Improved Macro- and Micronutrient Supply for Favorable Growth and Metabolomic Profile with Standardized Parenteral Nutrition Solutions for Very Preterm Infants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Development of the Standardized Parenteral Nutrition Solution MUC PREPARE
2.3. Parenteral Nutrition
2.4. Enteral Feeding
2.5. Clinical Monitoring
2.6. Metabolomics
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
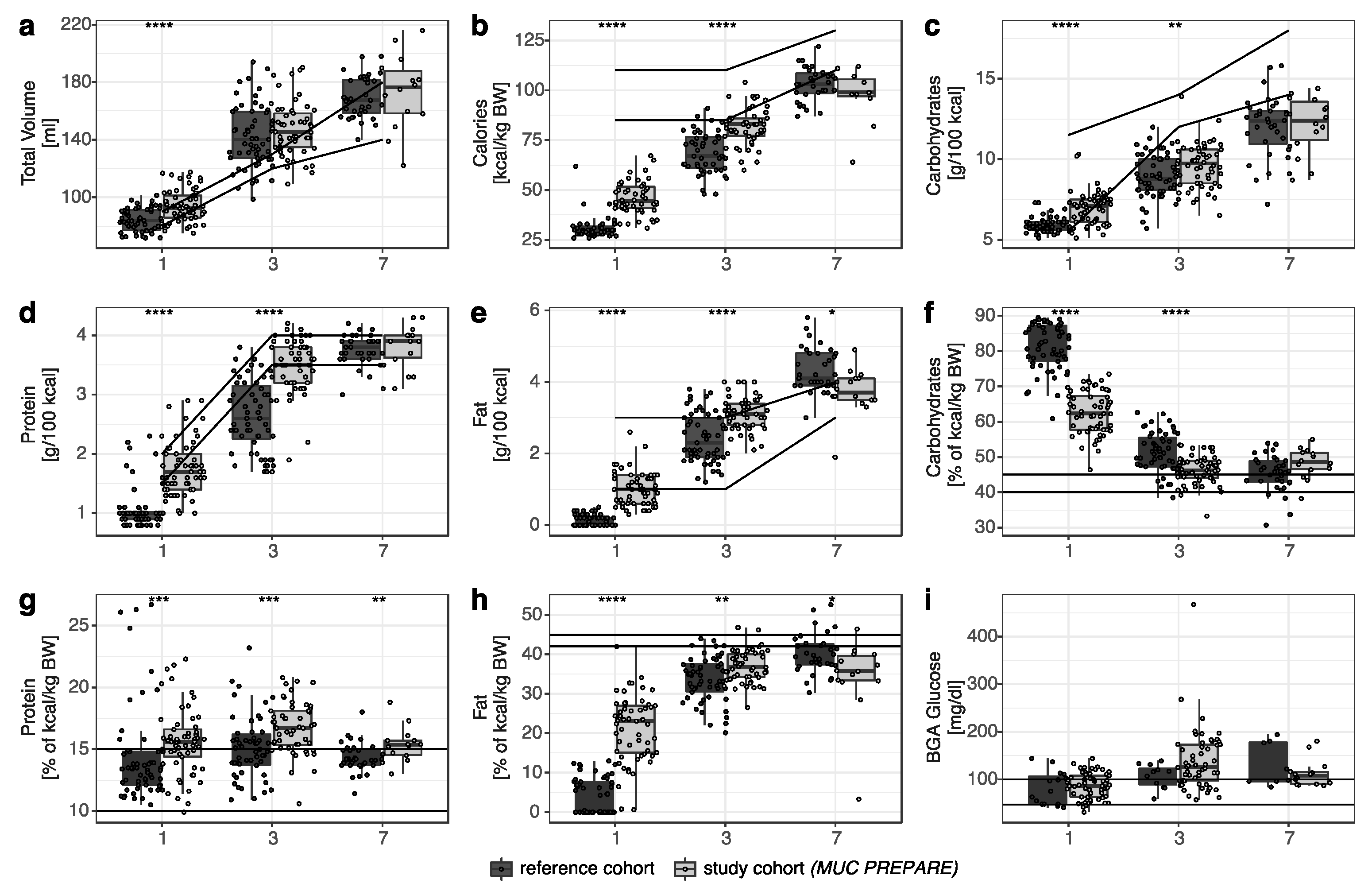
3.1. Improved Early Postnatal Energy and Nutrient Supply with the Standardized PN Solution MUC PREPARE in Very Premature Infants
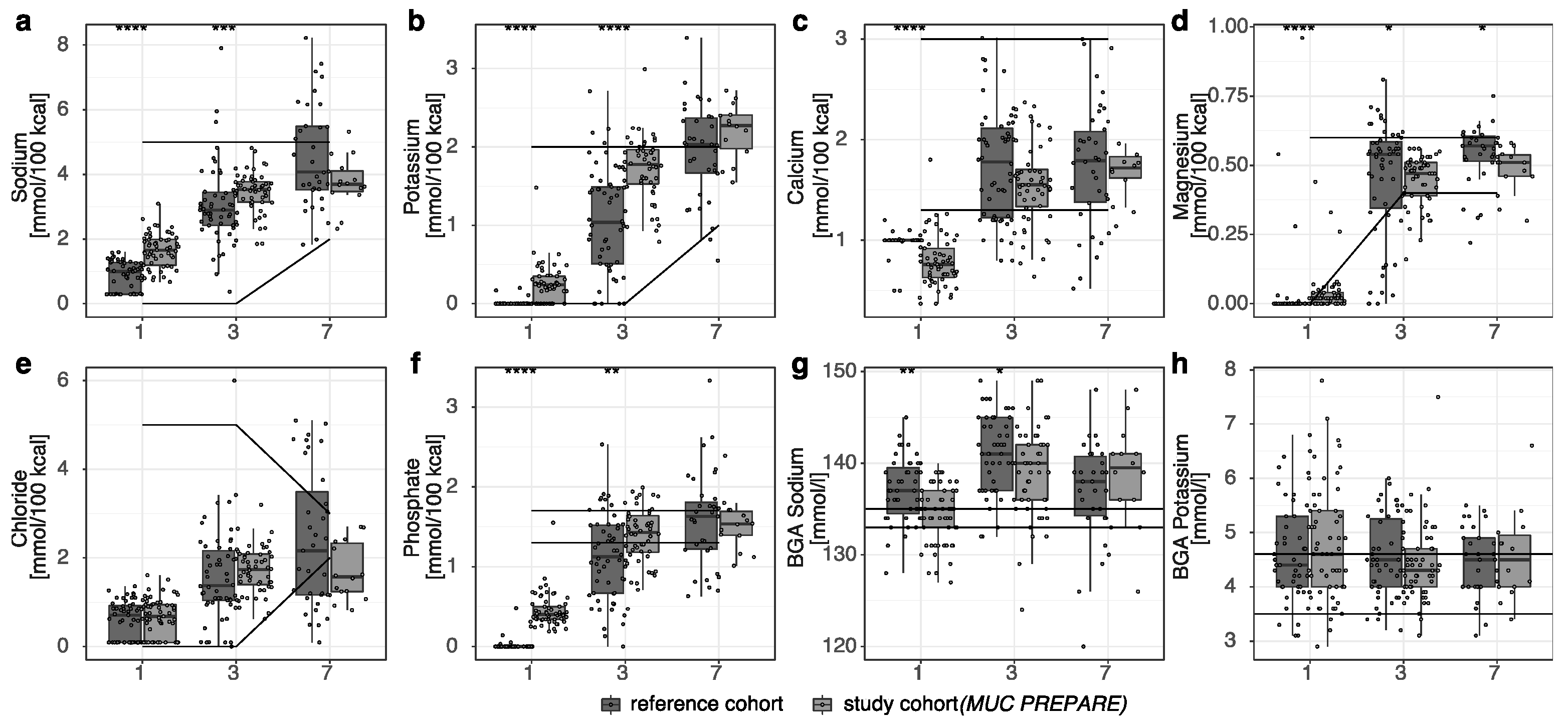
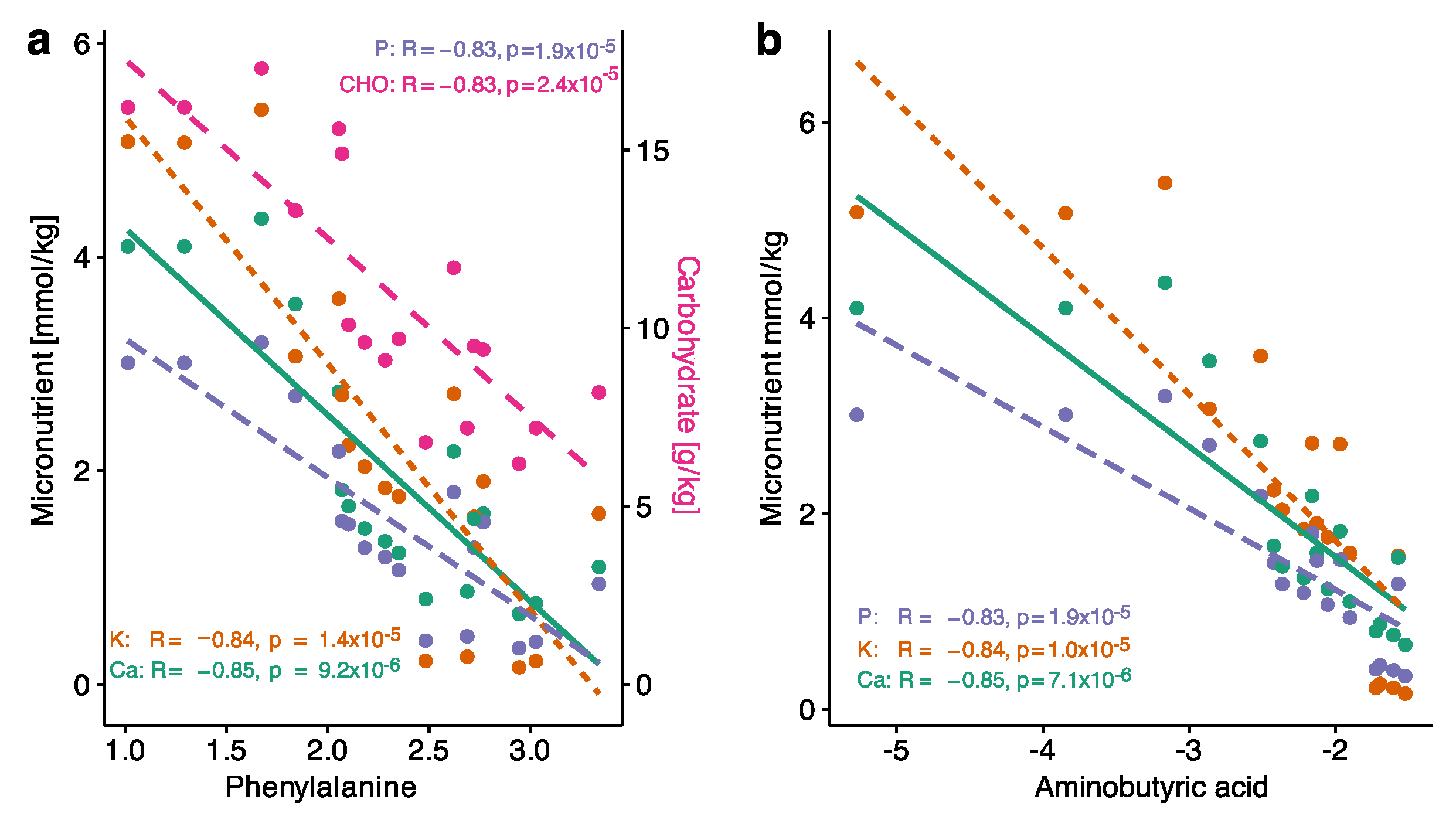
3.2. Balanced Indicators of Metabolism with Standardized PN Solution
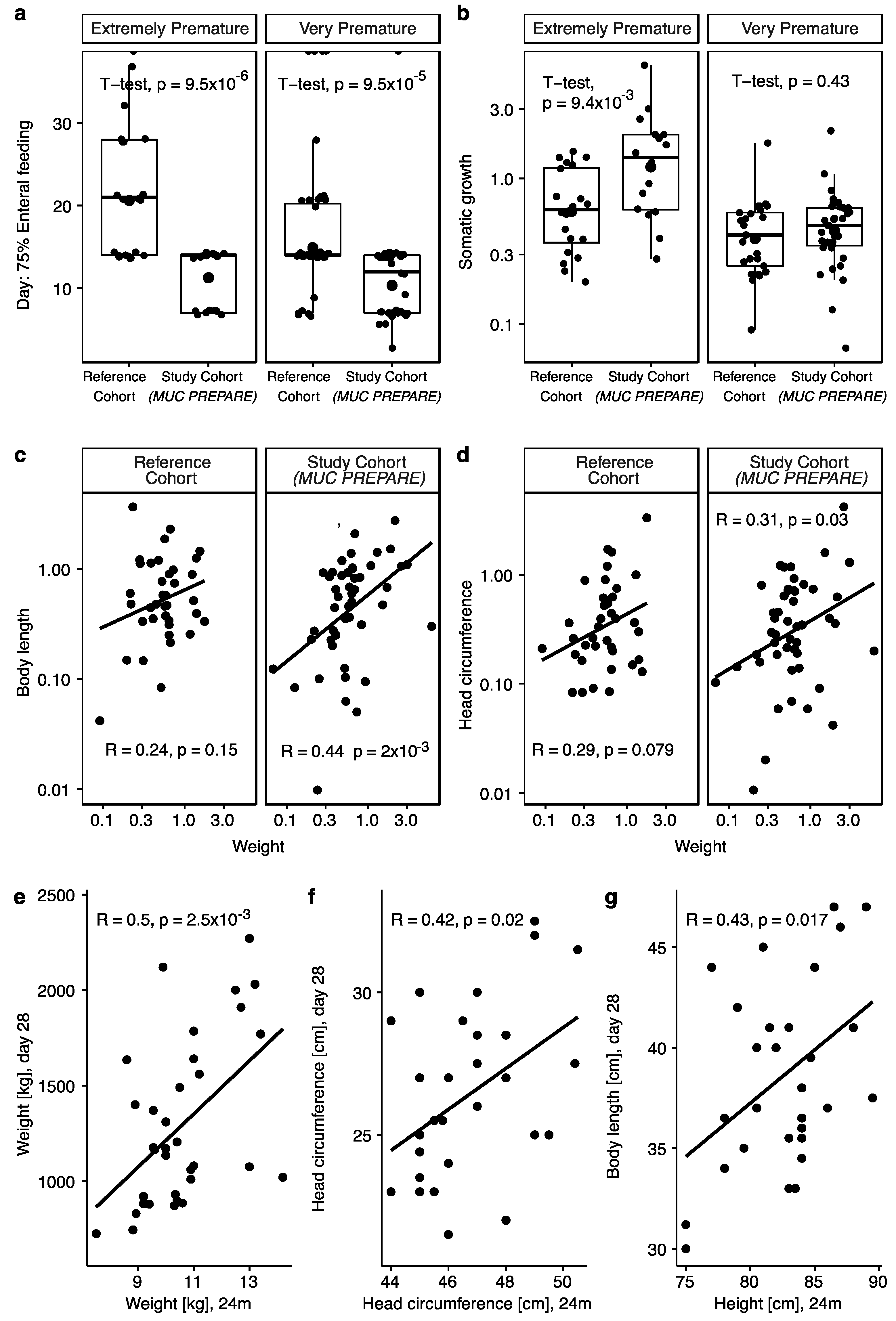
3.3. Improved Rate of Enteral Feeding and Postnatal Growth with Standardized PN Solutions
4. Discussion
4.1. Improved Early Postnatal Energy and Nutrient Supply with the Standardized PN Solution MUC PREPARE in Very Preterm Infants
4.2. Balanced Metabolomic Profile with the Use of a Standardized PN Solution
4.3. Improved Rate of Enteral Nutrition and Postnatal Growth with Standardized PN Solutions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blondel, B.; Papiernik, E.; Delmas, D.; Künzel, W.; Weber, T.; Maier, R.; Kollée, L.; Zeitlin, J.; Mosaic Research Group. Organisation of Obstetric Services for Very Preterm Births in Europe: Results from the MOSAIC Project: Models of Regionalisation in Europe for Very Preterm Births. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2009, 116, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawn, J.E.; Davidge, R.; Paul, V.K.; von Xylander, S.; de Graft Johnson, J.; Costello, A.; Kinney, M.V.; Segre, J.; Molyneux, L. Born Too Soon: Care for the Preterm Baby. Reprod. Health 2013, 10, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, L.; Sosenko, I.R.S. Undernutrition as a Major Contributing Factor in the Pathogenesis of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1988, 138, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenkranz, R.A.; Dusick, A.M.; Vohr, B.R.; Wright, L.L.; Wrage, L.A.; Poole, W.K.; National Institutes of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Growth in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Influences Neurodevelopmental and Growth Outcomes of Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatrics 2006, 117, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletzko, B.; Cheah, F.-C.; Domellöf, M.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Poindexter, B.B.; Vain, N. Scientific Basis and Practical Application of Nutritional Care for Preterm Infants. In World Review of Nutrition and Dietetics; Koletzko, B., Cheah, F.-C., Domellöf, M., Poindexter, B.B., Vain, N., van Goudoever, J.B., Eds.; S. Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 122, pp. 