Influence of Parental and Offspring Dietary Behaviors on the Association of Overweight and Obesity between Two Generations: Results from a Cross-Sectional Analysis of Parent-Offspring Trios in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
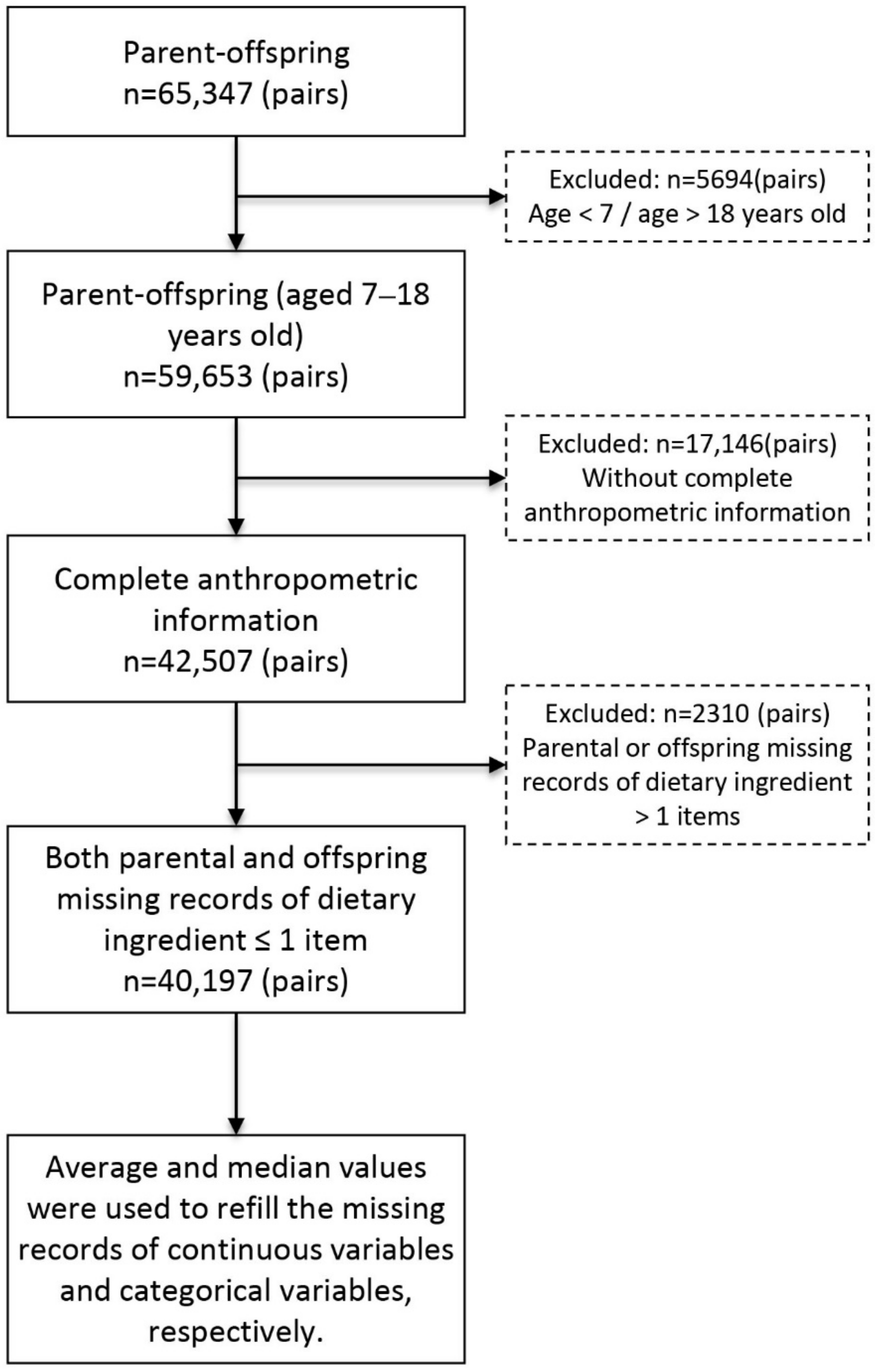
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Anthropometric Measurement and Definition
2.4. Definition of Healthy Dietary Behaviors
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Association of OW/OB between Two Generations
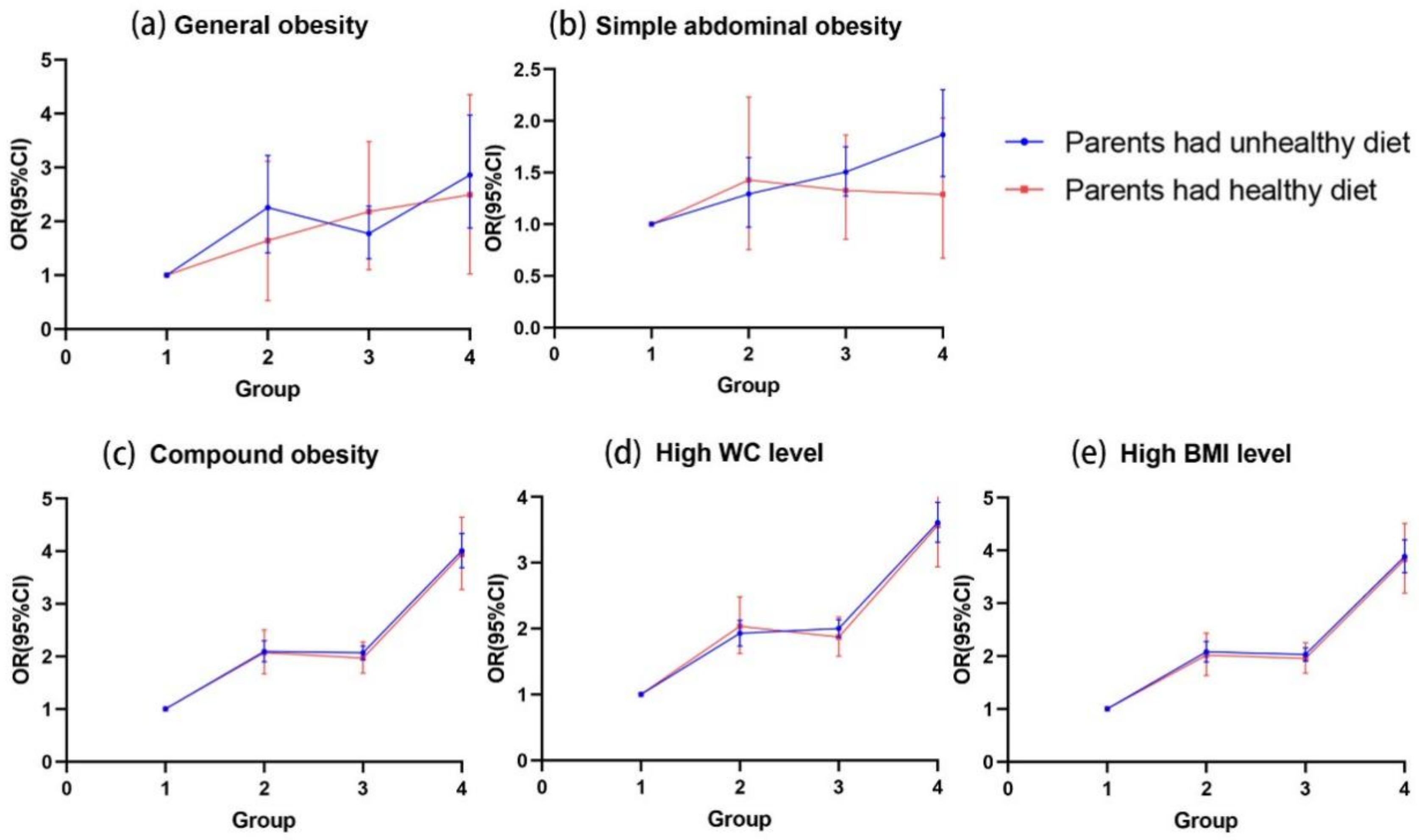
3.3. The Influence of Parental Dietary Behaviors on the Association of OW/OB between Two Generations
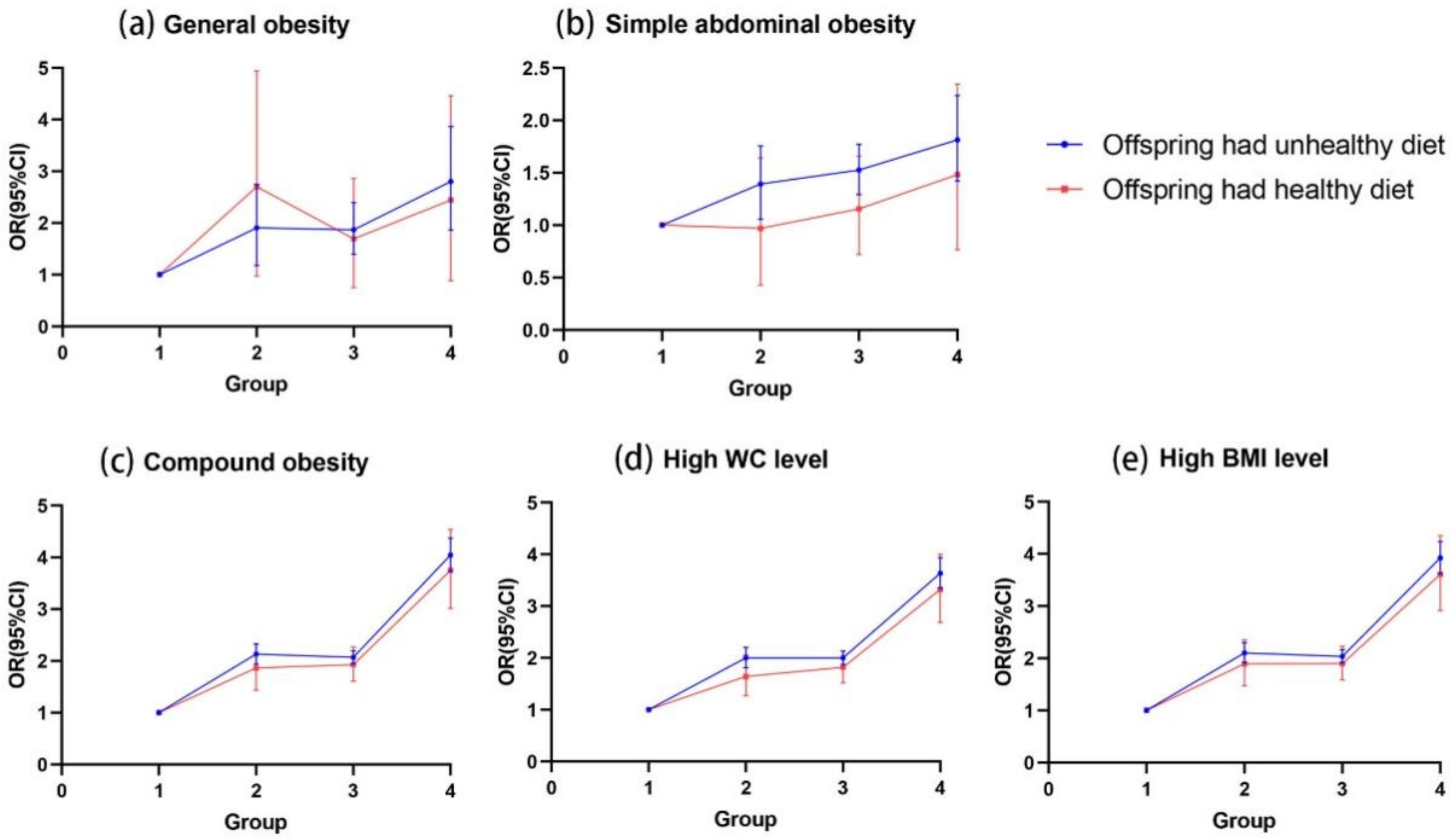
3.4. The Influence of Offspring Dietary Behaviors on the Association of OW/OB between Two Generations
3.5. Combined Effects of Parental and Offspring Dietary Behaviors on the Association of OW/OB between Two Generations
3.6. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Children: New Threats to Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/children-new-threats-to-health (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- WHO. Accelerates Work on Nutrition Targets with New Commitments. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/07-12-2021-who-accelerates-work-on-nutrition-targets-with-new-commitments (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Rankin, J.; Matthews, L.; Cobley, S.; Han, A.; Sanders, R.; Wiltshire, H.D.; Baker, J.S. Psychological consequences of childhood obesity: Psychiatric comorbidity and prevention. Adolesc. Health