estimate of people with clinical Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment in the United States (2020–2060). Alzheimer’s Dement. 2021, 17, 1966–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nianogo, R.A.; Rosenwohl-Mack, A.; Yaffe, K.; Carrasco, A.; Hoffmann, C.M.; Barnes, D.E. Risk Factors Associated With Alzheimer Disease and Related Dementias by Sex and Race and Ethnicity in the US. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, S.; Matthews, F.E.; Barnes, D.E.; Yaffe, K.; Brayne, C. Potential for primary prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: An analysis of population-based data. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, M.-H.; Liu, J.-L.; Nguyen, U.-S.D.T. Trends in Diet Quality by Race/Ethnicity among Adults in the United States for 2011–2018. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Sun, D. Adherence to Mediterranean diet and risk of developing cognitive disorders: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaugler, J.; James, B.; Johnson, T.; Scholz, K.; Weuve, J. 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016, 12, 459–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhra, V.; Galappaththy, S.L.; Bulchandani, S.; Cabandugama, P.K. Obesity and the Western diet: How we got here. Mo. Med. 2020, 117, 436–538. [Google Scholar]
- Berti, V.; Walters, M.; Sterling, J.; Quinn, C.G.; Logue, M.; Andrews, R.; Matthews, D.C.; Osorio, R.S.; Pupi, A.; Vallabhajosula, S.; et al. Mediterranean diet and 3-year Alzheimer brain biomarker changes in middle-aged adults. Neurology 2018, 90, e1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolters, F.J.; Zonneveld, H.I.; Hofman, A.; van der Lugt, A.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Vernooij, M.W.; Ikram, M.A. Cerebral Perfusion and the Risk of Dementia. Circulation 2017, 136, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoscheidt, S.; Sanderlin, A.H.; Baker, L.D.; Jung, Y.; Lockhart, S.; Kellar, D.; Whitlow, C.T.; Hanson, A.J.; Friedman, S.; Register, T.; et al. Mediterranean and Western diet effects on Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers, cerebral perfusion, and cognition in mid-life: A randomized trial. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 18, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmer, R.A.; Gustafson, D.R.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Haan, M.N.; Gunderson, E.P.; Yaffe, K. Central obesity and increased risk of dementia more than three decades later. Neurology 2008, 71, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughrey, D.G.; Lavecchia, S.; Brennan, S.; Lawlor, B.A.; Kelly, M.E. The Impact of the Mediterranean Diet on the Cognitive Functioning of Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brink, A.C.; Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; Berendsen, A.A.M.; van de Rest, O. The Mediterranean, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH), and Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) Diets Are Associated with Less Cognitive Decline and a Lower Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease—A Review. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 1040–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veronese, N.; Facchini, S.; Stubbs, B.; Luchini, C.; Solmi, M.; Manzato, E.; Sergi, G.; Maggi, S.; Cosco, T.; Fontana, L. Weight loss is associated with improvements in cognitive function among overweight and obese people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 72, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, R.; Sacanella, E.; Urpí-Sardà, M.; Corella, D.; Castañer, O.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.-M.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Martínez-González, M.-A.; Ros, E.; Estruch, R. Long-Term Immunomodulatory Effects of a Mediterranean Diet in Adults at High Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in the PREvención con DIeta MEDiterránea (PREDIMED) Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1684–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaacks, L.M.; Sher, S.; De Staercke, C.; Porkert, M.; Alexander, W.R.; Jones, D.P.; Vaccarino, V.; Ziegler, T.R.; Quyyumi, A.A. Pilot randomized controlled trial of a Mediterranean diet or diet supplemented with fish oil, walnuts, and grape juice in overweight or obese US adults. BMC Nutr. 2018, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valls-Pedret, C.; Sala-Vila, A.; Serra-Mir, M.; Corella, D.; De La Torre, R.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Martínez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Fitó, M.; Pérez-Heras, A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; et al. Mediterranean diet and age-related cognitive decline: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaffe, K.; Lindquist, K.; Penninx, B.W.; Simonsick, E.M.; Pahor, M.; Kritchevsky, S.; Launer, L.; Kuller, L.; Rubin, S.; Harris, T. Inflammatory markers and cognition in well-functioning African-American and white elders. Neurology 2003, 61, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Han, Z.; Sun, B.-L.; Liu, G. Cognitive performance protects against Alzheimer’s disease independently of educational attainment and intelligence. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 4297–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markesbery, W.R. The role of oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 1449–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magkos, F.; Fraterrigo, G.; Yoshino, J.; Luecking, C.; Kirbach, K.; Kelly, S.C.; de Las Fuentes, L.; He, S.; Okunade, A.L.; Patterson, B.W.; et al. Effects of Moderate and Subsequent Progressive Weight Loss on Metabolic Function and Adipose Tissue Biology in Humans with Obesity. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claesson, M.J.; Jeffery, I.B.; Conde, S.; Power, S.E.; O’connor, E.M.; Cusack, S.; Harris, H.M.B.; Coakley, M.; Lakshminarayanan, B.; O’sullivan, O.; et al. Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature 2012, 488, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogt, N.M.; Kerby, R.L.; Dill-McFarland, K.A.; Harding, S.J.; Merluzzi, A.P.; Johnson, S.C.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, T.T.T.; Corsini, S.; Kellingray, L.; Hegarty, C.; Le Gall, G.; Narbad, A.; Müller, M.; Tejera, N.; O’Toole, P.W.; Minihane, A.-M.; et al. APOE genotype influences the gut microbiome structure and function in humans and mice: Relevance for Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2019, 33, 8221–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louis, S.; Tappu, R.M.; Damms-Machado, A.; Huson, D.H.; Bischoff, S.C. Characterization of the gut microbial community of obese patients following a weight-loss intervention using whole metagenome shotgun sequencing. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, A.; Penalver-Bernabe, B.; Xia, Y.; Sanchez-Flack, J.; Lamar, M.; Schiffer, L.; Castellanos, K.; Fantuzzi, G.; Maki, P.; Fitzgibbon, M.; et al. Comparing the Gut Microbiome of Obese, African American, Older Adults with and without Mild Cognitive Impairment. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remely, M.; Tesar, I.; Hippe, B.; Gnauer, S.; Rust, P.; Haslberger, A.G. Gut microbiota composition correlates with changes in body fat content due to weight loss. Benef. Microbes 2015, 6, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Ling, Y.; Wang, F.; Gong, T.; Yang, C.; Ye, S.; Ye, K.; Wei, D.; Song, Z.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation alleviated Alzheimer’s disease-like pathogenesis in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Lamar, M.; McLeod, A.; Schiffer, L.; Blumstein, L.; Dakers, R.; Karstens, A.; Hemphill, N.O.N.; Strahan, D.; Siegel, L.; et al. Effect of Mediterranean diet and Mediterranean diet plus calorie restriction on cognition, lifestyle, and cardiometabolic health: A randomized clinical trial. Prev. Med. Rep. 2022, 29, 101955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Lamar, M.; Blumenthal, J.A.; Babyak, M.; Fantuzzi, G.; Blumstein, L.; Schiffer, L.; Fitzgibbon, M.L. Building research in diet and cognition: The BRIDGE randomized controlled trial. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2017, 59, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachinski, V.; Iadecola, C.; Petersen, R.C.; Breteler, M.M.; Nyenhuis, D.L.; Black, S.E.; Powers, W.J.; DeCarli, C.; Merino, J.G.; Kalaria, R.N.; et al. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke-Canadian Stroke Network vascular cognitive impairment harmonization standards. Stroke 2006, 37, 2220–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielska, N.; Sokołowski, R.; Mazur, E.; Podhorecka, M.; Polak-Szabela, A.; Kędziora-Kornatowska, K. Is the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) test better suited than the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) detection among people aged over 60? Meta-analysis. Psychiatr. Pol. 2016, 50, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-González, M.A.; García-Arellano, A.; Toledo, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Corella, D.; Covas, M.I.; Schröder, H.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; et al. A 14-item mediterranean diet assessment tool and obesity indexes among high-risk subjects: The PREDIMED trial. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anthony, W.E.; Wang, B.; Sukhum, K.V.; D’Souza, A.W.; Hink, T.; Cass, C.; Seiler, S.; Reske, K.A.; Coon, C.; Dubberke, E.R.; et al. Acute and persistent effects of commonly used antibiotics on the gut microbiome and resistome in healthy adults. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauber, C.L.; Zhou, N.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Effect of storage conditions on the assessment of bacterial community structure in soil and human-associated samples. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 307, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naqib, A.; Poggi, S.; Wang, W.; Hyde, M.; Kunstman, K.; Green, S.J. Making and sequencing heavily multiplexed, high-throughput 16S ribosomal RNA gene amplicon libraries using a flexible, two-stage PCR protocol. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1783, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonsamy, P.V.; Williams, T.; Bonella, P.; Holcomb, C.L.; Höglund, B.N.; Hillman, G.; Goodridge, D.; Turenchalk, G.S.; Blake, L.A.; Daigle, D.A.; et al. High throughput HLA genotyping using 454 sequencing and the Fluidigm Access ArrayTM system for simplified amplicon library preparation. Tissue Antigens 2013, 81, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Green, S.J.; Chlipala, G.E.; Turek, F.W.; Vitaterna, M.H. Reproducible changes in the gut microbiome suggest a shift in microbial and host metabolism during spaceflight. Microbiome 2019, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kobert, K.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. PEAR: A fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glöckner, F.O.; Yilmaz, P.; Quast, C.; Gerken, J.; Beccati, A.; Ciuprina, A.; Bruns, G.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Westram, R.; et al. 25 years of serving the community with ribosomal RNA gene reference databases and tools. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 261, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, D.J.; Chen, Y.; Smyth, G.K. Differential expression analysis of multifactor RNA-Seq experiments with respect to biological variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4288–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 30 January 2022).
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2 Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Young, P.; Holtrop, G.; Flint, H.J. Diversity of human colonic butyrate-producing bacteria revealed by analysis of the butyryl-CoA:acetate CoA-transferase gene. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Development of a semiquantitative degenerate real-time pcr-based assay for estimation of numbers of butyryl-coenzyme A (CoA) CoA transferase genes in complex bacterial samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 2009–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kinney, J.W.; Bemiller, S.M.; Murtishaw, A.S.; Leisgang, A.M.; Salazar, A.M.; Lamb, B.T. Inflammation as a central mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2018, 4, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Munckhof, I.C.L.; Kurilshikov, A.; ter Horst, R.; Riksen, N.P.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Zhernakova, A.; Fu, J.; Keating, S.T.; Netea, M.G.; de Graaf, J.; et al. Role of gut microbiota in chronic low-grade inflammation as potential driver for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A systematic review of human studies. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 1719–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Chen, L.; Kurilshikov, A.; Kavousi, M.; Ahmadizar, F.; Ikram, M.A.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Zhernakova, A.; Fu, J.; et al. Association of Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes With Gut Microbial Diversity: A Microbiome-Wide Analysis From Population Studies. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2118811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, J.A.; Zheng, T.; Meric, G.; Marques, F.Z. The gut microbiome and hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, M.M.; Kaur, S.; Eagan, D.E.; Goudarzi, K.; Pasha, E.; Doan, D.C.; Tanaka, H.; Haley, A.P. Central adiposity and the functional magnetic resonance imaging response to cognitive challenge. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Qin, Q.; Chen, J.; Yan, S.; Li, T.; Gao, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, A.; Ding, S. Gut Microbiome Alterations in Patients with Visceral Obesity Based on Quantitative Computed Tomography. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 823262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W.C.; Sampson, L.; Stampfer, M.J.; Rosner, B.; Bain, C.; Witschi, J.; Hennekens, C.H.; Speizer, F.E. Reproducibility and validity of a semiquantitative food frequency questionnaire. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1985, 122, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W. Nutritional Epidemiology; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Arvaniti, F.; Stefanadis, C. Adherence to the Mediterranean food pattern predicts the prevalence of hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes and obesity, among healthy adults; the accuracy of the MedDietScore. Prev. Med. 2007, 44, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangney, C.C.; Kwasny, M.J.; Li, H.; Wilson, R.S.; Evans, D.A.; Morris, M.C. Adherence to a Mediterranean-type dietary pattern and cognitive decline in a community population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale: Technical and Interpretative Manual-Fourth Edition (WAIC-IV): Administration and Scoring Manual; Pearson: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stroop, J.R. Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. J. Exp. Psychol. 1935, 18, 643–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitan, R.; Wolfson, D. The Halstead-Reitan neuropsychological test battery: Theory and clinical interpretation. In Specific Learning Disabilities and Difficulties in Children and Adolescents: Psychological Assessment and Evaluation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Lezak, M.; Howieson, D.; Loring, D.; Fischer, J. Neuropsychological Assessment; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Delis, D.; Kramer, J.; Kaplan, E.; Antonio, B.O.-S.; Psychological, T.T. Manual for the California Verbal Learning Test (CVLT-II); Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Lozano, A.; Marín, P.J.; Torres-Luque, G.; Ruiz, J.R.; Lucía, A.; Garatachea, N. Technical variability of the GT3X accelerometer. Med. Eng. Phys. 2012, 34, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, M.; Shiroma, E.J.; Harris, T.B.; Lee, I.-M. Comparison of physical activity assessed using hip- and wrist-worn accelerometers. Gait Posture 2016, 44, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewinsohn, P.M.; Seeley, J.R.; Roberts, R.E.; Allen, N.B. Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) as a screening instrument for depression among community-residing older adults. Psychol. Aging 1997, 12, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weersma, R.K.; Zhernakova, A.; Fu, J. Interaction between drugs and the gut microbiome. Gut 2020, 69, 1510–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, D.; Whelan, K.; Rossi, M.; Morrison, M.; Holtmann, G.; Kelly, J.T.; Shanahan, E.R.; Staudacher, H.M.; Campbell, K.L. Dietary fiber intervention on gut microbiota composition in healthy adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 965–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Moreno, A.; Suárez, A.; Avanzi, C.; Monteoliva-Sánchez, M.; Aguilera, M. Probiotic Strains and Intervention Total Doses for Modulating Obesity-Related Microbiota Dysbiosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bastard, Q.; Chapelet, G.; Javaudin, F.; Lepelletier, D.; Batard, E.; Montassier, E. The effects of inulin on gut microbial composition: A systematic review of evidence from human studies. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 39, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, I.; Winkeler, M.; Imgart, H. Ascertaining minimal clinically meaningful changes in symptoms of depression rated by the 15-item Centre for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2022, 28, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, C.; Montes-Borrego, M.; Rangel-Zúñiga, O.A.; Alcalã-Diaz, J.F.; Gamez-Delgado, F.; Pérez-Martinez, P.