iTRAQ-Based Quantitative Proteomics Reveals the Energy Metabolism Alterations Induced by Chlorogenic Acid in HepG2 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Coffee Ingredients
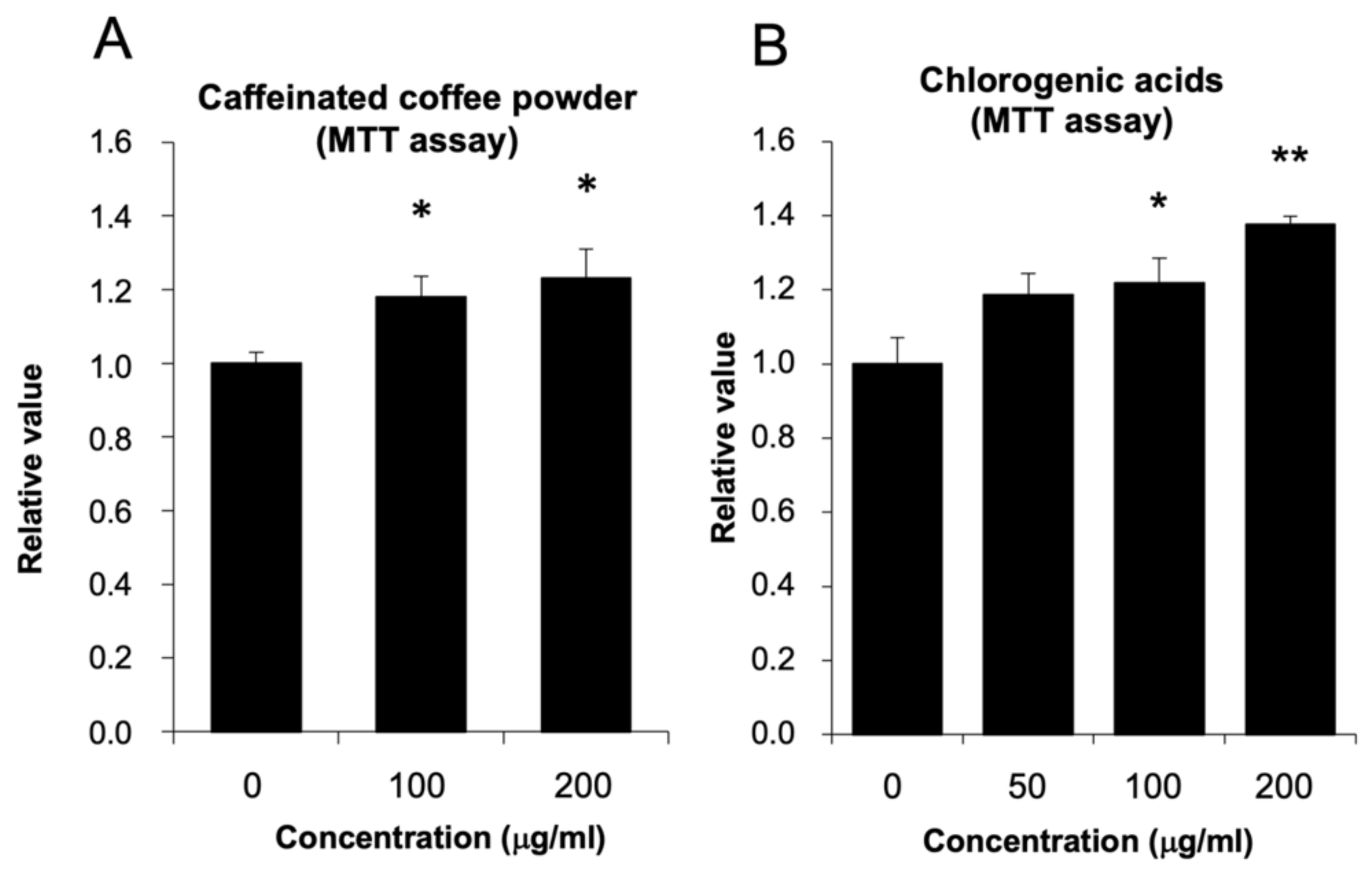
2.3. MTT (3-[4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) Assay
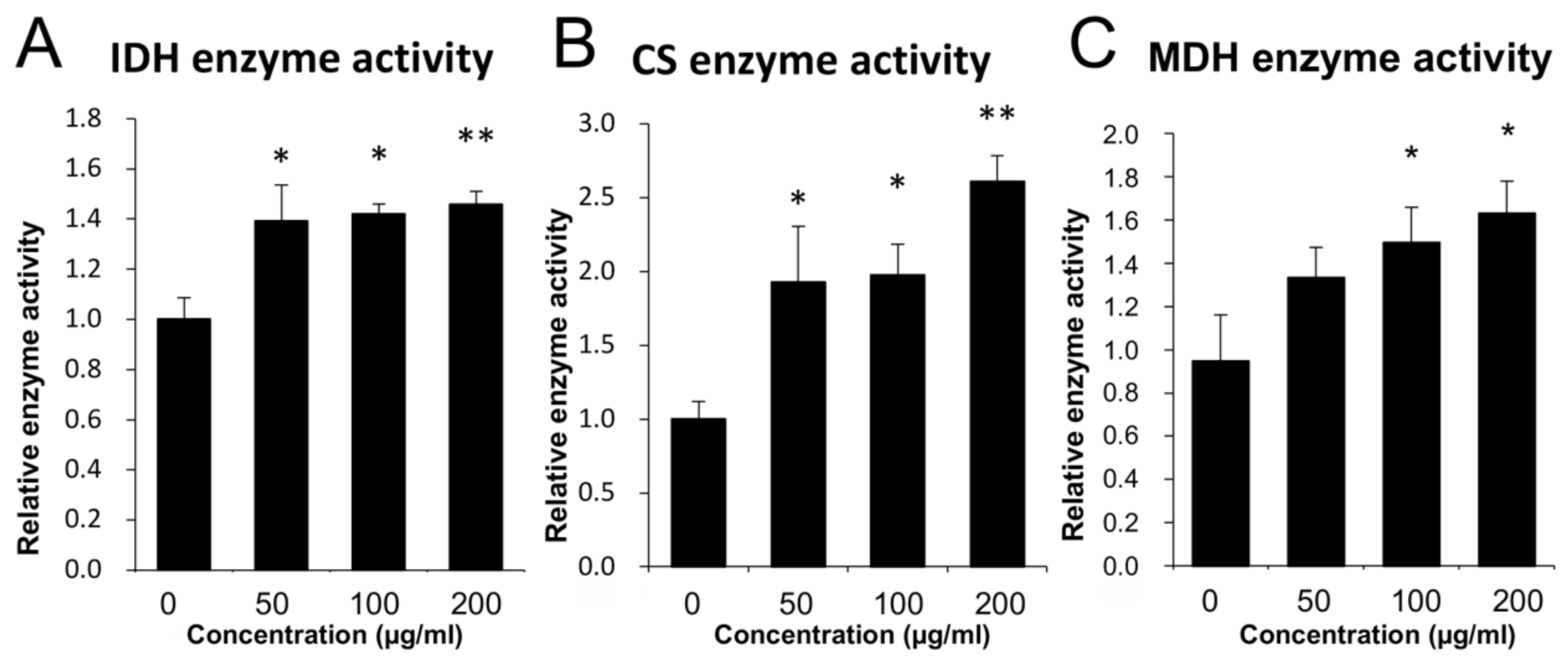
2.4. Enzyme Activity Measurement
2.5. Total RNA Extraction
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR Analysis
2.7. Proteomics Using Isobaric Tags for Relative and Absolute Quantitation (iTRAQ) Methods and Identification of Regulated Proteins
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Effect of Coffee Powder and Chlorogenic Acid (CGA) on HepG2 Cell Viability
3.2. Mitochondrial Enzyme Activity Analysis
3.3. Proteomics Using the iTRAQ Method
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Dam, R.M.; Hu, F.B. Coffee consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. JAMA 2005, 294, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, S.; Hammar, N.; Grill, V.; Kaprio, J. Coffee consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes in Finnish twins. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 33, 616–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxley, R.; Lee, C.M.; Barzi, F.; Timmermeister, L.; Czernichow, S.; Perkovic, V.; Grobbee, D.E.; Batty, D.; Woodward, M. Coffee, decaffeinated coffee, and tea consumption in relation to incident type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.C.; Wolk, A. Coffee consumption and risk of liver cancer: A meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Na, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Yuan, Z.; Zhu, B.W.; Tan, M. The effects of carbon dots produced by the Maillard reaction on the HepG2 cell substance and energy metabolism. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 6487–6495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, K.; Rengarajan, R.L.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Mathew, S.; Qadri, I.; Vijaya Anand, A. Psidium guajava Leaf Extracts and Their Quercetin Protect HepG2 Cell Lines Against CCL4 Induced Cytotoxicity. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 34, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, A.; Hochkogler, C.M.; Lang, R.; Bytof, G.; Lantz, I.; Hofmann, T.; Somoza, V. N-methylpyridinium, a degradation product of trigonelline upon coffee roasting, stimulates respiratory activity and promotes glucose utilization in HepG2 cells. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaynshteyn, D.; Jeong, H. Caffeine induces CYP1A2 expression in rat hepatocytes but not in human hepatocytes. Drug Metab. Lett. 2012, 6, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kalthoff, S.; Ehmer, U.; Freiberg, N.; Manns, M.P.; Strassburg, C.P. Coffee induces expression of glucuronosyltransferases by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and Nrf2 in liver and stomach. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1699–1710.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Saito, K.; Jia, H.; Kato, H. An integrated multi-omics study revealed metabolic alterations underlying the effects of coffee consumption. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Egashira, K.; Saito, K.; Jia, H.J.; Abe, K.; Kato, H. Coffee intake down-regulates the hepatic gene expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in C57BL/6J mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 6, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, S.W.; Okun, J.G.; Schwab, M.A.; Crnic, L.R.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Goodman, S.I.; Koeller, D.M.; Kolker, S. Bioenergetics in glutaryl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency: A role for glutaryl-coenzyme A. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 21830–21836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, D.; Garland, P.B. [2] Citrate synthase from rat liver: [EC 4.1.3.7 Citrate oxaloacetage-lyase (CoA-acetylating)]. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1969; Volume 13, pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wen, Y.; Aw, W.; Saito, K.; Kato, H. Ameliorating Effects of Coriander on Gastrocnemius Muscles Undergoing Precachexia in a Rat Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Proteomics Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, M.; Farah, A.; Perrone, D.; Trugo, L.C.; Donangelo, C. Chlorogenic acid compounds from coffee are differentially absorbed and metabolized in humans. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 2196–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, G.; Dionisi, F.; Renouf, M. Flavanols from green tea and phenolic acids from coffee: Critical quantitative evaluation of the pharmacokinetic data in humans after consumption of single doses of beverages. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, D.; Lv, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhou, F.; Tang, M.; Mao, T.; Li, M.; et al. Inhibitory effect of blueberry polyphenolic compounds on oleic acid-induced hepatic steatosis in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12254–12263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Protein | Name | Protein ID | 50 μg/mL | 100 μg/mL | 200 μg/mL | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC | p-Value | FC | p-Value | FC | p-Value | |||
