SNPs in lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 Modulate Its Expression and Confer Susceptibility to Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure in a Chinese Han Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects and Sample Collection
2.2. Assessment of SSBP
2.3. Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR
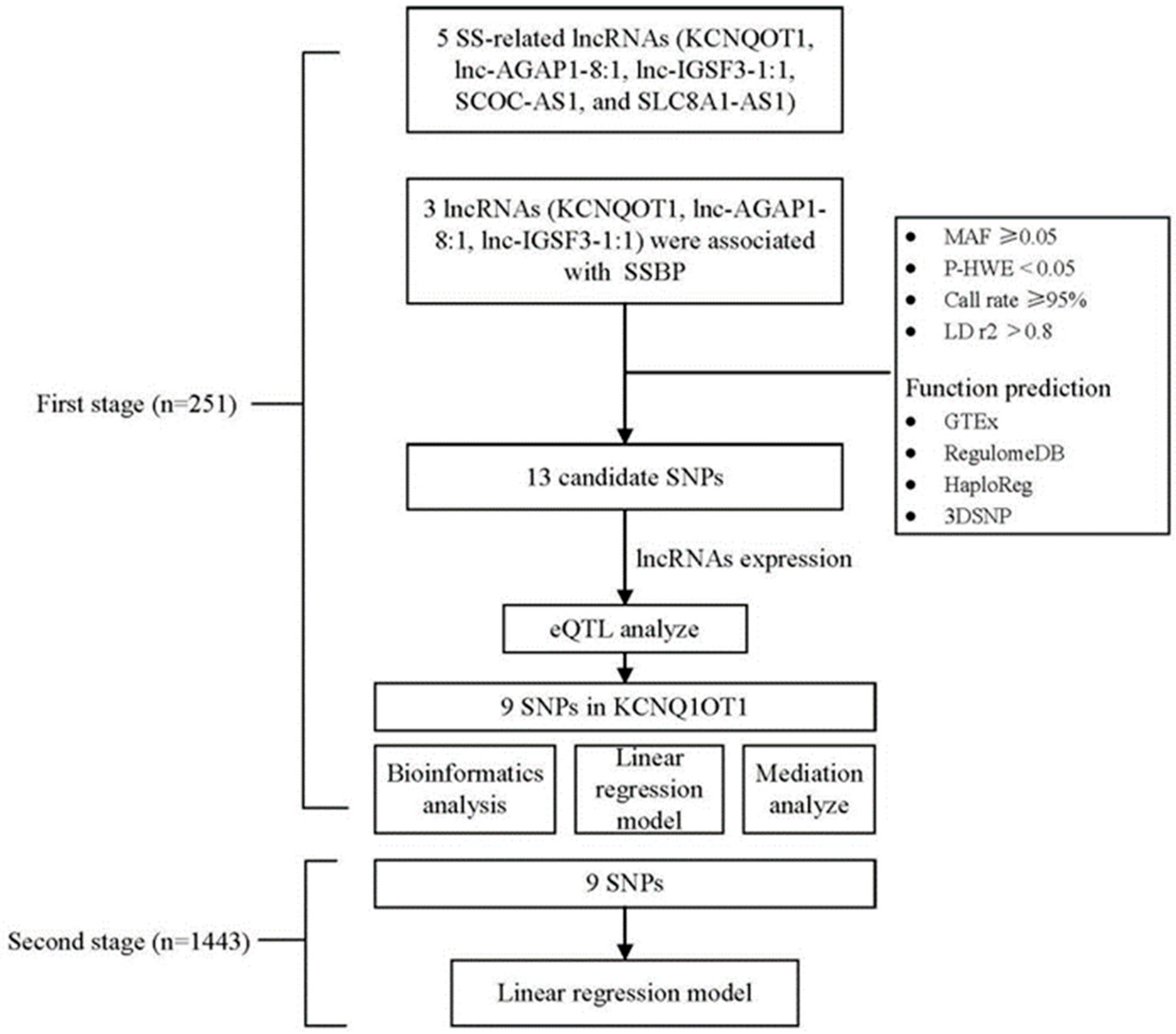
2.4. Candidate SNP Selection and Genotyping
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.6. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Enrolled Participants
3.2. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1, lnc-AGAP1-8:1, and lnc-IGSF3-1:1 Levels Were Associated with SSBP
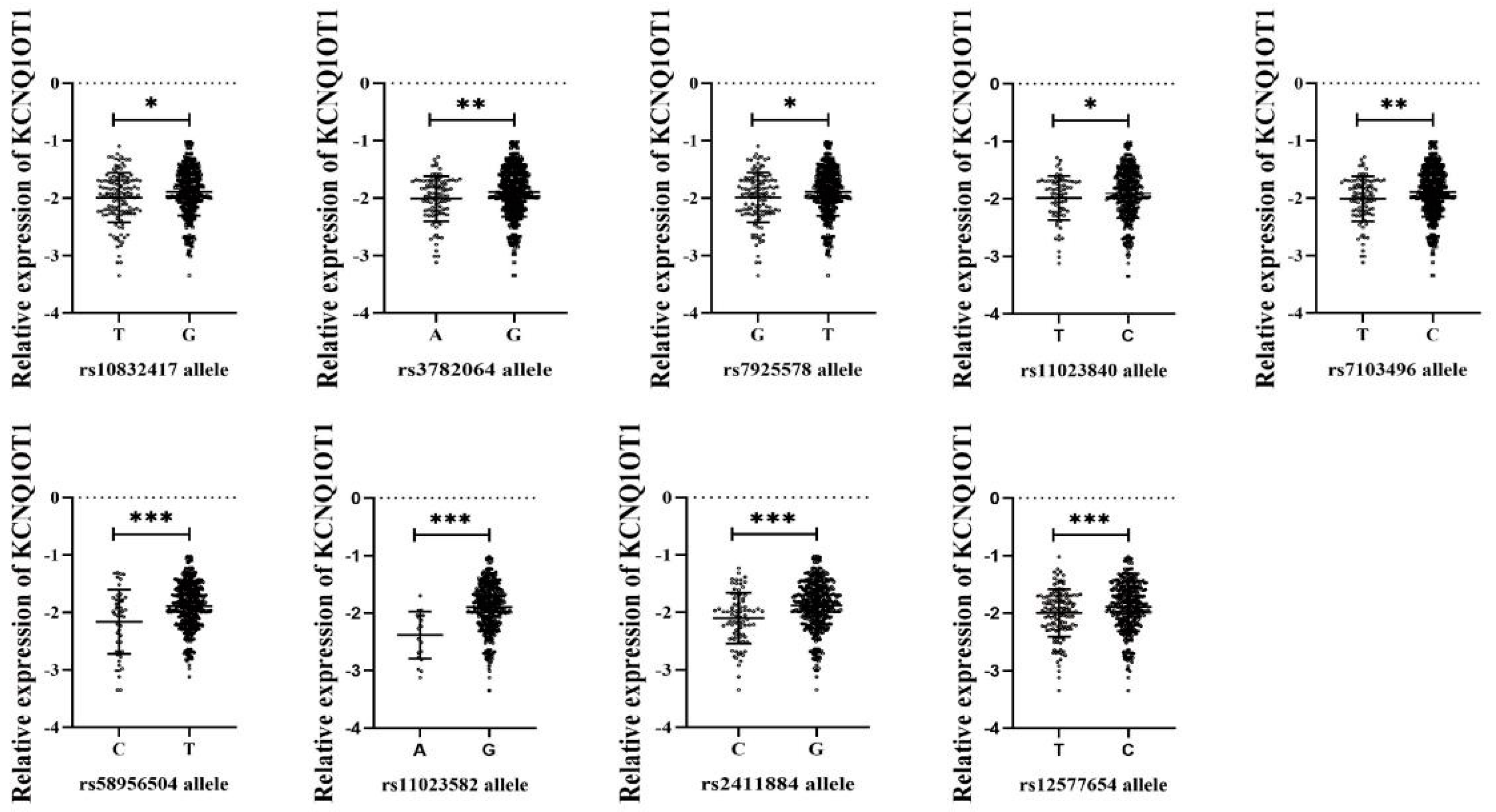
3.3. Genotype Distributions of lncRNA SNPs and Their Association with lncRNA Expression
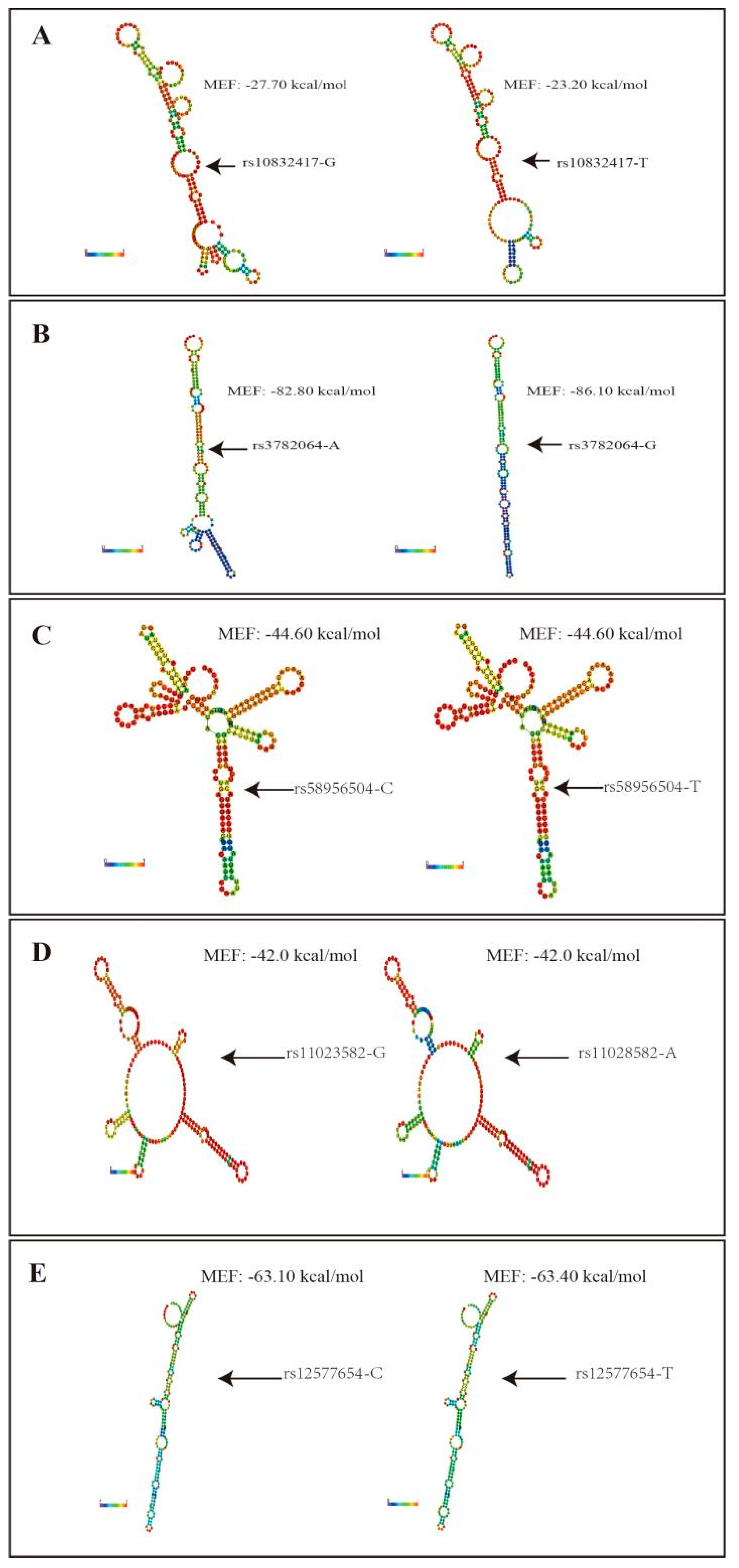
3.4. Functional Prediction for lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 SNPs
3.5. Association Study for lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 SNPs and Risk of SSBP
3.6. Risk SNPs Mediated SSBP through lncRNA KCNQ1OT1
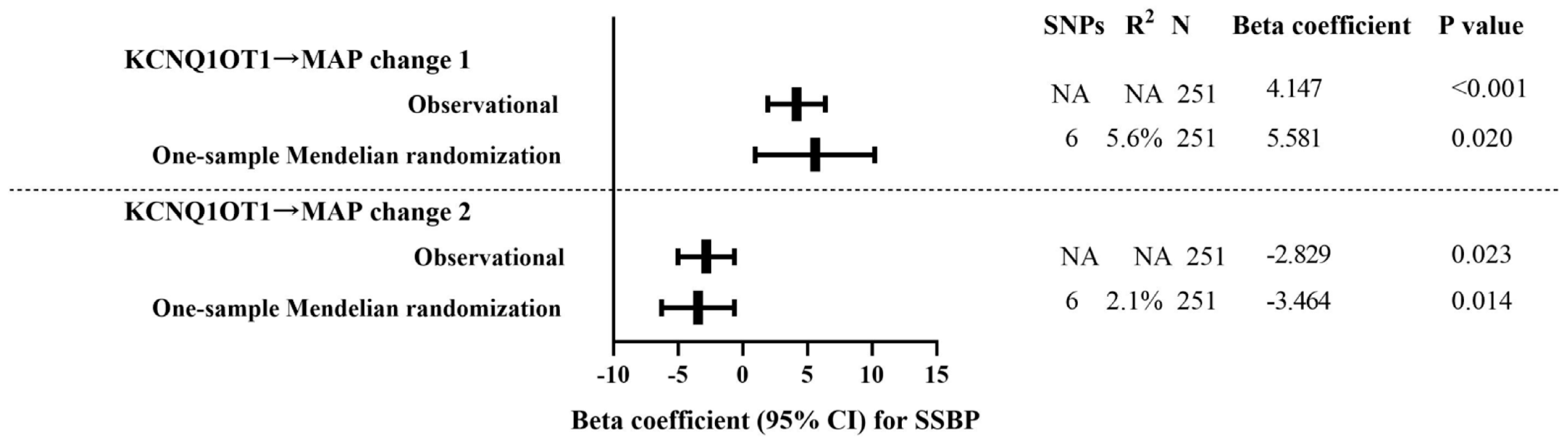
3.7. One-Sample Mendelian Randomization: Observational Versus Genetic Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sullivan, J.M. Salt sensitivity. Definition, conception, methodology, and long-term issues. Hypertension 1991, 17, I61–I68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazzullo, P.; D’Elia, L. Encyclopedia of Endocrine Diseases; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, M.; Dolan, J.; He, J. Sodium sensitivity of blood pressure in Chinese populations. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2020, 34, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, V.; Oparil, S. Salt sensitivity, a determinant of blood pressure, cardiovascular disease and survival. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2006, 25, 247S–255S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, M.H. Salt sensitivity is associated with an increased mortality in both normal and hypertensive humans. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2002, 4, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elijovich, F.; Weinberger, M.H.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Appel, L.J.; Bursztyn, M.; Cook, N.R.; Dart, R.A.; Newton-Cheh, C.H.; Sacks, F.M.; Laffer, C.L. Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2016, 68, e7–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shastry, B.S. SNPs: Impact on gene function and phenotype. In Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.N.; He, J. Genomic epidemiology of blood pressure salt sensitivity. J. Hypertens. 2012, 30, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, K.; Qi, H.; Peng, W.; Cao, H.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Wen, F.; Zhang, F.; et al. Candidate Gene Polymorphisms Influence the Susceptibility to Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure in a Han Chinese Population: Risk Factors as Mediators. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 675230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; He, J.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Gu, D.; Hixson, J.E.; Rao, D.C.; Jaquish, C.E.; Gu, C.C.; Chen, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Gene-Sodium Interaction Analyses on Blood Pressure: The Genetic Epidemiology Network of Salt-Sensitivity Study. Hypertension 2016, 68, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citterio, L.; Simonini, M.; Zagato, L.; Salvi, E.; Delli Carpini, S.; Lanzani, C.; Messaggio, E.; Casamassima, N.; Frau, F.; D’Avila, F.; et al. Genes involved in vasoconstriction and vasodilation system affect salt-sensitive hypertension. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Qi, H.; Liu, B.; Liu, K.; Wu, J.; Cao, H.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, L. Genetic susceptibility to salt-sensitive hypertension in a Han Chinese population: A validation study of candidate genes. Hypertens. Res. 2017, 40, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djebali, S.; Davis, C.A.; Merkel, A.; Dobin, A.; Lassmann, T.; Mortazavi, A.; Tanzer, A.; Lagarde, J.; Lin, W.; Schlesinger, F.; et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 2012, 489, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, M.C.; Daulagala, A.C.; Kourtidis, A. LNCcation: lncRNA localization and function. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e202009045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, P.J.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell 2013, 152, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qi, H.; Liu, Z.; Peng, W.-J.; Cao, H.; Guo, C.-Y.; Sun, Y.-Y.; Pao, C.; Xiang, Y.