Predictive Roles of Basal Metabolic Rate and Body Water Distribution in Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity: The link to Carbohydrates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Anthropometric Parameters
2.2.2. Body Composition
2.2.3. Handgrip Strength Function
2.3. Definition of Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity
2.4. Dietary Variables
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic, Clinical, and Body Composition Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Association between Dietary Components and Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity
3.3. Association of Body Composition and Dietary Components with SMI
3.4. The Roles of BMR and Body Water Distribution in Predicting Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity
3.5. Association of Carbohydrates with BMR and SMI
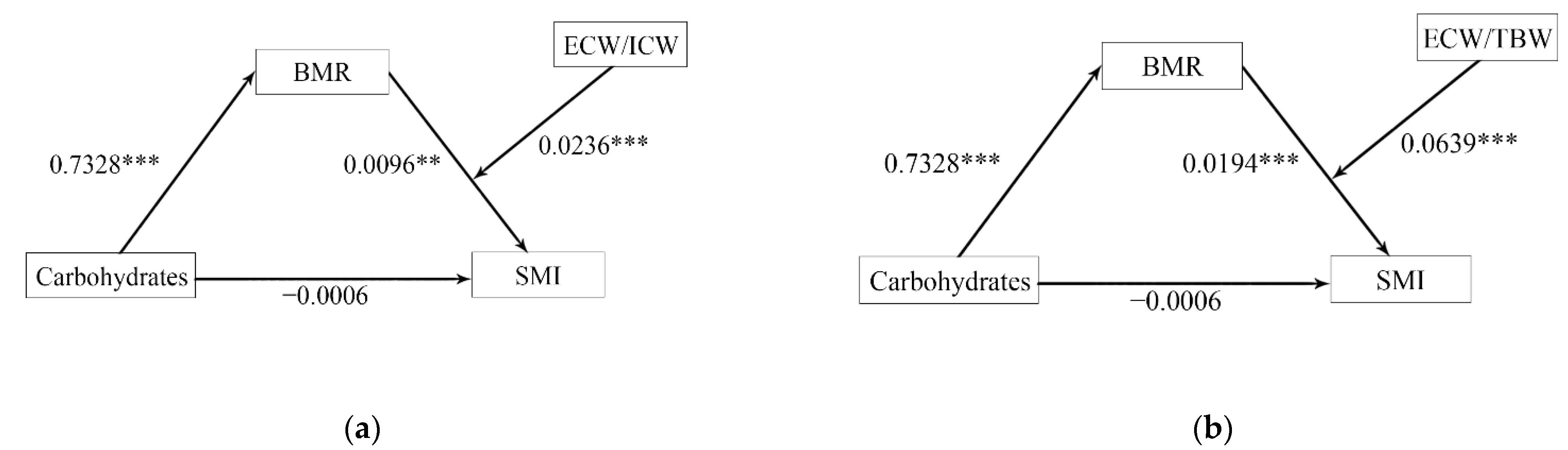
3.6. Mediation Analysis for Body Water Distribution, BMR, and SMI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. World Population Aging 2019; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nianogo, R.A.; Rosenwohl-Mack, A.; Yaffe, K.; Carrasco, A.; Hoffmann, C.M.; Barnes, D.E. Risk Factors Associated With Alzheimer Disease and Related Dementias by Sex and Race and Ethnicity in the US. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero-Jimenez, B.; Conde-Caballero, D.; Mariano-Juarez, L. Health and Nutritional Beliefs and Practices among Rural Elderly Population: An Ethnographic Study in Western Spain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyere, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsis, J.A.; Villareal, D.T. Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: Aetiology, epidemiology and treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Li, Y.; Ma, L. Sarcopenic Obesity: An Emerging Public Health Problem. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahat, G.; Kilic, C.; Ozkok, S.; Ozturk, S.; Karan, M.A. Associations of sarcopenic obesity versus sarcopenia alone with functionality. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2851–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.W.; Yu, K.; Shyh-Chang, N.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, T.; Ma, S.; Luo, L.; Guang, L.; Liang, K.; Ma, W.; et al. Pathogenesis of sarcopenia and the relationship with fat mass: Descriptive review. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.K.; Son, D.H.; Kwon, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.W. Association between Basal Metabolic Rate and Handgrip Strength in Older Koreans. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soysal, P.; Ates Bulut, E.; Yavuz, I.; Isik, A.T. Decreased Basal Metabolic Rate Can Be an Objective Marker for Sarcopenia and Frailty in Older Males. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2019, 20, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontzer, H.; Yamada, Y.; Sagayama, H.; Ainslie, P.N.; Andersen, L.F.; Anderson, L.J.; Arab, L.; Baddou, I.; Bedu-Addo, K.; Blaak, E.E.; et al. Daily energy expenditure through the human life course. Science 2021, 373, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullie, L.; Obrand, A.; Bendayan, M.; Trnkus, A.; Ouimet, M.C.; Moss, E.; Chen-Tournoux, A.; Rudski, L.G.; Afilalo, J. Phase Angle as a Biomarker for Frailty and Postoperative Mortality: The BICS Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Kitamura, G.; Nankaku, M.; Taniguchi, M.; Shide, K.; Fujita, M.; Ida, M.; Oshima, S.; Kikuchi, T.; Maki, T.; et al. Association of Physical Activity and Nutritional Intake with Muscle Quantity and Quality Changes in Acute Stroke Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022, 31, 106442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Cunha de Sa-Caputo, D.; Sonza, A.; Coelho-Oliveira, A.C.; Pessanha-Freitas, J.; Reis, A.S.; Francisca-Santos, A.; Dos Anjos, E.M.; Paineiras-Domingos, L.L.; de Rezende Bessa Guerra, T.; da Silva Franco, A.; et al. Evaluation of the Relationships between Simple Anthropometric Measures and Bioelectrical Impedance Assessment Variables with Multivariate Linear Regression Models to Estimate Body Composition and Fat Distribution in Adults: Preliminary Results. Biology 2021, 10, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Dolatshahi, M.; Zare-Shahabadi, A.; Rahmani, F. Untangling narcolepsy and diabetes: Pathomechanisms with eyes on therapeutic options. Brain Res. 2019, 1718, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, A.; Cebeci, A.N. Evaluation of hydration status of children with obesity-a pilot study. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 34, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Gao, S.; Wu, C.; Song, Q.; Shi, Z.; Su, J.; Zang, J. Effects of Internet-Based Nutrition and Exercise Interventions on the Prevention and Treatment of Sarcopenia in the Elderly. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidmayvan, M.; Sharifan, P.; Darroudi, S.; Saffar Soflaei, S.; Salaribaghoonabad, R.; Safari, N.; Yousefi, M.; Honari, M.; Ghazizadeh, H.; Ferns, G.; et al. Association between dietary patterns and body composition in normal-weight subjects with metabolic syndrome. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord 2022, 21, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrampour, N.; Mirzababaei, A.; Shiraseb, F.; Clark, C.C.T.; Mirzaei, K. The mediatory role of inflammatory markers on the relationship between dietary energy density and body composition among obese and overweight adult women: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, L.C.; Yang, Y.C.; Lin, H.C.