Hydrolyzed Collagen Induces an Anti-Inflammatory Response That Induces Proliferation of Skin Fibroblast and Keratinocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Experimental Design
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Cell Proliferation Measurements
2.4. Inflammatory Mediators, Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS), and Pro-Collagen-1α Expression
2.5. Cell Proliferation
2.6. Cytokines and Growth Factors Measurement
2.7. Nitrite (NO2) and Nitrate (NO3) Measurements
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
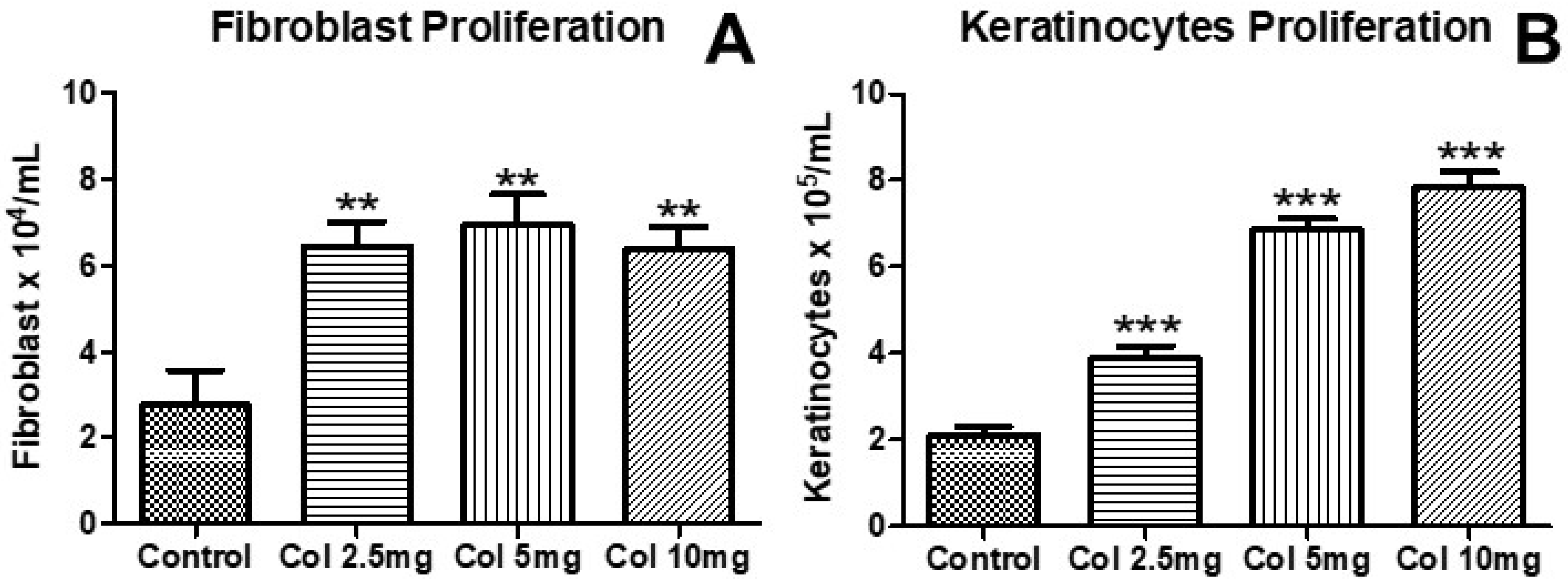
3.1. Effects of Collagen Supplementation on Cell Proliferation
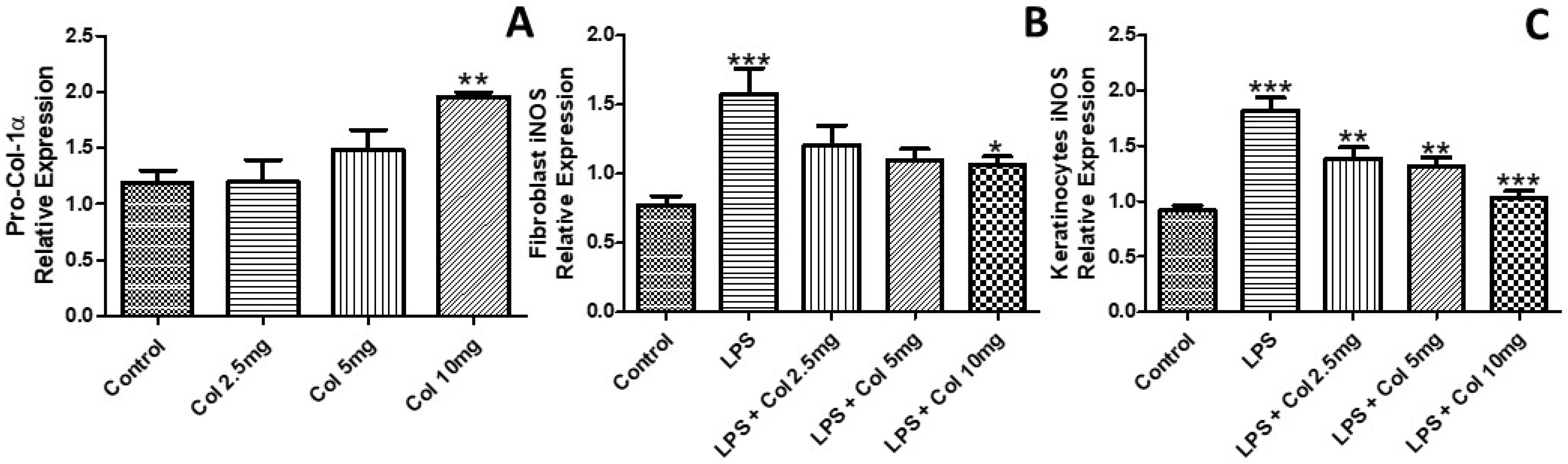
3.2. Effects of Collagen Supplementation on the Expression of Pro-Collagen-1α and iNOS
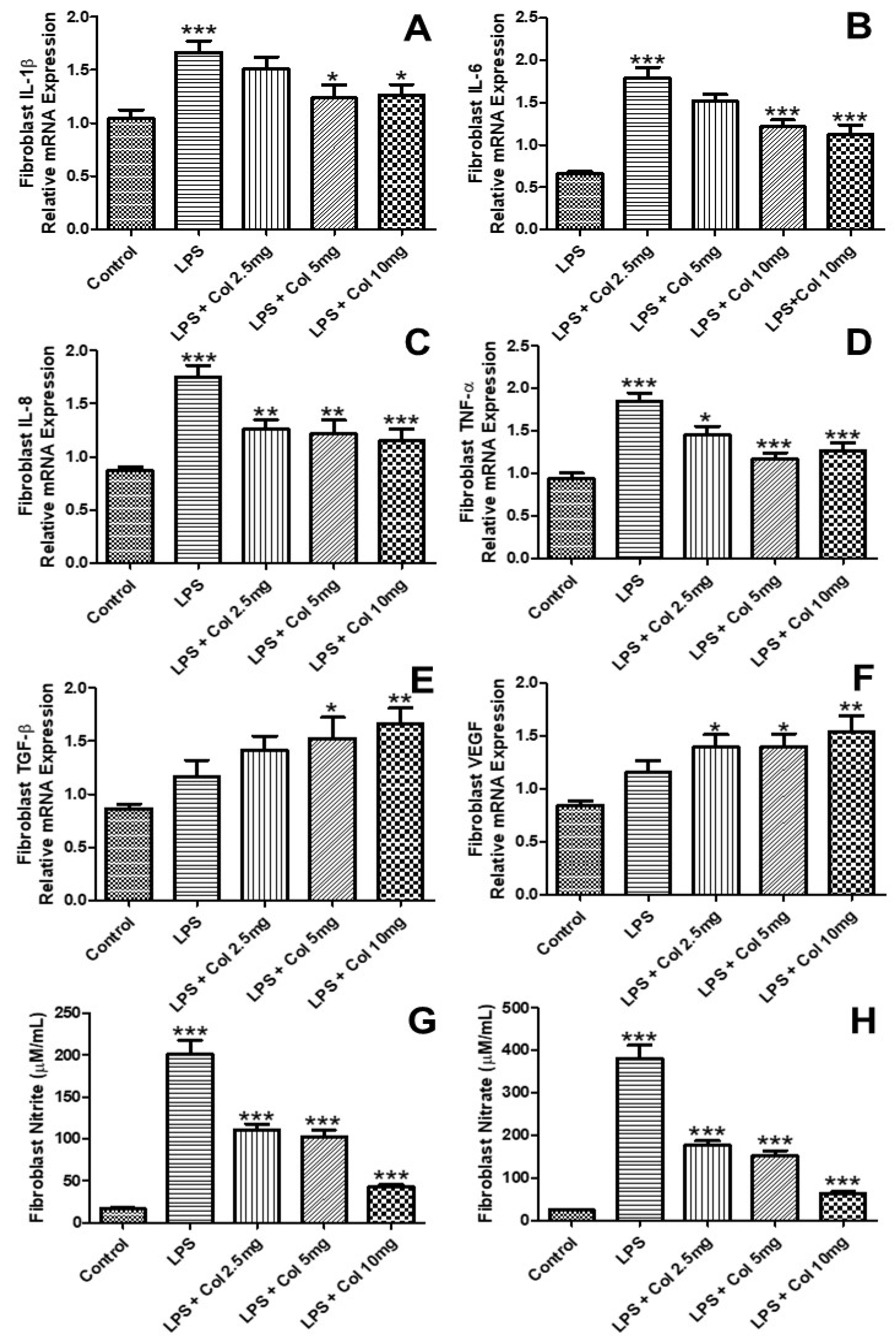
3.3. Effects of Collagen Supplementation on Cytokine Gene Expression in Fibroblasts
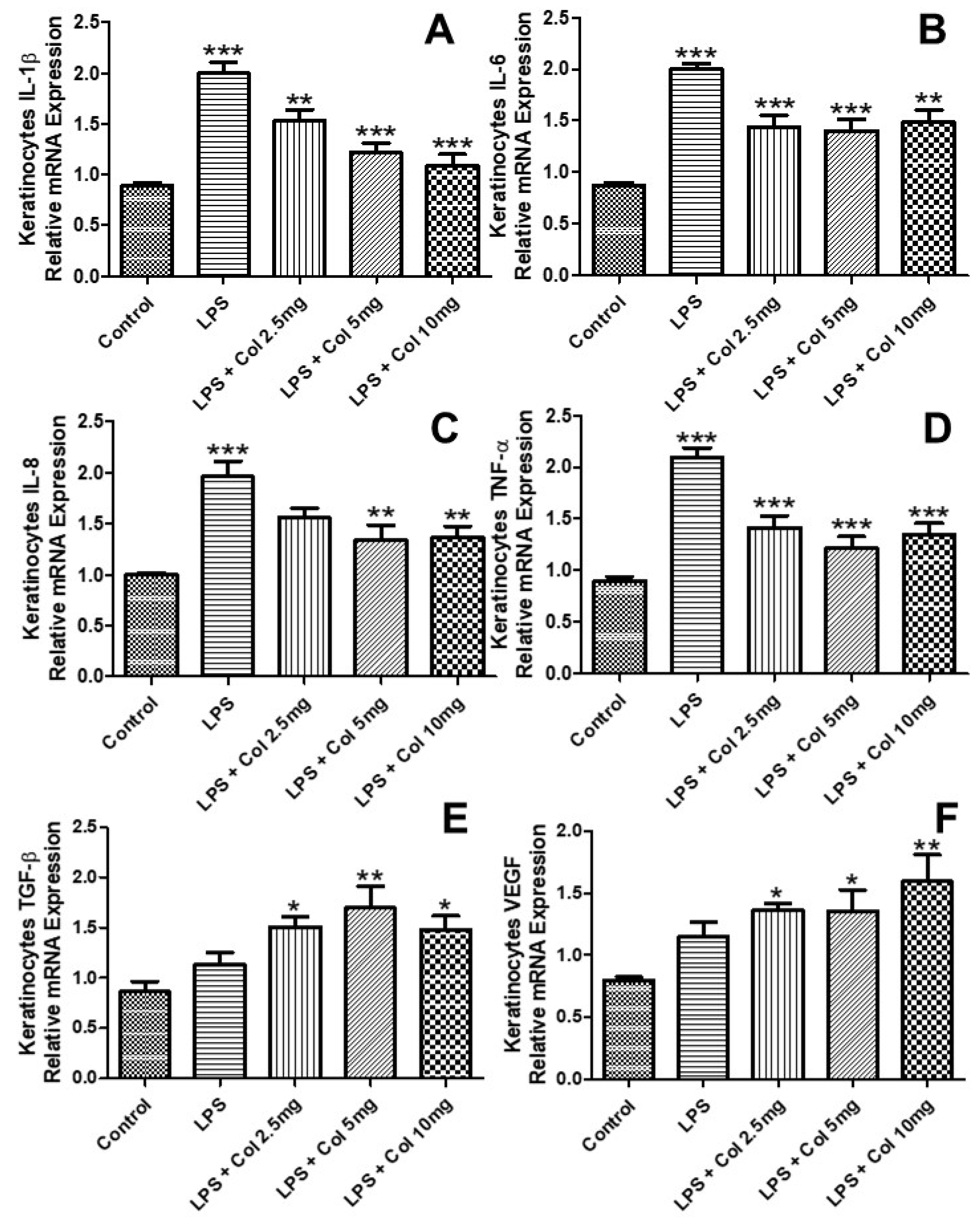
3.4. Effects of Collagen Supplementation on Cytokine Gene Expression in Keratinocytes
3.5. Effects of Collagen Supplementation on Cytokine Protein Levels in Fibroblasts
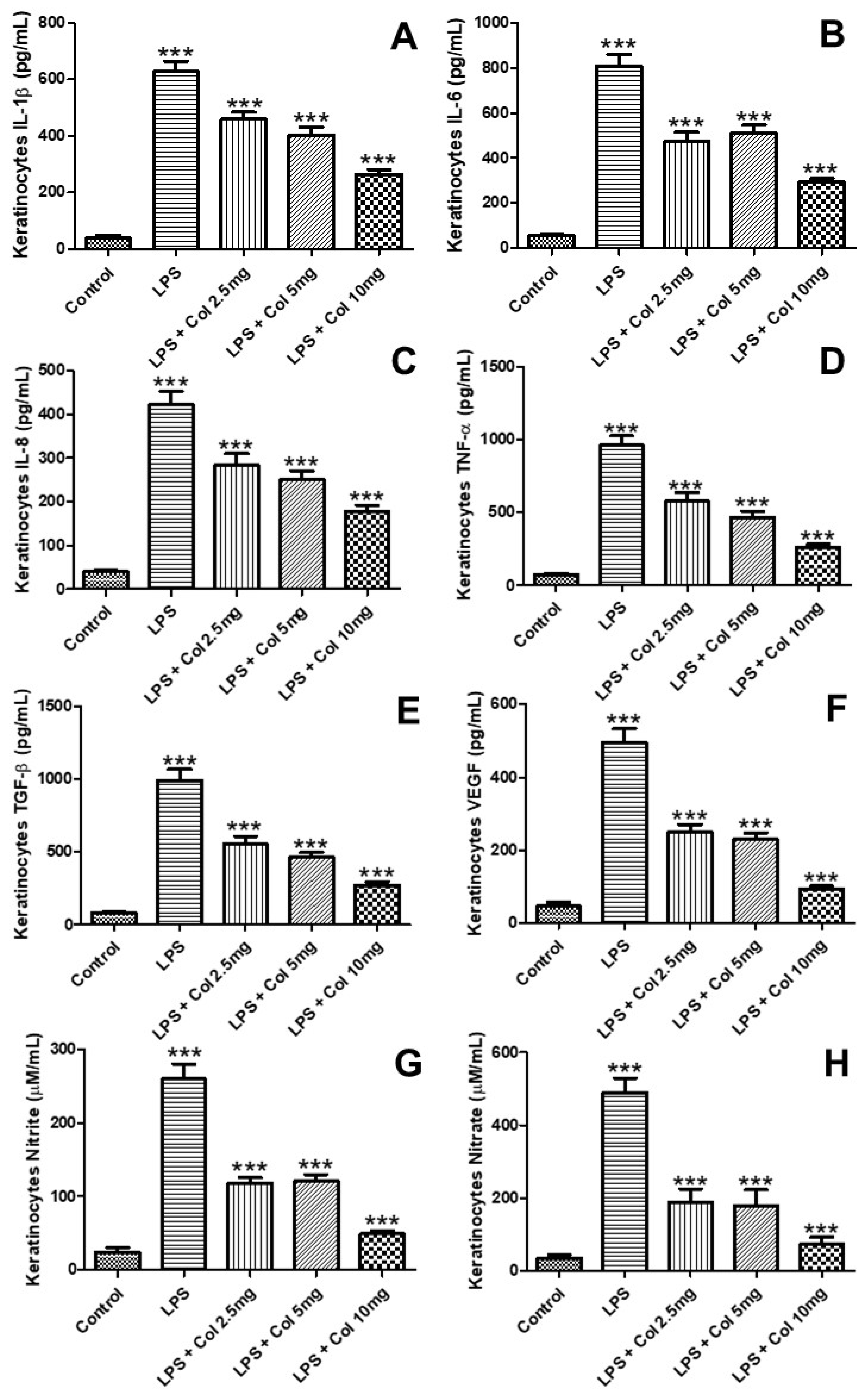
3.6. Effects of Collagen Supplementation on Cytokine Protein Levels in Keratinocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tricarico, P.M.; Mentino, D.; De Marco, A.; Del Vecchio, C.; Garra, S.; Cazzato, G.; Foti, C.; Crovella, S.; Calamita, G. Aquaporins Are One of the Critical Factors in the Disruption of the Skin Barrier in Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisiel, M.A.; Klar, A.S. Isolation and Culture of Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1993, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Song, Y.; Zhang, D.; Hao, F. Skin Immunosenescence and Type 2 Inflammation: A Mini-Review with an Inflammaging Perspective. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 835675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftime, M.M.; Rosca, I.; Sandu, A.I.; Marin, L. Chitosan crosslinking with a vanillin isomer toward self-healing hydrogels with antifungal activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, Q.V.; Faass, L.; Sähr, A.; Hildebrand, D.; Eigenbrod, T.; Heeg, K.; Nurjadi, D. Inflammatory Response Against Staphylococcus aureus via Intracellular Sensing of Nucleic Acids in Keratinocytes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 828626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Midwood, K.S.; Varga, J. Tenascin-C in fibrosis in multiple organs: Translational implications. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2022, 128, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. A Review of the Effects of Collagen Treatment in Clinical Studies. Polymers 2021, 13, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.R.; Vieira, R.P. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Miodesin™: Modulation of Inflammatory Markers and Epigenetic Evidence. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 6874260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thur, J.; Nischt, R.; Krieg, T.; Hunzelmann, N. Quantitative analysis of alpha 1 (I) procollagen transcripts in vivo by competitive polymerase chain reaction. Matrix Biol. 1996, 15, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werfel, T.; Irvine, A.D.; Bangert, C.; Seneschal, J.; Grond, S.; Cardillo, T.; Brinker, D.; Zhong, J.; Riedl, E.; Wollenberg, A. An integrated analysis of