Postnatal Leptin Levels Correlate with Breast Milk Leptin Content in Infants Born before 32 Weeks Gestation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
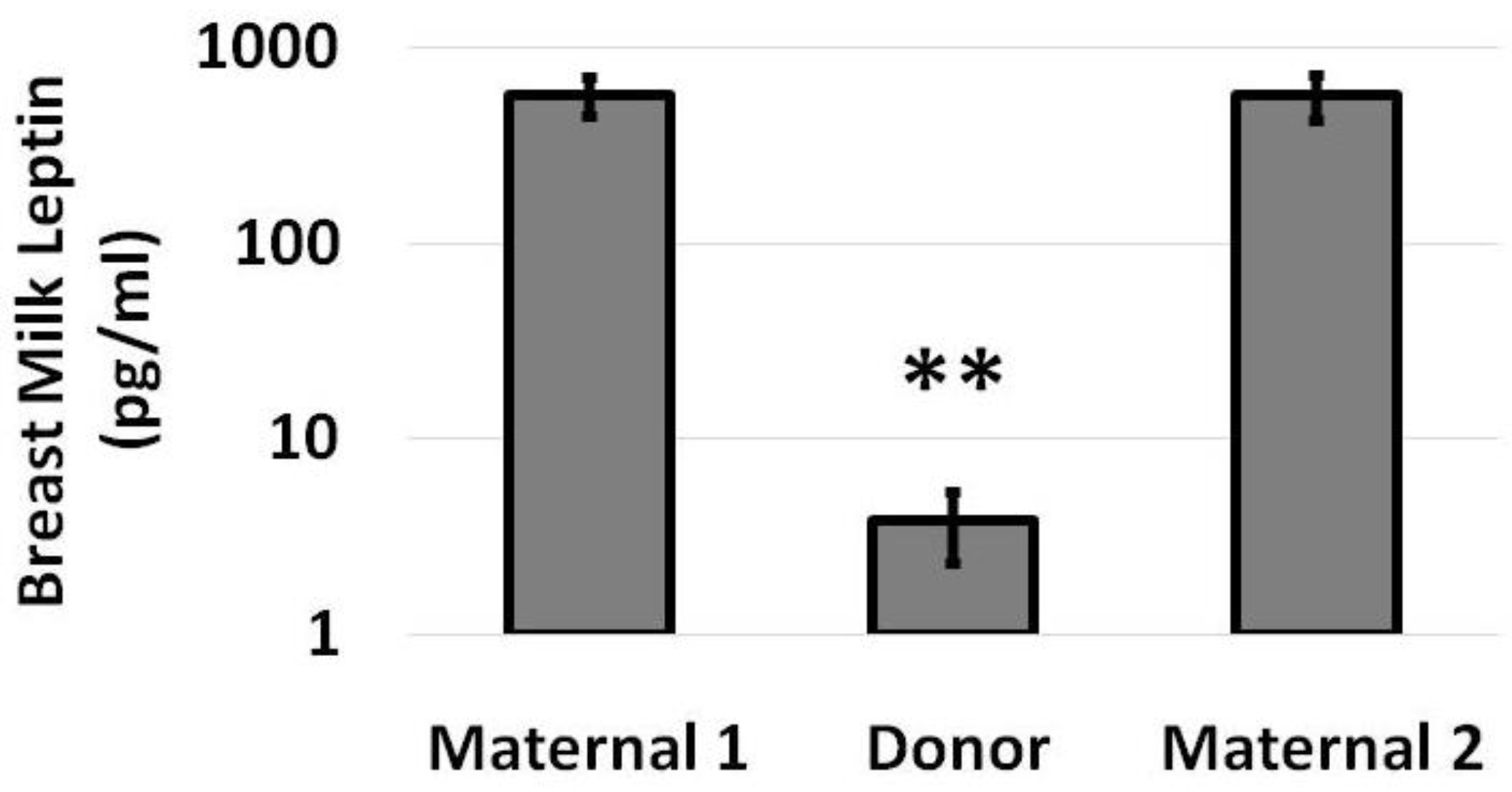
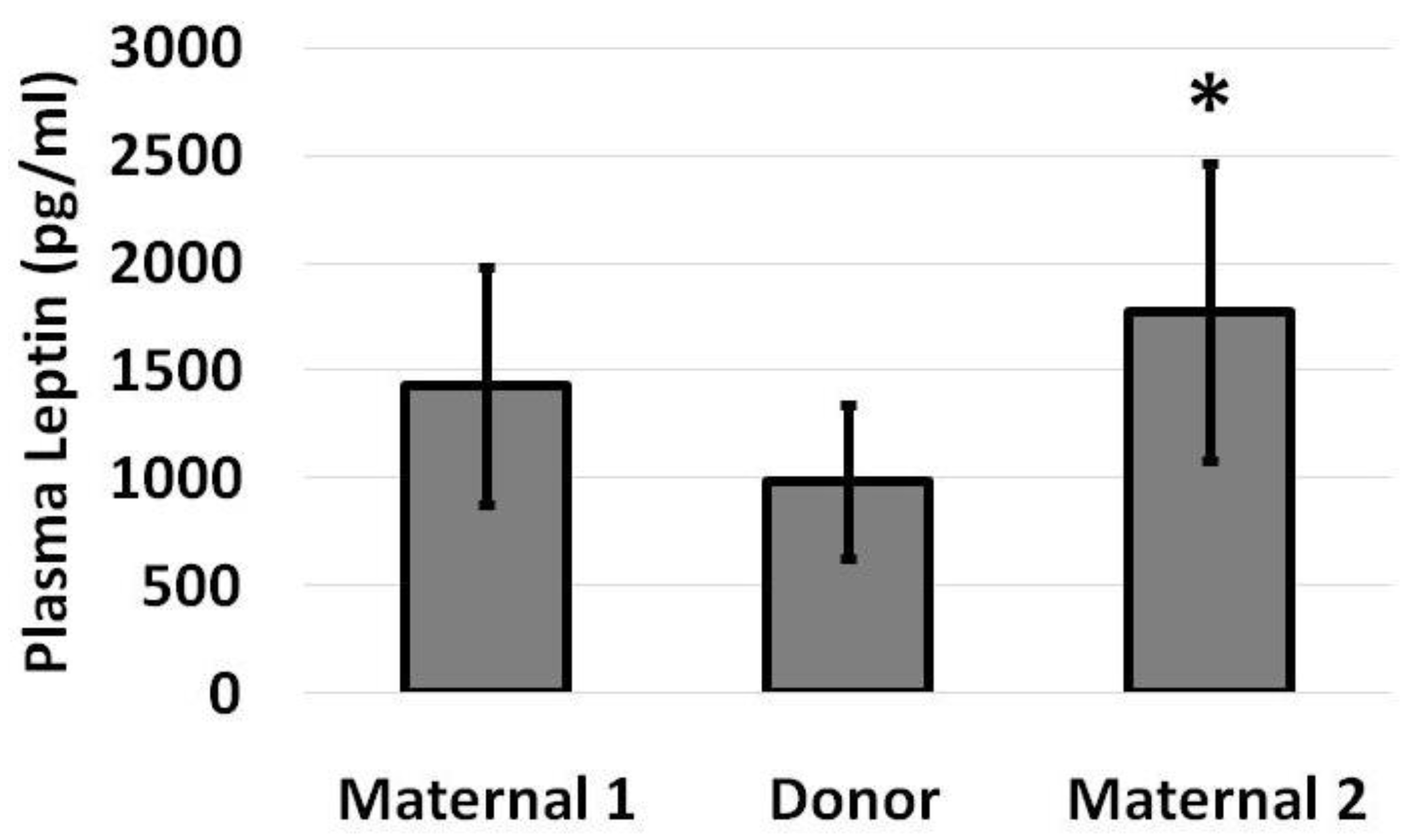
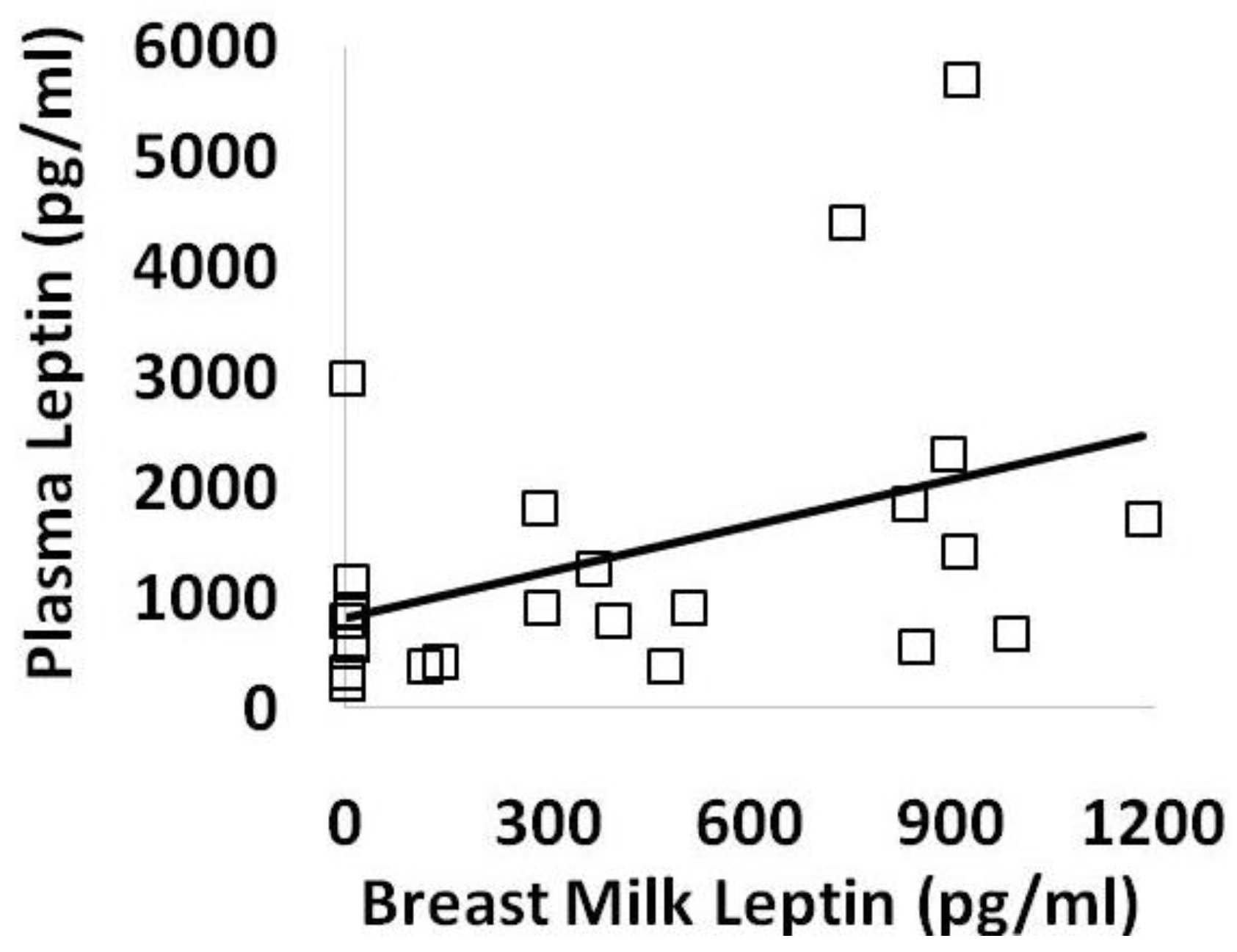
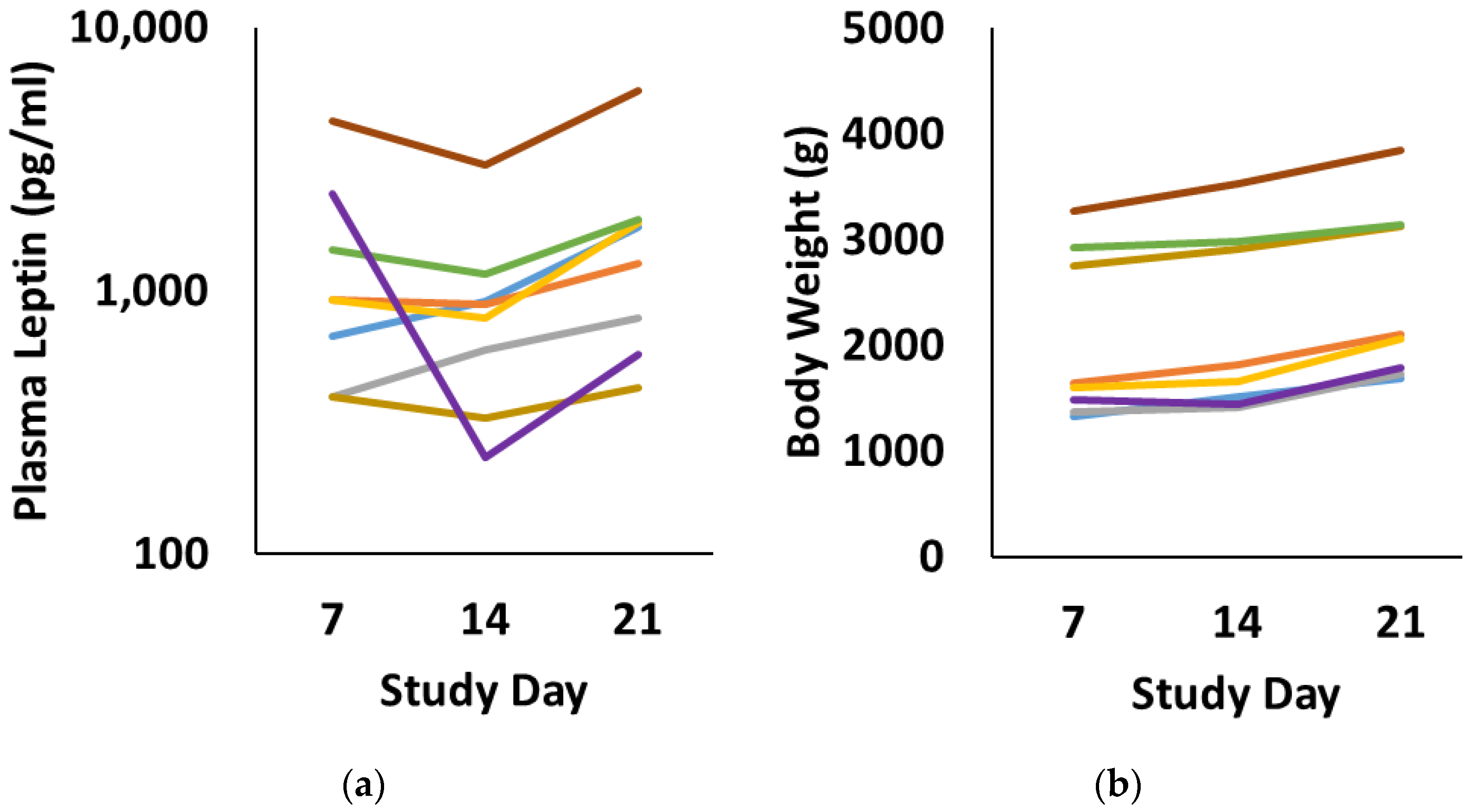
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ElSaeed, G.; Mousa, N.; El-Mougy, F.; Hafez, M.; Khodeera, S.; Alhelbawy, M.; Fouda, E.; Elsheikh, S.; ElKaffas, R.; Eldeeb, S.; et al. Monogenic leptin deficiency in early childhood obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2020, 15, e12574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadge, A.A.; Khaire, A.A. Leptin as a predictive marker for metabolic syndrome. Cytokine 2019, 121, 154735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montague, C.T.; Farooqi, I.S.; Whitehead, J.P.; Soos, M.A.; Rau, H.; Wareham, N.J.; Sewter, C.P.; Digby, J.E.; Mohammed, S.N.; Hurst, J.A.; et al. Congenital leptin deficiency is associated with severe early-onset obesity in humans. Nature 1997, 387, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrekera, B.; Roghair, R. Modeling the impact of growth and leptin deficits on the neuronal regulation of blood pressure. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 231, R47–R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Liguori, S.A.; Lupica, M.M. Adipokines in breast milk and preterm infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2010, 86 (Suppl. S1), 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbrekera, B.; Colaizy, T.T.; Vasilakos, L.K.; Johnson, K.J.; Santillan, D.A.; Haskell, S.E.; Roghair, R.D. Origins of neonatal leptin deficiency in preterm infants. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 85, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, T.N.K.; Pemberton, V.L.; Saigal, S.; Blaisdell, C.J.; Moxey-Mims, M.; Buist, S.; Adults Born Preterm Conference Speakers and Discussants. Long-term healthcare outcomes of preterm birth: An executive summary of a conference sponsored by the National Institutes of Health. J. Pediatr. 