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; Hung, Y.J.; Lee, M.S. Nutrition counseling is associated with less sarcopenia in diabetes: A cross-sectional and retrospective cohort study. Nutrition 2021, 91–92, 111269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M.F.; Wu, L.F.; Chen, Y.H.; Cao, R.R.; Deng, F.Y.; Lei, S.F. Body Surface Area (BSA) is a Better Osteoporosis Associated Anthropometric Parameter Than Other Anthropometric Parameters in Elderly Population. J. Clin. Densitom. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, J.; Afonso, C.; Moreira, P.; Padrao, P.; Santos, A.; Borges, N.; Negrao, R.; Amaral, T.F. Association of Anthropometric and Nutrition Status Indicators with Hand Grip Strength and Gait Speed in Older Adults. JPEN J. Parenter Enteral. Nutr. 2019, 43, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, Z.A.; Turkbeyler, I.H.; Abiyev, A.; Kul, S.; Edizer, B.; Yakaryilmaz, F.D.; Soylu, G. Health-related quality of life and fall risk associated with age-related body composition changes; sarcopenia, obesity and sarcopenic obesity. Intern. Med. J. 2018, 48, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Liu, X.; Zheng, K.; Liu, P.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhao, L.; Liang, T.; Cui, J.; Li, W. Thresholds of visceral fat area and percent of body fat to define sarcopenic obesity and its clinical consequences in Chinese cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandham, A.; Scott, D.; Bonham, M.P.; Kulkarni, B.; Kinra, S.; Ebeling, P.R.; Zengin, A. Sex Differences in Bone Health Among Indian Older Adults with Obesity, Sarcopenia, and Sarcopenic Obesity. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2022, 111, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.K.; Wee, S.L.; Pang, B.W.J.; Lau, L.K.; Jabbar, K.A.; Seah, W.T.; Ng, T.P. Relationship between BMI with percentage body fat and obesity in Singaporean adults–The Yishun Study. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donini, L.M.; Busetto, L.; Bischoff, S.C.; Cederholm, T.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.D.; Batsis, J.A.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Dicker, D.; et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria for sarcopenic obesity: ESPEN and EASO consensus statement. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hao, Q.; Yue, J.; Hou, L.; Xia, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, M.; Ge, N.; Dong, B. Sarcopenia, Obesity and Sarcopenia Obesity in Comparison: Prevalence, Metabolic Profile, and Key Differences: Results from WCHAT Study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2020, 24, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Y.; Yang, K.C.; Chang, H.H.; Lee, L.T.; Lu, C.W.; Huang, K.C. The Association between Total Protein and Vegetable Protein Intake and Low Muscle Mass among the Community-Dwelling Elderly Population in Northern Taiwan. Nutrients 2016, 8, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossenaar, M.; Solomons, N.W.; Muslimatun, S.; Faber, M.; Garcia, O.P.; Monterrosa, E.; van Zutphen, K.G.; Kraemer, K. Nutrient Density as a Dimension of Dietary Quality: Findings of the Nutrient Density Approach in a Multi-Center Evaluation. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; He, L.; Zhang, R.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Serum ferritin is a good indicator for predicting the efficacy of adult HLH induction therapy. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, K.; Chen, R.; Willcox, B.; Ohara, T.; Wen, A.; Takenaka, C.; Masaki, K. Association of sarcopenic obesity predicted by anthropometric measurements and 24-y all-cause mortality in elderly men: The Kuakini Honolulu Heart Program. Nutrition 2018, 46, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, E.J. The Influence of Obesity and Metabolic Health on Vascular Health. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, H.M.; Lee, Y.J. Using Dietary Macronutrient Patterns to Predict Sarcopenic Obesity in Older Adults: A Representative Korean Nationwide Population-Based Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abete, I.; Konieczna, J.; Zulet, M.A.; Galmes-Panades, A.M.; Ibero-Baraibar, I.; Babio, N.; Estruch, R.; Vidal, J.; Toledo, E.; Razquin, C.; et al. Association of lifestyle factors and inflammation with sarcopenic obesity: Data from the PREDIMED-Plus trial. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Yuan, T.; Liang, X.; Chen, N.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Weng, Y.; Hu, Y. Sarcopenic Obesity with Normal Body Size May Have Higher Insulin Resistance in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, C.; Chiang, J.M.; Kittiskulnam, P.; Sheshadri, A.; Grimes, B.; Segal, M.; Kaysen, G.A.; Johansen, K.L. Longitudinal Assessment of Body Composition and Its Association With Survival Among Participants of the ACTIVE/ADIPOSE Study. J. Ren. Nutr. 2022, 32, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hioka, A.; Akazawa, N.; Okawa, N.; Nagahiro, S. Extracellular water-to-total body water ratio is an essential confounding factor in bioelectrical impedance analysis for sarcopenia diagnosis in women. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2022, 13, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Lee, G.Y.; Seo, Y.M.; Seo, S.H.; Yoo, J.I. The relationship between extracellular water-to-body water ratio and sarcopenia according to the newly revised Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 33, 2471–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, S.; Pooyan, S.; Mirzababaei, A.; Arghavani, H.; Hasani, H.; Mirzaei, K. Interaction of MC4R rs17782313 variants and dietary carbohydrate quantity and quality on basal metabolic rate and general and central obesity in overweight/obese women: A cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glabska, D.; Cackowska, K.; Guzek, D. Comparison of the Body Composition of Caucasian Young Normal Body Mass Women, Measured in the Follicular Phase, Depending on the Carbohydrate Diet Level. Medicina 2018, 54, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, I.; Della Gatta, P.A.; Garnham, A.; Porter, J.; Burke, L.M.; Costa, R.J.S. The Effects of an Acute "Train-Low" Nutritional Protocol on Markers of Recovery Optimization in Endurance-Trained Male Athletes. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2021, 16, 1764–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolis, L.M.; Allen, J.T.; Hatch-McChesney, A.; Pasiakos, S.M. Coingestion of Carbohydrate and Protein on Muscle Glycogen Synthesis after Exercise: A Meta-analysis. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
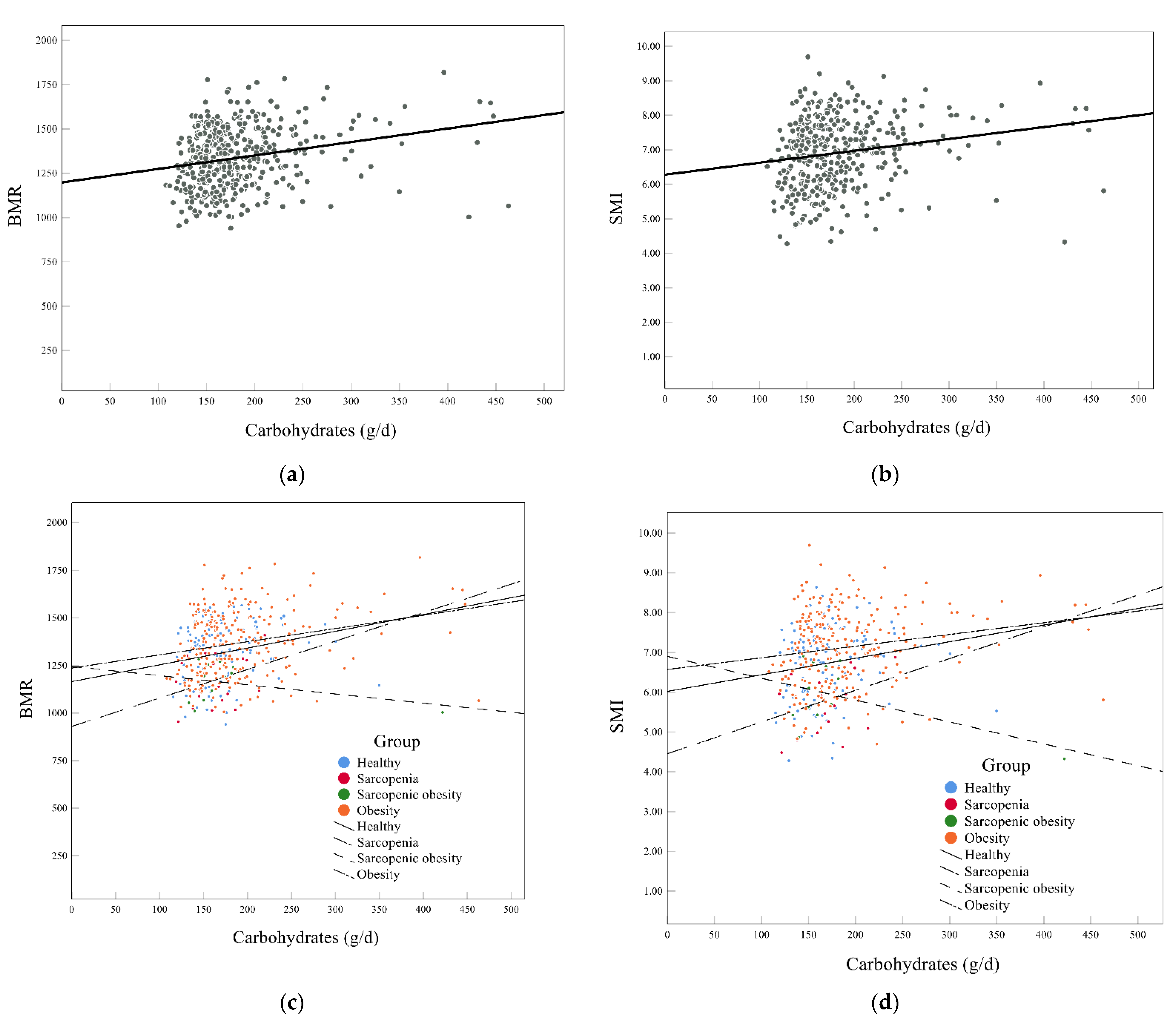

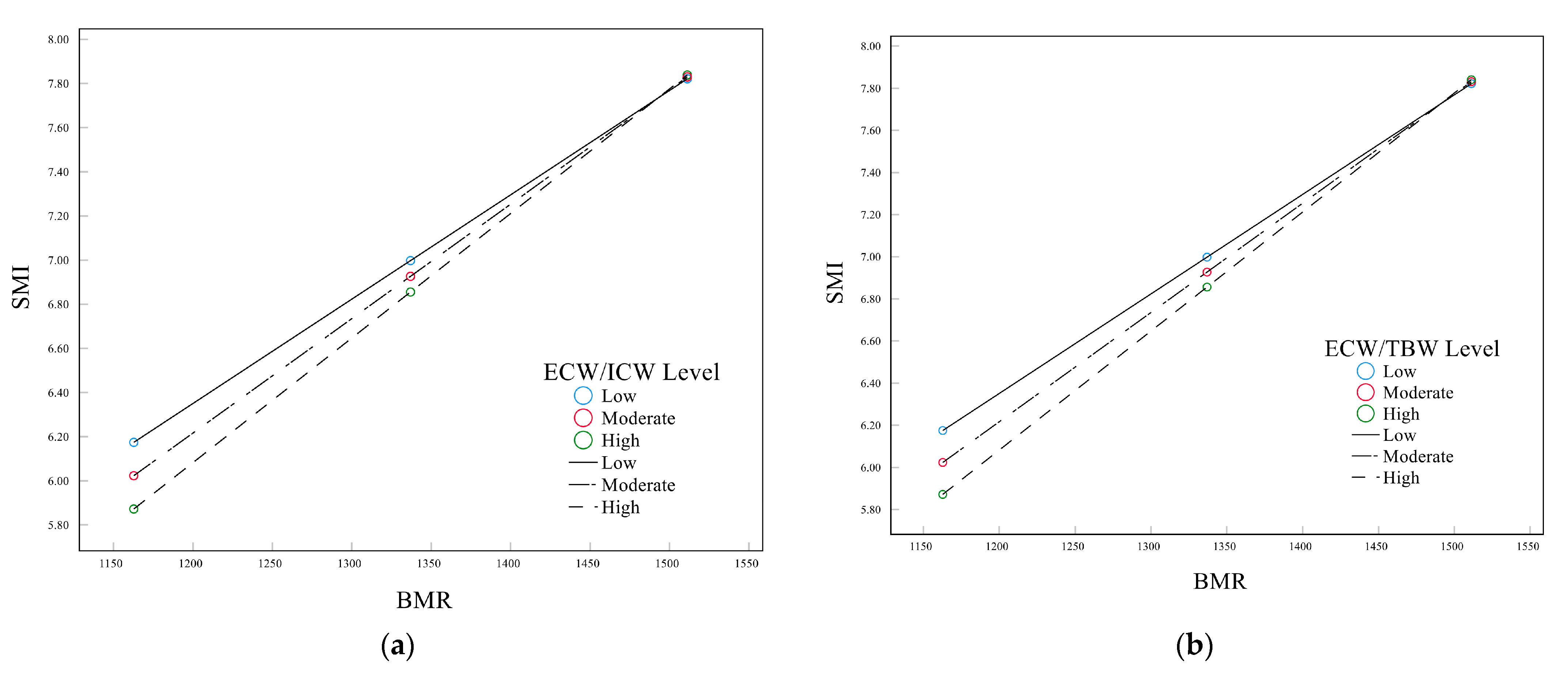
| Characteristics | Total | Healthy | Sarcopenia | Sarcopenic Obesity | Obesity | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMR, (kcal/d) | 1338.46 ± 174.40 | 1352.13 (1167.34, 1446.96) a,b,c | 1182.07 ± 133.69 a,d | 1158.01 ± 102.75 b,e | 1373.26 (1230.35, 1505.21) c,d,e | <0.001 *** |
| BMI, (kg/m2) | 24.07 ± 3.26 | 21.51 ± 2.22 a,b | 19.15 ± 2.08 a,c,d | 23.53 ± 2.91 c,e | 25.47 (24.00, 27.08) b,d,e | <0.001 *** |
| BMR/BMI | 56.17 ± 8.22 | 61.51 ± 7.54 a,b | 62.31 ± 8.87 c,d | 49.59 ± 5.14 a,c | 53.50 ± 6.98 b,d | <0.001 *** |
| BMR/BSA | 800.12 (762.31, 832.94) | 827.77 ± 42.22 a,b | 821.76 (792.43, 829.97) c | 753.63 ± 42.38 a,c | 787.25 ± 45.84 b | <0.001 *** |
| BMR/Height2 | 0.051 ± 0.003 | 0.050 ± 0.003 a,b | 0.047 ± 0.003 a,c | 0.049 ± 0.003 d | 0.052 ± 0.003 b,c,d | <0.001 *** |
| TBW | 33.17 (28.14, 37.55) | 33.53 (27.27, 36.71) a,b | 27.72 ± 4.60 a,c | 26.87 ± 3.55 b,d | 34.28 (29.28, 38.72) c,d | <0.001 *** |
| ICW | 20.36 (17.31, 23.00) | 20.54 (16.78, 22.73) a,b | 16.84 ± 2.82 a,c | 16.40 ± 2.22 b,d | 20.90 ± 3.70 c,d | <0.001 *** |
| ECW | 12.78 ± 2.28 | 12.88 (10.49, 14.16) a,b | 10.89 ± 1.80 a,c | 10.46 ± 1.36 b,d | 13.19 ± 2.28 c,d | <0.001 *** |
| ECW/ICW | 0.632 ± 0.001 | 0.629 ± 0.001 a | 0.647 ± 0.004 a,b | 0.639 ± 0.006 | 0.632 ± 0.001 b | 0.001 *** |
| ECW/TBW | 0.387 ± 0.007 | 0.386 ± 0.006 a | 0.393 ± 0.006 a,b | 0.390 ± 0.007 | 0.387 ± 0.008 b | 0.001 *** |