herpes virus infections from eight randomised clinical studies of baricitinib in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humeau, M.; Boniface, K.; Bodet, C. Cytokine-Mediated Crosstalk Between Keratinocytes and T Cells in Atopic Dermatitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 801579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, J.H.; Wang, Z.X.; Lo, Y.H.; Lee, C.N.; Chang, Y.; Chang, R.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Wong, T.W. Rose Bengal-Mediated Photodynamic Therapy to Inhibit Candida albicans. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 181, 63558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laube, S.; Farrell, A.M. Bacterial skin infections in the elderly: Diagnosis and treatment. Drugs Aging 2002, 19, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhan, C.; Juturu, V.; Sahin, E.; Tuzcu, M.; Ozercan, I.H.; Durmus, A.S.; Sahin, N.; Sahin, K. Undenatured Type II Collagen Ameliorates Inflammatory Responses and Articular Cartilage Damage in the Rat Model of Osteoarthritis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 617789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaarour, R.F.; Saha, D.; Dey, R.; Dutta, A.; Kumar, P.; Rana, I.; Pulianmackal, A.; Rizvi, A.; Misra, N.; Breton, L.; et al. The neuropeptide Substance P facilitates the transition from an inflammatory to proliferation phase-associated responses in dermal fibroblasts. Exp. Derm. 2022. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Lopez, L.I.; Choudhary, V.; Bollag, W.B. Updated Perspectives on Keratinocytes and Psoriasis: Keratinocytes are More Than Innocent Bystanders. Psoriasis 2022, 12, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, N.; Luo, L.; Zhu, X.; Xu, X.; Cong, W.; Jin, L.; Zhu, Z. Suppression of Cutibacterium acnes-Mediated Inflammatory Reactions by Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.Z.; Stevenson, A.W.; Prêle, C.M.; Fear, M.W.; Wood, F.M. The Role of IL-6 in Skin Fibrosis and Cutaneous Wound Healing. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Zheng, F.; Jiang, W.; Lei, K.; Li, H.; Liu, D.; Zhang, B.; He, M. Pharmacological Mechanisms of Shangke Huangshui against Skin and Soft Tissue Infection. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2022, 2022, 9312611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsunomiya, A.; Chino, T.; Kasamatsu, H.; Hasegawa, T.; Utsunomiya, N.; Luong, V.H.; Matsushita, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Ogura, D.; Niwa, S.I.; et al. The compound LG283 inhibits bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis via antagonizing TGF-β signaling. Arthritis Res. 2022, 24, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbialy, Z.I.; Assar, D.H.; Abdelnaby, A.; Asa, S.A.; Abdelhiee, E.Y.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Almeer, R.; Atiba, A. Healing potential of Spirulina platensis for skin wounds by modulating bFGF, VEGF, TGF-ß1 and α-SMA genes expression targeting angiogenesis and scar tissue formation in the rat model. Biomed. Pharm. 2021, 137, 111349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Paul, N.C.; Paul, S.K.; Saikat, A.S.M.; Akter, H.; Mandal, M.; Lee, S.S. Natural Product-Based Potential Therapeutic Interventions of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Molecules 2022, 27, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, P.; Kodra, A.