Med. Ther. 2016, 7, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, A.; Simmonds, M.; Owen, C.G.; Woolacott, N. Childhood obesity as a predictor of morbidity in adulthood: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, M.; Burch, J.; Llewellyn, A.; Griffiths, C.; Yang, H.; Owen, C.; Duffy, S.; Woolacott, N. The use of measures of obesity in childhood for predicting obesity and the development of obesity-related diseases in adulthood: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Technol. Assess. 2015, 19, 1–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Næss, M.; Holmen, T.L.; Langaas, M.; Bjørngaard, J.H.; Kvaløy, K. Intergenerational Transmission of Overweight and Obesity from Parents to Their Adolescent Offspring-The HUNT Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jääskeläinen, A.; Pussinen, J.; Nuutinen, O.; Schwab, U.; Pirkola, J.; Kolehmainen, M.; Järvelin, M.R.; Laitinen, J. Intergenerational transmission of overweight among Finnish adolescents and their parents: A 16-year follow-up study. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silventoinen, K.; Kaprio, J. Genetics of tracking of body mass index from birth to late middle age: Evidence from twin and family studies. Obes. Facts 2009, 2, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wen, L.M.; Rissel, C. Associations of parental influences with physical activity and screen time among young children: A systematic review. J. Obes. 2015, 2015, 546925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, A.B.; Lubans, D.R.