| SMI, (kg/m2) | ||||||
| Men | 7.49 ± 0.69 | 7.28 ± 0.52 a,b,c | 6.31 ± 0.52 a,d | 6.59 ± 0.31 b,e | 7.74 ± 0.62 c,d,e | <0.001 *** |
| Women | 6.05 ± 0.74 | 5.64 ± 0.57 a,b | 5.03 ± 0.41 a,c | 5.23 ± 0.53 d | 6.31 ± 0.65 b,c,d | <0.001 *** |
| HGS, (kg) | ||||||
| Men | 34.20 ± 7.33 | 35.17 ± 5.84 a,b | 22.60 ± 3.36 a,c | 24.82 ± 3.37 b,d | 35.03 ± 7.34 c,d | <0.001 *** |
| Women | 23.00 (20.15, 24.80) | 23.00 ± 2.68 a,b | 15.16 ± 2.33 a,c | 14.87 ± 1.31 b,d | 23.25 (20.83, 24.88) c,d | <0.001 *** |
| Waist, (cm) | 88.00 (80.50, 93.00) | 78.00 (75.00, 85.00) a | 75.00 ± 5.69 b | 82.83 ± 5.61 c | 92.00 (88.00, 96.00) a,b,c | <0.001 *** |
| Hip, (cm) | 93.63 ± 5.34 | 89.93 ± 3.87 a,b | 85.76 ± 3.23 a,c,d | 89.89 ± 2.65 c,e | 96.18 ± 4.34 b,d,e | <0.001 *** |
| WHR | ||||||
| Men | 0.896 ± 0.066 | 0.854 ± 0.045 a | 0.836 ± 0.055 b | 0.855 ± 0.052 c | 0.925 ± 0.061 a,b,c | <0.001 *** |
| Women | 0.879 (0.858, 0.18) | 0.860 (0.829, 0.871) a | 0.828 ± 0.035 b,c | 0.899 ± 0.047 b | 0.900 ± 0.044 a,c | <0.001 *** |
| FM, (kg) | 17.74 ± 5.95 | 12.46 ± 3.81 a,b | 10.81 ± 3.01 c,d | 17.14 ± 3.32 a,c,e | 20.81 ± 4.72 b,d,e | <0.001 *** |
| Percentage Body Fat, (%) | 28.41 (23.18, 33.43) | 22.31 (18.64, 25.74) a,b | 22.39 ± 6.07 c,d | 32.07 ± 6.03 a,c | 31.06 ± 5.95 b,d | <0.001 *** |
| VFA, (cm2) | 81.78 (64.15, 107.55) | 57.60 ± 19.41 a,b | 53.36 ± 15.43 c,d | 88.29 ± 26.98 a,c | 97.49 (79.77, 118.49) b,d | <0.001 *** |
| TSM, (kg) | 24.59 (20.58, 28.01) | 24.79 (19.89, 27.64) a,b | 19.96 ± 3.68 a,c | 19.39 ± 2.89 b,d | 25.30 ± 4.83 c,d | <0.001 *** |
| ASM, (kg) | 18.45 (15.01, 21.23) | 18.68 (14.57, 21.02) a,b | 14.83 ± 3.33 a,c | 14.00 ± 2.41 b,d | 18.85 ± 3.98 c,d | <0.001 *** |
| Total | Healthy | Sarcopenia | Sarcopenic Obesity | Obesity | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total energy (kcal/d) | 1442.50 (1228.07, 1715.92) | 1401.03 (1215.04, 1651.26) | 1523.75 (1189.21, 1644.23) | 1285.54 (1169.97, 1652.64) | 1470.18 (1238.49, 1756.24) | 0.353 |
| Macronutrients | ||||||
| Carbohydrates (g/d) | 168.86 (148.71, 201.16) | 164.50 (144.71, 187.70) a | 165.39 (139.66, 193.49) | 157.20 (145.97, 179.80) | 173.20 (150.43, 209.10) a | 0.023 * |
| Carbohydrate density (%E) | 48.11 (42.95, 53.51) | 46.69 (41.81, 51.82) | 46.18 (43.68, 51.38) | 48.83 (42.49, 54.90) | 49.36 (43.56, 54.19) | 0.101 |
| Total proteins (g/d) | 53.52 (44.44, 65.30) | 54.62 (44.06, 63.56) | 57.84 (44.26, 69.87) | 48.07 (40.81, 56.13) | 53.21 (44.86, 65.70) | 0.475 |
| Total protein density (%E) | 15.18 (13.69, 16.72) | 15.20 (13.84, 16.85) | 15.75 (13.64, 19.78) | 14.17 (12.65, 17.05) | 15.15 (17.66, 16.43) | 0.397 |
| Lipids (g/d) | 79.70 (65.86, 96.25) | 81.62 (67.65, 95.88) | 81.15 (67.93, 89.02) | 71.58 (67.25, 99.85) | 78.26 (65.30, 96.83) | 0.895 |
