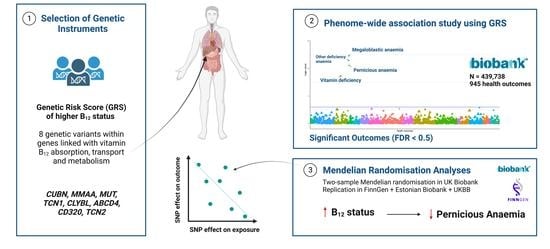
Associations of Genetically Predicted Vitamin B12 Status across the Phenome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Populations
2.3. Selection of Genetic Instruments Characterising Vitamin B12 Status
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Phenome-Wide Association Analysis
2.4.2. Mendelian Randomisation Analyses
2.4.3. Sensitivity Analyses
2.4.4. Replication
2.5. Statistical Software
3. Results
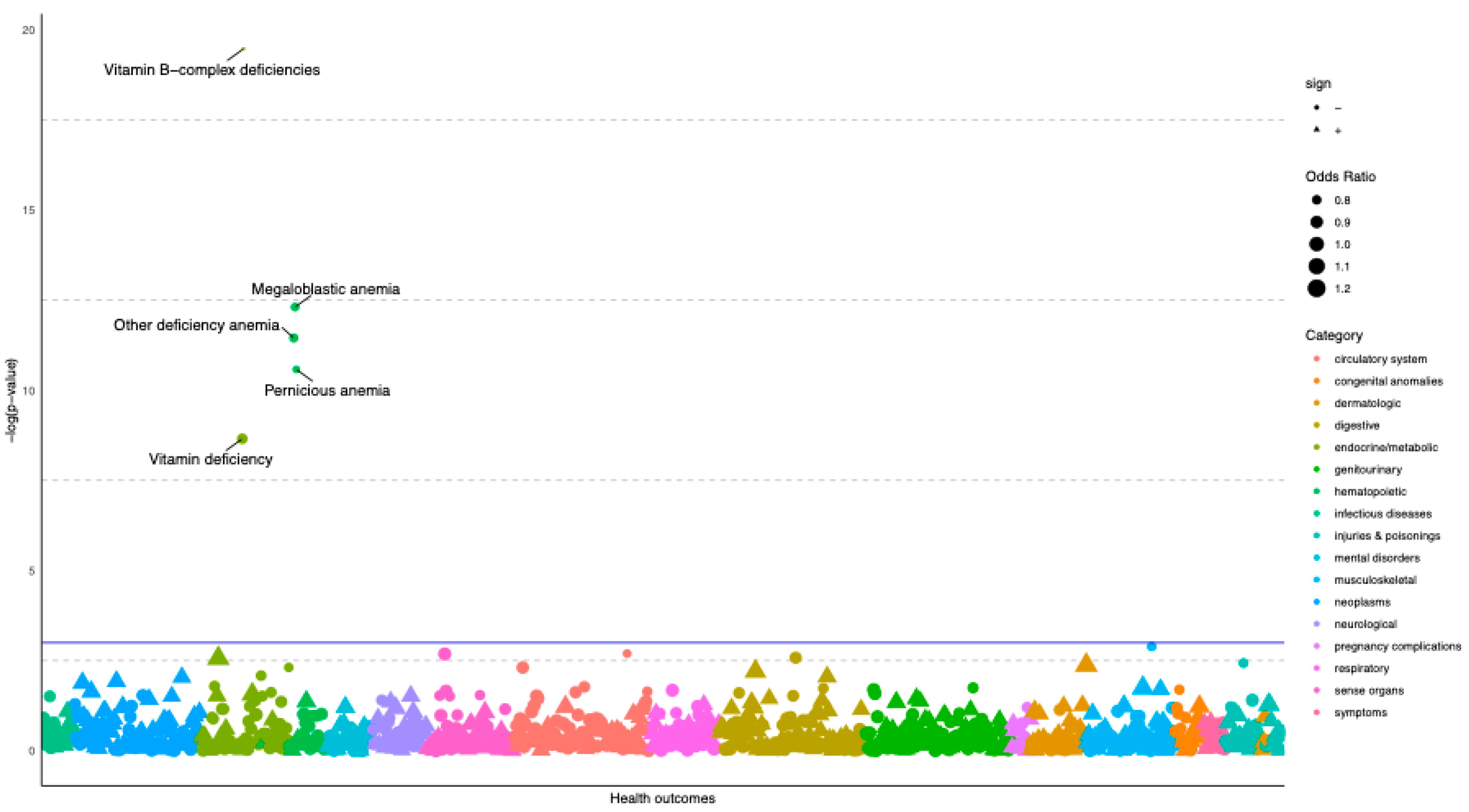
3.1. Vitamin B12 GRS-PheWAS Highlights Associations with Pernicious and Megaloblastic Anaemia
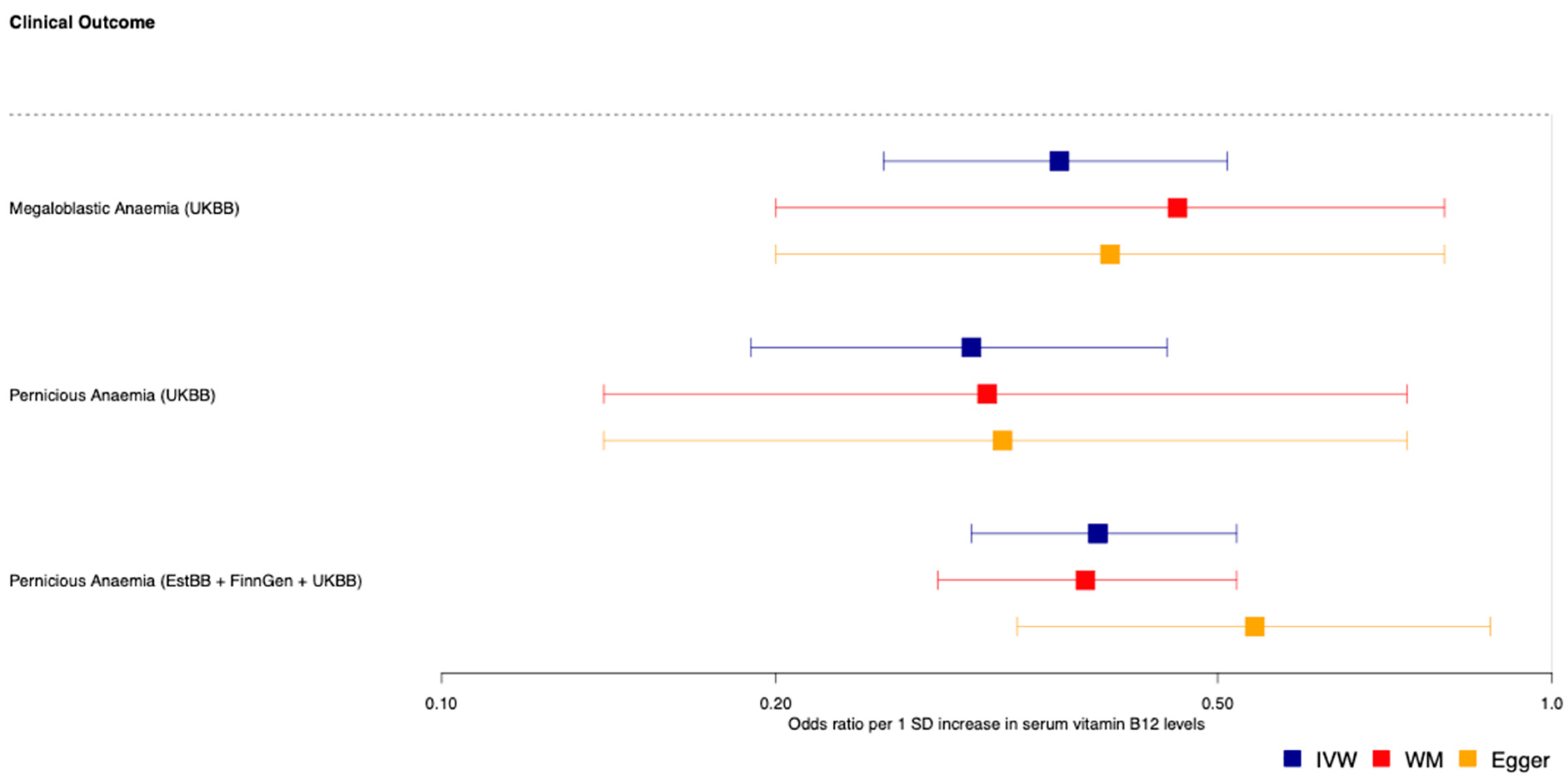
3.2. Mendelian Randomisation Analyses Support Potentially Protective Effect of Genetically-Predicted Vitamin B12 Status on Pernicious and Megaloblastic Anaemia
4. Discussion
4.1. MR-PheWAS Highlights Supporting Evidence of the Effect of B12 on Pernicious and Megaloblastic Anaemia
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carmel, R.; Jacobsen, D.W. Homocysteine in Health and Disease; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Dalmia, A.; Dib, M.J.; Maude, H.; Harrington, D.J.; Sobczynska-Malefora, A.; Andrew, T.; Ahmadi, K.R. A genetic epidemiological study in British adults and older adults shows a high heritability of the combined indicator of vitamin B12 status (cB12) and connects B12 status with utilization of mitochondrial substrates and energy metabolism. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 70, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, F.; Samman, S. Vitamin B12 in health and disease. Nutrients 2010, 2, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolffenbuttel, B.H.R.; Wouters, H.; Heiner-Fokkema, M.R.; van der Klauw, M.M. The Many Faces of Cobalamin (Vitamin B12) Deficiency. Mayo Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual. Outcomes 2019, 3, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devalia, V.; Hamilton, M.S.; Molloy, A.M.; The British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cobalamin and folate disorders. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 166, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.; Grimley Evans, J.; Schneede, J.; Nexo, E.; Bates, C.; Fletcher, A.; Prentice, A.; Johnston, C.; Ueland, P.M.; Refsum, H.; et al. Vitamin B12 and folate deficiency in later life. Age Ageing 2004, 33, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, T.; Gill, R.; Gillham-Nasenya, I.; Ahmadi, K.R. Unravelling the basis of variability in cobalamin levels in the general population. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, A.; Harrington, D.; Robinson, S. Vitamin B12 deficiency. BMJ 2014, 349, g5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, L.A.; Davies, N.M.; Timpson, N.J.; Tilling, K.; Flach, P.A.; Davey Smith, G. MR-PheWAS: Hypothesis prioritization among potential causal effects of body mass index on many outcomes, using Mendelian randomization. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudlow, C.; Gallacher, J.; Allen, N.; Beral, V.; Burton, P.; Danesh, J.; Downey, P.; Elliott, P.; Green, J.; Landray, M.; et al. UK biobank: An open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bycroft, C.; Freeman, C.; Petkova, D.; Band, G.; Elliott, L.T.; Sharp, K.; Motyer, A.; Vukcevic, D.; Delaneau, O.; O’Connell, J.; et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 2018, 562, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grarup, N.; Sulem, P.; Sandholt, C.H.; Thorleifsson, G.; Ahluwalia, T.S.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Bjarnason, H.; Gudbjartsson, D.; Magnusson, O.T.; Sparsø, T.; et al. Genetic architecture of vitamin B12 and folate levels uncovered applying deeply sequenced large datasets. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igo, R.P., Jr.; Kinzy, T.G.; Cooke Bailey, J.N. Genetic Risk Scores. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2019, 104, e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moen, G.H.; Qvigstad, E.; Birkeland, K.I.; Evans, D.M.; Sommer, C. Are serum concentrations of vitamin B-12 causally related to cardiometabolic risk factors and disease? A Mendelian randomization study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, S.M. Folate and B12 in prostate cancer. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2013, 60, 1–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Gifford, A.; Meng, X.; Li, X.; Campbell, H.; Varley, T.; Zhao, J.; Carroll, R.; Bastarache, L.; Denny, J.C.; et al. Mapping ICD-10 and ICD-10-CM Codes to Phecodes: Workflow Development and Initial Evaluation. JMIR Med. Inform. 2019, 7, e14325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Bradford, Y.; Dudek, S.; Lucas, A.M.; Verma, S.S.; Pendergrass, S.A.; Ritchie, M.D. A simulation study investigating power estimates in phenome-wide association studies. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.R.; Minelli, C.; Del Greco, M.F. Mendelian Randomization using Public Data from Genetic Consortia. Int. J. Biostat. 