| SPTAN1 | Isoform 3 of Spectrin alpha chain, brain | Q13813-3 | 0.93 | 0.01 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 0.88 | 0.00 |
| HMGB1 | High mobility group protein B1 | P09429 | 0.59 | 0.00 | 0.42 | 0.00 | 0.55 | 0.00 |
| AHNAK | Neuroblast differentiation-associated protein AHNAK | Q09666 | 0.96 | 0.36 | 0.83 | 0.00 | 0.86 | 0.00 |
| VSNL1 | Visinin-like protein 1 | P62760 | 1.07 | 0.63 | 1.27 | 0.01 | 1.46 | 0.00 |
| PSAP | Proactivator polypeptide | P07602 | 0.95 | 0.83 | 1.12 | 0.11 | 0.52 | 0.01 |
| HPCAL1 | Hippocalcin-like protein 1 | P37235 | 1.08 | 0.50 | 1.10 | 0.21 | 1.33 | 0.01 |
| ZC3H15 | Zinc finger CCCH domain-containing protein 15 | Q8WU90 | 0.85 | 0.19 | 0.72 | 0.00 | 0.82 | 0.01 |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | P04406 | 1.30 | 0.16 | 1.22 | 0.00 | 1.38 | 0.01 |
| CPLX2 | Complexin-2 | Q6PUV4 | 1.34 | 0.14 | 1.33 | 0.01 | 1.70 | 0.01 |
| CFL1 | Cofilin-1 | P23528 | 0.47 | 0.01 | 0.96 | 0.54 | 0.66 | 0.01 |
| PGK1 | Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 | P00558 | 1.08 | 0.43 | 1.16 | 0.00 | 1.21 | 0.01 |
| KRT18 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 18 | P05783 | 1.20 | 0.02 | 1.17 | 0.02 | 1.21 | 0.02 |
| GLUD1 | Glutamate dehydrogenase 1, mitochondrial | P00367 | 1.08 | 0.23 | 1.07 | 0.12 | 1.12 | 0.02 |
| ATP5B | ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial | P06576 | 1.10 | 0.51 | 1.08 | 0.10 | 1.18 | 0.02 |
| IDH1 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NADP] cytoplasmic | O75874 | 1.11 | 0.34 | 1.16 | 0.01 | 1.21 | 0.03 |
| EIF3A | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit A | Q14152 | 0.95 | 0.32 | 0.96 | 0.39 | 0.90 | 0.03 |
| TPR | Nucleoprotein TPR | P12270 | 0.99 | 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.06 | 0.87 | 0.04 |
| PRDX6 | Peroxiredoxin-6 | P30041 | 0.83 | 0.11 | 0.96 | 0.54 | 0.88 | 0.04 |
| SRRT | Serrate RNA effector molecule homolog | Q9BXP5 | 0.79 | 0.12 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.81 | 0.05 |
| LMO7 | LIM domain only protein 7 | Q8WWI1 | 0.97 | 0.64 | 0.78 | 0.01 | 0.86 | 0.05 |
| NASP | Nuclear autoantigenic sperm protein | P49321 | 0.84 | 0.07 | 0.87 | 0.07 | 0.85 | 0.05 |