| Lipid density (%E) | 50.23 (45.77, 54.38) | 52.09 (47.45, 55.15) a | 50.02 (46.63, 54.06) | 51.67 (48.14, 54.40) | 49.62 (44.24, 53.66) a | 0.028 * |
| Dietary fiber (g/d) | 13.63 (11.38, 16.46) | 12.80 (11.24, 15.67) | 13.99 (11.63, 16.48) | 13.95 (11.62, 15.51) | 13.69 (11.41, 16.86) | 0.553 |
| Micronutrients | ||||||
| Potassium (mg/d) | 1811.75 (1534.11, 2172.01) | 1743.51 (1494.08, 2049.12) | 2131.51 (1536.93, 2496.12) | 1593.52 (1517.71, 2335.03) | 1843.12 (1555.04, 2207.02) | 0.143 |
| Magnesium (mg/d) | 307.96 (266.48, 373.41) | 295.39 (261.77, 353.80) | 347.26 (284.25, 391.39) | 303.52 (249.45, 370.94) | 309.36 (268.15, 380.47) | 0.411 |
| Manganese (mg/d) | 5.68 (5.29, 6.22) | 5.58 (5.20, 6.20) | 5.48 (5.21, 5.83) | 5.61 (5.07, 6.13) | 5.75 (5.37, 6.46) | 0.060 |
| Phosphorus (mg/d) | 920.98 (769.18, 7090.43) | 895.61 (747.90, 1061.79) | 969.23 (772.61, 1129.42) | 786.57 (731.82, 998.35) | 925.40 (782.35, 1131.52) | 0.249 |
| Ferrum (mg/d) | 18.94 (17.13, 22.47) | 18.32 (16.56, 21.92) | 19.45 (17.55, 22.15) | 18.75 (16.10, 22.17) | 19.18 (17.27, 22.89) | 0.281 |
| Calcium (mg/d) | 575.02 (412.00, 751.03) | 533.23 (364.90, 708.55) | 643.82 (476.83, 756.19) | 611.03 (353.74, 775.06) | 580.38 (425.21, 773.83) | 0.240 |
| Vitamin A (µg/d) | 569.50 (267.51, 1078.39) | 712.40 (272.77, 1107.14) | 769.44 (326.50, 1020.27) | 459.68 (246.40, 1022.73) | 476.91 (256.80, 1086.06) | 0.855 |
| Vitamin B1 (µg/d) | 0.74 (0.64, 0.89) | 0.74 (0.61, 0.89) | 0.74 (0.65, 0.85) | 0.66 (0.62, 0.87) | 0.75 (0.64, 0.90) | 0.447 |
| Vitamin B2 (µg/d) | 3.49 (3.34, 3.70) | 3.48 (3.35, 3.73) | 3.49 (3.33, 3.70) | 3.32 (3.29, 3.52) | 3.50 (3.35, 3.70) | 0.172 |
| Vitamin B3 (µg/d) | 11.54 (9.76, 14.48) | 11.60 (9.76, 13.99) | 12.22 (9.97, 13.51) | 10.60 (8.84, 13.67) | 11.52 (9.74, 15.01) | 0.721 |
| Vitamin C (mg/d) | 150.70 (81.67, 231.61) | 146.50 (80.76, 225.09) | 156.37 (100.32, 215.49) | 190.33 (85.70, 212.57) | 148.43 (81.20, 244.77) | 0.948 |
| Healthy vs. Sarcopenia | Healthy vs. Sarcopenic Obesity | Sarcopenia vs. Sarcopenic Obesity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | |
| BMR | ||||||
| MODEL 1 | 0.085 (0.019, 0.381) | 0.001 ** | 0.047 (0.006, 0.374) | 0.004 ** | 0.244 (0.042, 1.414) | 0.116 |
| MODEL 2 | 0.051 (0.009, 0.278) | 0.001 ** | 0.007 (0.000, 0.087) | <0.001 *** | 0.195 (0.022, 1.726) | 0.142 |
| BMR/BMI | ||||||
| MODEL 1 | 2.476 (0.780, 7.865) | 0.124 | 0.031 (0.004, 0.250) | 0.001 ** | 0.030 (0.003, 0.297) | 0.003 ** |
| MODEL 2 | 3.262 (0.800, 13.310) | 0.099 | 0.003 (0.000, 0.051) | <0.001 *** | — | 0.999 |
| BMR/BSA | ||||||
| MODEL 1 | 0.100 (0.022, 0.452) | 0.003 ** | 0.035 (0.004, 0.284) | 0.002 * | 0.083 (0.015, 0.459) | 0.004 ** |