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Collins, C.E.; Morgan, P.J. Maternal and paternal parenting practices and their influence on children’s adiposity, screen-time, diet and physical activity. Appetite 2014, 79, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razaz, N.; Villamor, E.; Muraca, G.M.; Bonamy, A.E.; Cnattingius, S. Maternal obesity and risk of cardiovascular diseases in offspring: A population-based cohort and sibling-controlled study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowatte, G.; Bui, D.; Priyankara, S.; Lowe, A.J.; Perret, J.L.; Lodge, C.J.; Hamilton, G.S.; Erbas, B.; Thomas, P.; Thompson, B.; et al. Parental preconception BMI trajectories from childhood to adolescence and asthma in the future offspring. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 67–74.e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Dong, B.; Gao, D.; Wen, B.; Ma, J. Relationship between parental overweight and obesity and childhood metabolic syndrome in their offspring: Result from a cross-sectional analysis of parent-offspring trios in China. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e036332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostoni, C.; Braegger, C.; Decsi, T.; Kolacek, S.; Koletzko, B.; Mihatsch, W.; Moreno, L.A.; Puntis, J.; Shamir, R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. Role of dietary factors and food habits in the development of childhood obesity: A commentary by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 52, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, M.; Macias, N.; Rivera, M.; Lozada, A.; Barquera, S.; Rivera-Dommarco, J.; Tucker, K.L. Dietary patterns in Mexican adults are associated with risk of being overweight or obese. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1869–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Ramírez, S.; Mundo-Rosas, V.; García-Guerra, A.; Shamah-Levy, T. Dietary patterns are associated with overweight and obesity in Mexican school-age children. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 2011, 61, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Godfrey, K.M.; Pasupathy, D.; Levin, J.; Flynn, A.C.; Hayes, L.; Briley, A.L.; Bell, R.; Lawlor, D.A.; Oteng-Ntim, E.; et al. Infant adiposity following a randomised controlled trial of a behavioural intervention in obese pregnancy. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrin, C.M.; Heinen, M.M.; Kelleher, C.C. Are Dietary Patterns of Mothers during Pregnancy Related to Children’s Weight Status? Evidence from the Lifeways Cross- Generational Cohort Study. AIMS. Public Health 2015, 2, 274–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X.; Luo, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Pan, D.; et al. A national school-based health lifestyles interventions among Chinese children and adolescents against obesity: Rationale, design and methodology of a randomized controlled trial in China. BMC. Public Health 2015, 15, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Physical Activity Guidelines for Chinese Population. 2021. Available online: https://www.chinanutri.cn/yyjkzxpt/yyjkkpzx/hdjl/202201/t20220104_255480.html (accessed on 4 January 2022).
