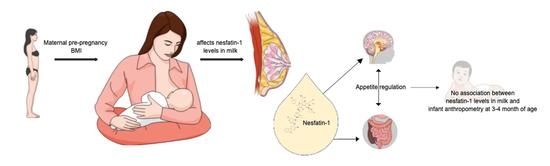
Nesfatin-1 in Human Milk and Its Association with Infant Anthropometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Infants’ Anthropometry
2.3. Human Milk
2.4. Nesfatin-1 Analyses
2.5. Ethics
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Participants
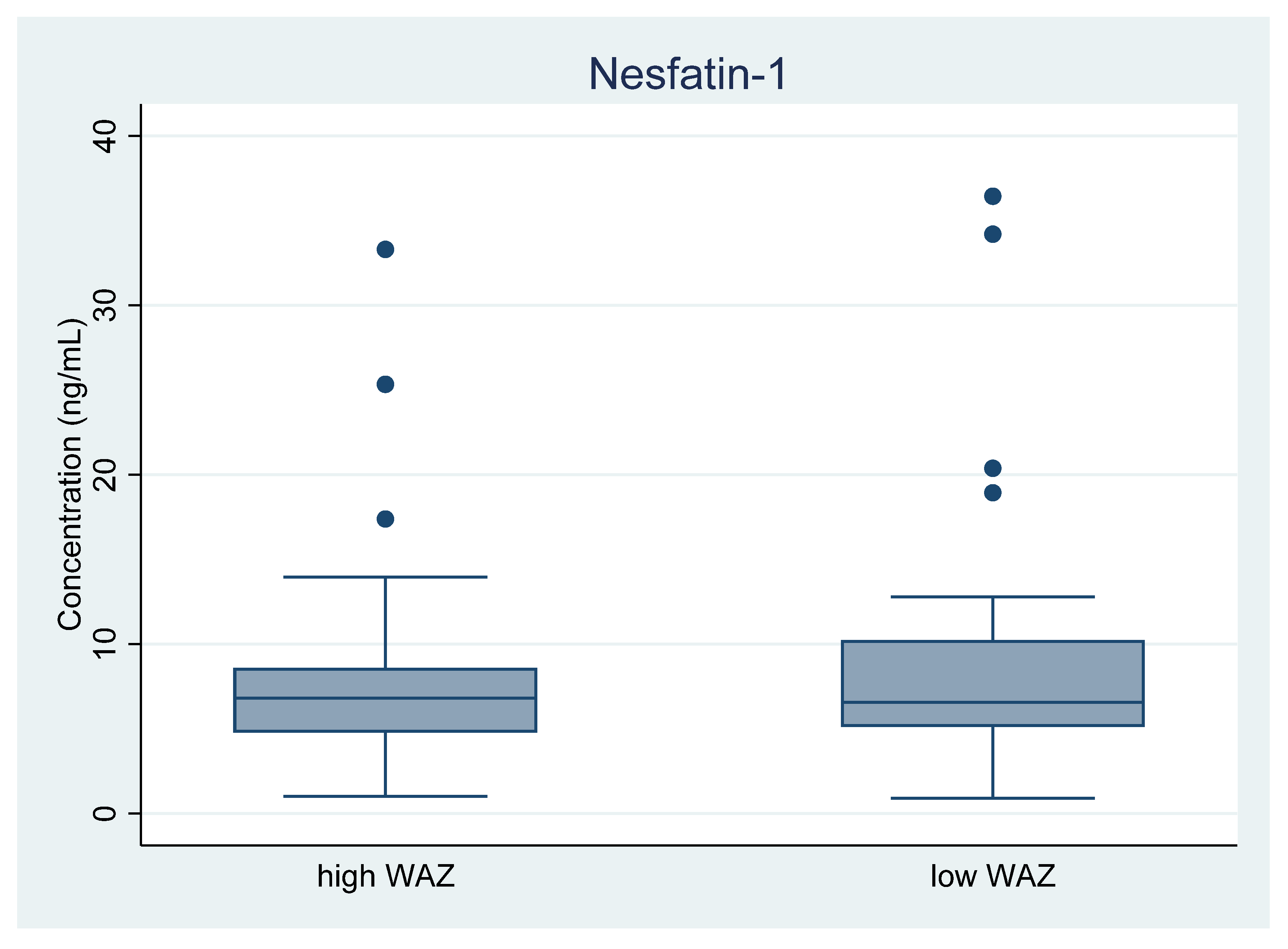
3.2. Nesfatin-1 Levels in Human Milk, Low and High WAZ Group
3.3. Nesfatin-1 and Infant Anthropometry at 3–4 Months of Age
3.4. Factors Possibly Influencing Nesfatin-1 Levels in Human Milk
4. Discussion
4.1. Nesfatin-1 Levels in Human Milk
4.2. Nesfatin-1 Levels in Human Milk and Infant Anthropometry
4.3. Nesfatin-1 Levels in Umbilical Cord Blood and Birth Weight
4.4. Nesfatin-1 Levels in Serum and Associations with Childhood Weight
4.5. Milk Sample Handling Affects Hormone Levels in Human Milk
4.6. Factors Influencing Adipokines in Human Milk
4.7. Milk Expression Methods, Circadian Patterns, and Adipokine Levels
4.8. Nesfatin-1 Levels in Infant and Maternal Serum
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Cesare, M.; Sorić, M.; Bovet, P.; Miranda, J.J.; Bhutta, Z.; Stevens, G.A.; Laxmaiah, A.; Kengne, A.-P.; Bentham, J. The epidemiological burden of obesity in childhood: A worldwide epidemic requiring urgent action. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonds, M.E.; Sebert, S.; Hyatt, M.A.; Budge, H. Nutritional programming of the metabolic syndrome. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2009, 5, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badillo-Suárez, P.A.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.; Nieves-Morales, X. Impact of Metabolic Hormones Secreted in Human Breast Milk on Nutritional Programming in Childhood Obesity. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2017, 22, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelsen, K.F.; Larnkjær, A.; Larsson, M.W.; Mølgaard, C. Early Nutrition and Its Effects on Growth, Body Composition and Later Obesity. World Rev. Nutr. Diet 2016, 114, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horta, B.L.; Rollins, N.; Dias, M.S.; Garcez, V.; Pérez-Escamilla, R. Systematic review and meta-analysis of breastfeeding and later overweight or obesity expands on previous study for World Health Organization. Acta Paediatr. 2022, 112, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyermann, M.; Beermann, C.; Brenner, H.; Rothenbacher, D. Adiponectin and Leptin in Maternal Serum, Cord Blood, and Breast Milk. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Liguori, S.A. Update on breast milk hormones: Leptin, ghrelin and adiponectin. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilcol, Y.O.; Hizli, Z.B.; Eroz, E. Resistin is present in human breast milk and it correlates with maternal hormonal status and serum level of C-reactive protein. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2008, 46, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzsch, J.; Bae, Y.J.; Kiess, W. Adipokines in human breast milk. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 32, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh-I, S.; Shimizu, H.; Satoh, T.; Okada, S.; Adachi, S.; Inoue, K.; Eguchi, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Imaki, T.; Hashimoto, K.; et al. Identification of nesfatin-1 as a satiety molecule in the hypothalamus. Nature 2006, 443, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, M.; Stengel, A.; Wang, L.; Lambrecht, N.W.; Taché, Y. Nesfatin-1 immunoreactivity in rat brain and spinal cord autonomic nuclei. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 452, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel-Stengel, M.; Wang, L.; Stengel, A.; Taché, Y. Localization of nesfatin-1 neurons in the mouse brain and functional implication. Brain Res. 2011, 1396, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupp, S.K.; Stengel, A. Interactions between nesfatin-1 and the autonomic nervous system—An overview. Peptides 2022, 149, 170719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stengel, A.; Goebel, M.; Yakubov, I.; Wang, L.; Witcher, D.; Coskun, T.; Taché, Y.; Sachs, G.; Lambrecht, N.W.G. Identification and Characterization of Nesfatin-1 Immunoreactivity in Endocrine Cell Types of the Rat Gastric Oxyntic Mucosa. Endocrinology 2008, 150, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Dag, E.; Ozkan, Y.; Erman, F.; Dagli, A.F.; Kilic, N.; Sahin, I.; Karatas, F.; Yoldas, T.; Barim, A.O.; et al. Nesfatin-1 and ghrelin levels in serum and saliva of epileptic patients: Hormonal changes can have a major effect on seizure disorders. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 328, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.-C.; Wang, H.-Y.; Chen, X.; Guan, H.-Z.; Jiang, Z.-Y. Fasting plasma levels of nesfatin-1 in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus and the nutrient-related fluctuation of nesfatin-1 level in normal humans. Regul. Pept. 2010, 159, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S. The presence of the peptides apelin, ghrelin and nesfatin-1 in the human breast milk, and the lowering of their levels in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus. Peptides 2010, 31, 2236–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- nbsp; Schalla, M.A.; Stengel, A. Current Understanding of the Role of Nesfatin-1. J. Endocr. Soc. 2018, 2, 1188–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filibeli, B.E.; Bayraktar, M.K.; Aksun, S.; Çatlı, G.; Yıldırım, J.G.; Dündar, B.N. The effect of breast milk nesfatin-1 and ghrelin levels on growth in infants with sga. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2022, 64, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyhl, H.B.; Jensen, T.K.; Barington, T.; Buhl, S.; Norberg, L.A.; Jørgensen, J.S.; Jensen, D.F.G.; Christesen, H.T.; Lamont, R.F.; Husby, S. The Odense Child Cohort: Aims, Design, and Cohort Profile. Paediatr. Périnat. Epidemiol. 2015, 29, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, S.; Gouveia-Figueira, S.; Domellöf, M.; Husby, S.; Neergaard Jacobsen, L.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Fowler, C.J.; Zachariassen, G. Satiety Factors Oleoylethanolamide, Stearoylethanolamide, and Palmitoylethanolamide in Mother’s Milk Are Strongly Associated with Infant Weight at Four Months of Age-Data from the Odense Child Cohort. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maršál, K.; Persson, P.-H.; Larsen, T.; Lilja, H.; Selbing, A.; Sultan, B. Intrauterine growth curves based on ultrasonically estimated foetal weights. Acta Paediatr. 1996, 85, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Onis, M.; Garza, C.; Onyango, A.W.; Rolland-Cachera, M.F. WHO growth standards for infants and young children. Arch. Pediatr. 