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.K.; Singhal, A.; Vaidya, U.; Banerjee, S.; Anwar, F.; Rao, S. Optimizing Nutrition in Preterm Low Birth Weight Infants—Consensus Summary. Front. Nutr. 2017, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiltunen, H.; Löyttyniemi, E.; Isolauri, E.; Rautava, S. Early Nutrition and Growth until the Corrected Age of 2 Years in Extremely Preterm Infants. Neonatology 2018, 113, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppänen, M.; Lapinleimu, H.; Lind, A.; Matomäki, J.; Lehtonen, L.; Haataja, L.; Rautava, P. Antenatal and Postnatal Growth and 5-Year Cognitive Outcome in Very Preterm Infants. Pediatrics 2014, 133, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Fischer Fumeaux, C.J.; Duerden, E.G.; Guo, T.; Foong, J.; Graz, M.B.; Hagmann, P.; Chakravarty, M.M.; Hüppi, P.S.; Beauport, L.; et al. Nutrient Intake in the First Two Weeks of Life and Brain Growth in Preterm Neonates. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20172169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, A.-M.; Fenton, S.; Murphy, B.P.; Kiely, M.E. Transition Phase Nutrition Recommendations: A Missing Link in the Nutrition Management of Preterm Infants. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2017, 42, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronsky, J.; Campoy, C.; Braegger, C.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN Guidelines on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition: Vitamins. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2366–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domellöf, M.; Szitanyi, P.; Simchowitz, V.; Franz, A.; Mimouni, F.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN Guidelines on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition: Iron and Trace Minerals. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2354–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jochum, F.; Moltu, S.J.; Senterre, T.; Nomayo, A.; Goulet, O.; Iacobelli, S.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN Guidelines on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition: Fluid and Electrolytes. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2344–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosten, K.; Embleton, N.; Yan, W.; Senterre, T.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN Guidelines on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition: Energy. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2309–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolaček, S.; Puntis, J.W.L.; Hojsak, I.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN Guidelines on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition: Venous Access. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2379–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapillonne, A.; Fidler Mis, N.; Goulet, O.; van den Akker, C.H.P.; Wu, J.; Koletzko, B.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN Guidelines on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition: Lipids. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2324–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesotten, D.; Joosten, K.; van Kempen, A.; Verbruggen, S.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN Guidelines on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition: Carbohydrates. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2337–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihatsch, W.; Shamir, R.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Fewtrell, M.; Lapillonne, A.; Lohner, S.; Mihályi, K.; Decsi, T.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN Guidelines on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition: Guideline Development Process for the Updated Guidelines. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2306–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Goudoever, J.B.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; Sainz de Pipaon, M.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN Guidelines on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition: Amino Acids. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2315–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Early Nutrition Programming Project; Koletzko, B.; Brands, B.; Demmelmair, H. The Early Nutrition Programming Project (EARNEST): 5 y of Successful Multidisciplinary Collaborative Research. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 1749S–1753S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletzko, B.; Poindexter, B.; Uauy, R. Recommended Nutrient Intake Levels for Stable, Fully Enterally Fed Very Low Birth Weight Infants. In World Review of Nutrition and Dietetics; Koletzko, B., Poindexter, B., Uauy, R., Eds.; S. Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 110, pp. 297–299. ISBN 978-3-318-02640-5. [Google Scholar]
- Carnielli, V.P.; Correani, A.; Giretti, I.; Apos Ascenzo, R.D.; Bellagamba, M.P.; Burattini, I.; Biagetti, C. Practice of Parenteral Nutrition in Preterm Infants. In World Review of Nutrition and Dietetics; Koletzko, B., Cheah, F.-C., Domellöf, M., Poindexter, B.B., Vain, N., van Goudoever, J.B., Eds.; S. Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 122, pp. 198–211. ISBN 978-3-318-06646-3. [Google Scholar]
- Mustapha, M.; Wilson, K.A.; Barr, S. Optimising Nutrition of Preterm and Term Infants in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Paediatr. Child Health 2021, 31, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESPGHAN and ESPEN Guidelines Paediatric Parenteral Nutrition—Annex: List of Products. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2005, 41, S85–S87. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, H. Visite2000. Available online: www.Visite2000.de (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Agostoni, C.; Buonocore, G.; Carnielli, V.; De Curtis, M.