Risk of Heart Failure between Different Metabolic States of Health and Weight: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
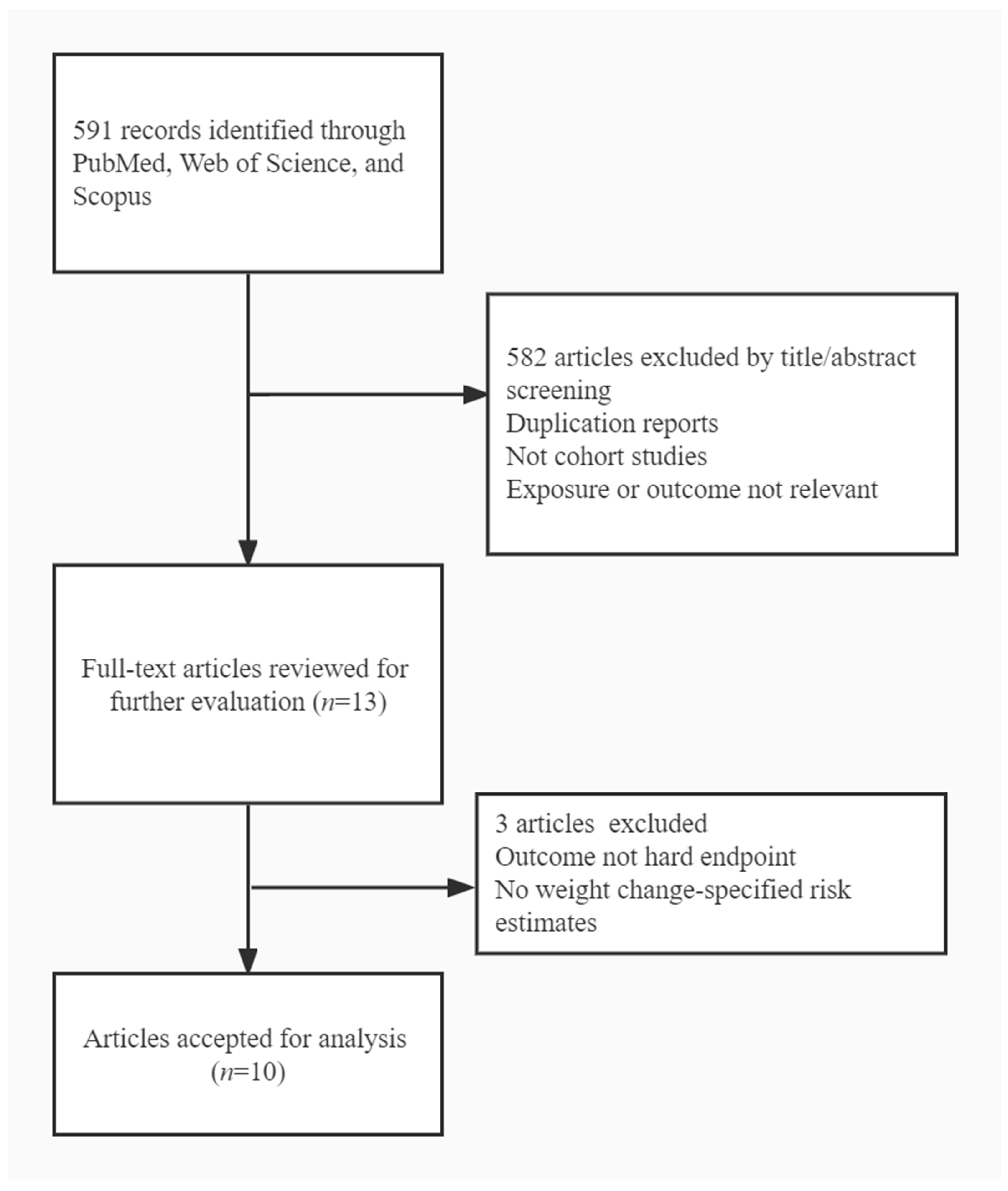
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
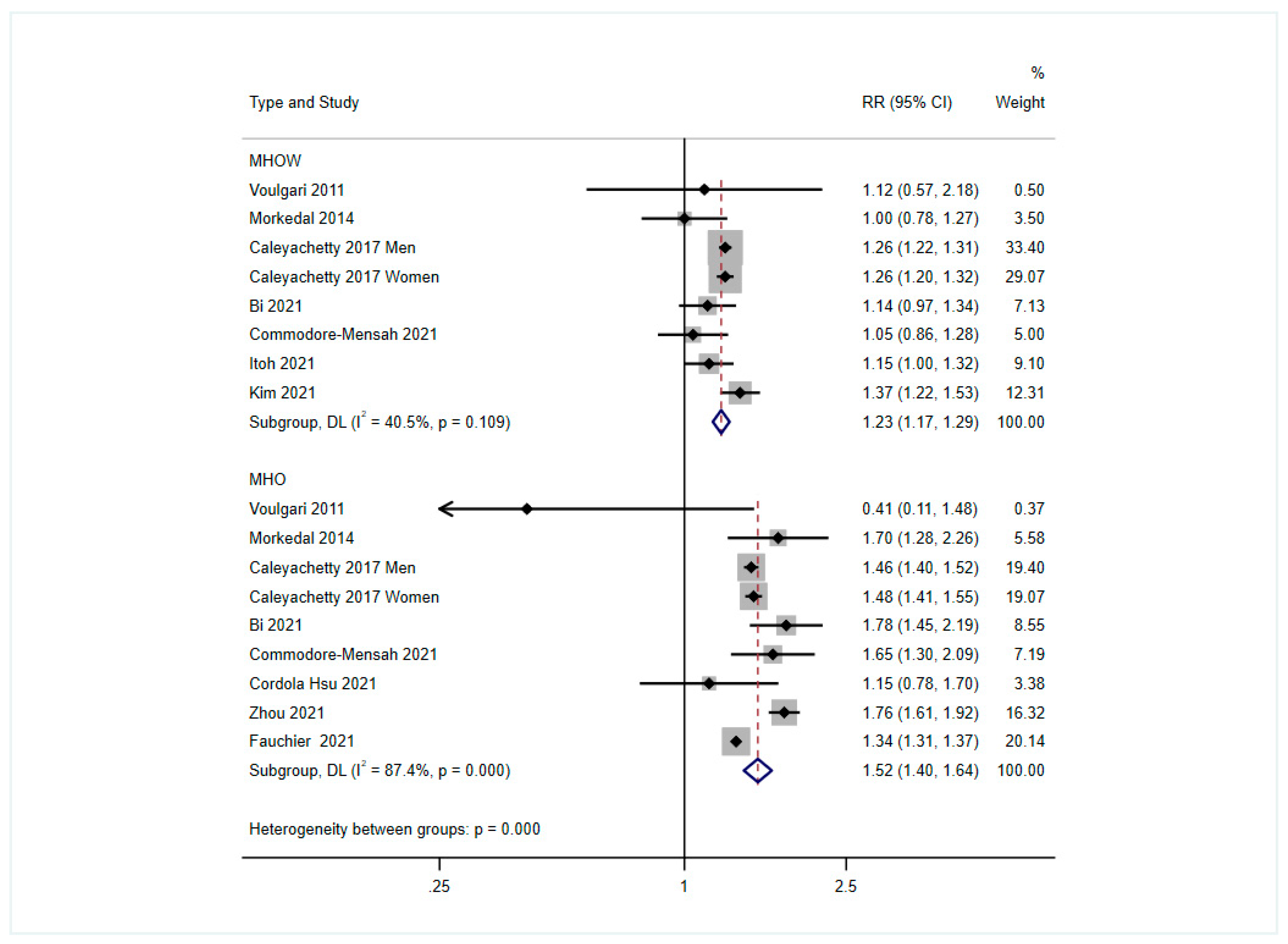
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lippi, G.; Sanchis-Gomar, F. Global epidemiology and future trends of heart failure. AME Med. J. 2020, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, A.; Asahi, K.; Satoh, H.; Iseki, K.; Moriyama, T.; Yamagata, K.; Tsuruya, K.; Fujimoto, S.; Narita, I.; Konta, T.; et al. Fast eating is a strong risk factor for new-onset diabetes among the Japanese general population. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunwald, E. The war against heart failure: The Lancet lecture. Lancet 2015, 385, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenny-Avital, E.R. Obesity and the risk of heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1887–1889. [Google Scholar]
- Aune, D.; Sen, A.; Norat, T.; Janszky, I.; Romundstad, P.; Tonstad, S.; Vatten, L.J. Body Mass Index, Abdominal Fatness, and Heart Failure Incidence and Mortality: A Systematic Re-view and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Circulation 2016, 133, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumbers, T.; Katsoulis, M.; Henry, A.; Mordi, I.; Lang, C.; Hemingway, H.; Langenberg, C.; Holmes, M.; Sattar, N. Body mass index and heart failure risk: A cohort study in 1.5 million individuals and Mendelian randomisation analysis. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.K.; Pinsky, J.L.; Kannel, W.B.; Levy, D. The epidemiology of heart failure: The Framingham Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1993, 22, 6A–13A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelsson, E.; Ärnlöv, J.; Sundström, J.; Zethelius, B.; Vessby, B.; Lind, L. Novel Metabolic Risk Factors for Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-López, J.P.; de Rezende, L.F.; de Sá, T.H.; Stamatakis, E. Is the Metabolically Healthy Obesity Phenotype an Irrelevant Artifact for Public Health? Am. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 182, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. Are metabolically healthy obese individuals really healthy? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 171, R209–R219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüher, M. Metabolically Healthy Obesity. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, M.B. Metabolic health in normal-weight and obese individuals. Diabetologia 2018, 62, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Zorita, S.; Queralt, M.; Vicente, M.A.; González, M.; Portillo, M.P. Metabolically healthy obesity and metabolically obese normal weight: A review. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 77, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulgari, C.; Tentolouris, N.; Dilaveris, P.; Tousoulis, D.; Katsilambros, N.; Stefanadis, C. Increased Heart Failure Risk in Normal-Weight People With Metabolic Syndrome Compared With Metabolically Healthy Obese Individuals. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mørkedal, B.; Vatten, L.J.; Romundstad, P.R.; Laugsand, L.E.; Janszky, I. Risk of myocardial infarction and heart failure among metabolically healthy but obese individuals: HUNT (Nord-Trondelag Health Study), Norway. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Macpherson, J.; Gray, S.R.; Gill, J.M.R.; Welsh, P.; Celis-Morales, C.; Sattar, N.; Pell, J.P.; Ho, F.K. Are people with metabolically healthy obesity really healthy? A prospective cohort study of 381,363 UK Biobank participants. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzababaei, A.; Djafarian, K.; Mozafari, H.; Shab-Bidar, S. The long-term prognosis of heart diseases for different metabolic phenotypes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Endocrine 2019, 63, 439–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caleyachetty, R.; Thomas, G.N.; Toulis, K.A.; Mohammed, N.; Gokhale, K.M.; Balachandran, K.; Nirantharakumar, K. Metabolically Healthy Obese and Incident Cardiovascular Disease Events Among 3.5 Million Men and Women. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, H.; Kaneko, H.; Kiriyama, H.; Kamon, T.; Fujiu, K.; Morita, K.; Michihata, N.; Jo, T.; Takeda, N.; Morita, H.; et al. Met-abolically Healthy Obesity and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in the General Population- Analysis of a Nationwide Epidemiological Database. Circ. J. 2021, 85, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.; Cho, Y.K.; Park, J.-Y.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Jung, C.H. Differential Effect of Metabolic Health and Obesity on Incident Heart Failure: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 625083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-B.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, N.H.; Choi, K.M.; Baik, S.H.; Park, Y.G.; Han, K.; Yoo, H.J. Hospitalization for heart failure incidence according to the transition in metabolic health and obesity status: A nationwide population-based study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauchier, G.; Bisson, A.; Bodin, A.; Herbert, J.; Semaan, C.; Angoulvant, D.; Ducluzeau, P.H.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Fauchier, L.; Msc, J.H. Metabolically healthy obesity and cardiovascular events: A nationwide cohort study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 2492–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordola Hsu, A.R.; Xie, B.; Peterson, D.V.; LaMonte, M.J.; Garcia, L.; Eaton, C.B.; Going, S.B.; Phillips, L.S.; Manson, J.E.; An-ton-Culver, H.; et al. Metabolically Healthy/Unhealthy Overweight/Obesity Associations With Incident Heart Failure in Postmenopausal Women: The Women’s Health Initiative. Circ. Heart Fail. 2021, 14, e007297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwig, L.; Macaskill, P.; Berry, G.; Glasziou, P. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Graphical test is itself biased. BMJ 1998, 316, 470–471. [Google Scholar]