2009, 16, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, J.L. zscore06: Stata Command for the Calculation of Anthropometric z-Scores Using the 2006 WHO Child Growth Standards [Internet]; International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Available online: http://fmwww.bc.edu/RePEc/bocode/z/zscore06 (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Lind, M.V.; Larnkjær, A.; Mølgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F. Breastfeeding, Breast Milk Composition, and Growth Outcomes. Nestle Nutr. Inst. Workshop Ser. 2018, 89, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Marousez, L.; Tran, L.; Micours, E.; De Lamballerie, M.; Gottrand, F.; Pierrat, V.; Eberlé, D.; Ley, D.; Lesage, J. Metabolic hormones in human breast milk are preserved by high hydrostatic pressure processing but reduced by Holder pasteurization. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 131957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröschl, M.; Uhr, M.; Kraus, T. Evaluation of the Comparability of Commercial Ghrelin Assays. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 457–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, M.; Celik, O.; Celik, N.; Turkcuoglu, I.; Yilmaz, E.; Karaer, A.; Simsek, Y.; Celik, E.; Aydin, S. Cord blood nesfatin-1 and apelin-36 levels in gestational diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 2011, 41, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutsikou, T.; Briana, D.D.; Boutsikou, M.; Kafalidis, G.; Piatopoulou, D.; Baka, S.; Hassiakos, D.; Gourgiotis, D.; Malamitsi-Puchner, A. Cord blood nesfatin-1 in large for gestational age pregnancies. Cytokine 2013, 61, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abaci, A.; Catli, G.; Anik, A.; Kume, T.; Bober, E. The relation of serum nesfatin-1 level with metabolic and clinical parameters in obese and healthy children. Pediatr. Diabetes 2013, 14, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, G.M.; Yamamah, G.; Ibrahim, A.; El-Lebedy, D.; Farid, T.M.; Mahmoud, R. Nesfatin-1 in childhood and adolescent obesity and its association with food intake, body composition and insulin resistance. Regul. Pept. 2014, 188, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Ahn, M.B.; Cho, W.K.; Cho, K.S.; Jung, M.H.; Suh, B.K. The relation of serum nesfatin-1 level with anthropometric and metabolic parameters in children and adolescents: A prospective observational study. Medicine 2019, 98, e15460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Dios, O.; Herrero, L.; Gavela-Pérez, T.; Soriano-Guillén, L.; Garcés, C. Sex-specific association of plasma nesfatin-1 concentrations with obesity in children. Pediatr. Obes. 2019, 14, e12567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokumacioglu, E.; Iskender, H.; Sahin, A.; Erturk, E.Y.; Kaynar, O. Serum levels of nesfatin-1 and irisin in obese children. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2020, 31, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kaba, S.; Karaman, K.; Kömüroğlu, U.; Bala, K.A.; Demir, N.; Kocaman, S.; Doğan, M.; Ceylan, N. Role of circulating nesfatin-1 in the underweight children with poor appetite. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 4703–4706. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.D.; McArthur, A.; Munn, Z. Safe management of expressed breast milk: A systematic review. Women Birth 2016, 29, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Santana, C.; Pérez-Cano, F.; Audí, C.; Castell, M.; Moretones, M.; López-Sabater, M.; Castellote, C.; Franch, A. Effects of cooling and freezing storage on the stability of bioactive factors in human colostrum. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 2319–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrabi, A.F.; Handa, D.; Codipilly, C.N.; Shah, S.; Williams, J.E.; McGuire, M.A.; Potak, D.; Aharon, G.G.; Schanler, R.J. Effects of Extended Freezer Storage on the Integrity of Human Milk. J. Pediatr. 2016, 177, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handa, D.; Ahrabi, A.F.; Codipilly, C.N.; Shah, S.; Ruff, S.; Potak, D.; Williams, J.E.; McGuire, M.A.; Schanler, R.J. Do thawing and warming affect the integrity of human milk? J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Fang, L.-J.; Tsai, C.-R.; Chang, Y.-C.; Wang, T.-M. Influence of Prolonged Storage Process, Pasteurization, and Heat Treatment on Biologically-active Human Milk Proteins. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2013, 54, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, S.H.; Hanley, A.J.; Stone, D.; O’Connor, D.L. Effects of Pasteurization on Adiponectin and Insulin Concentrations in Donor Human Milk. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 70, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mank, E.; Naninck, E.F.G.; van den Akker, C.H.P.; Heijboer, A.C. Rapid quantification of insulin in human milk by immunoassay. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 1152–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugananthan, S.; Lai, C.T.; Gridneva, Z.; Mark, P.J.; Geddes, D.T.; Kakulas, F. Leptin Levels Are Higher in Whole Compared to Skim Human Milk, Supporting a Cellular Contribution. Nutrients 2016, 8, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatas, Z.; Durmus Aydogdu, S.; Dinleyici, E.C.; Colak, O.; Dogruel, N. Breastmilk ghrelin, leptin, and fat levels changing foremilk to hindmilk: Is that important for self-control of feeding? Eur. J. Pediatr. 2011, 170, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Italianer, M.F.; Naninck, E.F.G.; Roelants, J.A.; Van Der Horst, G.T.; Reiss, I.K.M.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Joosten, K.F.M.; Chaves, I.; Vermeulen, M.J. Circadian Variation in Human Milk Composition, a Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwaydi, M.A.; Gridneva, Z.; Perrella, S.L.; Wlodek, M.E.; Lai, C.T.; Geddes, D.T. Human Milk Metabolic Hormones: Analytical Methods and Current Understanding. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Low WAZ 1 | High WAZ | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 50 | 50 | |
| WAZ at 4 months of age, SD 2 | −0.9 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | <0.001 * |
| Maternal characteristics | |||
| Age at child’s birth, years | 31.5 ± 5.3 | 30.9 ± 4.0 | 0.538 |
| mBMI 3, kg/m2 | 22.6 (21.1–24.0) | 23.5 (21.1–28.7) | 0.046 * |
| Post-delivery parity, n (%) | |||
| Primiparous | 25 (50%) | 22 (44%) | |
| Parity 2 | 14 (28%) | 20 (40%) | 0.481 |
| ≥Parity 3 | 11 (22%) | 8 (16%) | |
| Educational level, n (%) | |||
| Low | 7 (14%) | 8 (16%) | |
| Intermediate | 21 (41%) | 25 (50%) | |
| High | 9 (18%) | 5 (10%) | 0.519 |
| Unknown | 13 (26%) | 12 (24%) | |
| Smoking status, n (%) | |||
| Non-smoking | 50 (100%) | 49 (98%) | n/a |
| Unknown | 1 (2%) | ||
| Weight gain during pregnancy, n (%) | |||
| >15 kg | 13 (26%) | 20 (40%) | |
| ≤15 kg | 31 (62%) | 27 (54%) | 0.275 |
| unknown | 6 (12%) | 3 (6%) | |
| Gestational diabetes, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 0 | 0 | |