2017, 181, 309–318.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Filho, G.; Mastronardi, C.A.; Licinio, J. Leptin treatment, facts and expectations. Metabolism 2015, 64, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.; Oliver, P.; Miralles, O.; Ceresi, E.; Pico, C.; Palou, A. Leptin orally supplied to neonate rats is directly uptaken by the immature stomach and may regulate short-term feeding. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 2575–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Filho, G.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J. Ten years of leptin replacement therapy. Obes Rev. 2011, 12, e315–e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newburg, D.S.; Woo, J.G.; Morrow, A.L. Characteristics and potential functions of human milk adiponectin. J. Pediatr. 2010, 156, S41–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vass, R.A.; Bell, E.F.; Colaizy, T.T.; Schmelzel, M.L.; Johnson, K.J.; Walker, J.R.; Ertl, T.; Roghair, R.D. Hormone levels in preterm and donor human milk before and after Holder pasteurization. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 88, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemas, D.J.; Young, B.E.; Baker, P.R., 2nd; Tomczik, A.C.; Soderborg, T.K.; Hernandez, T.L.; de la Houssaye, B.A.; Robertson, C.E.; Rudolph, M.C.; Ir, D.; et al. Alterations in human milk leptin and insulin are associated with early changes in the infant intestinal microbiome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio, V.A.; Ocon, O.; Diaz-Castro, J.; Acosta-Manzano, P.; Coll-Risco, I.; Borges-Cosic, M.; Romero-Gallardo, L.; Moreno-Fernández, J.; Ochoa-Herrera, J.J. Influence of a concurrent exercise training program during pregnancy on colostrum and mature human milk inflammatory markers: Findings from the GESTAFIT project. J. Hum. Lact. 2018, 34, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, T.R.; Kim, J.H. A systematic review and meta-analysis to revise the Fenton growth chart for preterm infants. BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.H.; Roumiantsev, S.; Singh, R. PediTools electronic growth chart calculators: Applications in clinical care, research, and quality improvement. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e16204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouret, S.G.; Draper, S.J.; Simerly, R.B. Trophic action of leptin on hypothalamic neurons that regulate feeding. Science 2004, 304, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahima, R.S.; Bjorbaek, C.; Osei, S.; Flier, J.S. Regulation of neuronal and glial proteins by leptin: Implications for brain development. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 2755–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereiter, D.A.; Jeanrenaud, B. Altered neuroanatomical organization in the central nervous system of the genetically obese (ob/ob) mouse. Brain Res. 1979, 165, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuzaki, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Sagawa, N.; Hosoda, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Mise, H.; Nishimura, H.; Yoshimasa, Y.; Tanaka, I.; Mori, T.; et al. Nonadipose tissue production of leptin: Leptin as a novel placenta-derived hormone in humans. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Toro, A.; Vilariño-García, T.; Maymó, J.; Guadix, P.; Dueñas, J.L.; Fernández-Sánchez, M.; Varone, C.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Leptin action in normal and pathological pregnancies. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peotta, V.; Rahmouni, K.; Segar, J.L.; Morgan, D.A.; Pitz, K.M.; Rice, O.M.; Roghair, R.D. Neonatal growth restriction-related leptin deficiency enhances leptin-triggered sympathetic activation and central angiotensin II receptor-dependent stress-evoked hypertension. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 80, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Erkonen, G.E.; Hermann, G.M.; Miller, R.L.; Thedens, D.L.; Nopoulos, P.C.; Wemmie, J.A.; Roghair, R.D. Neonatal leptin administration alters regional brain volumes and blocks neonatal growth restriction-induced behavioral and cardiovascular dysfunction in male mice. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 69, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picó, C.; Oliver, P.; Sánchez, J.; Miralles, O.; Caimari, A.; Priego, T.; Palou, A. The intake of physiological doses of leptin during lactation in rats prevents obesity in later life. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, J.; Priego, T.; Palou, M.; Tobaruela, A.; Palou, A.; Picó, C. Oral supplementation with physiological doses of leptin during lactation in rats improves insulin sensitivity and affects food preferences later in life. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabiell, X.; Pineiro, V.; Tome, M.A.; Peino, R.; Dieguez, C.; Casanueva, F.F. Presence of leptin in colostrum and/or breast milk from lactating mothers: A potential role in the regulation of neonatal food intake. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 4270–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poissonnet, C.M.; LaVelle, M.; Burdi, A.R. Growth and development of adipose tissue. J. Pediatr. 1988, 113, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepercq, J.; Challier, J.C.; Guerre-Millo, M.; Cauzac, M.; Vidal, H.; Hauguel-de Mouzon, S. Prenatal leptin production: Evidence that fetal adipose tissue produces leptin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 2409–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helland, I.B.; Reseland, J.E.; Saugstad, O.D.; Drevon, C.A. Leptin levels in pregnant women and newborn infants: Gender differences and reduction during the neonatal period. Pediatrics 1998, 101, E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hytinantti, T.; Koistinen, H.A.; Koivisto, V.A.; Karonen, S.L.; Andersson, S. Changes in leptin concentration during the early postnatal period: Adjustment to extrauterine life? Pediatr. Res. 1999, 45, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kawamata, R.; Suzuki, Y.; Yada, Y.; Koike, Y.; Kono, Y.; Yada, T.; Takahashi, N. Gut hormone profiles in preterm and term infants during the first 2 months of life. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 27, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertl, T.; Funke, S.; Sarkany, I.; Szabo, I.; Rascher, W.; Blum, W.F.; Sulyok, E. Postnatal changes of leptin levels in full-term and preterm neonates: Their relation to intrauterine growth, gender and testosterone. Biol. Neonate 1999, 75, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellgren, G.; Engstrom, E.; Smith, L.E.; Lofqvist, C.; Hellstrom, A. Effect of preterm birth on postnatal apolipoprotein and adipocytokine profiles. Neonatology 2015, 108, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resto, M.; O’Connor, D.; Leef, K.; Funanage, V.; Spear, M.; Locke, R. Leptin levels in preterm human breast milk and infant formula. Pediatrics 2001, 108, E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, D.; Funanage, V.; Locke, R.; Spear, M.; Leef, K. Leptin is not present in infant formulas. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2003, 26, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, J.Y.; Noble, L.; Section on Breastfeeding. Policy statement: Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2022057988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on Nutrition, Section on Breastfeeding; Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Donor human milk for the high-risk infant: Preparation, safety, and usage options in the United States. Pediatrics 2017, 139, E20163440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Liguori, S.A.; Benetti, S.; Sorrenti, M.; Fissore, M.F.; Cordero di Montezemolo, L. High serum leptin levels in infancy can potentially predict obesity in childhood, especially in formula-fed infants. Acta Paediatr. 2013, 102, e455–e459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doneray, H.; Orbak, Z.; Yildiz, L. The relationship between breast milk leptin and neonatal weight gain. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, D.A.; Demerath, E.W. Relationship of insulin, glucose, leptin, IL-6 and TNF-alpha in human breast milk with infant growth and body composition. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, D.A.; George, B.; Williams, M.; Whitaker, K.; Allison, D.B.; Teague, A.; Demerath, E.W. Associations between human breast milk hormones and adipocytokines and infant growth and body composition in the first 6 months of life. Pediatr. Obes. 2017, 12 (Suppl. S1), 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.; Hechler, C.; Gebauer, C.; Kiess, W.; Kratzsch, J. Leptin in maternal serum and breast milk: Association with infants’ body weight gain in a longitudinal study over 6 months of lactation. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 70, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreas, N.J.; Hyde, M.J.; Gale, C.; Parkinson, J.R.C.; Jeffries, S.; Holmes, E.; Modi, N. Effect of maternal body mass index on hormones in breast milk: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, R.; Petrova, A. Urinary levels of energy metabolism hormones in association with the proportional intake of maternal milk and weight gain in very preterm neonates. J. Neonatal Perinat. Med. 2022, 15, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Mean (SD) or N (%) |
|---|---|
| Maternal age in years, mean (SD) | 26.9 (3.9) |
| Maternal race (white) | 7 (88%) |
| Antenatal steroids (yes) | 7 (88%) |
| Mode of delivery (vaginal) | 3 (38%) |
| Place of birth (inborn) | 6 (75%) |
| Infant sex (female) | 3 (38%) |
| Birth | Day 0 | Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 21 | Discharge | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Postmenstrual age (weeks) | 25.6 (1.4) | 32.6 (2.7) | 33.6 (2.7) | 34.6 (2.7) | 35.6 (2.7) | 43.3 (2.5) |
| Feeding volume (mL/kg/day) | 131 (18) | 135 (13) | 129 (14) | |||