- Lind, L.; Risérus, U.; Ärnlöv, J. Impact of the Definition of Metabolically Healthy Obesity on the Association with Incident Cardiovascular Disease. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2020, 18, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponholtz, T.R.; Heuvel, E.R.V.D.; Xanthakis, V.; Vasan, R.S. Association of Variability in Body Mass Index and Metabolic Health With Cardiometabolic Disease Risk. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e010793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commodore-Mensah, Y.; Lazo, M.; Tang, O.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Ndumele, C.E.; Nambi, V.; Wang, D.; Ballantyne, C.; Selvin, E. High Burden of Subclinical and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Adults With Metabolically Healthy Obesity: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Song, L.; Wang, L.; Su, B.; Wu, M.; Li, D.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Transitions in metabolic health status over time and risk of heart failure: A prospective study. Diabetes Metab. 2022, 48, 101266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, U.I.; Wang, D.; Thurston, R.C.; Sowers, M.; Sutton-Tyrrell, K.; Matthews, K.A.; Barinas-Mitchell, E.; Wildman, R.P. Burden of subclinical cardiovascular disease in “metabolically benign” and “at-risk” overweight and obese women: The Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN). Atherosclerosis 2011, 217, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, L.; Siegbahn, A.; Ingelsson, E.; Sundström, J.; Ärnlöv, J. A Detailed Cardiovascular Characterization of Obesity Without the Metabolic Syndrome. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, e27–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, G.-Y.; Baik, I.; Lim, H.E.; Park, C.G.; Lee, J.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Lim, S.Y.; Kim, H.; et al. Obesity phenotype and incident hypertension: A prospective community-based cohort study. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, M.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Myocardial Infarction and Ischemic Heart Disease in Overweight and Obesity With and Without Metabolic Syndrome. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.-Z.; Sun, F.-R.; Wang, Z.-T.; Tan, L.; Hou, X.-H.; Ou, Y.-N.; Dong, Q.; Yu, J.-T.; Tan, L. Metabolically healthy obesity and risk of stroke: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, M.A.; Lavie, C.J.; Agrawal, H.; Aggarwal, K.B.; Kumar, S.A. Obesity and heart failure: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Transl. Res. 2014, 164, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilner, B.; Garg, S.; Ayers, C.R.; Maroules, C.D.; McColl, R.; Matulevicius, S.A.; de Lemos, J.A.; Drazner, M.H.; Peshock, R.; Neeland, I.J. Dynamic Relation of Changes in Weight and Indices of Fat Distribution With Cardiac Structure and Function: The Dallas Heart Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Zheng, S.; He, A.; Chen, C.; Zhao, X.; Hua, M.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, M. Combined associations of obesity and metabolic health with subclinical left ventricular dysfunctions: Danyang study. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 3058–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Deswal, A.; Dunbar, S.B.; Francis, G.S.; Horwich, T.; Jessup, M.; Kosiborod, M.; Pritchett, A.M.; Ramasubbu, K.; et al. Contributory Risk and Management of Comorbidities of Hypertension, Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Hyperlipidemia, and Metabolic Syndrome in Chronic Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 134, e535–e578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel, N.; Meidtner, K.; Kalle-Uhlmann, T.; Stefan, N.; Schulze, M.B. Metabolically healthy obesity and cardiovascular events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2016, 23, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hui, R.; Zhang, W. Combined effect of obesity and cardio-metabolic abnormality on the risk of cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 4761–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckel, N.; Li, Y.; Kuxhaus, O.; Stefan, N.; Hu, F.B.; Schulze, M.B. Transition from metabolic healthy to unhealthy phenotypes and association with cardiovascular disease risk across BMI categories in 90,257 women (the Nurses’ Health Study): 30 year follow-up from a prospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.-C.; Arthur, R.; Iyengar, N.M.; Kamensky, V.; Xue, X.; Wassertheil-Smoller, S.; Allison, M.A.; Shadyab, A.H.; Wild, R.A.; Sun, Y.; et al. Association between regional body fat and cardiovascular disease risk among postmenopausal women with normal body mass index. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 2849–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Schick, F.; Häring, H.-U. Causes, Characteristics, and Consequences of Metabolically Unhealthy Normal Weight in Humans. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study | Design (Duration) | Country | Sample Size | Definition of Metabolic Health | Obesity Assessment | Outcome Assessment (Cases) | Study Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voulgari, 2011 [14] | Prospective (6.0 years) | Greece | 550 men and women | Without metabolic syndrome | Overweight: BMI of 25–29.9 kg/m2; obesity: BMI of ≥30 kg/m2 | MR (185) | High |
| Morkedal, 2014 [15] | Prospective (12.2 years) | Norway | 61,299 men and women | Without metabolic syndrome | Overweight: BMI of 25–29.9 kg/m2; obesity: BMI of ≥30 kg/m2 | MR (2547) | High |
| Caleyachetty, 2017 [18] | Prospective (5.4 years) | United Kingdom | 3,495,777 men and women | Having <3 of diabetes, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia | Overweight: BMI of 25–29.9 kg/m2; obesity: BMI of ≥30 kg/m2 | MR (25,254) | High |
| Cordola, 2021 [23] | Prospective (11.3 years) | United States | 19,412 postmenopausal women | Having <2 of diabetes, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia | Overweight/obesity: BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 or WC ≥ 88 cm | MR (455) | High |