| No | 50 (100%) | 49 (98%) | n/a |
| unknown | 1 (2%) | ||
| Infant characteristics | |||
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Female | 23 (46%) | 22 (44%) | 1.00 |
| Male | 27 (54%) | 28 (56%) | |
| Gestational age, days | 279 (273–285) | 285 (277–295) | 0.071 |
| Birth weight, g | 3253 ± 544 | 3893 ± 487 | <0.001 * |
| BWZ 4, SD | −0.7 ± 1.1 | 0.6 ± 1.1 | <0.001 * |
| BWZ group, n (%) | |||
| ≤−2 SD | 4 (8%) | 0 | |
| >−2 SD and ≤2 SD | 45 (90%) | 44 (88%) | 0.024 * |
| >2 SD | 1 (2%) | 6 (12%) | |
| Birth length, cm | 50.8 ± 2.5 | 53.3 ± 2.1 | <0.001 * |
| Early formula supplementation, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 7 (14%) | 15 (30%) | |
| No | 34 (68%) | 25 (50%) | 0.048 * |
| Unknown | 9 (18%) | 10 (20%) | |
| Exclusive breastfeeding, at time of milk sampling n (%) | |||
| Yes | 17 (34%) | 26 (52%) | |
| No | 24 (48%) | 15 (30% | |
| Unknown | 9 (18%) | 9 (18%) | 0.076 |
| Infant weight at time of sampling, g | 6053 (5770–6490) | 8140 (7630–8565) | <0.001 * |
| Predictor Variables | Log[nesfatin-1] 1 ng/mL | mBMI 2 | BW 3 | Infant Sex | IF 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome Measure | β (95% CI), p | p | p | p | p |
| Δ Weight since birth (g) | 68.57 (−326.80–463.94), 0.73 | 0.06 | 0.97 | 0.03 | 0.41 |
| Δ WAZ 5 since birth (SD) | 0.13 (−0.31–0.58), 0.51 | 0.11 | 0.001 * | 0.81 | 0.11 |
| Δ Weight since birth per day (g) | 0.49 (−2.30–3.27), 0.73 | 0.12 | 0.87 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| Length at sampling (cm) | 0.19 (−0.74–1.13), 0.68 | 0.89 | <0.001 * | 0.16 | 0.28 |
| Weight at sampling (g) | 68.57 (−326.80–463.94), 0.73 | 0.06 | <0.001 * | 0.03 | 0.41 |
| Abdominal circumference (cm) | 0.08 (−1.10–1.25), 0.89 | 0.35 | <0.001 * | 0.61 | 0.02 |
| Triceps skinfold thickness (mm) | 0.17 (−0.57–0.91), 0.65 | 0.10 | 0.98 | 0.71 | 0.33 |
| Subscapular skinfold thickness (mm) | 0.05 (−0.46–0.55), 0.86 | 0.006 | 0.98 | 0.87 | 0.33 |
| WAZ (SD) | 0.08 (−0.33–0.50), 0.69 | 0.08 | <0.001 * | 0.62 | 0.09 |
| HAZ 6 (SD) | 0.09 (−0.25–0.43), 0.61 | 0.84 | <0.001 * | 0.01 | 0.99 |
| WHZ 7 (SD) | 0.05 (−0.37–0.47), 0.8 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.33 | 0.02 |
| BMIZ 8 (SD) | 0.05 (−0.38–0.48), 0.81 | 0.02 | 0.004 | 0.5 | 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Honoré, K.D.; Bruun, S.; Jacobsen, L.N.; Domellöf, M.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Husby, S.; Zachariassen, G. Nesfatin-1 in Human Milk and Its Association with Infant Anthropometry. Nutrients 2023, 15, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010176
Honoré KD, Bruun S, Jacobsen LN, Domellöf M, Michaelsen KF, Husby S, Zachariassen G. Nesfatin-1 in Human Milk and Its Association with Infant Anthropometry. Nutrients. 2023; 15(1):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010176
Chicago/Turabian StyleHonoré, Karina D., Signe Bruun, Lotte N. Jacobsen, Magnus Domellöf, Kim F. Michaelsen, Steffen Husby, and Gitte Zachariassen. 2023. "Nesfatin-1 in Human Milk and Its Association with Infant Anthropometry" Nutrients 15, no. 1: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010176
APA StyleHonoré, K. D., Bruun, S., Jacobsen, L. N., Domellöf, M., Michaelsen, K. F., Husby, S., & Zachariassen, G. (2023). Nesfatin-1 in Human Milk and Its Association with Infant Anthropometry. Nutrients, 15(1), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010176