-T. Construction of a ceRNA coregulatory network and screening of hub biomarkers for salt-sensitive hypertension. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 7254–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Xie, Y.; Xia, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, F.; Wen, F.; Liu, K.; Cao, H.; Qi, H.; Zhang, L. Association of Circulating Biomarkers of lnc-IGSF3-1:1, SCOC-AS1, and SLC8A1-AS1 with Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure in Chinese Population. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Miao, X.; Guo, A.-Y. lncRNASNP: A database of SNPs in lncRNAs and their potential functions in human and mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D181–D186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Liu, B.; Guo, C.; Liu, Z.; Cao, H.; Liu, K.; Sun, W.; Zhang, L. Effects of environmental and genetic risk factors for salt sensitivity on blood pressure in northern China: The systemic epidemiology of salt sensitivity (EpiSS) cohort study. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e023042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, J.J.; Liu, Z.; Yang, D.Y.; Xu, X.L. Erythrocyte Sodium-Lithium Countertransport and Urinary Kall Ikrein Excret Ion in Children with Hypertension. Chin. J. Hypertens. 1993, 2, 76–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sesso, H.D.; Stampfer, M.J.; Rosner, B.; Hennekens, C.H.; Gaziano, J.M.; Manson, J.E.; Glynn, R.J. Systolic and diastolic blood pressure, pulse pressure, and mean arterial pressure as predictors of cardiovascular disease risk in Men. Hypertension 2000, 36, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, G. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.D.; Kellis, M. HaploReg v4: Systematic mining of putative causal variants, cell types, regulators and target genes for human complex traits and disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D877–D881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Quan, C.; Chen, H.; Bo, X.; Zhang, C. 3DSNP: A database for linking human noncoding SNPs to their three-dimensional interacting genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D643–D649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, L.; Rühle, F.; Witten, A.; Meder, B.; Katus, H.A.; Arbustini, E.; Hasenfuß, G.; Sinner, M.F.; Kääb, S.; Pankuweit, S.; et al. A genetic variant alters the secondary structure of the lncRNA H19 and is associated with dilated cardiomyopathy. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Höner Zu Siederdissen, C.; Tafer, H.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.F.; Hofacker, I.L. ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2011, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.-R.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, A.-Y. lncRNASNP2: An updated database of functional SNPs and mutations in human and mouse lncRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D276–D280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumbley, J.R.; Friston, K.J. False discovery rate revisited: FDR and topological inference using Gaussian random fields. Neuroimage 2009, 44, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K.; Keele, L.; Tingley, D. A general approach to causal mediation analysis. Psychol. Methods 2010, 15, 309–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Uddin, M.J.; Cheng, J.; Huang, T. Instrumental variable analysis in the presence of unmeasured confounding. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Huang, X.; Tan, W.; Yu, D.; Du, Z.; Chang, J.; Wei, L.; Han, Y.; Wang, C.; Che, X.; et al. Pancreatic cancer risk variant in LINC00673 creates a miR-1231 binding site and interferes with PTPN11 degradation. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ahmed, M.; Zhang, F.; Yao, C.Q.; Li, S.; Liang, Y.; Hua, J.; Soares, F.; Sun, Y.; Langstein, J.; et al. Modulation of long noncoding RNAs by risk SNPs underlying genetic predispositions to prostate cancer. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, J.; Shu, J.; Su, G.; Cao, Q.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, P. SNP rs7130280 in lncRNA NONHSAT159216.1 confers susceptibility to Behcet’s disease in a Chinese Han population. Rheumatology, 2022; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, D.A.; Judd, C.M. Power anomalies in testing mediation. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 25, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agler, R.; De Boeck, P. On the Interpretation and Use of Mediation: Multiple Perspectives on Mediation Analysis. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.; Velkoska, E.; Wainford, R.D. An exploratory analysis of comparative plasma metabolomic and lipidomic profiling in salt-sensitive and salt-resistant individuals from The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension Sodium Trial. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 1972–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B. MIAT, a potent CVD-promoting lncRNA. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 79, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Feng, N.; Zhu, T.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhou, B.; Yu, H.; Zheng, M.; et al. A SNP-mediated lncRNA (LOC146880) and microRNA (miR-539-5p) interaction and its potential impact on the NSCLC risk. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Yan, T.; Wang, Z.; Su, H.-C.; Zhu, X.; Tian, X.; Fang, J.-Y.; Chen, H.; Hong, J. Variant of SNP rs1317082 at CCSlnc362 (RP11-362K14.5) creates a binding site for miR-4658 and diminishes the susceptibility to CRC. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Qu, K.; Zhang, Q.C.; Flynn, R.A.; Manor, O.; Ouyang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Spitale, R.C.; Snyder, M.P.; Segal, E.; et al. Landscape and variation of RNA secondary structure across the human transcriptome. Nature 2014, 505, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Kelly, T.N.; Zhao, Q.; Li, H.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Jaquish, C.E.; Sung, Y.J.; Shimmin, L.C.; Lu, F.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 8 novel loci associated with blood pressure responses to interventions in Han Chinese. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2013, 6, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduri, C. Kcnq1ot1: A chromatin regulatory RNA. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y.; Park, H.C.; Ha, S.K. Salt Sensitivity and Hypertension: A Paradigm Shift from Kidney Malfunction to Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction. Electrolyte Blood Press 2015, 13, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dai, Y.; Yan, S.; Shi, Y.; Han, B.; Li, J.; Cha, L.; Mu, J. Down-regulation of lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury following acute myocardial infarction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 491, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Wu, Z.-H.; Tsui, T.Y.; Zhang, B.-F.; Su, X.; Qiu, Y.-H.; Zheng, X.-T. lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 Suppresses the Inflammation and Proliferation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells through IκBa in Intimal Hyperplasia. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| SNP | SNP Causes miRNA Target Gain | SNP Causes miRNA Target Loss |