2016, 12, 20150074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Fall, T.; Ingelsson, E.; Thompson, S.G. Sensitivity Analyses for Robust Causal Inference from Mendelian Randomization Analyses with Multiple Genetic Variants. Epidemiology 2017, 28, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laisk, T.; Lepamets, M.; Koel, M.; Abner, E.; Metspalu, A.; Nelis, M.; Milani, L.; Esko, T.; Mägi, R.; Estonian Biobank Research Team. Genome-wide association study identifies five risk loci for pernicious anemia. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitsalu, L.; Haller, T.; Esko, T.; Tammesoo, M.L.; Alavere, H.; Snieder, H.; Perola, M.; Ng, P.C.; Mägi, R.; Milani, L.; et al. Cohort Profile: Estonian Biobank of the Estonian Genome Center, University of Tartu. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, R.J.; Bastarache, L.; Denny, J.C. R PheWAS: Data analysis and plotting tools for phenome-wide association studies in the R environment. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2375–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. elife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.; Lumley, T. forestplot: Advanced Forest Plot Using ‘grid’ Graphics. R Package Version 2.0.1. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=forestplot2021 (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Banka, S.; Ryan, K.; Thomson, W.; Newman, W.G. Pernicious anemia–genetic insights. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Thomsen, H.; Sundquist, K.; Sundquist, J.; Forsti, A.; Hemminki, K. Familial Risks between Pernicious Anemia and Other Autoimmune Diseases in the Population of Sweden. Autoimmune Dis. 2021, 2021, 8815297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, M.; Hudson, P.; Porter, F.; McCaddon, A. Patient journeys: Diagnosis and treatment of pernicious anaemia. Br. J. Nurs. 2014, 23, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Carter, P.; Vithayathil, M.; Kar, S.; Mason, A.M.; Burgess, S.; Larsson, S.C. Genetically predicted circulating B vitamins in relation to digestive system cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1997–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CHR | Gene Name | Gene Symbol | Reference SNP | Effect Allele | Other Allele | EAF | Beta | SE | p-Value | F-Statistic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | Methylmalonic aciduria (cobalamin deficiency) cblA type | MMAA | rs2270655 | G | C | 0.941 | 0.099 | 0.015 | 5.68 × 10−12 | 46 |
| 6 | Methylmalonyl-CoA Mutase | MUT | rs1141321 | C | T | 0.627 | 0.07 | 0.007 | 5.11 × 10−25 | 105 |
| 10 | Cubulin | CUBN | rs1801222 | G | A | 0.593 | 0.119 | 0.007 | 7.24 × 10−74 | 329 |
| 11 | Transcobalamin 1 | TCN1 | rs34324219 | C | A | 0.881 | 0.235 | 0.011 | 2.54 × 10−109 | 492 |