| CALR | Calreticulin | P27797 | 0.83 | 0.30 | 0.87 | 0.01 | 0.86 | 0.05 |
| PNPO | Pyridoxine-5′-phosphate oxidase | Q9NVS9 | 1.06 | 0.60 | 1.11 | 0.15 | 1.17 | 0.05 |
| HSPA5 | 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein | P11021 | 1.24 | 0.01 | 1.04 | 0.36 | 1.12 | 0.05 |
| CALD1 | Isoform HELA L-CAD II of Caldesmon | Q05682-5 | 0.81 | 0.04 | 0.75 | 0.02 | 0.82 | 0.05 |
| PTGES3 | Prostaglandin E synthase 3 | Q15185 | 0.36 | 0.07 | 0.92 | 0.78 | 0.67 | 0.05 |
| VDAC1 | Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 1 | P21796 | 1.20 | 0.14 | 1.22 | 0.11 | 1.32 | 0.05 |
| WDR1 | WD repeat-containing protein 1 | O75083 | 1.11 | 0.38 | 1.14 | 0.05 | 1.19 | 0.05 |
| ENO1 | Alpha-enolase | P06733 | 1.26 | 0.14 | 1.17 | 0.02 | 1.28 | 0.05 |
| ATIC | Bifunctional purine biosynthesis protein PURH | P31939 | 1.09 | 0.31 | 1.10 | 0.18 | 1.14 | 0.06 |
| RPLP2 | 60S acidic ribosomal protein P2 | P05387 | 1.37 | 0.22 | 1.10 | 0.27 | 1.50 | 0.06 |
| HSPA9 | Stress-70 protein, mitochondrial | P38646 | 0.85 | 0.22 | 0.91 | 0.30 | 0.85 | 0.06 |
| MYL6 | Myosin light polypeptide 6 | P60660 | 1.12 | 0.22 | 1.09 | 0.34 | 1.24 | 0.06 |
| FKBP4 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP4 | Q02790 | 1.16 | 0.25 | 1.11 | 0.33 | 1.23 | 0.06 |
| RPL23A | 60S ribosomal protein L23a | P62750 | 0.70 | 0.21 | 0.63 | 0.01 | 0.68 | 0.06 |
| TPD52L2 | Tumor protein D54 | O43399 | 0.87 | 0.27 | 0.75 | 0.02 | 0.82 | 0.06 |
| NIPSNAP3A | Protein NipSnap homolog 3A | Q9UFN0 | 0.82 | 0.17 | 1.08 | 0.34 | 1.20 | 0.06 |
| TPM3 | Isoform TM30nm of Tropomyosin alpha-3 chain | P06753-2 | 1.28 | 0.29 | 1.09 | 0.35 | 1.45 | 0.06 |
| NDUFAB1 | Acyl carrier protein, mitochondrial | O14561 | 1.35 | 0.33 | 1.30 | 0.11 | 1.87 | 0.06 |
| CYCS | Cytochrome c | P99999 | 0.73 | 0.03 | 0.69 | 0.02 | 0.80 | 0.07 |
| PDLIM5 | PDZ and LIM domain protein 5 | Q96HC4 | 0.83 | 0.02 | 0.81 | 0.02 | 0.87 | 0.07 |
| ANPEP | Aminopeptidase N | P15144 | 0.92 | 0.13 | 0.91 | 0.09 | 0.90 | 0.07 |
| ADK | Adenosine kinase | P55263 | 0.81 | 0.15 | 0.91 | 0.36 | 0.79 | 0.07 |
| ATP5J | ATP synthase-coupling factor 6, mitochondrial | P18859 | 2.10 | 0.12 | 1.46 | 0.23 | 2.29 | 0.08 |
| PCBD1 | Pterin-4-alpha-carbinolamine dehydratase | P61457 | 1.10 | 0.54 | 1.12 | 0.25 | 1.37 | 0.08 |
| UGDH | UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase | O60701 | 1.10 | 0.38 | 1.10 | 0.08 | 1.15 | 0.08 |
| NDUFAF2 | Mimitin, mitochondrial | Q8N183 | 1.18 | 0.22 | 1.11 | 0.37 | 1.31 | 0.08 |
| TTC1 | Tetratricopeptide repeat protein 1 | Q99614 | 1.01 | 0.89 | 1.05 | 0.56 | 1.17 | 0.09 |