|---|---|---|
| rs10832417 | - | hsa-miR-8068 |
| rs3782064 | hsa-miR-6834-5p, hsa-miR-6786-3p, hsa-miR-6875-5p, hsa-miR-3126-5p | hsa-miR-3184-5p, hsa-miR-423-5p, hsa-miR-6734-5p, hsa-miR-6789-3p |
| rs7925578 | - | - |
| rs11023840 | - | - |
| rs7103496 | - | - |
| rs58956504 | - | hsa-miR-29a-5p, hsa-miR-4728-3p |
| rs11023582 | - | hsa-miR-103a-2-5p |
| rs2411884 | - | - |
| rs12577654 | hsa-miR-6867-5p | hsa-miR-210-3p, hsa-miR-6790-5p |
| SNP | Model | Genotype | N = 1443 | MAP Change 1 | MAP Change 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect Size | p-Value a | Effect Size | p-Value a | |||||
| KCNQOT1 | rs10832417 | Log-Additive | TT vs. TG vs. GG | 147/574/712 | 0.164 | 0.550 | 0.547 | 0.034 * |
| rs3782064 | Log-Additive | AA vs. AG vs. GG | 45/428/925 | −0.203 | 0.546 | 0.762 | 0.016 ** | |
| rs7925578 | Log-Additive | GG vs. GT vs. TT | 146/546/701 | 0.157 | 0.572 | 0.610 | 0.019 ** | |
| rs11023840 | Log-Additive | CC vs. CT vs. TT | 35/360/1021 | 0.259 | 0.468 | 0.779 | 0.020 ** | |
| rs7103496 | Log-Additive | TT vs. TC vs. CC | 39/417/954 | −0.294 | 0.409 | 0.676 | 0.036 * | |
| rs58956504 | Log-Additive | CC vs. CT vs. TT | 9/218/1206 | −0.291 | 0.528 | 0.009 | 0.903 | |
| rs11023582 | Log-Additive | AA vs. AG vs. GG | 5/141/1287 | −0.363 | 0.532 | −0.719 | 0.188 | |
| rs12577654 | Log-Additive | TT vs. TC vs. CC | 144/640/649 | −0.227 | 0.409 | 0.653 | 0.011 ** | |
| KCNQ1 | rs2411884 | Log-Additive | CC vs. CG vs. GG | 59/434/875 | 0.063 | 0.063 | 0.137 | 0.708 |
| Combined risk–effect of genotypes b | ||||||||
| Simple-GRS | 0–7 scores | Ref. | - | Ref. | - | |||
| 8–11 scores | −0.421 | 0.433 | 0.540 | 0.293 | ||||
| 12–13 scores | −0.710 | 0.039 | 0.564 | 0.072 | ||||
| 14 scores | −0.132 | 0.424 | 0.420 | 0.009 | ||||
| SNPs | Mediator | Outcome | ACME | ADE | Total Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs10832417 | KCNQ1OT1 | MAP change 1 | −0.392 [−0.843, −0.040] * | −0.759 [−2.257, 0.630] | −1.151 [−2.709, 0.250] |
| rs3782064 | −0.395 [−0.873, −0.030] * | −0.882 [−2.451, 0.780] | −1.278 [−2.889, 0.400] | ||
| rs7925578 | −0.317 [−0.731, 0.050] | −0.262 [−1.760, 1.230] | −0.578 [−2.112, 0.960] | ||
| rs11023840 | −0.322 [−0.784, 0.050] | −1.134 [ −2.815, 0.540] | −1.456 [−3.181, 0.240] | ||
