The Use of Probiotics Combined with Exercise Affects Thiol/Disulfide Homeostasis, an Oxidative Stress Parameter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Probiotic Administration Protocol
2.3. Exercise Protocol
2.4. Biochemical Parameters
2.5. Thiol/Disulfide Analyses
2.5.1. Precision
2.5.2. Analytical Recovery
2.5.3. Linearity
2.5.4. Lower Detection Limit
2.5.5. Analytical Sensitivity
2.5.6. Interference
2.5.7. Storage
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. The Use of Probiotics Alone Did Not Affect Oxidative Stress
4.2. The Use of Probiotics Combined with Exercise Reduced Oxidative Stress
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| CE | Conformite Europeene |
| Cn | Control |
| CV | Coefficient variation |
| DD | Dynamic disulfide |
| Ex | Exercise |
| Mn-SOD | Manganese superoxide dismutase |
| NT | Native thiol |
| OT | Oxidized-thiol |
| P | Probiotic |
| PEx | Probiotic + exercise |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RT | Reduced thiol |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| SH | Sulfhydryl |
| TOR | Thiol oxidation reduction |
| TT | Total thiol |
| η2 | Eta Squared |
References
- Carey, R.A.; Montag, D. Exploring the relationship between gut microbiota and exercise: Short-chain fatty acids and their role in metabolism. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2021, 7, e000930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, H.S.; Guarner, F. Probiotics and human health: A clinical perspective. Postgrad. