Abstract
Lipodystrophy syndromes are rare diseases that could be of genetic or acquired origin. The main complication of lipodystrophy is the dysfunction of adipose tissue, which leads to an ectopic accumulation of triglycerides in tissues such as the liver, pancreas and skeletal muscle. This abnormal fat distribution is associated with hypertriglyceridemia, insulin resistance, liver steatosis, cardiomyopathies and chronic inflammation. Although the origin of acquired lipodystrophies remains unclear, patients show alterations in genes related to genetic lipodystrophy, suggesting that this disease could be improved or aggravated by orchestrating gene activity, for example by diet. Nowadays, the main reason for adipose tissue dysfunction is an imbalance in metabolism, caused in other pathologies associated with adipose tissue dysfunction by high-fat diets. However, not all dietary fats have the same health implications. Therefore, this article aims to summarize the main genes involved in the pathophysiology of lipodystrophy, identify connections between them and provide a systematic review of studies published between January 2017 and January 2022 of the dietary fats that can modulate the development of lipodystrophy through transcriptional regulation or the regulation of protein expression in adipocytes.
1. Introduction
Lipodystrophy syndromes are rare disorders characterized by adipose tissue (AT) dysfunction [1]. The dysfunction of adipocytes leads to immunometabolic complications such as chronic inflammation, ectopic fat accumulation, insulin resistance, hypoleptinemia, hypoadiponectinemia and hypertriglyceridemia [2]. These comorbidities should be managed to avoid the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), diabetes mellitus type 2 (DMT2) and cardiomyopathies associated with lipodystrophy syndromes [3]. Lipodystrophy syndromes may be of congenital or acquired origin. Certain genes have been selected as the main contributors to different types of lipodystrophies [2]. However, in the case of acquired lipodystrophy, the origin remains unclear, despite the expression of specific genes, such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), being implicated in lipodystrophy associated with antiretroviral therapy (ART) [4].
Certain exogenous factors such as pharmacological or nutritional factors can modulate AT by orchestrating gene activity. Obesogenic diets, characterized by a high-fat composition, can downregulate certain gene expression in adipocytes that are related to adipogenesis and lipid metabolism alteration [5]. However, dietary fats have different metabolic targets based on their composition in terms of fatty acids and not all have the same effects on health [6]. Therefore, the aim of this article was to summarize the main genes involved in the pathophysiology of lipodystrophy, to identify the connection between them and to analyze in a systematic review the dietary fats that can modulate the development of lipodystrophy through transcriptional regulation or the regulation of protein expression in adipocytes.
2. Materials and Methods
The methodology has been divided into:
- Initial research on the most common types of lipodystrophies and the main genes involved in the development of congenital lipodystrophy as well as the genes implicated in acquired lipodystrophy.
- Analysis of the proteins involved in lipodystrophy via the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Proteins 11 (STRING 11) (a database under a Creative Commons by 4.0’ license) with a minimum required interaction score (high confidence (0.700)) [7]. This analysis was performed to determine the interaction between the different proteins implicated in lipodystrophy and to identify which ones played a more relevant role and the main biological processes in which they were involved. In addition, it allowed us to determine the relationship between the implicated proteins in congenital and acquired lipodystrophy.
- A systematic review of the scientific evidence on the modulation of the expression and activity of the selected genes (PPARγ and Perilipin 1 (PLIN1)) by dietary lipids. The PubMed database was searched from January 2017 to January 2022. Due to the lack of studies analyzing the impact of diet on lipodystrophy, the following search strategy was used: ((PPARG) OR (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma) OR (PLIN1) OR (PERILIPIN1)) AND ((oil) OR (fatty acid) OR (high-fat diet) OR (dietary lipid) OR (capric acid) OR (lauric acid) OR (myristic acid) OR (palmitic acid) OR (stearic acid) OR (arachidic acid) OR (behenic acid) OR (caprylic acid) OR (oleic acid) OR (linoleic acid) OR (eicosapentaenoic acid) OR (linolenic acid) OR (arachidonic acid) OR (docosatetraenoic acid) OR (palmitoleic acid)) NOT (review [Publication Type]). The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) experimental model: cells, mice, rats and clinical trials; (2) intervention with dietary oils, fats or isolated fatty acids (i.e., conjugated linoleic, palm oil or omega-3 fatty acids); (3) analysis of PPARγ or PLIN1 gene/protein expression; (4) original papers (not reviews); (5) articles written in the English language. The eligibility for inclusion and exclusion criteria were evaluated by reading both (1) the title and abstract and (2) the full text (Supplementary Figure S1).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Lipodystrophy Syndromes Classification
Lipodystrophy syndromes are disorders characterized by a redistribution of AT. They affect either localized areas (partial) or the whole body (generalized) [8]. Lipodystrophy may appear as an undesirable effect of certain drugs (i.e., insulin, antiretroviral therapies, etc.), due to autoimmune mechanisms, or has a genetic origin (autosomal dominant or recessive subtypes) [1]. Acquired lipodystrophy occurs with metabolic syndromes, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), connective tissue disorders and some inflammatory conditions.
The different types of lipodystrophy syndromes can be classified as follows (Figure 1):
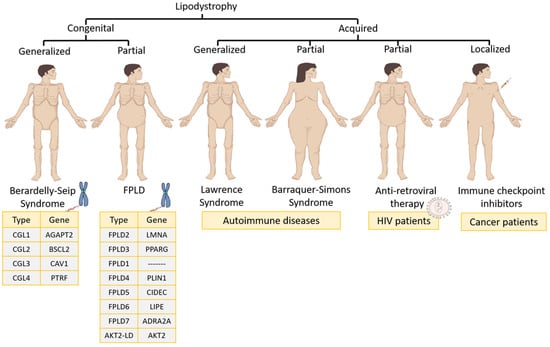
Figure 1.
Lipodystrophy syndromes classification. FPLD, familial partial lipodystrophy.
3.1.1. Congenital Lipodystrophies
- Familial partial lipodystrophy (FPLD) is usually an autosomal dominant syndrome characterized by a selective loss of fat from the lower and upper extremities as well as the trunk [1]. During childhood, patients have a normal fat distribution but at puberty start to lose fat from the chest, anterior abdomen and extremities. There are eight varieties of FPLD: (1) FLPD2, the most common subtype (also called the Dunnigan type), which is characterized by mutations in the lamin A/C gene (LMNA); (2) FPLD3, the second most common subtype, which is based on mutations in the PPARγ gene; (3) FPLD1 (or the Kobberling type), whose genetic mutation is unknown; (4) FPDL4, which is characterized by heterozygous mutations in the PLIN1 gene; (5) FPDL5 and (6) FPDL6, both of which are autosomal recessive disorders in the cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector C (CIDEC) and lipase E (LIPE) genes, respectively; (7) FPDL7, which features a genetic mutation in the adrenoceptor alpha 2A (ADRA2A) gene; and (8) AKT2-linked lipodystrophy (AKT2-LD), which is based on a mutation in the (AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase 2) AKT2 gene [1].
- Congenital generalized lipodystrophy (CGL), or Berardinelli–Seip syndrome, is an autosomal recessive disease that is distinguished by the absence of AT both at birth and in early childhood [1]. Four distinct subtypes exist depending on the gene that is altered: (1) CGL1 is the most common subtype, and the associated altered gene is 1-Acylglycerol-3-Phosphate O-Acyltransferase 2 (AGPAT2), which is involved in triglyceride biosynthesis; (2) CGL2 is the second most common subtype and the altered gene in that case is lipid droplet biogenesis associated (BSCL2), which plays a relevant role in adipocyte differentiation and small lipid droplet fusion in adipocytes; (3) CGL3 has only been reported in one patient and the altered gene was caveolin 1 (CAV1), which translocates fatty acids to lipid droplets; (4) CGL4 has been reported in 20 patients and is very close to CGL3 because its gene (caveolae-associated protein 1) is regulated by CAV1 expression [1].
3.1.2. Acquired Lipodystrophies
- Acquired generalized lipodystrophy or Lawrence syndrome is characterized by the generalized loss of subcutaneous fat. The loss of fat usually begins in childhood or adolescence [1]. Most patients have related autoimmune diseases [8,9,10,11,12,13]. In certain autoimmune diseases, the role of the PPARγ gene is essential to modulate inflammation. In fact, therapy is based on agonists of the PPARγ gene [14].
- Acquired partial lipodystrophy, or Barraquer–Simons syndrome, is characterized by a gradual loss of subcutaneous fat from the upper trunk, upper extremities, neck and face. In the case of females, after puberty, excess fat can accumulate in the lower extremities, hips and lower abdomen. It is often related to autoimmune diseases and this syndrome affects mostly women [1,15,16,17].
- Antiretroviral therapy-induced lipodystrophy occurs in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus who, after 2–4 years of treatment with ART, start to have an increased accumulation of both intra-abdominal and upper trunk fat, while they lose subcutaneous fat in the lower and upper extremities [1,18]. This is related to PPARγ protein downregulation. However, by stopping ART, PPARγ protein expression is restored in macrophages and adipocytes [4].
- Recent cases of acquired lipodystrophy have been associated with the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors to treat cancer [19,20,21]. Among them, childhood cancer survivors transplanted with hematopoietic stem cells and treated with chemotherapy developed acquired lipodystrophy over time [22]. Furthermore, other types of cancer, such as craniopharyngioma, may lead to chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy together with acquired lipodystrophy [23]. This pathology is associated with certain cancer therapies against programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), which promotes apoptosis in antigen-specific T cells in lymph nodes and leads to adverse events of an immune nature [24].
3.2. Relationship of Genes Involved in the Development of Lipodystrophy
The main genes involved in the development of lipodystrophy of congenital origin and those implicated in specific cases of acquired lipodystrophy are summarized below:
- BSCL2: a protein expressed mainly in AT, which is involved in lipid droplet biogenesis, in the regulation of energy homeostasis and adipocyte differentiation [25].
- LIPE or hormone-sensitive lipase, which promotes the hydrolysis of triglycerides stored in lipid droplets during adipocyte differentiation [26].
- CAV1: a protein located in lipid droplets of adipocytes which has a key role in cholesterol homeostasis, endothelial transcytosis and cellular metabolism [27].
- LMNA: a protein involved in telomere dynamics, the nuclear membrane, chromatin organization and nuclear assembly [28].
- AKT2: a kinase involved in processes such as angiogenesis, cell growth, proliferation and metabolism [29].
- ADRA2A: a receptor involved in the inhibition of adenylate cyclase induced by catecholamine [30].
- PPARγ: a nuclear receptor that controls insulin sensitivity, glucose metabolism and adipocyte differentiation. PPARγ protein is a major adipogenic factor [31].
- AGPAT2: an acyltransferase involved in the transformation of lysophosphatidic acid into phosphatidic acid, which belongs to the triglyceride biosynthetic pathway [32].
- CIDEC: a protein that modulates triglyceride storage by restricting lipolysis and is involved in the enlargement of lipid droplets [31].
- PLIN1: a modulator of the lipid metabolism in adipocytes which protects lipid droplets from breakdown by HSL, and its interaction with CIDEC promotes the enlargement of lipid droplets [33].