- Chinese Students Physique and Health Research Group. Chinese Students’ Physical Fitness and Health Research Report 2010; High Education Publication: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese National Health Commission. Screening for Overweight and Obesity among School-Age Children and Adolescents; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.S.; Ji, C.Y.; Ma, J.; Mi, J.; Yt Sung, R.; Xiong, F.; Yan, W.L.; Hu, X.Q.; Li, Y.P.; Du, S.M.; et al. Waist circumference reference values for screening cardiovascular risk factors in Chinese children and adolescents. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2010, 23, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manman, C. Cross-sectional survey on the effects of different types of obesity on high blood pressure in children and adolescents from seven provinces in China. Chin. J. Child. Health Care 2021, 29, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.F. Effect of body mass index on all-cause mortality and incidence of cardiovascular diseases—Report for meta-analysis of prospective studies open optimal cut-off points of body mass index in Chinese adults. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2002, 15, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, Z.H.; Zhu, Y.N.; Cai, L.; Sun, F.H.; Ma, Y.H.; Jing, J.; Chen, Y.J. Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Consumption and Risks of Obesity and Hypertension in Chinese Children and Adolescents: A National Cross-Sectional Analysis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Chen, M.; Dong, Y.; Zou, Z.; Ma, J. The Association Between Single-Child Status and Risk of Abdominal Obesity: Result From a Cross-Sectional Study of China. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 697047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, T.M.; Knowles, S.O.; Farouk, M.M. Global Provisioning of Red Meat for Flexitarian Diets. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Chinese Dietary Guidelines. 2016. Available online: http://dg.cnsoc.org/article/2016b.html (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Hong, Y.; Labarthe, D.; Mozaffarian, D.; Appel, L.J.; Van Horn, L.; Greenlund, K.; Daniels, S.; Nichol, G.; Tomaselli, G.F.; et al. Defining and setting national goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: The American Heart Association’s strategic Impact Goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation 2010, 121, 586–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, D.; Zou, Z.; Dong, B.; Ma, J.; Arnold, L. Association Between Maternal Lifestyle and Risk of Metabolic Syndrome in Offspring-A Cross-Sectional Study From China. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 552054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereń, K.; Wyszyńska, J.; Nyankovskyy, S.; Nyankovska, O.; Łuszczki, E.; Sobolewski, M.; Mazur, A. Assessment of the Impact of Parental BMI on the Incidence of Overweight and Obesity in Children from Ukraine. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahreynian, M.; Qorbani, M.; Khaniabadi, B.M.; Motlagh, M.E.; Safari, O.; Asayesh, H.; Kelishadi, R. Association between Obesity and Parental Weight Status in Children and Adolescents. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2017, 9, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Mehegan, J.; Murrin, C.M.; Kelleher, C.C.; Phillips, C.M. Predictors of the dietary inflammatory index in children and associations with childhood weight status: A longitudinal analysis in the Lifeways Cross-Generation Cohort Study. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2169–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, H.H.; Neale, M.C.; Eaves, L.J. Genetic and environmental factors in relative body weight and human adiposity. Behav. Genet. 1997, 27, 325–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardle, J.; Carnell, S.; Haworth, C.M.A.; Plomin, R. Evidence for a strong genetic influence on childhood adiposity despite the force of the obesogenic environment. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega Anta, R.M.; López-Solaber, A.M.; Pérez-Farinós, N. Associated factors of obesity in Spanish representative samples. Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 28, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, I.; Kaspi, A.; Ziemann, M.; Block, T.; Connor, T.; Spolding, B.; Cooper, A.; Zimmet, P.; El-Osta, A.; Walder, K. DNA methylation regulates hypothalamic gene expression linking parental diet during pregnancy to the offspring’s risk of obesity in Psammomys obesus. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakali, K.M.; Zhong, Y.; Cleves, M.; Andres, A.; Shankar, K. Associations between maternal body mass index and diet composition with placental DNA methylation at term. Placenta 2020, 93, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slyvka, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Nowak, F.V. Epigenetic effects of paternal diet on offspring: Emphasis on obesity. Endocrine 2015, 48, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silventoinen, K.; Rokholm, B.; Kaprio, J.; Sørensen, T.I. The genetic and environmental influences on childhood obesity: A systematic review of twin and adoption studies. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, A.; Jumean, M.; Murad, M.H.; Okorodudu, D.; Kumar, S.; Somers, V.K.; Sochor, O.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Diagnostic performance of body mass index to identify obesity as defined by body adiposity in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Obes. 2015, 10, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Low Diagnostic Accuracy of Body Mass Index-Based and Waist Circumference-Based References of Childhood Overweight and Obesity in Identifying Overfat among Chinese Children and Adolescents. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4570706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeberli, I.; Gut-Knabenhans, M.; Kusche-Ammann, R.S.; Molinari, L.; Zimmermann, M.B. A composite score combining waist circumference and body mass index more accurately predicts body fat percentage in 6- to 13-year-old children. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardinha, L.B.; Santos, D.A.; Silva, A.M.; Grøntved, A.; Andersen, L.B.; Ekelund, U. A Comparison between BMI, Waist Circumference, and Waist-To-Height Ratio for Identifying Cardio-Metabolic Risk in Children and Adolescents. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto Mdo, R.; Benício, M.H.; Jardim, P.C. Validity of self-reported weight and height: The Goiânia study, Brazil. Rev. Saude Publica 2006, 40, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.J.; Ho, S.C.; Liu, Z.M.; Hui, S.S. Comparisons of measured and self-reported anthropometric variables and blood pressure in a sample of Hong Kong female nurses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parental OW/OB Status | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Total n = 40,197 | Both Parental OW/OB n = 5182 | Only Paternal OW/OB n = 14,366 | Only Maternal OW/OB n = 4034 | None OW/OB n = 16,425 | p-Value |
| Offspring factors | ||||||
| Age, year | 10.9 ± 3.0 | 11.0 ± 3.0 | 10.7 ± 3.0 | 11.3 ± 3.0 | 10.9 ± 3.0 | <0.001 |
| WC, cm | 64.9 ± 10.3 | 68.9 ± 11.8 | 65.4 ± 10.5 | 66.0 ± 10.4 | 62.9 ± 9.2 | <0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 18.5 ± 3.6 | 20.1 ± 4.2 | 18.7 ± 3.7 | 19.0 ± 3.7 | 17.7 ± 3.2 | <0.001 |
| Residence area (n, %) | <0.001 | |||||
| Urban | 24,519 (61.0) | 2964 (57.2) | 9280 (64.3) | 2164 (53.3) | 10,111 (61.2) | |
| Rural | 15,678 (39.0) | 2218 (42.8) | 5156 (35.7) | 1895 (46.7) | 6409 (38.8) | |
| Sex (n, %) | <0.001 | |||||
| Boys | 21,197 (52.7) | 2848 (55.0) | 7710 (53.4) | 2074 (51.1) | 8565 (51.8) | |
| Girls | 19,000 (47.3) | 2334 (45.0) | 6726 (46.6) | 1985 (48.9) | 7955 (48.2) | |