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.; Fusch, C.; Genzel-Boroviczeny, O.; et al. Enteral Nutrient Supply for Preterm Infants: Commentary from the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 50, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutrition and Feeding of Preterm Infants. Committee on Nutrition of the Preterm Infant, European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. Acta Paediatr. Scand. Suppl. 1987, 336, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Voigt, M.; Fusch, C.; Olbertz, D.; Hartmann, K.; Rochow, N.; Renken, C.; Schneider, K. Analyse des Neugeborenenkollektivs der Bundesrepublik Deutschland. Geburtsh. Frauenheilk. 2006, 66, 956–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, K.T.; Wahl, S.; Raffler, J.; Molnos, S.; Laimighofer, M.; Adamski, J.; Suhre, K.; Strauch, K.; Peters, A.; Gieger, C.; et al. Characterization of Missing Values in Untargeted MS-Based Metabolomics Data and Evaluation of Missing Data Handling Strategies. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodological) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A.S.P.E.N. Board of Directors and Task Force on Parenteral Nutrition Standardization; Kochevar, M.; Guenter, P.; Holcombe, B.; Malone, A.; Mirtallo, J. A.S.P.E.N. Statement on Parenteral Nutrition Standardization. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2007, 31, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieff, M.K. Nutrition and the Developing Brain: Nutrient Priorities and Measurement. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 614S–620S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreissl, A.; Repa, A.; Binder, C.; Thanhaeuser, M.; Jilma, B.; Berger, A.; Haiden, N. Clinical Experience with Numeta in Preterm Infants: Impact on Nutrient Intake and Costs. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2016, 40, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmer, K.; Rakshasbhuvankar, A.; Deshpande, G. Standardised Parenteral Nutrition. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisaki, N.; Belfort, M.B.; McCormick, M.C.; Mori, R.; Noma, H.; Kusuda, S.; Fujimura, M.; The Neonatal Research Network of Japan. Brief Parenteral Nutrition Accelerates Weight Gain, Head Growth Even in Healthy VLBWs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinerstein, A.; Nieto, R.M.; Solana, C.L.; Perez, G.P.; Otheguy, L.E.; Larguia, A.M. Early and Aggressive Nutritional Strategy (Parenteral and Enteral) Decreases Postnatal Growth Failure in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. J. Perinatol. 2006, 26, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacobelli, S.; Bonsante, F.; Vintéjoux, A.; Gouyon, J.