STRING11 software was used to analyze if there was any relationships between the main proteins implicated in the different types of lipodystrophies. The results of the analysis showed that there was an interaction between certain proteins: PPARγ, CIDEC, CAV1, LIPE, PLIN1, BSCL2 and AGPAT2 (Figure 2). We observed that there were strong interactions between PPARγ and PLIN1 and most proteins. In fact, the network had significantly more interactions than expected, which means that proteins have more interactions among themselves than what would be expected from a random set of proteins, demonstrating that the proteins are partially biologically connected as a group. This group is mainly involved in biological processes that are closely related to lipodystrophy such as the lipid metabolism and lipid droplet formation. Thus, the data suggested that PPARγ and PLIN1 proteins can play an important role in the dysfunction of adipose tissue by modulating the activity of other proteins. Surprisingly, PPARγ protein expression is also altered in specific types of acquired lipodystrophy, which could be the link between congenital and acquired lipodystrophy and a key target for the management of the disease. Therefore, the next step was to identify how the expression of both proteins can be modulated by nutritional factors such as dietary fatty acids.
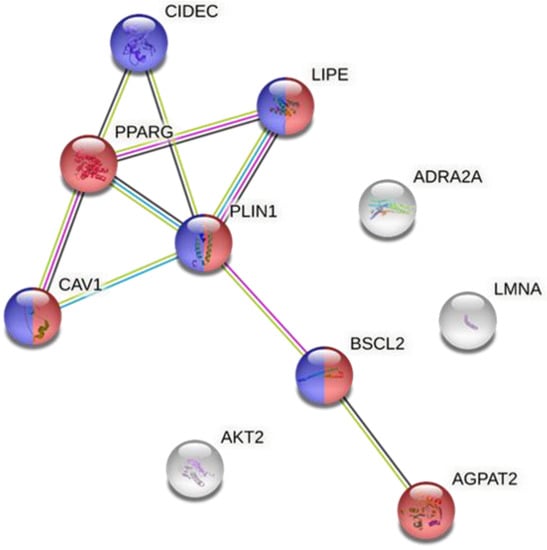
Figure 2.
Protein–protein interaction network. Colored nodes in red: proteins involved in lipid metabolism. Colored nodes in blue: proteins involved in lipid droplet formation. Colored nodes in white: the second shell of interactions. Edges represent protein–protein associations. Associations are meant to be specific and meaningful, i.e., proteins jointly contribute to a shared function; this does not necessarily mean that they are physically binding to each other. Depending on the color of the line, the association has been determined from curated databases (blue line) or experimentally (pink line). If the genes are neighbors, the interaction line is green and if the genes are co-expressed, the lines are black. The more interaction lines between two genes, the stronger the evidence of their interaction.
3.3. Nutrigenomic Effects of Dietary Lipids on PPARγ and PLIN1
Gene regulation in AT can be produced by diet. Dietary fat composition can affect ectopic lipid accumulation and dietary fatty acids are involved in the composition of cellular membranes, organelles membranes and can regulate toll-like receptor (TLR) activity, contributing to the inflammatory response [34,35]. However, studies that have analyzed the effect of dietary lipids on lipodystrophy are limited. After a review of the scientific literature, 37 articles were selected for discussion in this section (Supplementary Figure S1).
Interventions with oils have been developed primarily in murine models, although there are clinical trials on diabetic and healthy adults (Table 1). Patients with metabolic dysregulation such as DMT2 have common complications such as cardiomyopathy, a typical outcome in certain lipodystrophic patients [36]. A study analyzed the effect of Krill oil (an oil rich in n-3 polyunsaturated acid (PUFA) of marine origin) in the prevention of cardiomyopathy in diabetic mice [37]. This oil was able to upregulate the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α), which is involved in the inhibition of the inflammasome (NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3)). PGC-1α is a transcriptional coactivator that interacts with PPARγ and primarily regulates genes involved in energy metabolism (e.g., mitochondrial biogenesis). However, this transcriptional network mainly modulates the key signaling pathways of the production and differentiation of white and brown adipocytes [38]. In the same way, supplementation with flaxseed oil (rich in n-3 PUFAs) in diabetic patients with coronary heart disease significantly downregulated the expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and upregulated PPARγ protein in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of patients [39]. Supplementation with oil rich in n-3 PUFA was closely related to the fatty acid composition of different tissues and positively regulated the expression of PPARγ protein in the AT of turkeys, regulating fat metabolism [40]. An oils’ composition is directly associated with its impact on health. In the case of palm oil or butter, which is composed mainly of saturated fatty acids, these are related to the development of NAFLD, while the substitution of these oils with others rich in unsaturated fatty acids such as rapeseed oil can attenuate the progression of NAFLD by reducing the levels of lipopolysaccharide, downregulating the activation of TLR4 and increasing PPARγ activity in the small intestine [41]. While peanut oil and lard induced inflammation, hepatic steatosis and high blood pressure, a blended oil rich in oleic acid and ALA was able to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL), serum triglycerides, TLR4 expression, TNF-α and C-reactive protein but increased PPARγ protein expression. These results demonstrate that an appropriate ratio of monounsaturated and n-6/n-3 PUFAs could prevent immunometabolic disturbances [42].

Table 1.
Effect of oils on PPARγ modulation.
Virgin olive oil and fish oil have been demonstrated to be one of the healthiest fat sources in terms of maintaining body weight, regulating metabolism and promoting an anti-inflammatory status. However, there is no evidence of PPARγ activity modulation by virgin olive oil using the above search strategy. Regarding fish oil, its supplementation can significantly enhance lipoprotein lipase, PPARγ and PGC-1α protein expression, even during a high-fat diet intervention in rats [43]. Supplementation with fish oil enriched in docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in diabetic patients increased PPARγ activity significantly in PBMCs, improving patient metabolism [44].
