Mumefural Improves Recognition Memory and Alters ERK-CREB-BDNF Signaling in a Mouse Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
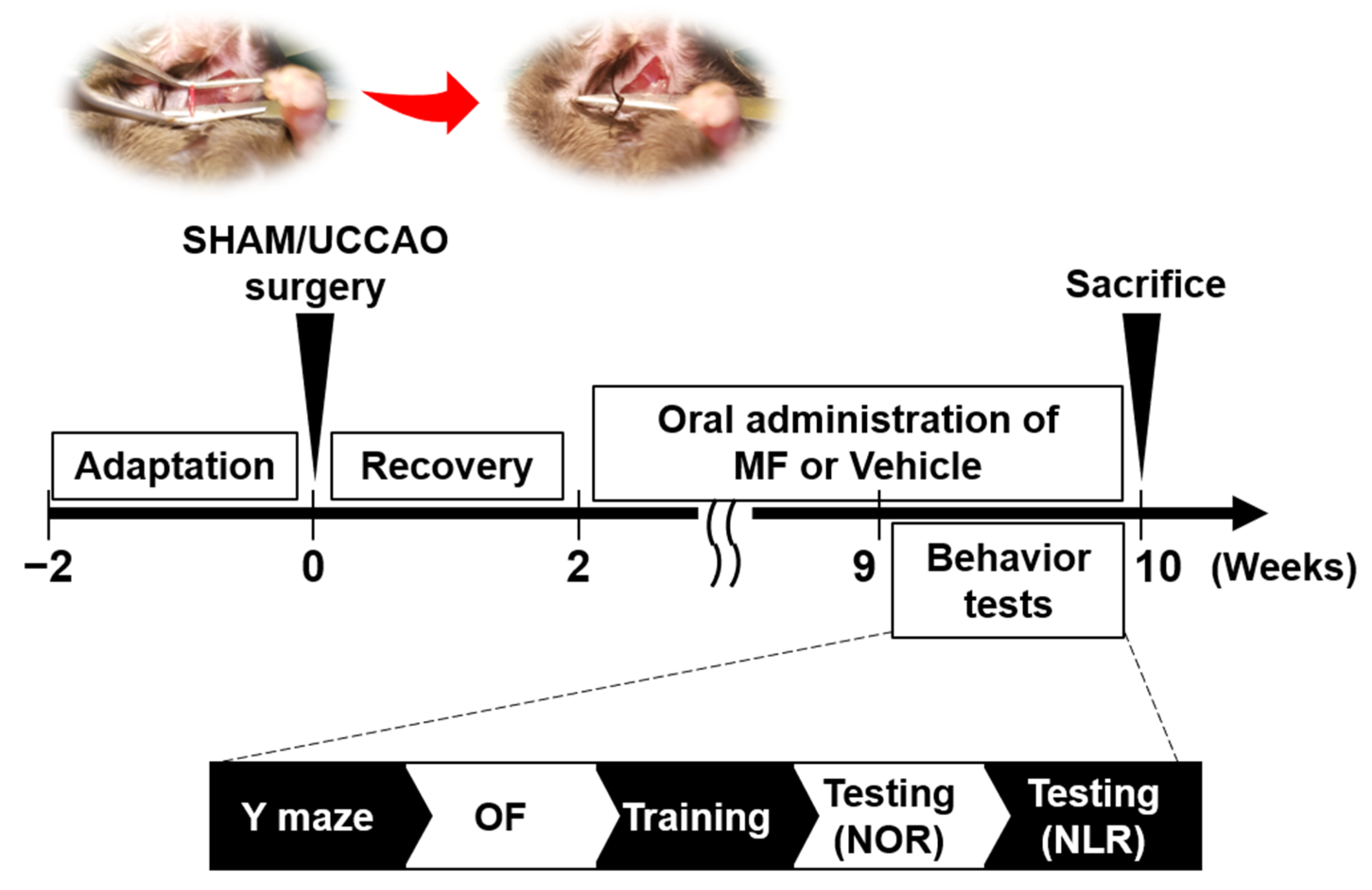
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Surgery
2.4. Behavioral Tasks
2.4.1. Y-Maze Test
2.4.2. Open Field Test
2.4.3. NOR/NLR Test
2.5. Brain Sample Preparation
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Protein Digestion and Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)/MS Analysis
2.8. Isolating Differentially Expressed Proteins
2.9. Functional Network of Gene Ontology (GO) Terms
2.10. Measurement of Pathway Activity
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of MF on the Body Weight
3.2. Effects of MF on the Cognitive Impairment Induced by CCH
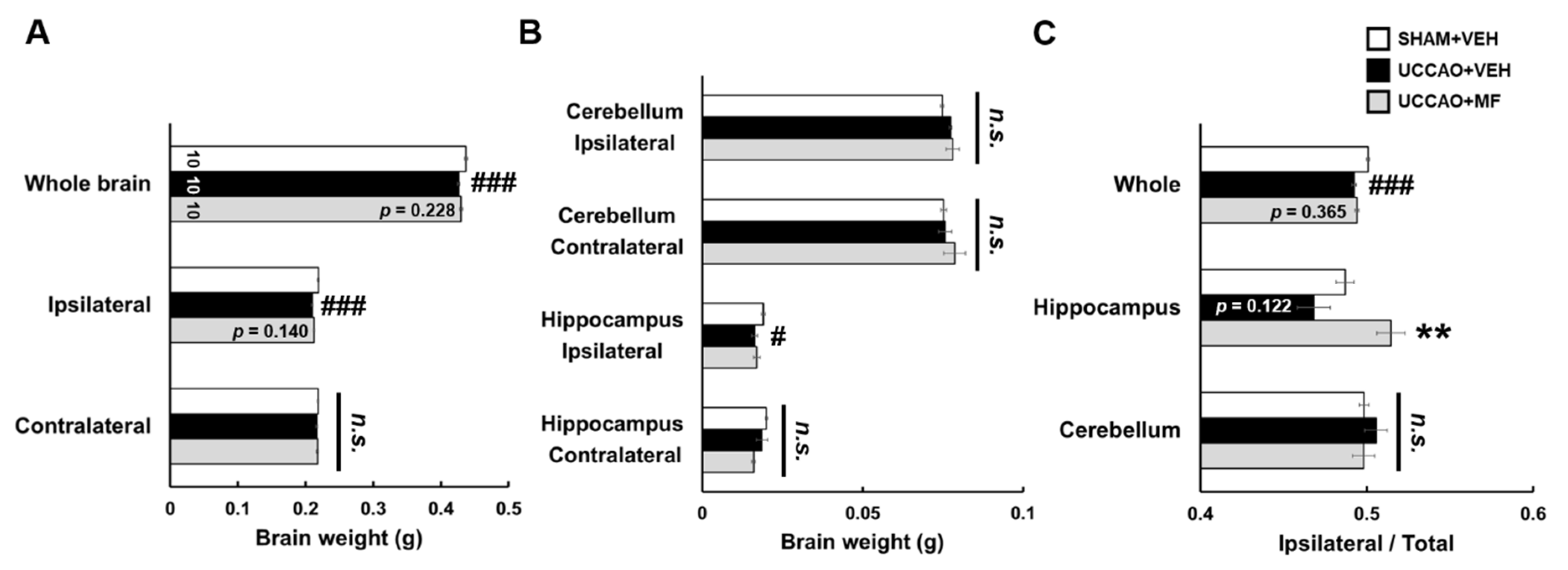
3.3. Effects of MF on the Brain Weight
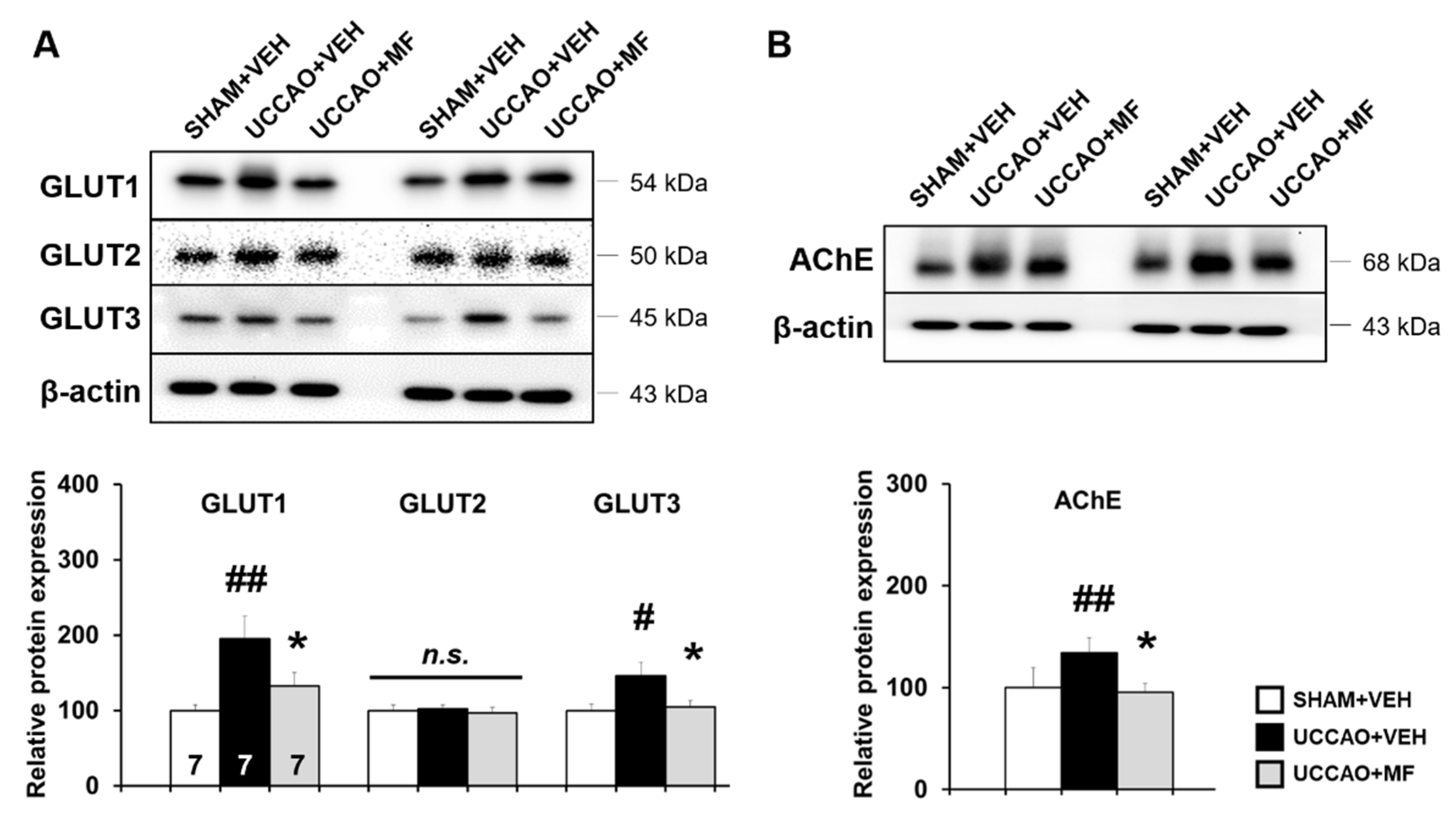
3.4. Effects of MF on Glucose Transporter (GLUT) Expression Induced by CCH
3.5. Effects of MF on Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Levels Induced by CCH
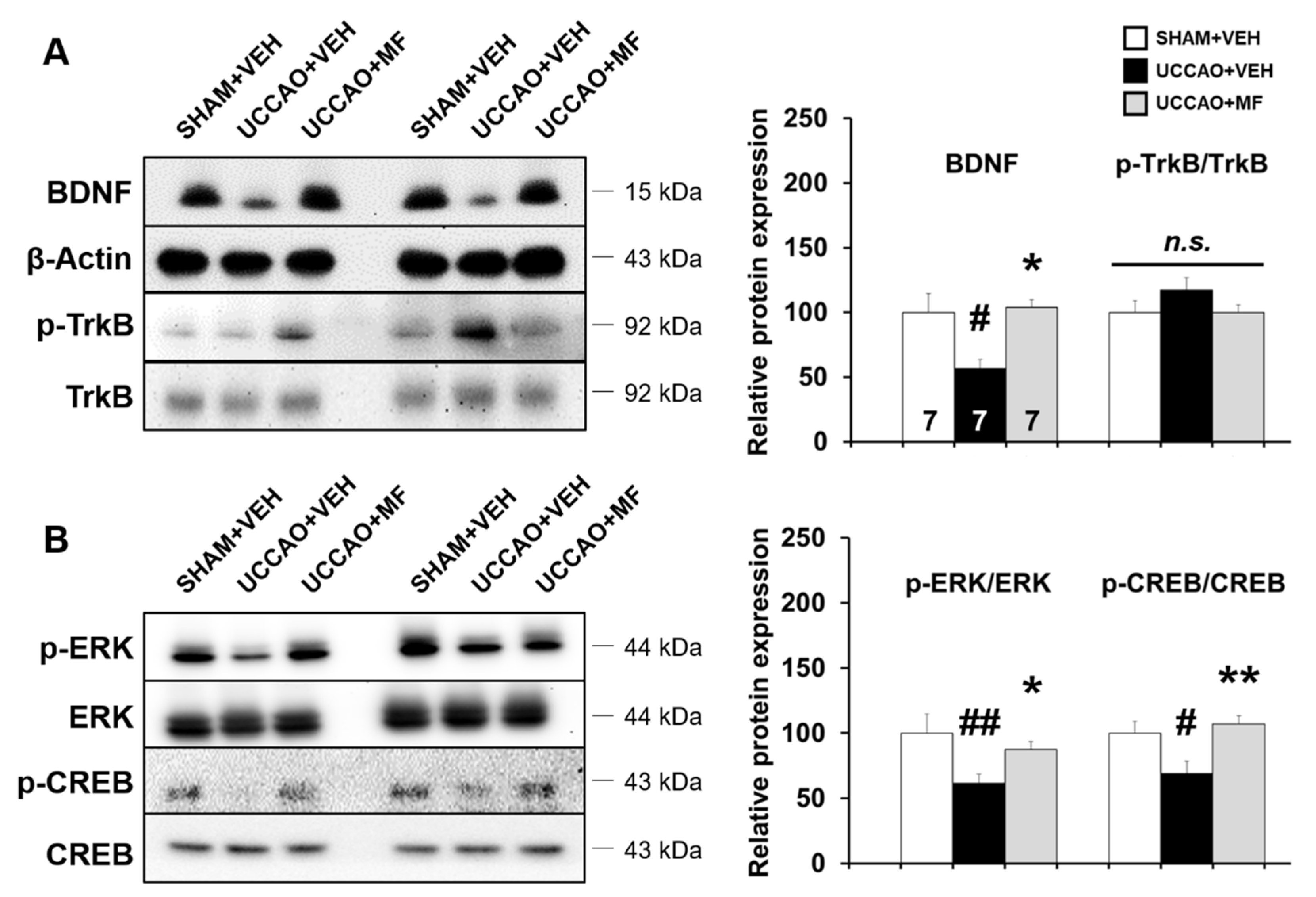
3.6. Effects of MF on Protein Expression Involved in Learning and Memory Pathways
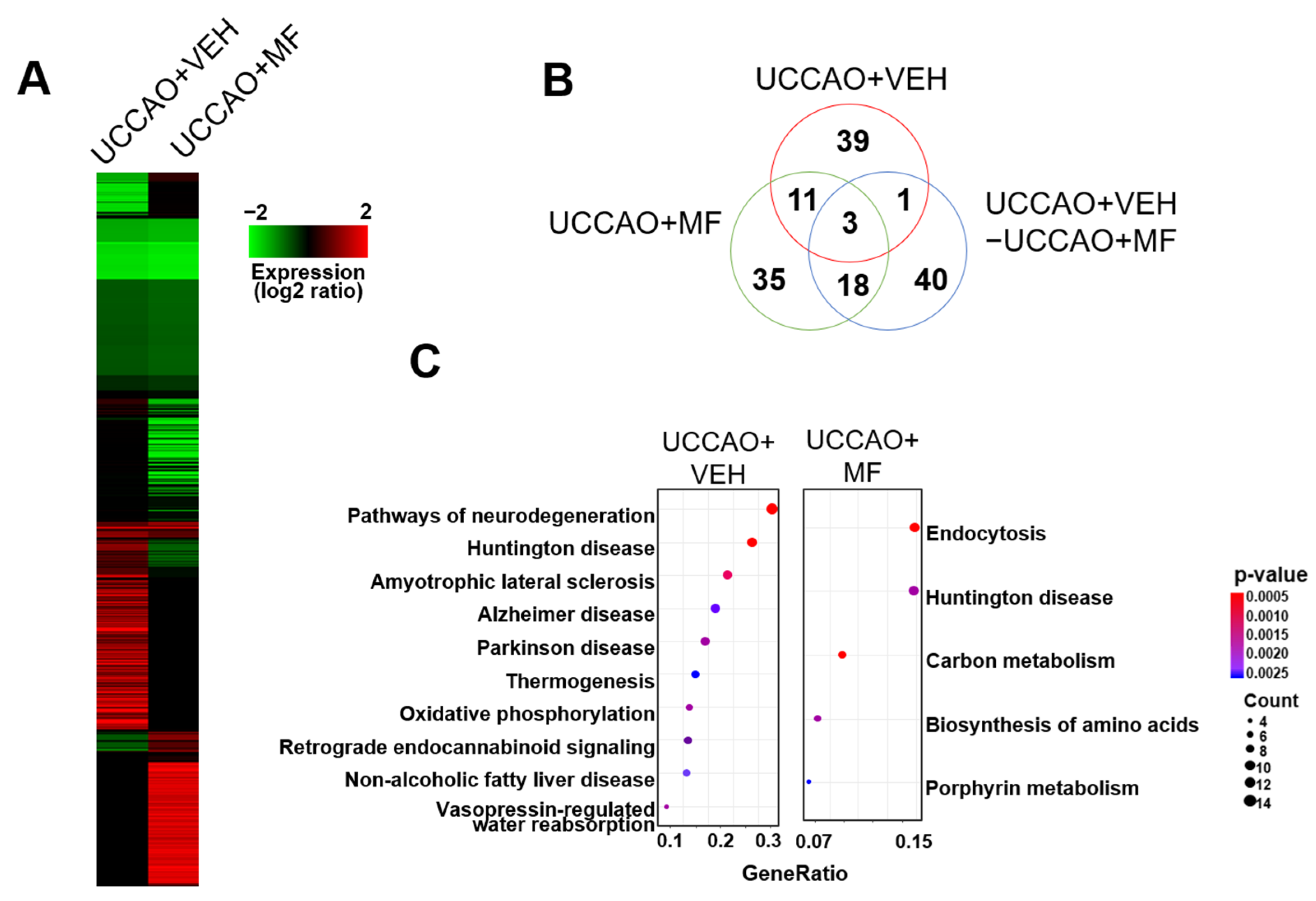
3.7. Effects of MF on Proteomic Profiling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bir, S.C.; Khan, M.W.; Javalkar, V.; Toledo, E.G.; Kelley, R.E. Emerging concepts in vascular dementia: A review. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 30, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X.L.; Guo, Z.N.; Yang, Y. Pathological changes in neurovascular units: Lessons from cases of vascular dementia. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Pol, L.; Gertz, H.J.; Scheltens, P.; Wolf, H. Hippocampal atrophy in subcortical vascular dementia. Neurodegener. Dis. 2011, 8, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Tang, X.C. Cholinergic deficiency involved in vascular dementia: Possible mechanism and strategy of treatment. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihl, R.; Tribanek, M.; Bachinskaya, N.; GOTADAY Study Group. Efficacy and tolerability of a once daily formulation of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia: Results from a randomised controlled trial. Pharmacopsychiatry 2012, 45, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.D.; Yuan, X.; Chu, S.F.; Chen, C.; Ren, Q.; Luo, P.; Lin, M.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Zhu, T.B.; Ai, Q.D.; et al. CZ-7, a new derivative of Claulansine F, ameliorates 2VO-induced vascular dementia in rats through a Nrf2-mediated antioxidant responses. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, E.T.; Yazdanian, M.; Tahmasebi, E.; Tebyanian, H.; Ranjbar, R.; Yazdanian, A.; Seifalian, A.; Tafazoli, A. Current herbal medicine as an alternative treatment in dentistry: In vitro, in vivo and clinical studies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 889, 173665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuda, Y.; Ono, H.; Ohnishi-Kameyama, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Nagata, T.; Kikuchi, Y. Mumefural, citric acid derivative improving blood fluidity from fruit-juice concentrate of Japanese apricot (Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Matsuda, H.; Gato, N.; Kotani, T. Effect of fruit-juice concentrate of Japanese apricot (Prunus mume SEIB. et ZUCC.) on improving blood fluidity. Nat. Med. 2005, 59, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Takemura, S.; Yoshimasu, K.; Fukumoto, J.; Mure, K.; Nishio, N.; Kishida, K.; Yano, F.; Mitani, T.; Takeshita, T.; Miyashita, K. Safety and adherence of Umezu polyphenols in the Japanese plum (Prunus mume) in a 12-week double-blind randomized placebo-controlled pilot trial to evaluate antihypertensive effects. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2014, 19, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Bang, J.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, I.S.; Han, J.S.; Hwang, B.Y.; Jeon, W.K. Fructus mume alleviates chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced white matter and hippocampal damage via inhibition of inflammation and downregulation of TLR4 and p38 MAPK signaling. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Bang, J.H.; Lee, J.; Han, J.S.; Kang, H.W.; Jeon, W.K. Fructus mume ethanol extract prevents inflammation and normalizes the septohippocampal cholinergic system in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J. Med. Food. 2016, 19, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, J.; Kim, M.S.; Jeon, W.K. Mumefural ameliorates cognitive impairment in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion via regulating the septohippocampal cholinergic system and neuroinflammation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Bang, J.; Kim, B.Y.; Jeon, W.K. Impaired cognitive flexibility induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in the 5XFAD transgenic mouse model of mixed dementia. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Bang, J.; Jeon, W.K. The involvement of canonical Wnt signaling in memory impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in mice. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.C.; Ma, J.; Jeon, W.K.; Han, J.S. Fructus mume extracts alleviate cognitive impairments in 5XFAD transgenic mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Choi, B.R.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, D.H.; Han, Y.S.; Jeon, W.K.; Han, J.S. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induces alterations of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and angiopoietin-2 levels in the rat hippocampus. Exp. Neurobiol. 2018, 27, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrioli, P.G.; Eng, J.K.; Hubley, R.; Vogelzang, M.; Deutsch, E.W.; Raught, B.; Pratt, B.; Nilsson, E.; Angeletti, R.H.; Apweiler, R.; et al. A common open representation of mass spectrometry data and its application to proteomics research. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oughtred, R.; Stark, C.; Breitkreutz, B.J.; Rust, J.; Boucher, L.; Chang, C.; Kolas, N.; O’Donnell, L.; Leung, G.; McAdam, R.; et al. The BioGRID interaction database: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D529–D541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Hackl, H.; Charoentong, P.