-B. Standardized Parenteral Nutrition in Preterm Infants: Early Impact on Fluid and Electrolyte Balance. Neonatology 2010, 98, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborn, D.A.; Schindler, T.; Jones, L.J.; Sinn, J.K.; Bolisetty, S. Higher versus Lower Amino Acid Intake in Parenteral Nutrition for Newborn Infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regan, F.M.; Cutfield, W.S.; Jefferies, C.; Robinson, E.; Hofman, P.L. The Impact of Early Nutrition in Premature Infants on Later Childhood Insulin Sensitivity and Growth. Pediatrics 2006, 118, 1943–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, B.E.; Walden, R.V.; Gargus, R.A.; Tucker, R.; McKinley, L.; Mance, M.; Nye, J.; Vohr, B.R. First-Week Protein and Energy Intakes Are Associated with 18-Month Developmental Outcomes in Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, M.; Smyth, J.; Maheshwari, R.; Shah, S. Evaluation of Standardized versus Individualized Total Parenteral Nutrition Regime for Neonates Less than 33 Weeks Gestation. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2003, 39, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouroliakou, M.; Koutri, K.; Stathopoulou, M.; Vourvouhaki, E.; Giannopoulou, I.; Gounaris, A. Comparison of Two Types of TPN Prescription Methods in Preterm Neonates. Pharm. World Sci. 2009, 31, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolisetty, S.; Osborn, D.; Schindler, T.; Sinn, J.; Deshpande, G.; Wong, C.S.; Jacobs, S.E.; Phad, N.; Pharande, P.; Tobiansky, R.; et al. Standardised Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Formulations—Australasian Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Consensus Update 2017. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.J.; MacGregor, G.A. Neonatal Salt Intake and Blood Pressure. Lancet 2001, 357, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posner, A.S. Crystal Chemistry of Bone Mineral. Physiol. Rev. 1969, 49, 760–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohlandt, F. Prevention of Postnatal Bone Demineralization in Very Low-Birth-Weight Infants by Individually Monitored Supplementation with Calcium and Phosphorus. Pediatr. Res. 1994, 35, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohlandt, F. Bone Mineral Deficiency as the Main Factor of Dolichocephalic Head Flattening in Very-Low-Birth-Weight Infants. Pediatr. Res. 1994, 35, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotter, A.; Pohlandt, F. Calcium and Phosphorus Retention in Extremely Preterm Infants Supplemented Individually. Acta Paediatr. 2002, 91, 680–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.C.; Cairns, P.; Halliday, H.L.; Reid, M.; McClure, G.; Dodge, J.A. Randomised Controlled Trial of an Aggressive Nutritional Regimen in Sick Very Low Birthweight Infants. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal. Ed. 1997, 77, F4–F11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.; Fewtrell, M.; Cole, T.J.; Lucas, A. Low Nutrient Intake and Early Growth for Later Insulin Resistance in Adolescents Born Preterm. Lancet 2003, 361, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.H.; Kelleher, A.S.; Chace, D.H.; Spitzer, A.R. Gestational Age and Age at Sampling Influence Metabolic Profiles in Premature Infants. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e37–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, A.K.; Tebani, A.; Malmodin, D.; Pedersen, A.; Hellgren, G.; Löfqvist, C.; Hansen-Pupp, I.; Uhlén, M.; Hellström, A. Longitudinal Serum Metabolomics in Extremely Premature Infants: Relationships with Gestational Age, Nutrition, and Morbidities. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 830884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druml, W.; Heinzel, G.; Kleinberger, G. Amino Acid Kinetics in Patients with Sepsis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarla, C.; Giovannini, I.; Siegel, J.H. Characterization of Alpha-Amino-n-Butyric Acid Correlations in Sepsis. Transl. Res. 2011, 158, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltman, S.P.; Rogers, E.E.; Baer, R.J.; Jasper, E.A.; Anderson, J.G.; Steurer, M.A.; Pantell, M.S.; Petersen, M.A.; Partridge, J.C.; Karasek, D.; et al. Newborn Metabolic Vulnerability Profile Identifies Preterm Infants at Risk for Mortality and Morbidity. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanler, R.J.; Shulman, R.J.; Lau, C.; Smith, E.O.; Heitkemper, M.M. Feeding Strategies for Premature Infants: Randomized Trial of Gastrointestinal Priming and Tube-Feeding Method. Pediatrics 1999, 103, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPIPAGE 2 Writing Group; Ancel, P.-Y.; Goffinet, F. EPIPAGE 2: A Preterm Birth Cohort in France in 2011. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusick, A.M.; Poindexter, B.B.; Ehrenkranz, R.A.; Lemons, J.A. Growth Failure in the Preterm Infant: Can We Catch Up? Semin. Perinatol. 2003, 27, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmeier, J.E.; Joss-Moore, L.A.; Lane, R.H.; Neu, J. Early Postnatal Nutrition and Programming of the Preterm Neonate: Nutrition Reviews©. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.J.; Wiskin, A.E.; Pearson, F.; Beattie, R.M.; Leaf, A.A. How to Use: Nutritional Assessment in Neonates. Arch. Dis. Child. Educ. Pract. Ed. 2015, 100, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riskin, A.; Picaud, J.-C.; Shamir, R.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN Guidelines on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition: Standard versus Individualized Parenteral Nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study Cohort (MUC PREPARE) | Reference Cohort | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All (n = 58) | <27 Weeks (n = 18) | > 27 Weeks (n = 40) | All (n = 58) | <27 Weeks (n = 22) | >27 Weeks (n = 36) | |
| Gestational age [weeks PMA] | 27.8 ± 2.31 | 25.1 ± 1.03 | 29.1 ± 1.40 | 27.8 ± 2.23 | 25.5 ± 1.14 | 29.3 ± 1.23 |
| Birth weight [gram] | 989 ± 415 | 647 ± 415 | 1144 ± 655 | 991 ± 535 | 727 ± 535 | 1152 ± 550 |
| Maximal weight loss [% to birth weight] | −1.18 | −1.37 | −5.32 ± 4.17 | −0.66 | −0.64 | −0.64 |
| Gender [female, male] | 34/24 | 10/8 | 24/16 | 34/24 | 12/10 | 22/14 |