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Quintana-Navarro, G.M.; Tinahones, F.J.; Landa, B.B.; et al. Two healthy diets modulate gut microbial community improving insulin sensitivity in a human obese population. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagliai, G.; Russo, E.; Niccolai, E.; Dinu, M.; Di Pilato, V.; Magrini, A.; Bartolucci, G.; Baldi, S.; Menicatti, M.; Giusti, B.; et al. Influence of a 3-month low-calorie Mediterranean diet compared to the vegetarian diet on human gut microbiota and SCFA: The CARDIVEG Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2011–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinott, E.; Youngster, I.; Yaskolka Meir, A.; Tsaban, G.; Zelicha, H.; Kaplan, A.; Knights, D.; Tuohy, K.; Fava, F.; Scholz, M.U.; et al. Effects of Diet-Modulated Autologous Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on Weight Regain. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 158–173.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, J.; Moreno-Indias, I.; Bulló, M.; Lopez, J.V.; Corella, D.; Castañer, O.; Vidal, J.; Atzeni, A.; Fernandez-García, J.C.; Torres-Collado, L.; et al. Effect on gut microbiota of a 1-y lifestyle intervention with Mediterranean diet compared with energy-reduced Mediterranean diet and physical activity promotion: PREDIMED-Plus Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koopen, A.M.; Almeida, E.L.; Attaye, I.; Witjes, J.J.; Rampanelli, E.; Majait, S.; Kemper, M.; Levels, J.H.M.; Schimmel, A.W.M.; Herrema, H.; et al. Effect of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Combined With Mediterranean Diet on Insulin Sensitivity in Subjects With Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 662159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinott, E.; Meir, A.Y.; Tsaban, G.; Zelicha, H.; Kaplan, A.; Knights, D.; Tuohy, K.; Scholz, M.U.; Koren, O.; Stampfer, M.J.; et al. The effects of the Green-Mediterranean diet on cardiometabolic health are linked to gut microbiome modifications: A randomized controlled trial. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deledda, A.; Palmas, V.; Heidrich, V.; Fosci, M.; Lombardo, M.; Cambarau, G.; Lai, A.; Melis, M.; Loi, E.; Loviselli, A.; et al. Dynamics of Gut Microbiota and Clinical Variables after Ketogenic and Mediterranean Diets in Drug-Naïve Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, C.; Mego, M.; Sabater, C.; Vallejo, F.; Bendezu, R.A.; Masihy, M.; Guarner, F.; Espín, J.C.; Margolles, A.; Azpiroz, F. Differential Effects of Western and Mediterranean-Type Diets on Gut Microbiota: A Metagenomics and Metabolomics Approach. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haro, C.; Garcia-Carpintero, S.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Gomez-Delgado, F.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Rangel Zuñiga, O.A.; Quintana-Navarro, G.M.; Landa, B.B.; Clemente, J.C.; et al. The gut microbial community in metabolic syndrome patients is modified by diet. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 27, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, C.; García-Carpintero, S.; Rangel-Zúñiga, O.A.; Alcalá-Díaz, J.F.; Landa, B.B.; Clemente, J.C.; Pérez-Martínez, P.; López-Miranda, J.; Pérez-Jiménez, F.; Camargo, A. Consumption of Two Healthy Dietary Patterns Restored Microbiota Dysbiosis in Obese Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meslier, V.; Laiola, M.; Roager, H.M.; De Filippis, F.; De Filippis, F.; Roume, H.; Quinquis, B.; Giacco, R.; Mennella, I.; Ferracane, R.; et al. Mediterranean diet intervention in overweight and obese subjects lowers plasma cholesterol and causes changes in the gut microbiome and metabolome independently of energy intake. Gut 2020, 69, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, C.; Sawrey-Kubicek, L.; Beals, E.; Rhodes, C.H.; Houts, H.E.; Sacchi, R.; Zivkovic, A.M. Human gut microbiome composition and tryptophan metabolites were changed differently by fast food and Mediterranean diet in 4 days: A pilot study. Nutr. Res. 2020, 77, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancello, R.; Turroni, S.; Rampelli, S.; Cattaldo, S.; Candela, M.; Cattani, L.; Mai, S.; Vietti, R.; Scacchi, M.; Brigidi, P.; et al. Effect of Short-Term Dietary Intervention and Probiotic Mix Supplementation on the Gut Microbiota of Elderly Obese Women. Nutrients 2019, 11, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, T.S.; Rampelli, S.; Jeffery, I.B.; Santoro, A.; Neto, M.; Capri, M.; Giampieri, E.; Jennings, A.; Candela, M.; Turroni, S.; et al. Mediterranean diet intervention alters the gut microbiome in older people reducing frailty and improving health status: The NU-AGE 1-year dietary intervention across five European countries. Gut 2020, 69, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vitale, M.; Giacco, R.; Laiola, M.; Della Pepa, G.; Luongo, D.; Mangione, A.; Salamone, D.; Vitaglione, P.; Ercolini, D.; Rivellese, A.A. Acute and chronic improvement in postprandial glucose metabolism by a diet resembling the traditional Mediterranean dietary pattern: Can SCFAs play a role? Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Yacov, O.; Godneva, A.; Rein, M.; Shilo, S.; Lotan-Pompan, M.; Weinberger, A.; Segal, E. Gut microbiome modulates the effects of a personalised postprandial-targeting (PPT) diet on cardiometabolic markers: A diet intervention in pre-diabetes. Gut 2023, 72, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanu, S.; Palmas, V.; Madau, V.; Casula, E.; Deledda, A.; Cusano, R.; Uva, P.; Vascellari, S.; Boi, F.; Loviselli, A.; et al. Impact of a Moderately Hypocaloric Mediterranean Diet on the Gut Microbiota Composition of Italian Obese Patients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, M.; Ippolito, M.; Monge, T.; Violi, R.; Cappello, P.; Ferrocino, I.; Cocolin, L.S.; De Francesco, A.; Bo, S.; Finocchiaro, C. Gut microbiota composition after diet and probiotics in overweight breast cancer survivors: A randomized open-label pilot intervention trial. Nutrition 2020, 74, 110749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, K.M.; Yeo, G.W. Systematic review of dementia prevalence and incidence in United States race/ethnic populations. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEvoy, C.T.; Hoang, T.; Sidney, S.; Steffen, L.M.; Jacobs, D.R.J.; Shikany, J.M.; Wilkins, J.T.; Yaffe, K. Dietary patterns during adulthood and cognitive performance in midlife: The CARDIA study. Neurology 2019, 92, e1589–e1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siervo, M.; Arnold, R.; Wells, J.C.K.; Tagliabue, A.; Colantuoni, A.; Albanese, E.; Brayne, C.; Stephan, B.C.M. Intentional weight loss in overweight and obese individuals and cognitive function: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 968–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Witte, A.V.; Fobker, M.; Gellner, R.; Knecht, S.; Flöel, A. Caloric restriction improves memory in elderly humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
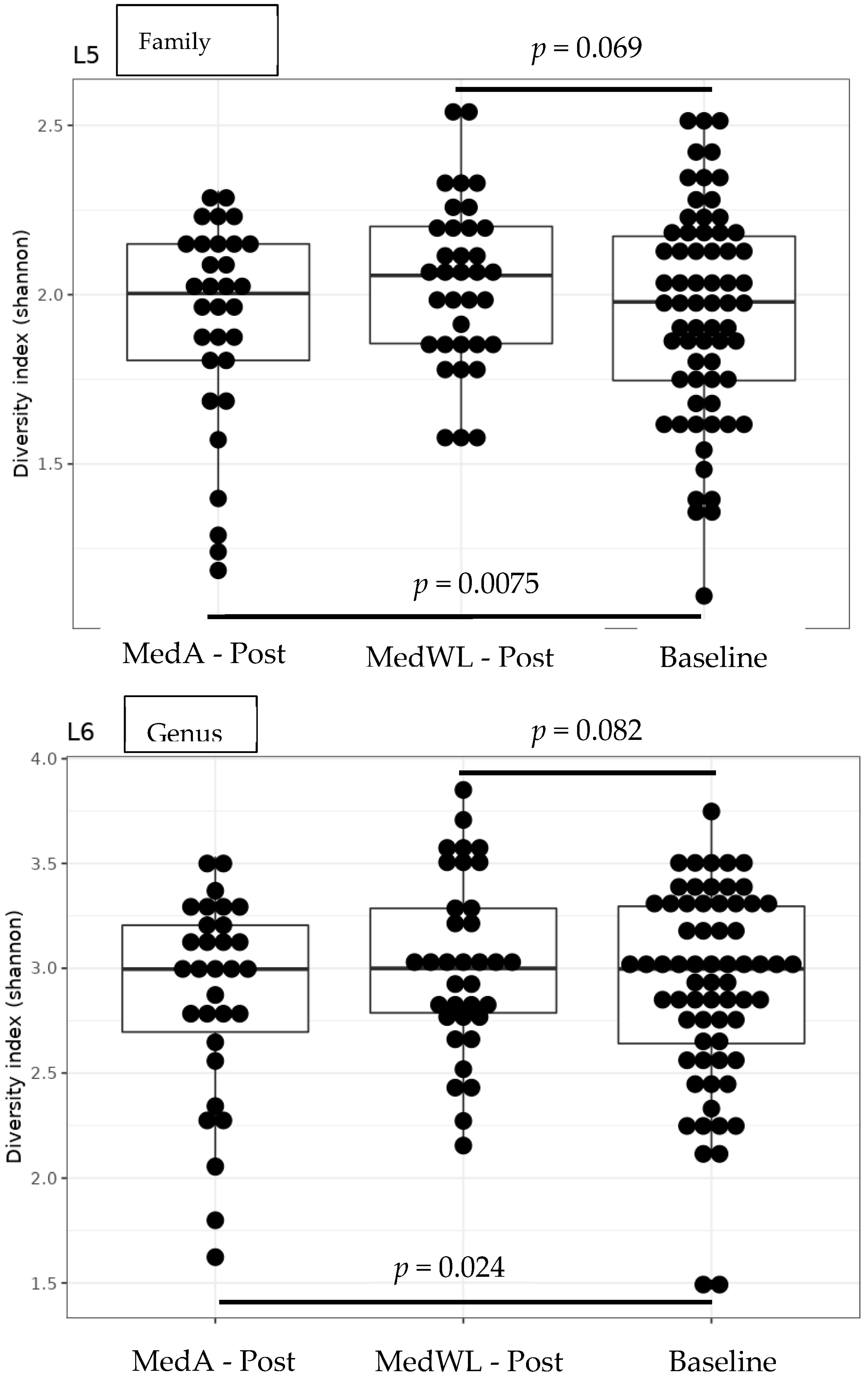

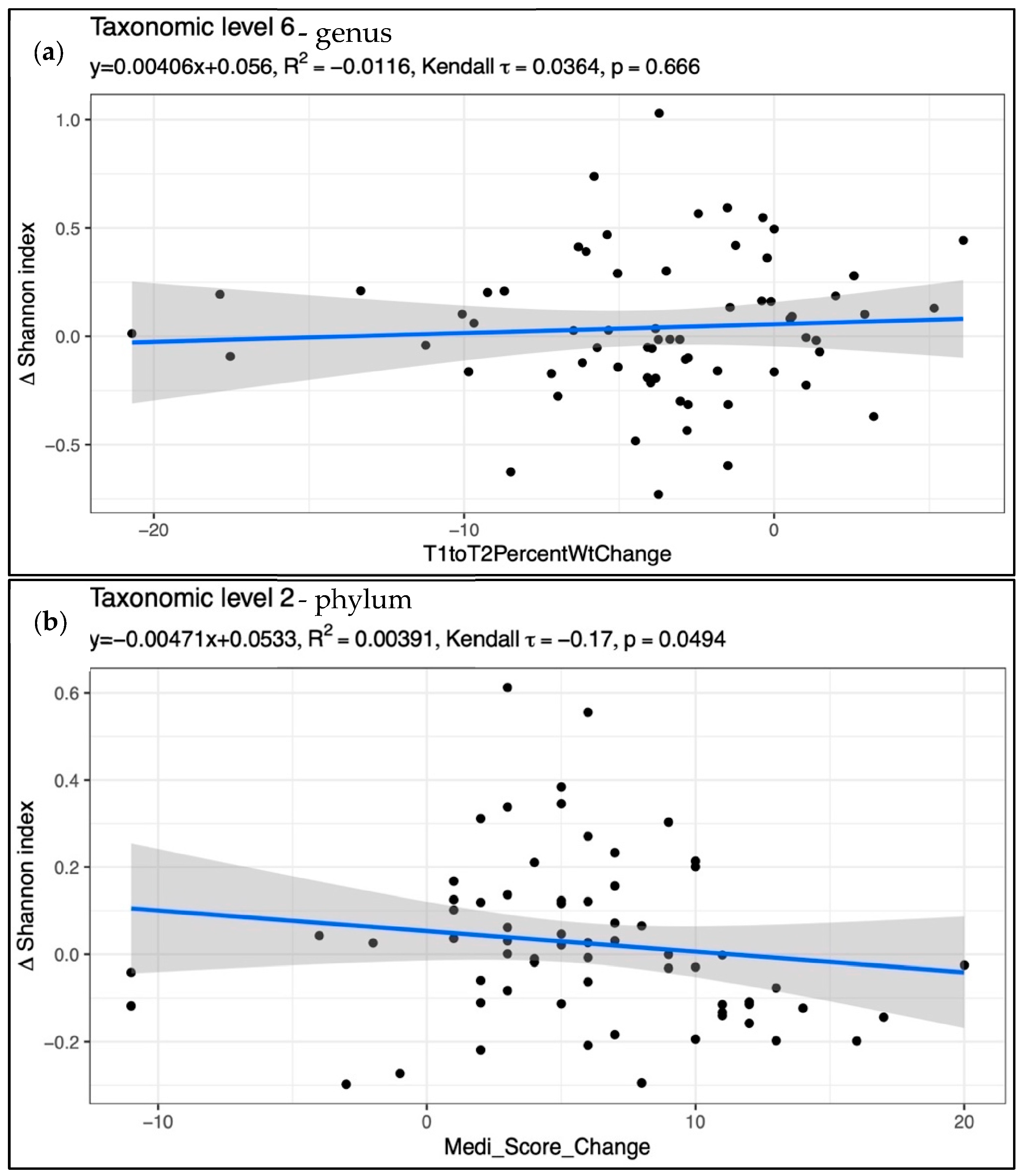
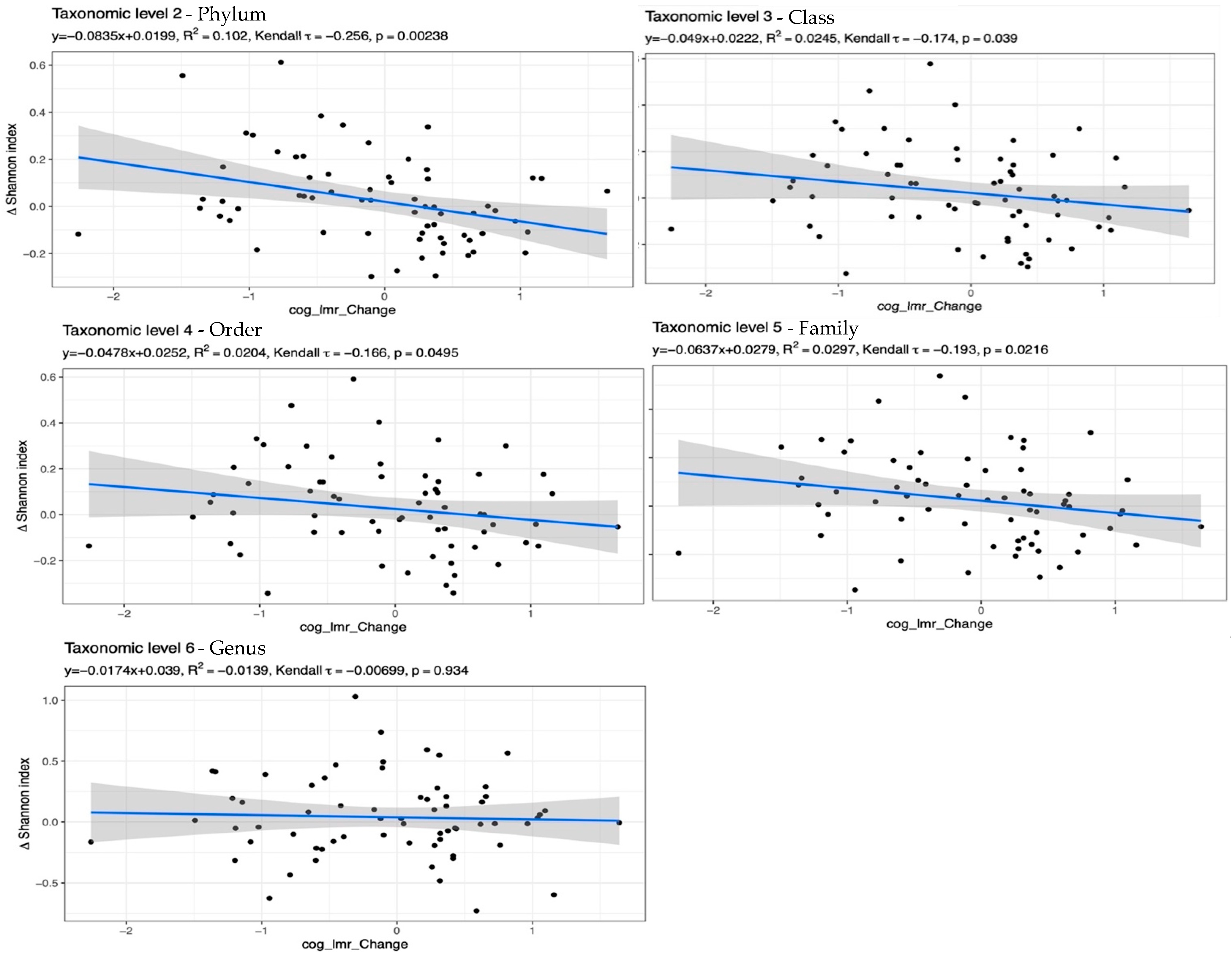
| Variable | MedA Baseline (n = 31) | MedWL Baseline (n = 35) | p d | MedA Post (n = 31) | MedWL Post (n = 35) | p e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic, Diet, and Physical Activity Variables | ||||||
| Age, years (mean (SD)) | 65.9 (6.7) | 65.3 (5.3) | 0.59 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Female (n,%) | 28, 90% | 29, 82% | 0.38 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| African American (n, %) | 29, 93.6% | 33, 94.3% | 0.81 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Any college education (n, %) | 30, 96.8% | 32, 91.4% | 0.32 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| College graduate (n, %) | 16, 51.6% | 19, 54.3% | 0.89 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| <USD 40 K annual household income (n, %) | 12, 40% | 17, 50% | 0.33 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| MED Score (range 0–55) (mean (SD)) | 32.9 (6.3) | 32.2 (4.8) | 0.56 | 38.6 ##,** (4.9) | 38.1 ##,** (4.8) | 0.9 |
| Sedentary time (minutes/valid day) (mean (SD)) a | 877.8 (147.6) | 893.3 (149.7) | 0.62 | 870.1 (134.3) | 889.7 (116.8) | 0.9 |
| Medication Use | ||||||
| Using microbiome-altering medications/supplements (n, %) b | 10, 32.3% | 21, 60% | 0.036 | 14, 45.2% | 19, 54.3% | 0.19 |
| Using anti-inflammatory medications (n, %) c | 5, 16% | 15, 43% | 0.032 | 5, 16.1% | 16, 45.7% | 0.88 |
| Clinical Variables | ||||||
| Weight (kg) (mean (SD)) | 97.8 (13.6) | 101.1 (16.4) | 0.47 | 94.8 (12.1) ##,* | 96.7 (18.6) ##,** | 0.13 |
| BMI (kg/m2) (mean (SD)) | 35.9 (4.8) | 37.7 (4.1) | 0.13 | 34.8 (4.2) ##,** | 36 (4.9) ##,** | 0.18 |
| Visceral fat (g)/Height (cm) (mean (SD)) | 8.8 (3.8) | 10.1 (4.8) | 0.63 | 7.8 (2.9) ##,* | 9 (4.9) ##,* | 0.68 |
| Depression score from CES-D (mean (SD)) | 5.7 (5.7) | 9 (6) [77] | 0.068 | 4.3 (4.5) | 8.7 (6.5) | 0.18 |
| Currently smoking (n, %) | 2, 6.5% | 2, 5.7% | 0.53 | 2, 6.5% | 2, 5.7% | 1.0 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) (mean (SD)) | 131.2 (17.6) | 132.6 (18.1) | 0.72 | 131.8 (17.0) | 134 (20.4) | 0.88 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) (mean (SD)) | 80.9 (12.6) | 80.8 (8.3) | 0.99 | 79.0 (10.0) | 81.9 (11.9) | 0.3 |
| Type 2 diabetes (n, %) | 8, 25.8% | 6, 17.1% | 0.48 | 7, 22.6% | 5, 14.3% | 0.98 |
| Fasting serum glucose (mg/dL) (mean (SD)) | 93.4 (12.6) | 100 (14.3) | 0.026 | 97.5 (19.5) | 97.4 (17.5) | 0.08 |