| LASP1 | LIM and SH3 domain protein 1 | Q14847 | 0.94 | 0.60 | 0.98 | 0.82 | 1.25 | 0.09 |
| ALDOA | Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase A | P04075 | 1.27 | 0.05 | 1.34 | 0.04 | 1.35 | 0.09 |
| FTH1 | Ferritin heavy chain | P02794 | 0.59 | 0.09 | 0.65 | 0.08 | 0.70 | 0.09 |
| ACAA2 | 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, mitochondrial | P42765 | 1.18 | 0.11 | 1.13 | 0.34 | 1.21 | 0.09 |
| ENSA | Isoform 8 of Alpha-endosulfine | O43768-8 | 2.26 | 0.19 | 1.57 | 0.17 | 2.77 | 0.09 |
| BAT1 | Spliceosome RNA helicase BAT1 | Q13838 | 0.76 | 0.22 | 1.04 | 0.62 | 0.76 | 0.09 |
| RPL13 | 60S ribosomal protein L13 | P26373 | 1.24 | 0.22 | 1.16 | 0.68 | 1.24 | 0.09 |
| UGGT1 | UDP-glucose:glycoprotein glucosyltransferase 1 | Q9NYU2 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 0.06 | 0.88 | 0.09 |
| UBQLN1 | Ubiquilin-1 | Q9UMX0 | 1.11 | 0.28 | 1.13 | 0.22 | 1.21 | 0.10 |
| MESDC2 | LDLR chaperone MESD | Q14696 | 0.83 | 0.12 | 0.72 | 0.06 | 0.82 | 0.10 |
| NUTF2 | Nuclear transport factor 2 | P61970 | 1.37 | 0.05 | 1.58 | 0.01 | 1.42 | 0.10 |
| STRAP | Serine-threonine kinase receptor-associated protein | Q9Y3F4 | 1.16 | 0.12 | 1.25 | 0.04 | 1.18 | 0.10 |
| COX5B | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 5B, mitochondrial | P10606 | 1.09 | 0.75 | 1.06 | 0.61 | 1.34 | 0.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takahashi, S.; Saito, K.; Li, X.; Jia, H.; Kato, H. iTRAQ-Based Quantitative Proteomics Reveals the Energy Metabolism Alterations Induced by Chlorogenic Acid in HepG2 Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081676
Takahashi S, Saito K, Li X, Jia H, Kato H. iTRAQ-Based Quantitative Proteomics Reveals the Energy Metabolism Alterations Induced by Chlorogenic Acid in HepG2 Cells. Nutrients. 2022; 14(8):1676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081676
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakahashi, Shoko, Kenji Saito, Xuguang Li, Huijuan Jia, and Hisanori Kato. 2022. "iTRAQ-Based Quantitative Proteomics Reveals the Energy Metabolism Alterations Induced by Chlorogenic Acid in HepG2 Cells" Nutrients 14, no. 8: 1676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081676
APA StyleTakahashi, S., Saito, K., Li, X., Jia, H., & Kato, H. (2022). iTRAQ-Based Quantitative Proteomics Reveals the Energy Metabolism Alterations Induced by Chlorogenic Acid in HepG2 Cells. Nutrients, 14(8), 1676. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14081676