| BPD (none/all grades) * | 33/23 | 7/11 | 28/12 | 49/7 | 17/5 | 34/2 |
| RDS ≥ grade 3 | 8 (13.79%) | 3 (16.67%) | 5 (12.5%) | 8 (13.79%) | 7 (31.82%) | 1 (2.78%) |
| IVH ≥ grade 3 | 2 (3.45%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (5%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| PDA | 21 (36.21%) | 12 (66.67%) | 9 (22.5%) | 30 (51.72%) | 20 (90.91%) | 10 (27.78%) |
| NEC | 1 (1.72%) | 1 (5.56%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (1.72%) | 1 (4.55%) | 0 (0%) |
| Early onset infection | 11 (18.97%) | 6 (33.33%) | 5 (12.5%) | 6 (10.34%) | 3 (13.64%) | 3 (8.33%) |
| Late onset neonatal sepsis | 16 (27.59%) | 9 (50%) | 7 (17.5%) | 18 (31.03%) | 11 (50%) | 7 (19.44%) |
| Invasive ventilation [days] | 20.7 ± 13.7 | 28 ± 14.1 * | 18.1 ± 12.7 | 22.1 ± 19.1 | 41.5 ± 14.6 * | 12.8 ± 13.1 |
| Non-invasive ventilation [days] | 10.5 ± 12.4 | 17.2 ± 15.0 | 5.58 ± 7.13 | 12.5 ± 11.4 | 17.2 ± 12.2 | 6.5 ± 6.43 |
| Oxygen supplementation [days] | 30.1 ± 26.9 | 43.9 ± 31.1 | 21.8 ± 20.6 | 34.3 ± 35.1 | 58.7 ± 36.7 | 14.4 ± 17.2 |
| Baxter AminopädR 10% | Dextrose | Potassium | Sodium | Calcium | Phosphate | Magnesium | Zinc Total | Baxter Addel Junior | Chloride | Volume | KJ | Osmolarity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Per Day/kg BW | g | g | mmol | mmol | mmol | mmol | mmol | µmol | mL | mmol | mL | KJ | mOsm |
| NeoPeri-1 | 2.3 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 80 | 158 | 731 |
| NeoPeri-2 | 2.5 | 8 | 1 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 0.5 | 7.3 | 1 | 1 | 97 | 179 | 735 |
| NeoPeri-3 | 3.5 | 8.5 | 1.5 | 3 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 7.3 | 1 | 1.5 | 115 | 204 | 727 |
| NeoZent-1 G(−) | 3 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 46 | 153 | 1231 |
| NeoZent-1 G(±) | 2.5 | 6.5 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 47 | 153 | 1238 |
| NeoZent-2 G(−) | 3.5 | 7 | 1 | 2.6 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 0.5 | 7.3 | 1 | 1 | 62 | 179 | 1205 |
| NeoZent-2 G(±) | 3 | 8 | 1 | 2.6 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 0.5 | 7.3 | 1 | 1 | 61 | 187 | 1226 |
| NeoZent-3 G(−) | 3.8 | 6.5 | 1.5 | 3 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 7.3 | 1 | 1.5 | 66 | 175 | 1179 |
| NeoZent-3 G(±) | 3.8 | 8.5 | 1.5 | 3 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 7.3 | 1 | 1.5 | 70 | 209 | 1229 |
| Per 100 mL | Baxter AminopädR 10% | Dextrose | KCl 7.45% | NaCl 5.85% | Calcium Solution 10% | Glycero-PO4-Na 1 M | Mg 0.3 M | Unizink | Baxter Addel Junior | Water for Injection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mL | mL | mL | mL | mL | mL | mL | mL | mL | mL | |
| NeoPeri-1 | 28.8 | 17.53 | 0 | 0 | 5.45 | 0.63 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 47.59 |
| NeoPeri-2 | 25.73 | 16.47 | 1.03 | 0 | 5.82 | 1.34 | 1.75 | 0.51 | 1.03 | 46.32 |
| NeoPeri-3 | 30.51 | 14.82 | 1.31 | 0 | 5.68 | 1.31 | 1.48 | 0.44 | 0.87 | 43.58 |