On the other hand, palm oil and palmitic acid-induced lipotoxicity in the liver enhances hepatic fatty acid and triglyceride uptake by the upregulation of CD36, a very-low-density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR), and PPARγ protein [45]. Despite their different effects on health, overfeeding promotes the methylation of PGC-1α and TNF-α in AT [46].
Regarding studies that analyze the effect of n-3 PUFAs in different research models (Table 2), all conclude that n-3 PUFAS can suppress metabolic disturbances associated with insulin resistance and the development of liver fibrosis. In the white adipose tissue of rats, these fatty acids induce browning by enhancing the activity and expression of PPARγ protein and enhancing the expression of neuregulin 4 (Nrg4), which is involved in the prevention of lipid accumulation in hepatic cells [47]. Furthermore, in murine models of metabolic syndrome, n-3 PUFAs supplementation increased the expression of PPARγ and glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) proteins, improving insulin sensitivity and the lipid profile [48]. Similarly, supplementation with n-3 PUFAs in athletes produced an upregulation of the protein levels of uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2) and PPARγ proteins in PBMCs, improving energy expenditure and controlling body weight [49].

Table 2.
Effect of n-3 PUFAS on PPARγ modulation.
Based on the protective effects of n-3 PUFAs supplementation, several studies have individually analyzed the effects of EPA and DHA to elucidate their mechanism of action (Table 3). Both EPA and DHA fatty acids have shown an anti-lipotoxic effect in different types of cells. In a high-fat diet or during the induction of lipotoxicity with palmitic acid in vitro, supplementation with EPA was able to promote fatty acid oxidation and lipid droplet formation [54]. Similarly, supplementation in obese mice attenuated the dysfunction of AT by enhancing the expression of PPAR-γ protein and reducing the inflammation associated with high levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and TNFα, attenuating the inflammatory-metabolic state [55]. Furthermore, in UCP1 knockout mice fed a high-fat diet, who are unable to regulate diet-induced thermogenesis and are at increased risk for obesity, EPA supplementation exerted protective effects, increasing PGC1α expression in brown adipose tissue and improving glucose tolerance [56]. Treatment with EPA and DHA, alone or combined, upregulated different genes involved in the mitochondrial function. In skeletal muscle cells, EPA improved the response to insulin via PGC1-α and countered the inflammation induced by palmitic acid, inhibiting the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cell (NFκB) signaling [57]. In the same way, EPA promotes adipogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells through the activation of PPARγ, while treatment with EPA, DHA or furan fatty acid 9-(3-methyl-5-pentylfuran-2-yl)-nonanoic acid (9M5) induced adipogenesis in preadipocytes [58,59,60]. Comparing the effects of EPA and DHA, the latter has been demonstrated to be more effective in immunometabolic regulation, enhancing fat oxidation in muscle cells (via PGC1-α), reducing the expression of TNFαR, improving adipocyte functionality through PPARγ activity and increasing adiponectin secretion [61,62]. In combination with arachidonic acid (ARA), DHA attenuated the AT dysfunction induced by an obesogenic diet and can reduce inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α IL-6 in AT [63].

Table 3.
Effect of eicosapentaenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid and arachidonic acid on PPARγ and PLIN1 modulation.
The effects of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) on the metabolism remain controversial (Table 4). Its supplementation has been shown to decrease the abundance of genes related to fatty acid oxidation and lipolysis and to increase genes involved in lipogenesis, such as the PPARγ gene [64]. In murine models, high doses of CLA are associated with lipid accumulation in the liver by negatively regulating PCG-1α, leading to steatogenic effects as well as a reduction in body fat through the modulation of PPARγ protein [65,66]. Contrary to the effects of n-3 PUFAS, CLA does not stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis or PCG-1α expression in murine models [67]. On the other hand, the in vitro effects of CLA in combination with alpha-lipoic acid exerted anti-inflammatory activity in murine macrophages through the modulation of the ERK1/PPARγ pathway [68].

Table 4.
Effect of Conjugated linoleic acid on PPARγ and PLIN1 modulation.

Table 5.
Effect of different fatty acids on PPARγ and PLIN1 modulation.
Overall, these results suggest that while SFA and CLA induce dysfunction in AT and negatively regulate adipogenesis and lipid metabolism, n-3 PUFAs and certain monounsaturated fatty acids can reverse the effects caused by saturated fatty acids and a high-fat diet (Figure 3).
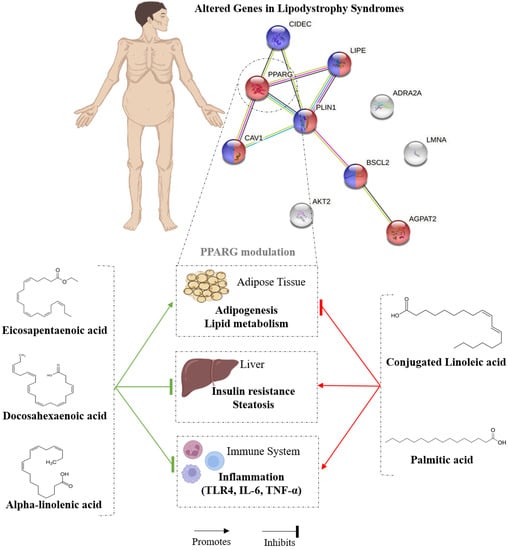
Figure 3.
PPARγ gene modulation by dietary fatty acids.