| 13 | Citrate Lyase Beta Like | CLYBL | rs41281112 | C | T | 0.948 | 0.181 | 0.015 | 4.60 × 10−34 | 147 |
| 14 | ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily D Member 4 | ABCD4 | rs3742801 | T | C | 0.294 | 0.053 | 0.007 | 2.28 × 10−13 | 52 |
| 19 | TCII-R transcobalamin II receptor | CD320 | rs2336573 | T | C | 0.031 | 0.313 | 0.019 | 2.89 × 10−60 | 267 |
| 22 | Transcobalamin 2 | TCN2 | rs1131603 | C | T | 0.055 | 0.222 | 0.015 | 2.11 × 10−48 | 112 |
| MR-IVW | MR-Egger | MR-Weighted Median | Outcome Cohort | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exposure | Outcome | NSNPs | OR | p | OR | p | OR | p | Cohort | Ncases | Ncontrols |
| B12 | Megaloblastic anaemia | 8 | 0.36 | 1.01 × 10−8 | 0.4 | 4.21 × 10−2 | 0.46 | 5.72 × 10−4 | UKBB | 1061 | 384,287 |
| B12 | Pernicious anaemia | 8 | 0.3 | 2.27 × 10−8 | 0.32 | 3.64 × 10−2 | 0.31 | 2.75 × 10−5 | UKBB | 698 | 384,287 |
| B12 | Pernicious anaemia | 7 | 0.39 | 6.30 × 10−11 | 0.54 | 5.57 × 10−2 | 0.38 | 1.89 × 10−9 | EstBB + FinnGen + UKBB | 2166 | 659,516 |
| B12 | Vitamin B-complex deficiencies | 8 | 0.22 | 2.46 × 10−8 | 0.29 | 6.84 × 10−2 | 0.19 | 1.97 × 10−10 | UKBB | 868 | 416,203 |
| B12 | Vitamin deficiency | 8 | 0.45 | 4.58 × 10−8 | 0.45 | 2.93 × 10−2 | 0.45 | 1.55 × 10−5 | UKBB | 1734 | 416,203 |
| B12 | Other deficiency anaemia | 8 | 0.39 | 6.12 × 10−8 | 0.39 | 3.39 × 10−2 | 0.42 | 9.47 × 10−5 | UKBB | 1131 | 384,287 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dib, M.-J.; Ahmadi, K.R.; Zagkos, L.; Gill, D.; Morris, B.; Elliott, P.; Dehghan, A.; Tzoulaki, I. Associations of Genetically Predicted Vitamin B12 Status across the Phenome. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5031. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235031
Dib M-J, Ahmadi KR, Zagkos L, Gill D, Morris B, Elliott P, Dehghan A, Tzoulaki I. Associations of Genetically Predicted Vitamin B12 Status across the Phenome. Nutrients. 2022; 14(23):5031. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235031
Chicago/Turabian StyleDib, Marie-Joe, Kourosh R. Ahmadi, Loukas Zagkos, Dipender Gill, Brooke Morris, Paul Elliott, Abbas Dehghan, and Ioanna Tzoulaki. 2022. "Associations of Genetically Predicted Vitamin B12 Status across the Phenome" Nutrients 14, no. 23: 5031. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235031
APA StyleDib, M.-J., Ahmadi, K. R., Zagkos, L., Gill, D., Morris, B., Elliott, P., Dehghan, A., & Tzoulaki, I. (2022). Associations of Genetically Predicted Vitamin B12 Status across the Phenome. Nutrients, 14(23), 5031. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14235031