| Hemoglobin A1c (% total Hb) (mean (SD)) | 6.0 (0.7) | 5.9 (0.8) | 0.82 | 5.8 (0.8) # | 5.8 (0.7) # | 0.98 |
| hs-CRP (mg/L) (mean (SD)) | 4.3 (6.3) | 5.0 (6.6) | 0.74 | 6.7 (7.6) | 6.4 (5.2) | 0.97 |
| Microbiome-Related Variables | ||||||
| BcoA abundance (cycles until threshold) (Mean (SD)) | 25.6 (3.1) | 26.4 (2.6) | 0.33 | 25.8 (3.4) | 27.4 (3.2) # | 0.1 |
| Cognitive Variables | ||||||
| MoCA Score (mean SD)) | 24.5 (2.6) | 25.2 (2.8) | 0.33 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Attention (AIP) (mean (SD)) | 0.06 (0.5) | 0.08 (0.7) | 0.7 | 0.06 (0.6) | 0.03 (0.7) | 0.51 |
| Executive Function (EF) (mean (SD)) | −0.1 (0.5) | 0.2 (0.6) | 0.056 | −0.2 | 0.2 (0.6) | 0.81 |
| Memory (LMR) (mean) (SD)) | −0.01 (0.7) | 0.03 (0.9) | 0.89 | −0.07 (0.8) | −0.05 (0.8) | 0.9 |
| Mediation Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | Standard Error | Wald 95% Confidence Limits | Z | Pr > |Z| | ||
| Total Effect (MED score + Phylum Alpha Diversity) on LMR Score | 0.0454 | 0.0181 | 0.009827 | 0.08094 | 2.50 | 0.0124 |
| Direct Effect (DE) (MED score) on LMR Score | 0.0483 | 0.0185 | 0.01207 | 0.08453 | 2.61 | 0.0090 |
| Indirect Effect (IE) (Phylum Alpha Diversity) on LMR Score | −0.00291 | 0.00422 | −0.01119 | 0.005363 | −0.69 | 0.4903 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McLeod, A.; Bernabe, B.P.; Xia, Y.; Sanchez-Flack, J.; Lamar, M.; Schiffer, L.; Hemphill, N.O.-N.; Fantuzzi, G.; Maki, P.; Fitzgibbon, M.; et al. Exploring the Effects of a Mediterranean Diet and Weight Loss on the Gut Microbiome and Cognitive Performance in Older, African American Obese Adults: A Post Hoc Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3332. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153332
McLeod A, Bernabe BP, Xia Y, Sanchez-Flack J, Lamar M, Schiffer L, Hemphill NO-N, Fantuzzi G, Maki P, Fitzgibbon M, et al. Exploring the Effects of a Mediterranean Diet and Weight Loss on the Gut Microbiome and Cognitive Performance in Older, African American Obese Adults: A Post Hoc Analysis. Nutrients. 2023; 15(15):3332. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153332
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcLeod, Andrew, Beatriz Penalver Bernabe, Yinglin Xia, Jennifer Sanchez-Flack, Melissa Lamar, Linda Schiffer, Nefertiti Oji-Njideka Hemphill, Giamila Fantuzzi, Pauline Maki, Marian Fitzgibbon, and et al. 2023. "Exploring the Effects of a Mediterranean Diet and Weight Loss on the Gut Microbiome and Cognitive Performance in Older, African American Obese Adults: A Post Hoc Analysis" Nutrients 15, no. 15: 3332. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153332
APA StyleMcLeod, A., Bernabe, B. P., Xia, Y., Sanchez-Flack, J., Lamar, M., Schiffer, L., Hemphill, N. O.-N., Fantuzzi, G., Maki, P., Fitzgibbon, M., & Tussing-Humphreys, L. (2023). Exploring the Effects of a Mediterranean Diet and Weight Loss on the Gut Microbiome and Cognitive Performance in Older, African American Obese Adults: A Post Hoc Analysis. Nutrients, 15(15), 3332. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15153332