However, there are important aspects to highlight for future analysis in both the diagnosis of congenital lipodystrophy and in the approach to genetic alterations through diet. On the one hand, the alterations in PPARs expression in patients only reflect the alteration in the PPARγ isoform, and there are no data on the PPARα and PPARβ/δ isoforms that are also involved in adipocyte metabolism. On the other hand, it would be interesting to analyze if alterations in PPARγ are a consequence and not a cause of adipose tissue atrophy. Lipodystrophic adipose tissue is characterized by both a high infiltration of M1 (proinflammatory phenotype) and a reduction in resident M2 macrophages. It has been observed that PPARγ is also involved in the polarization toward M2 phenotype macrophages, so their downregulation in adipose tissue could be the cause of the decrease in PPARγ expression. However, further studies are needed to elucidate the mechanism of lipodystrophy development. Furthermore, in order to obtain results that can be extrapolated to clinical practice, the effect of dietary fats and oils on the modulation of adipose tissue function in patients with lipodystrophy needs to be analyzed in clinical trials.
4. Conclusions
Congenital and acquired lipodystrophy share a common pathophysiology: adipose tissue dysfunction, an alteration that results in most cases in hypertriglyceridemia, ectopic fat accumulation, insulin resistance, chronic inflammation and low levels of leptin and adiponectin. Consequently, a low-fat diet is usually recommended to lipodystrophy patients, but not all fats have harmful effects on the health of these patients. In this article, we determined a common link through genetic alteration in specific congenital and acquired lipodystrophies. We observed that PPARγ is a gene involved in lipodystrophy development and is closely associated with the regulation of the other genes altered in this pathology. The PPARγ gene may be up-regulated in adipose tissue by omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids such as EPA, DHA and ALA, while saturated fatty acids such as palmitic acid lead to PPARγ up-regulation in non-adipose tissues such as the liver, favouring ectopic fat accumulation. Omega-3 may prevent or reduce the typical comorbidities of lipodystrophy such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, NAFLD and cardiomyopathies, improving the symptomatology of lipodystrophy, whereas saturated fatty acids may worsen these comorbidities. However, more clinical studies are required to determine the role of dietary fat in PPAR-γ gene modulation to control adipose tissue dysfunction in lipodystrophic patients.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu14224742/s1, Figure S1: Flowchart of studies through systematic review process.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation: C.R.-G.; J.J.G., M.J.M.-R. and C.S.-Q. edited and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
9M5: furan fatty acid 9-(3-methyl-5-pentylfuran-2-yl)-nonanoic acid; ADRA2A: adrenoceptor alpha 2A; AGPAT2: 1-Acylglycerol-3-Phosphate O-Acyltransferase 2; AKT2: AKT serine/threonine kinase 2; ALA: α- linolenic acid; ARA: arachidonic acid; ART: antiretroviral therapy; AT: adipose tissue; BSCL2: lipid droplet biogenesis associated; CAV1: caveolin 1; CGL: congenital generalized lipodystrophy; CIDEC: cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector C; CLA: conjugated linoleic acid; DMT2: diabetes mellitus type 2; DHA: docosahexaenoic acid; EPA: eicosapentaenoic acid; FPLD: familial partial lipodystrophy; GLUT4: glucose transporter type 4; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; IL-6: interleukin-6; KO: krill oil; LDL: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LIPE: lipase E; LMNA: lamin A/C; LO: linseed oil; MSCs: mesenchymal stem cells; NAFLD: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NFκB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NGR4: neuregulin 4; NLRP3: NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; NOS3: nitric oxide synthase 3; PBMCs: peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PD-1: programmed cell death protein 1; PGC-1α: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α; PLIN 1: perilipin 1; PPARγ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; PUFA: n-3 polyunsaturated acid; SFA: saturated fatty acids; STRING 11: Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Proteins 11; TLR: toll-like receptor; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor alpha; UCP2: uncoupling protein 2; VLDLR: very-low-density lipoprotein receptor.
References
- Hussain, I.; Garg, A. Lipodystrophy Syndromes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 45, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.J.; Araujo-Vilar, D.; Cheung, P.T.; Dunger, D.; Garg, A.; Jack, M.; Mungai, L.; Oral, E.A.; Patni, N.; Rother, K.I.; et al. The Diagnosis and Management of Lipodystrophy Syndromes: A Multi-Society Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 4500–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinci, B.; Oral, E.A.; Neidert, A.; Rus, D.; Cheng, W.Y.; Thompson-Leduc, P.; Cheung, H.C.; Bradt, P.; Foss de Freitas, M.C.; Montenegro, R.M.; et al. Comorbidities and Survival in Patients with Lipodystrophy: An International Chart Review Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 5120–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, M.; Vigouroux, C.; Bastard, J.-P.; Capeau, J. Antiretroviral-Related Adipocyte Dysfunction and Lipodystrophy in HIV-Infected Patients: Alteration of the PPARγ-Dependent Pathways. PPAR Res. 2009, 2009, 507141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinel, A.; Rigaudière, J.P.; Morio, B.; Capel, F. Adipose Tissue Dysfunctions in Response to an Obesogenic Diet Are Reduced in Mice after Transgenerational Supplementation with Omega 3 Fatty Acids. Metabolites 2021, 11, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, K.A.; Homeida, A.M.; El Mazoudy, R.H.; Hashim, K.S.; Garelnabi, M. Dietary Lipids in Health and Disease. J. Lipids 2019, 5729498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharawat, I.K.; Yadav, J.; Dawman, L. Multiple sites acquired lipodystrophy in two siblings: A rare adverse effect of intramuscular triamcinolone. BMJ Case Rep. 2019, 12, e231017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvillo, F.; Aparicio, V.; López-Lera, A.; Garrido, S.; Araújo-Vilar, D.; de Miguel, M.P.; López-Trascasa, M. Autoantibodies Against Perilipin 1 as a Cause of Acquired Generalized Lipodystrophy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, C.E.; Calder, P.C.; Miles, E.A. Diet and Immune Function. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzel, A.; Muller, D.N.; Hafler, D.A.; Erdman, S.E.; Linker, R.A.; Kleinewietfeld, M. Role of “Western diet” in inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014, 14, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, S.M.; Pagovich, O.E.; Kriegel, M.A. Diet, microbiota and autoimmune diseases. Lupus 2014, 23, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahinoz, M.; Khairi, S.; Cuttitta, A.; Brady, G.F.; Rupani, A.; Meral, R.; Tayeh, M.K.; Thomas, P.; Riebschleger, M.; Camelo-Piragua, S.; et al. Potential association of LMNA-associated generalized lipodystrophy with juvenile dermatomyositis. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Luo, S.; Zhan, Y.; Lu, Q. The roles of PPARγ and its agonists in autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 113, 102510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvillo, F.; Nozal, P.; López-Lera, A.; De Miguel, M.P.; Piñero-Fernández, J.A.; De Lucas, R.; García-Concepción, M.D.; Beato, M.J.; Araújo-Vilar, D.; López-Trascasa, M. Evidence of ongoing complement activation on adipose tissue from an 11-year-old girl with Barraquer–Simons syndrome. J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvillo, F.; Ceccarini, G.; Nozal, P.; Magno, S.; Pelosini, C.; Garrido, S.; López-Lera, A.; Moraru, M.; Vilches, C.; Fornaciari, S.; et al. Immunological features of patients affected by Barraquer-Simons syndrome. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidemann, L.N.; Thomsen, J.B.; Sørensen, J.A. Barraquer-Simons syndrome: A unique patient’s perspective on diagnosis, disease progression and recontouring treatment. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2016216134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, S.; Suzuki, K.; Yoshimoto, H.; Ohtsuru, A.; Hirano, A.; Yamashita, S. Cellular Mechanism Underlying Highly-Active or Antiretroviral Therapy-Induced Lipodystrophy: Atazanavir, a Protease Inhibitor, Compromises Adipogenic Conversion of Adipose-Derived Stem/Progenitor Cells through Accelerating ER Stress-Mediated Cell Death in Differentiating Adipocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2114. [Google Scholar]
- Gnanendran, S.S.; Miller, J.A.; Archer, C.A.; Jain, S.V.; Hwang, S.J.E.; Peters, G.; Miller, A. Acquired lipodystrophy associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Melanoma Res. 2020, 30, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosokawa, M.; Shibata, H.; Hosokawa, T.; Irie, J.; Ito, H.; Hasegawa, T. Acquired partial lipodystrophy with metabolic disease in children following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A report of two cases and a review of the literature. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 32, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcao, C.K.; Cabral, M.C.S.; Mota, J.M.; Arbache, S.T.; Costa-Riquetto, A.D.; Muniz, D.Q.B.; Cury-Martins, J.; Almeida, M.Q.; Kaczemorska, P.C.; Nery, M.; et al. Acquired Lipodystrophy Associated with Nivolumab in a Patient with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 3245–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayama, A.; Ashida, K.; Moritaka, K.; Hidaka, M.; Gobaru, M.; Tanaka, S.; Hasuzawa, N.; Akasu, S.; Goto, Y.; Motomura, S.; et al. Metreleptin Supplementation for Improving Lipid and Glycemic Profiles in Acquired Diabetes Lipodystrophy: A Case Report. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 2179–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockemer, H.E.; Sumpter, K.M.; Cope-Yokoyama, S.; Garg, A. A novel paraneoplastic syndrome with acquired lipodystrophy and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy in an adolescent male with craniopharyngioma. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 31, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigentler, T.; Lomberg, D.; Machann, J.; Stefan, N. Lipodystrophic Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Ann. Intern Med. 2020, 172, 836–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xu, C.; Lee, H.; Yoon, Y.; Chen, W. Berardinelli–Seip congenital lipodystrophy 2/SEIPIN determines brown adipose tissue maintenance and thermogenic programing. Mol. Metab. 2020, 36, 100971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollier, C.; Capel, E.; Aguilhon, C.; Smirnov, V.; Auclair, M.; Douillard, C.; Ladsous, M.; Defoort-Dhellemmes, S.; Gorwood, J.; Braud, L.; et al. LIPE-related lipodystrophic syndrome: Clinical features and disease modeling using adipose stem cells. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 184, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrauwen, I.; Szelinger, S.; Siniard, A.L.; Kurdoglu, A.; Corneveaux, J.J.; Malenica, I.; Richholt, R.; Van Camp, G.; De Both, M.; Swaminathan, S.; et al. A Frame-Shift Mutation in CAV1 Is Associated with a Severe Neonatal Progeroid and Lipodystrophy Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vigouroux, C.; Guénantin, A.C.; Vatier, C.; Capel, E.; Le Dour, C.; Afonso, P.; Bidault, G.; Béréziat, V.; Lascols, O.; Capeau, J.; et al. Lipodystrophic syndromes due to LMNA mutations: Recent developments on biomolecular aspects, pathophysiological hypotheses and therapeutic perspectives. Nucleus 2018, 9, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearin, A.L.; Monks, B.R.; Seale, P.; Birnbaum, M.J. Lack of AKT in adipocytes causes severe lipodystrophy. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Sankella, S.; Xing, C.; Agarwal, A.K. Whole-exome sequencing identifies ADRA2A mutation in atypical familial partial lipodystrophy. JCI Insight 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammouri, J.; Vatier, C.; Capel, E.; Auclair, M.; Storey-London, C.; Bismuth, E.; Mosbah, H.; Donadille, B.; Janmaat, S.; Fève, B.; et al. Molecular and Cellular Bases of Lipodystrophy Syndromes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 803189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarini, G.; Magno, S.; Pelosini, C.; Ferrari, F.; Sessa, M.R.; Scabia, G.; Maffei, M.; Jéru, I.; Lascols, O.; Vigouroux, C.; et al. Congenital Generalized Lipoatrophy (Berardinelli-Seip Syndrome) Type 1: Description of Novel AGPAT2 Homozygous Variants Showing the Highly Heterogeneous Presentation of the Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jéru, I.; Vantyghem, M.