| Single child (n, %) | <0.001 | |||||
| Yes | 26,526 (66.0) | 3029 (58.5) | 9916 (68.7) | 2348 (57.8) | 11,233 (68.0) | |
| No | 13,671 (34.0) | 2153 (41.5) | 4520 (31.3) | 1711 (42.2) | 5287 (32.0) | |
| Breastfeeding (n, %) | ||||||
| Yes | 34,256 (85.2) | 4430 (85.5) | 12,302 (85.2) | 3463 (85.3) | 14,061 (85.1) | 0.925 |
| No | 5941 (14.8) | 752 (14.5) | 2134 (14.8) | 596 (14.7) | 2459 (14.9) | |
| Types of obesity (n, %) | ||||||
| Normal | 29,340 (73.0) | 2979 (57.5) | 9978 (69.1) | 2916 (71.8) | 13,467 (81.5) | <0.001 |
| General obesity | 350 (0.9) | 55 (1.1) | 145 (1.0) | 39 (1.0) | 111 (0.7) | |
| Simple abdominal obesity | 966 (2.4) | 126 (2.4) | 393 (2.7) | 91 (2.2) | 356 (2.2) | |
| Compound obesity | 9541 (23.7) | 2022 (39.0) | 3920 (27.2) | 1013 (25.0) | 2586 (15.7) | |
| Dietary behaviors (n, %) | ||||||
| Meat consumption ≤ 3 services/week | 10,399 (25.9) | 1540 (29.7) | 3680 (25.5) | 1178 (29.0) | 4001 (24.2) | <0.001 |
| SSBs consumption ≤ 3 sevices/week | 31,070 (77.3) | 3864 (74.6) | 11,243 (77.9) | 3071 (75.7) | 12,892 (78.0) | <0.001 |
| Eating breakfast ≥ 6 days/week | 35,537 (88.4) | 4496 (86.8) | 12,855 (89.0) | 3506 (86.4) | 14,680 (88.9) | <0.001 |
| Fast-food consumption < 1 times/month | 21,316 (53.0) | 2908 (56.1) | 7458 (51.7) | 2324 (57.3) | 8626 (52.2) | <0.001 |
| Physical activity (n, %) | ||||||
| MVPA ≥ 1 h/day | 19,526 (48.6) | 2633(50.8) | 6869(47.6) | 2040(50.3) | 7984(48.3) | <0.001 |
| Parental factors (n, %) | ||||||
| Paternal BMI | 24.1 ± 3.2 | 27.0 ± 2.7 | 26.6 ± 2.2 | 21.8 ± 1.6 | 21.6 ± 1.7 | <0.001 |
| Maternal BMI | 22.2 ± 3.0 | 26.5 ± 2.7 | 21.1 ± 1.7 | 26.3 ± 2.4 | 20.8 ± 1.8 | <0.001 |
| Paternal highest educational attainment (n, %) | ||||||
| Primary school or below | 2867 (7.1) | 492 (9.5) | 797 (5.5) | 469 (11.6) | 1109 (6.7) | <0.001 |
| Junior high school and Senior high school | 25,959 (64.6) | 3542 (68.4) | 8913 (61.7) | 2875 (70.8) | 10,629 (64.3) | |
| Junior college or above | 11,371 (28.3) | 1148 (22.2) | 4726 (32.7) | 715 (17.6) | 4782 (28.9) | |
| Maternal highest educational attainment (n, %) | ||||||
| Primary school or below | 4016 (10.0) | 683 (13.2) | 1168 (8.1) | 623 (15.3) | 1542 (9.3) | <0.001 |
| Junior high school and Senior high school | 25,835 (64.3) | 3515 (67.8) | 8964 (62.1) | 2774 (68.3) | 10,582 (64.1) | |
| Junior college or above | 10,346 (25.7) | 984 (19.0) | 4304 (29.8) | 662 (16.3) | 4396 (26.6) | |
| Dietary behaviors (n, %) | ||||||
| Meat consumption ≤ 3 services/week | 10,281 (25.6) | 1637 (31.6) | 3683 (25.5) | 1202 (29.6) | 3759 (22.8) | <0.001 |
| SSBs consumption ≤ 3 sevices/week | 35,586 (88.5) | 4552 (87.8) | 12,809 (88.7) | 3593 (88.5) | 14,632 (88.6) | 0.391 |
| Fast-food consumption < 1 times/month | 26,808 (66.7) | 3594 (69.4) | 9406 (65.2) | 2916 (71.8) | 10,892 (65.9) | <0.001 |
| Eating breakfast ≥ 6 days/week | 35,627 (88.6) | 4556 (87.9) | 12,772 (88.5) | 3583 (88.3) | 14,716 (89.1) | 0.079 |
| Physical activity (n, %) | ||||||
| MVPA ≥ 1 h/day | 19,526 (48.6) | 2633 (50.8) | 6869 (47.6) | 2040 (50.3) | 7984 (48.3) | <0.001 |
| Variables | General Obesity OR (95% CI) | Simple Abdominal Obesity OR (95% CI) | Compound Obesity OR (95% CI) | High WC Level OR (95% CI) | High BMI Level OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Both parental OW/OB | 2.66 (1.91–3.71) *** | 1.72 (1.40–2.12) *** | 4.04 (3.75–4.35) *** | 3.65 (3.38–3.93) *** | 3.92 (3.65–4.21) *** |
| Only paternal OW/OB | 1.80 (1.41–2.32) *** | 1.46 (1.26–1.69) *** | 2.06 (1.94–2.18) *** | 1.99 (1.87–2.11) *** | 2.03 (1.91–2.14) *** |
| Only maternal OW/OB | 1.98 (1.37–2.87) ** | 1.28 (1.01–1.62) * | 2.11 (1.93–2.30) *** | 1.96 (1.79–2.15) *** | 2.09 (1.92–2.27) *** |
| No parental OW/OB | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| Variables | General Obesity OR (95% CI) | Simple Abdominal Obesity OR (95% CI) | Compound Obesity OR (95% CI) | High WC Level OR (95% CI) | High BMI Level OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Both parents and offspring had unhealthy dietary behaviors | |||||