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Golinko, M.S.; Ehrlich, H.P.; Brem, H. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in wound healing. J. Surg. Res. 2009, 153, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Ye, J.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, Z.; He, C.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Heparin-Based Coacervate of FGF2 Improves Dermal Regeneration by Asserting a Synergistic Role with Cell Proliferation and Endogenous Facilitated VEGF for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 2168–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidyanathan, L. Growth Factors in Wound Healing—A Review. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2021, 14, 1469–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Molecular Weight (M. W.) in Daltons (Da) | |
|---|---|
| Total M. W. | <3 Da |
| >7000 Da | 31.15% |
| 5000 Da–6999 Da | 13.99% |
| 4000 Da–4999 Da | 46.15% |
| 3000 Da–3999 Da | 3.72% |
| 2000 Da–2999 Da | 1.58% |
| <2000 Da | 3.41% |
| Protein Combustion | |
| Protein | 100% |
| Nitrogen combustion | 16.48% |
| Protein factor | 6.5 |
| Aminogram | |
| Alanine | 9.02% |
| Arginine | 7.53% |
| Aspartic acid | 5.70% |
| Glutamic acid | 10.06% |
| Glycine | 23.61% |
| Histidine | 0.72% |
| Isoleucine | 1.43% |
| Leucine | 2.76% |
| Phenylalanine | 1.91% |
| Proline | 12.90% |
| Serine | 3.29% |
| Threonine | 1.89% |
| Lysine | 3.57% |
| Tyrosine | 0.48% |
| Valine | 2.27% |
| Ash in food | |
| Ash | 1.65 g/100 g |
| Cystine and Methionine | |
| Cystine | 0.03% |
| Methionine | 0.82% |
| Heavy metals | |
| Arsenic | 39.5 ppb |
| Cadmium | <5.00 ppb |
| Lead | <5.00 ppb |
| Mercury | <5.00 ppb |
| Hydroxyproline | |
| Hydroxyproline | 9.49% |