-C.; Bismuth, E.; Cervera, P.; Barraud, S.; Auclair, M.; Vatier, C.; Lascols, O.; Savage, D.B.; Vigouroux, C. Diagnostic Challenge in PLIN1-Associated Familial Partial Lipodystrophy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 6025–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Quintela, A.; Churruca, I.; Portillo, M.P. The role of dietary fat in adipose tissue metabolism. Public Health Nutr. 2007, 10, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.M.; Handa, P.; Tateya, S.; Schwartz, J.; Tang, C.; Mitra, P.; Oram, J.F.; Chait, A.; Kim, F. Apolipoprotein A-I attenuates palmitate-mediated NF-κB activation by reducing Toll-like receptor-4 recruitment into lipid rafts. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanon, V.P.; Handelsman, Y.; Pham, S.V.; Chilton, R. Cardiac Manifestations of Congenital Generalized Lipodystrophy. Clin. Diabetes 2016, 34, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Sun, X.; Meng, H.; Wu, J.; Guo, X.; Du, L.; Wu, H. Krill Oil Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in the Prevention of the Pathological Injuries of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Nutrients 2022, 14, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Cai, B.; Nie, Q. PGC-1α affects skeletal muscle and adipose tissue development by regulating mitochondrial biogenesis. Mol. Genet. Genomic. 2022, 297, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemzadeh, A.A.; Nasoohi, N.; Raygan, F.; Aghadavod, E.; Akbari, E.; Taghizadeh, M.; Memarzadeh, M.R.; Asemi, Z. Flaxseed Oil Supplementation Improve Gene Expression Levels of PPAR-γ, LP(a), IL-1 and TNF-α in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Coronary Heart Disease. Lipids 2017, 52, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalai, K.; Tempfli, K.; Zsédely, E.; Lakatos, E.; Gáspárdy, A.; Bali Papp, Á. Linseed oil supplementation affects fatty acid desaturase 2, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma, and insulin-like growth factor 1 gene expression in turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo). Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, A.; Rajcic, D.; Jin, C.J.; Sánchez, V.; Engstler, A.J.; Jung, F.; Nier, A.; Baumann, A.; Bergheim, I. Fortifying diet with rapeseed oil instead of butterfat attenuates the progression of diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and impairment of glucose tolerance. Metabolism 2020, 109, 154283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriho, A.; Yang, S.; Tang, X.; Liu, C.S.; Wang, S.; Cong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, P. Benefits of blended oil consumption over other sources of lipids on the cardiovascular system in obese rats. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5290–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Chiu, C.Y.; Wang, L.P.; Chiang, M.T. Omega-3 Fatty Acids-Enriched Fish Oil Activates AMPK/PGC-1α Signaling and Prevents Obesity-Related Skeletal Muscle Wasting. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeini, Z.; Toupchian, O.; Vatannejad, A.; Sotoudeh, G.; Teimouri, M.; Ghorbani, M.; Nasli-Esfahani, E.; Koohdani, F. Effects of DHA-enriched fish oil on gene expression levels of p53 and NF-κB and PPAR-γ activity in PBMCs of patients with T2DM: A randomized, double-blind, clinical trial. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajri, T.; Zaiou, M.; Fungwe, T.V.; Ouguerram, K.; Besong, S. Epigenetic Regulation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Mediates High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perfilyev, A.; Dahlman, I.; Gillberg, L.; Rosqvist, F.; Iggman, D.; Volkov, P.; Nilsson, E.; Risérus, U.; Ling, C. Impact of polyunsaturated and saturated fat overfeeding on the DNA-methylation pattern in human adipose tissue: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zhou, N.; Zhu, X.; Min, C.; Zhou, W.; Li, X. n-3 PUFAs protect against adiposity and fatty liver by promoting browning in postnatally overfed male rats: A role for NRG4. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 93, 108628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, E.A.; AinShoka, A.A.; El Shazly, K.A.; Abd El Latif, H.A. Improvement of insulin resistance via increase of GLUT4 and PPARγ in metabolic syndrome-induced rats treated with omega-3 fatty acid or l-carnitine. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Alivand, M.; KhajeBishak, Y.; AsghariJafarabadi, M.; Alipour, M.; Chilibeck, P.D.; Alipour, B. The effect of omega3 fatty acid supplementation on PPARγ and UCP2 expressions, resting energy expenditure, and appetite in athletes. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraky, S.M.; Ramadan, N.M. Effects of omega-3 fatty acids and metformin combination on diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats through autophagic pathway. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 97, 108798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.S.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Fang, L.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Feng, J.; Li, K.; Tang, J.; et al. Replication of a Gene-Diet Interaction at CD36, NOS3 and PPARG in Response to Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplements on Blood Lipids: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. EBioMedicine 2018, 31, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Bae, M.; Park, Y.K.; Lee, J.Y. n-3 PUFAs inhibit TGFβ1-induced profibrogenic gene expression by ameliorating the repression of PPARγ in hepatic stellate cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 85, 108452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandurangan, S.B.; Al-Maiman, S.A.; Al-Harbi, L.N.; Alshatwi, A.A. Beneficial Fatty Acid Ratio of Salvia hispanica L. (Chia Seed) Potentially Inhibits Adipocyte Hypertrophy, and Decreases Adipokines Expression and Inflammation in Macrophage. Foods 2020, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Takabatake, Y.; Minami, S.; Sakai, S.; Fujimura, R.; Takahashi, A.; Namba-Hamano, T.; Matsuda, J.; Kimura, T.; Matsui, I.; et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid attenuates renal lipotoxicity by restoring autophagic flux. Autophagy 2021, 17, 1700–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illesca, P.; Valenzuela, R.; Espinosa, A.; Echeverría, F.; Soto-Alarcon, S.; Campos, C.; Rodriguez, A.; Vargas, R.; Magrone, T.; Videla, L.A. Protective Effects of Eicosapentaenoic Acid Plus Hydroxytyrosol Supplementation Against White Adipose Tissue Abnormalities in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Molecules 2020, 25, 4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahlavani, M.; Ramalingam, L.; Miller, E.K.; Scoggin, S.; Menikdiwela, K.R.; Kalupahana, N.S.; Festuccia, W.T.