| MODEL 2 | 0.060 (0.011, 0.319) | 0.001 ** | — | 0.998 | — | 0.999 |
| BMR/Height2 | ||||||
| MODEL 1 | 0.135 (0.045, 0.400) | <0.001 *** | 0.439 (0.133, 1.454) | 0.178 | 7.500 (1.288, 43.687) | 0.025 * |
| MODEL 2 | 0.152 (0.045, 0.510) | 0.002 ** | 0.668 (0.151, 2.962) | 0.596 | 22.507 (1.792, 282.647) | 0.016 * |
| Predictors | On BMR | On SMI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coeff | t | p | Coeff | t | p | |
| ECW/ICW | ||||||
| Control variables | ||||||
| Age | −4.2375 | −3.3246 | 0.0010 ** | 0.0004 | 0.1474 | 0.8829 |
| Independent variable | ||||||
| Carbohydrates | 0.7328 | 4.7466 | <0.0001 *** | −0.0006 | −1.7520 | 0.0806 |
| Mediator | ||||||
| BMR | −0.0096 | −3.3917 | 0.0008 *** | |||
| Moderator | ||||||
| ECW/ICW | −35.3383 | −5.5645 | <0.0001 *** | |||
| Interaction term | ||||||
| BMR × ECW/ICW | 0.0236 | 5.2782 | <0.0001 *** | |||
| ECW/TBW | ||||||
| Control variables | ||||||
| Age | −4.2345 | −3.3246 | 0.0010 ** | 0.0004 | 0.1252 | 0.9004 |
| Independent variable | ||||||
| Carbohydrates | 0.7328 | 3.0519 | <0.0001 *** | −0.0006 | −1.7511 | 0.0807 |
| Mediator | ||||||
| BMR | −0.0194 | −4.1371 | <0.0001 *** | |||
| Moderator | ||||||
| ECW/TBW | −95.4461 | −5.5599 | <0.0001 *** | |||
| Interaction term | ||||||
| BMR × ECW/TBW | 0.0639 | 5.2767 | <0.0001 *** | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, L.; Li, T.; Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Xiao, R.; Xi, Y. Predictive Roles of Basal Metabolic Rate and Body Water Distribution in Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity: The link to Carbohydrates. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3911. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193911
Guan L, Li T, Wang X, Yu K, Xiao R, Xi Y. Predictive Roles of Basal Metabolic Rate and Body Water Distribution in Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity: The link to Carbohydrates. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):3911. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193911
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Lizheng, Tiantian Li, Xuan Wang, Kang Yu, Rong Xiao, and Yuandi Xi. 2022. "Predictive Roles of Basal Metabolic Rate and Body Water Distribution in Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity: The link to Carbohydrates" Nutrients 14, no. 19: 3911. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193911
APA StyleGuan, L., Li, T., Wang, X., Yu, K., Xiao, R., & Xi, Y. (2022). Predictive Roles of Basal Metabolic Rate and Body Water Distribution in Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity: The link to Carbohydrates. Nutrients, 14(19), 3911. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14193911