| Both parental OW/OB | 2.80 (1.87–4.18) *** | 1.98 (1.56–2.52) *** | 4.05 (3.72–4.41) *** | 3.67 (3.36–4.00) *** | 3.93 (3.60–4.27) *** |
| Only paternal OW/OB | 1.82 (1.35–2.44) *** | 1.58 (1.34–1.88) *** | 2.09 (1.96–2.23) *** | 2.04 (1.90–2.18) *** | 2.05 (1.92–2.19) *** |
| Only maternal OW/OB | 1.98 (1.25–3.12) ** | 1.40 (1.06–1.84) * | 2.12 (1.92–2.35) *** | 1.98 (1.78–2.20) *** | 2.10 (1.90–2.32) *** |
| No parental OW/OB | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| Only parents had unhealthy dietary behaviors | |||||
| Both parental OW/OB | 2.33 (0.83–6.54) | 1.10 (0.55–2.19) | 3.81 (2.93–4.96) *** | 3.26 (2.49–4.27) *** | 3.71 (2.87–4.81) *** |
| Only paternal OW/OB | 1.09 (0.44–2.71) | 0.93 (0.58–1.51) | 1.85 (1.50–2.30) *** | 1.68 (1.35–2.10) *** | 1.82 (1.47–2.24) *** |
| Only maternal OW/OB | 2.90 (1.07–7.84) * | 0.52 (0.20–1.34) | 1.84 (1.35–2.52) *** | 1.51 (1.08–2.11) *** | 1.94 (1.43–2.62) *** |
| No parental OW/OB | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| Only offspring had unhealthy dietary behaviors | |||||
| Both parental OW/OB | 2.20 (0.92–5.30) | 0.92 (0.47–1.83) | 4.03 (3.27–4.97) *** | 3.52 (2.83–4.37) *** | 3.96 (3.22–4.87) *** |
| Only paternal OW/OB | 1.85 (0.92–3.73) | 1.13 (0.73–1.75) | 1.94 (1.62–2.31) *** | 1.79 (1.49–2.16) *** | 1.93 (1.62–2.29) *** |
| Only maternal OW/OB | 1.20 (0.38–3.75) | 1.18 (0.62–2.24) | 2.16 (1.70–2.75) *** | 2.10 (1.63–2.69) *** | 2.11 (1.66–2.67) *** |
| No parental OW/OB | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
| Both parents and offspring had healthy dietary behaviors | |||||
| Both parental OW/OB | 1.75 (0.48–6.42) | 2.27 (0.82–6.26) | 3.62 (2.61–5.01) *** | 3.58 (2.55–5.02) *** | 3.45 (2.51–4.74) *** |
| Only paternal OW/OB | 2.28 (0.82–6.31) | 1.84 (0.77–4.38) | 1.98 (1.49–2.64) *** | 2.00 (1.47–2.72) *** | 1.97 (1.49–2.61) *** |
| Only maternal OW/OB | 1.45 (0.35–6.00) | 1.94 (0.67–5.61) | 1.75 (1.20–2.56) ** | 1.78 (1.20–2.66) * | 1.71 (1.18–2.48) ** |
| No parental OW/OB | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) | 1 (Reference) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Q.; Chen, T.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Gao, D.; Li, Y.; Ma, T.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Ma, Y.; et al. Influence of Parental and Offspring Dietary Behaviors on the Association of Overweight and Obesity between Two Generations: Results from a Cross-Sectional Analysis of Parent-Offspring Trios in China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4625. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214625
Ma Q, Chen T, Liu J, Chen M, Gao D, Li Y, Ma T, Wang X, Chen L, Ma Y, et al. Influence of Parental and Offspring Dietary Behaviors on the Association of Overweight and Obesity between Two Generations: Results from a Cross-Sectional Analysis of Parent-Offspring Trios in China. Nutrients. 2022; 14(21):4625. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214625
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Qi, Ting Chen, Jieyu Liu, Manman Chen, Di Gao, Yanhui Li, Tao Ma, Xinxin Wang, Li Chen, Ying Ma, and et al. 2022. "Influence of Parental and Offspring Dietary Behaviors on the Association of Overweight and Obesity between Two Generations: Results from a Cross-Sectional Analysis of Parent-Offspring Trios in China" Nutrients 14, no. 21: 4625. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214625
APA StyleMa, Q., Chen, T., Liu, J., Chen, M., Gao, D., Li, Y., Ma, T., Wang, X., Chen, L., Ma, Y., Zhang, Y., Dong, Y., Xing, Y., & Ma, J. (2022). Influence of Parental and Offspring Dietary Behaviors on the Association of Overweight and Obesity between Two Generations: Results from a Cross-Sectional Analysis of Parent-Offspring Trios in China. Nutrients, 14(21), 4625. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214625