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Eicosapentaenoic Acid Reduces Adiposity, Glucose Intolerance and Increases Oxygen Consumption Independently of Uncoupling Protein 1. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1800821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, D.; Luscombe-Marsh, N.; Heilbronn, L.K.; Birch-Machin, M.; Naumovski, N.; Lionetti, L.; Proud, C.G.; Abeywardena, M.Y.; O’Callaghan, N. The Inhibition of Metabolic Inflammation by EPA Is Associated with Enhanced Mitochondrial Fusion and Insulin Signaling in Human Primary Myotubes. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera-Heredia, N.; Lutfi, E.; Gutiérrez, J.; Navarro, I.; Capilla, E. Fatty acids from fish or vegetable oils promote the adipogenic fate of mesenchymal stem cells derived from gilthead sea bream bone potentially through different pathways. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.F.; Aguila, M.B.; Mandarim-de-Lacerda, C.A. Eicosapentaenoic and docosapentaenoic acids lessen the expression of PPARγ/Cidec affecting adipogenesis in cultured 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Acta Histochem. 2020, 122, 151504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauvai, J.; Becker, A.K.; Lehnert, K.; Schumacher, M.; Hieronimus, B.; Vetter, W.; Graeve, L. The Furan Fatty Acid 9M5 Acts as a Partial Ligand to Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor gamma and Enhances Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes. Lipids 2019, 54, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsnelson, G.; Ceddia, R.B. Docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic fatty acids differentially regulate glucose and fatty acid metabolism in L6 rat skeletal muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 319, C1120–C1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Li, C.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Amakye, W.K.; Mao, L. DHA increases adiponectin expression more effectively than EPA at relative low concentrations by regulating PPARγ and its phosphorylation at Ser273 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Lei, J.; Schoemaker, M.H.; Ma, B.; Zhong, Y.; Lambers, T.T.; Van Tol, E.A.F.; Zhou, Y.; Nie, T.; Wu, D. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and extensively hydrolyzed casein-induced browning in a Ucp-1 reporter mouse model of obesity. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 2362–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirandeh, E.; Ghorbanalinia, M.; Roodbari, A.R.; Colazo, M.G. Effects of dietary conjugated linoleic acid on metabolic status, BW and expression of genes related to lipid metabolism in adipose tissue of dairy cows during peripartum. Animal 2021, 15, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cristofano, M.; Ferramosca, A.; Di Giacomo, M.; Fusco, C.; Boscaino, F.; Luongo, D.; Aufiero, V.R.; Maurano, F.; Cocca, E.; Mazzarella, G.; et al. Mechanisms underlying the hormetic effect of conjugated linoleic acid: Focus on Nrf2, mitochondria and NADPH oxidases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 167, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelatty, A.M.; Mohamed, S.A.; Moustafa, M.M.A.; Al-Mokaddem, A.K.; Baker, M.R.; Elolimy, A.A.; Elmedany, S.A.; Hussein, S.; Farid, O.A.A.; Sakr, O.G.; et al. Nutrigenomic effect of conjugated linoleic acid on growth and meat quality indices of growing rabbit. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, R.; Sangiorgi, C.; Marino Gammazza, A.; D’Amico, D.; Salerno, M.; Cappello, F.; Pomara, C.; Zummo, G.; Farina, F.; Di Felice, V.; et al. Effects of Conjugated Linoleic Acid Associated With Endurance Exercise on Muscle Fibres and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Coactivator 1 α Isoforms. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Ko, Y.J.; Kang, S.K.; Kim, W.S.; Cho, C.S.; Choi, Y.J. Additive anti-inflammation by a combination of conjugated linoleic acid and α-lipoic acid through molecular interaction between both compounds. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, M.; Xue, T.; Wang, L. Plant sterol ester of α-linolenic acid ameliorates high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice: Association with regulating mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress via activating AMPK signaling. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 2171–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Rong, Y.; Bao, L.; Nie, B.; Ren, G.; Zheng, C.; Amin, R.; Arnold, R.D.; Jeganathan, R.B.; Huggins, K.W. Suppression of adipocyte differentiation and lipid accumulation by stearidonic acid (SDA) in 3T3-L1 cells. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Nogoy, K.M.C.; Sun, J.; Sun, B.; Wang, Y.; Tang, L.; Yu, J.; Jin, X.; Li, X.; et al. Effect of palmitoleic acid on the differentiation of bovine skeletal muscle satellite cells. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Han, J.; Feng, Z.; Li, X.; Wen, Y. The Nuclear Orphan Receptor Nur77 Alleviates Palmitate-induced Fat Accumulation by Down-regulating G0S2 in HepG2 Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.M.; Ni, X.X.; Xu, Q.Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.Y.; Hua, J. Regulation of lipid-induced macrophage polarization through modulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activity affects hepatic lipid metabolism via a Toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 1998–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).