| Caloric intake (Kcal/kg/day) | 113 (10) | 119 (10) | 115 (11) | |||
| Weight (g) | 816 (247) | 1790 (778) | 2044 (793) | 2158 (843) | 2433 (816) | 3990 (666) |
| Weight (z-score) | 0.05 (0.9) | −0.35 (0.5) | −0.17 (0.6) | −0.43 (0.6) | −0.28 (0.6) | −0.42 (0.35) |
| Head circumference (cm) | 23 (1.9) | 28 (2.6) | 29 (2.5) | 30 (2.4) | 31 (2.4) | 36 (1.2) |
| Head circumference (z-score) | −0.33 (0.7) | −0.73 (0.3) | −0.67 (0.4) | −0.65 (0.3) | −0.58 (0.6) | −0.55 (0.7) |
| Length (cm) | 32 (2.9) | 39 (4.1) | 40 (3.6) | 41 (3.9) | 42 (3.8) | 50 (1.6) |
| Length (z-score) | −0.40 (1.0) | −1.25 (0.6) | −1.19 (0.7) | −1.65 (0.6) | −1.70 (0.7) | −1.65 (0.9) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chatmethakul, T.; Schmelzel, M.L.; Johnson, K.J.; Walker, J.R.; Santillan, D.A.; Colaizy, T.T.; Roghair, R.D. Postnatal Leptin Levels Correlate with Breast Milk Leptin Content in Infants Born before 32 Weeks Gestation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5224. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245224
Chatmethakul T, Schmelzel ML, Johnson KJ, Walker JR, Santillan DA, Colaizy TT, Roghair RD. Postnatal Leptin Levels Correlate with Breast Milk Leptin Content in Infants Born before 32 Weeks Gestation. Nutrients. 2022; 14(24):5224. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245224
Chicago/Turabian StyleChatmethakul, Trassanee, Mendi L. Schmelzel, Karen J. Johnson, Jacky R. Walker, Donna A. Santillan, Tarah T. Colaizy, and Robert D. Roghair. 2022. "Postnatal Leptin Levels Correlate with Breast Milk Leptin Content in Infants Born before 32 Weeks Gestation" Nutrients 14, no. 24: 5224. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245224
APA StyleChatmethakul, T., Schmelzel, M. L., Johnson, K. J., Walker, J. R., Santillan, D. A., Colaizy, T. T., & Roghair, R. D. (2022). Postnatal Leptin Levels Correlate with Breast Milk Leptin Content in Infants Born before 32 Weeks Gestation. Nutrients, 14(24), 5224. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245224