| rs7103496 | −0.408 [−0.869, −0.040] * | −0.960 [−2.578, 0.660] | −1.368 [−2.976, 0.240] | ||
| rs12577654 | −0.452 [−0.865, −0.120] * | −0.444 [−1.846, 1.000] | −0.896 [−2.322, 0.580] | ||
| rs10832417 | KCNQ1OT1 | MAP change 2 | 0.279 [0.017, 0.610] * | −0.255 [−1.580, 1.100] | 0.024 [−1.329, 1.390] |
| rs3782064 | 0.282 [0.024, 0.600] * | −0.416 [−1.982, 1.170] | −0.134 [−1.734, 1.410] | ||
| rs7925578 | 0.227 [−0.041, 0.560] | −1.163 [−2.624, 0.390] | −0.936 [−2.432, 0.560] | ||
| rs11023840 | 0.230 [−0.040, 0.560] | −0.783 [−2.461. 0.950] | −0.553 [−2.216, 1.200] | ||
| rs7103496 | 0.288 [0.038, 0.660] * | −0.073 [−1.678, 1.610] | 0.215 [−1.437, 1.870] | ||
| rs12577654 | 0.327 [0.077, 0.640] * | −0.708 [−2.089, 0.780] | −0.381 [−1.768, 1.120] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Y.; Qi, H.; Peng, W.; Li, B.; Wen, F.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L. SNPs in lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 Modulate Its Expression and Confer Susceptibility to Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure in a Chinese Han Population. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3990. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193990
Xie Y, Qi H, Peng W, Li B, Wen F, Zhang F, Zhang L. SNPs in lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 Modulate Its Expression and Confer Susceptibility to Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure in a Chinese Han Population. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):3990. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193990
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Yunyi, Han Qi, Wenjuan Peng, Bingxiao Li, Fuyuan Wen, Fengxu Zhang, and Ling Zhang. 2022. "SNPs in lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 Modulate Its Expression and Confer Susceptibility to Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure in a Chinese Han Population" Nutrients 14, no. 19: 3990. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193990
APA StyleXie, Y., Qi, H., Peng, W., Li, B., Wen, F., Zhang, F., & Zhang, L. (2022). SNPs in lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 Modulate Its Expression and Confer Susceptibility to Salt Sensitivity of Blood Pressure in a Chinese Han Population. Nutrients, 14(19), 3990. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193990