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galon, J. ClueGO: A cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, G.; Sherman, B.T.; Hosack, D.A.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. DAVID: Database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, P3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.Y.; Lim, H.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Koo, I.; Jeong, S.J. Evaluation of animal models by comparison with human late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 9234–9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gu, J.H.; Dai, C.L.; Liu, Q.; Iqbal, K.; Liu, F.; Gong, C.X. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion causes decrease of O-GlcNAcylation, hyperphosphorylation of tau and behavioral deficits in mice. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuloaga, K.L.; Zhang, W.; Yeiser, L.A.; Stewart, B.; Kukino, A.; Nie, X.; Roese, N.E.; Grafe, M.R.; Pike, M.M.; Raber, J.; et al. Neurobehavioral and imaging correlates of hippocampal atrophy in a mouse model of vascular cognitive impairment. Transl. Stroke Res. 2015, 6, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, K.J.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, J.N.; Choi, B.R.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, K.S.; Han, J.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Shin, C.Y.; et al. Effects of donepezil, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, on neurogenesis in a rat model of vascular dementia. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 347, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numakawa, T.; Odaka, H. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease: Beneficial effects of flavonoids for neuroprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, S.W.; Futter, M.; Rosenblum, K.; Webber, M.J.; Hunt, S.P.; Bliss, T.V.; Bramham, C.R. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces long-term potentiation in intact adult hippocampus: Requirement for ERK activation coupled to CREB and upregulation of Arc synthesis. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 1532–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Han, M.; Jeon, W.K. Acute and subacute oral toxicity of mumefural, bioactive compound derived from processed fruit of Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc., in ICR Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkat, P.; Chopp, M.; Chen, J. Models and mechanisms of vascular dementia. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 272, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaschke, K.; Martin, E.; Bardenheuer, H.J. Effect of propentofylline on hippocampal brain energy state and amyloid precursor protein concentration in a rat model of cerebral hypoperfusion. J. Neural Transm. 1998, 105, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; Koibuchi, N.; Toyama, K.; Uekawa, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Lin, B.; Kim-Mitsuyama, S. DPP-4 inhibition with linagliptin ameliorates cognitive impairment and brain atrophy induced by transient cerebral ischemia in type 2 diabetic mice. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2015, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qazzaz, N.K.; Ali, S.H.; Ahmad, S.A.; Islam, S.; Mohamad, K. Cognitive impairment and memory dysfunction after a stroke diagnosis: A post-stroke memory assessment. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2014, 10, 1677–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiwa, N.S.; Garrard, P.; Hainsworth, A.H. Experimental models of vascular dementia and vascular cognitive impairment: A systematic review. J. Neurochem. 2010, 115, 814–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, G.A.; Shchelchkov, E.; Kaufer, D.I.; Ivanco, L.S.; Bohnen, N.I. White matter hyperintensities and cortical acetylcholinesterase activity in parkinsonian dementia. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2006, 113, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.O.; Lee, S.J.; Pyo, J.S. Effect of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors on post-stroke cognitive impairment and vascular dementia: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, R.C.; Souza, D.G.; Soletti, R.C.; López, M.G.; Rodrigues, A.L.; Gabilan, N.H. Involvement of PKA, MAPK/ERK and CaMKII, but not PKC in the acute antidepressant-like effect of memantine in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 395, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seely, K.A.; Brents, L.K.; Franks, L.N.; Rajasekaran, M.; Zimmerman, S.M.; Fantegrossi, W.E.; Prather, P.L. AM-251 and rimonabant act as direct antagonists at mu-opioid receptors: Implications for opioid/cannabinoid interaction studies. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, X.Q.; Ding, C.; Du, X.L. Genistein attenuates isoflurane-induced neurotoxicity and improves impaired spatial learning and memory by regulating cAMP/CREB and BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt signaling. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 21, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chen, Z.Y. The role of BDNF in depression on the basis of its location in the neural circuitry. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 32, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Tsuji, M.; Oguchi, T.; Kasuga, K.; Kimura, A.; Futamura, A.; Sugimoto, A.; Kasai, H.; Kuroda, T.; Yano, S.; et al. Serum BDNF as a potential biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease: Verification through assessment of serum, cerebrospinal fluid, and medial temporal lobe atrophy. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 653267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, F.; Yu, X.; Ling, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Jin, J.; Chen, W.; Pang, M.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of Clostridium butyricum against vascular dementia in mice via metabolic butyrate. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 412946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liemburg-Apers, D.C.; Willems, P.H.; Koopman, W.J.; Grefte, S. Interactions between mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and cellular glucose metabolism. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1209–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourdin, M.; Dubois, P. Impact of ischemia on cellular metabolism. Artery Bypass 2013, 54509, 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Farzaei, M.H.; Tewari, D.; Momtaz, S.; Argüelles, S.; Nabavi, S.M. Targeting ERK signaling pathway by polyphenols as novel therapeutic strategy for neurodegeneration. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 120, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarneshan, S.N.; Fakhri, S.; Khan, H. Targeting Akt/CREB/BDNF signaling pathway by ginsenosides in neurodegenerative diseases: A mechanistic approach. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 177, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podcasy, J.L.; Epperson, C.N. Considering sex and gender in Alzheimer disease and other dementias. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 18, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.-S.; Kim, B.-Y.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, J.; Jeon, W.K. Mumefural Improves Recognition Memory and Alters ERK-CREB-BDNF Signaling in a Mouse Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3271. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143271
Kim M-S, Kim B-Y, Kim JI, Lee J, Jeon WK. Mumefural Improves Recognition Memory and Alters ERK-CREB-BDNF Signaling in a Mouse Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion. Nutrients. 2023; 15(14):3271. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143271
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min-Soo, Bu-Yeo Kim, Jung Im Kim, Joungbok Lee, and Won Kyung Jeon. 2023. "Mumefural Improves Recognition Memory and Alters ERK-CREB-BDNF Signaling in a Mouse Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion" Nutrients 15, no. 14: 3271. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143271
APA StyleKim, M.-S., Kim, B.-Y., Kim, J. I., Lee, J., & Jeon, W. K. (2023). Mumefural Improves Recognition Memory and Alters ERK-CREB-BDNF Signaling in a Mouse Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion. Nutrients, 15(14), 3271. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143271