| Sodium | |
| Sodium (Na) | <66.5 mg/kg |
| Pesticide–glyphosate compounds | |
| Glufosinate | <0.01 mg/kg |
| Glyphosate | <0.01 mg/kg |
| Tryptophan | |
| Tryptophan | <0.01% |
| Zinc (Zn) in foods | |
| Zinc (Zn) | <3.29 mg/kg |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brandao-Rangel, M.A.R.; Oliveira, C.R.; da Silva Olímpio, F.R.; Aimbire, F.; Mateus-Silva, J.R.; Chaluppe, F.A.; Vieira, R.P. Hydrolyzed Collagen Induces an Anti-Inflammatory Response That Induces Proliferation of Skin Fibroblast and Keratinocytes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234975
Brandao-Rangel MAR, Oliveira CR, da Silva Olímpio FR, Aimbire F, Mateus-Silva JR, Chaluppe FA, Vieira RP. Hydrolyzed Collagen Induces an Anti-Inflammatory Response That Induces Proliferation of Skin Fibroblast and Keratinocytes. Nutrients. 2022; 14(23):4975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234975
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrandao-Rangel, Maysa Alves Rodrigues, Carlos Rocha Oliveira, Fabiana Regina da Silva Olímpio, Flavio Aimbire, José Roberto Mateus-Silva, Felipe Augusto Chaluppe, and Rodolfo P. Vieira. 2022. "Hydrolyzed Collagen Induces an Anti-Inflammatory Response That Induces Proliferation of Skin Fibroblast and Keratinocytes" Nutrients 14, no. 23: 4975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234975
APA StyleBrandao-Rangel, M. A. R., Oliveira, C. R., da Silva Olímpio, F. R., Aimbire, F., Mateus-Silva, J. R., Chaluppe, F. A., & Vieira, R. P. (2022). Hydrolyzed Collagen Induces an Anti-Inflammatory Response That Induces Proliferation of Skin Fibroblast and Keratinocytes. Nutrients, 14(23), 4975. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14234975