| Itoh, 2021 [19] | Retrospective (3.1 years) | Japan | 802,288 men and women | Without diabetes, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia | Overweight/obesity: BMI of ≥25 kg/m2 | MR (588) | High |
| Kim, 2021 [20] | Prospective (6.0 years) | Korea | 356,258 men and women | Having <2 of diabetes, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia | Overweight/obesity: BMI of ≥25 kg/m2 | MR (5406) | High |
| Commodore-Mensah, 2021 [30] | Prospective (17.0 years) | United States | 9477 men and women | Having <2 of diabetes, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia | Overweight: BMI of 25–29.9 kg/m2; obesity: BMI of ≥30 kg/m2 | MR (1531) | High |
| Zhou, 2021 [16] | Prospective (11.2 years) | United Kingdom | 381,363 men and women | Having <3 of diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, or C-reactive protein | Obesity: BMI of ≥30 kg/m2 | MR (6215) | High |
| Bi, 2021 [31] | Prospective (9.7 years) | China | 93,288 men and women | Having <2 of diabetes, hypertension, or hyperlipidemia | Overweight: BMI of 24–28 kg/m2; obesity: BMI of ≥28 kg/m2 or WC ≥ 80 cm | MR (1628) | High |
| Fauchier, 2021 [22] | Prospective (4.9 years) | France | 2,873,039 men and women | Without metabolic syndrome | ICD-10 code E65 | MR (391,637) | High |
| Western Countries | Eastern Countries | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Studies | RR (95% CI) | I2 | p for Heterogeneity | No. of Studies | RR (95% CI) | I2 | p for Heterogeneity | |
| MHOW | 5 | 1.23 (1.17, 1.30) | 39.4 | 0.16 | 3 | 1.23 (1.08, 1.39) | 61.1 | 0.08 |
| MHO | 8 | 1.48 (1.38, 1.52) | 87.9 | <0.001 | 1 | 1.78 (1.45, 2.19) | - | - |
| MUHNW | 8 | 1.65 (1.38, 1.98) | 97.2 | <0.001 | 2 | 1.35 (1.18, 1.55) | 52.8 | 0.15 |
| MUHOW | 5 | 1.80 (1.52, 2.13) | 90.6 | <0.001 | 2 | 1.65 (1.54, 1.77) | - | - |
| MUHO | 8 | 2.24 (1.50, 2.64) | 97.5 | <0.001 | 1 | 2.61 (2.22, 3.06) | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Dong, J.; Du, Z.; Jiang, J.; Hu, Y.; Qin, L.; Hao, Y. Risk of Heart Failure between Different Metabolic States of Health and Weight: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5223. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245223
Wang X, Dong J, Du Z, Jiang J, Hu Y, Qin L, Hao Y. Risk of Heart Failure between Different Metabolic States of Health and Weight: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Nutrients. 2022; 14(24):5223. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245223
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaowen, Jiayi Dong, Zhicheng Du, Jie Jiang, Yonghua Hu, Liqiang Qin, and Yuantao Hao. 2022. "Risk of Heart Failure between Different Metabolic States of Health and Weight: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies" Nutrients 14, no. 24: 5223. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245223
APA StyleWang, X., Dong, J., Du, Z., Jiang, J., Hu, Y., Qin, L., & Hao, Y. (2022). Risk of Heart Failure between Different Metabolic States of Health and Weight: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Nutrients, 14(24), 5223. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14245223