| NeoZent-1 G(−) | 64.04 | 25.62 | 0 | 0 | 9.29 | 1.06 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NeoZent-1 G(±) | 53.94 | 28.05 | 0 | 0 | 9.39 | 1.07 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.55 |
| NeoZent-2 G(−) | 56.43 | 22.57 | 1.61 | 0 | 10.51 | 2.1 | 2.74 | 0.81 | 1.61 | 1.61 |
| NeoZent-2 G(±) | 48.76 | 26.01 | 1.63 | 0 | 10.6 | 2.11 | 2.76 | 0.81 | 1.63 | 5.69 |
| NeoZent-3 G(−) | 57.38 | 19.63 | 2.27 | 0 | 9.85 | 2.27 | 2.57 | 0.76 | 1.51 | 3.78 |
| NeoZent-3 G(±) | 54.5 | 24.38 | 2.15 | 0 | 9.35 | 2.15 | 2.44 | 0.72 | 1.43 | 2.87 |
| Per Day/kg BW | Fat 20% 1 | Baxter SoluvitR N (In Vitalipid) | Baxter Vitalipid Infant | Vol | KJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g | mL | mL | mL | KJ | |
| NeoFett Low 1 ± Vit | 1 | 1 | 3 | 6.5 | 42 |
| NeoFett Med 2 ± Vit | 2 | 1 | 3 | 11.5 | 84 |
| NeoFett High 3 ± Vit | 3 | 1 | 3 | 16.5 | 125 |
| Per 100 mL | Fat 20% 1 | Baxter SoluvitR N (In Vitalipid) | Baxter Vitalipid Infant |
|---|---|---|---|
| mL | mL | mL | |
| NeoFett Low 1 ± Vit | 53.85 | 15.38 | 46.15 |
| NeoFett Med 2 ± Vit | 73.91 | 8.7 | 26.09 |
| NeoFett High 3 ± Vit | 81.82 | 6.06 | 18.18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kindt, A.; Kraus, Y.; Rasp, L.D.; Foerster, K.M.; Ahmidi, N.; Flemmer, A.W.; Herber-Jonat, S.; Heinen, F.; Weigand, H.; Hankemeier, T.; et al. Improved Macro- and Micronutrient Supply for Favorable Growth and Metabolomic Profile with Standardized Parenteral Nutrition Solutions for Very Preterm Infants. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3912. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193912
Kindt A, Kraus Y, Rasp LD, Foerster KM, Ahmidi N, Flemmer AW, Herber-Jonat S, Heinen F, Weigand H, Hankemeier T, et al. Improved Macro- and Micronutrient Supply for Favorable Growth and Metabolomic Profile with Standardized Parenteral Nutrition Solutions for Very Preterm Infants. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):3912. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193912
Chicago/Turabian StyleKindt, Alida, Yvonne Kraus, Livia Dahlia Rasp, Kai M. Foerster, Narges Ahmidi, Andreas W. Flemmer, Susanne Herber-Jonat, Florian Heinen, Heike Weigand, Thomas Hankemeier, and et al. 2022. "Improved Macro- and Micronutrient Supply for Favorable Growth and Metabolomic Profile with Standardized Parenteral Nutrition Solutions for Very Preterm Infants" Nutrients 14, no. 19: 3912. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193912
APA StyleKindt, A., Kraus, Y., Rasp, L. D., Foerster, K. M., Ahmidi, N., Flemmer, A. W., Herber-Jonat, S., Heinen, F., Weigand, H., Hankemeier, T., Koletzko, B., Krumsiek, J., Babl, J., & Hilgendorff, A. (2022). Improved Macro- and Micronutrient Supply for Favorable Growth and Metabolomic Profile with Standardized Parenteral Nutrition Solutions for Very Preterm Infants. Nutrients, 14(19), 3912. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193912






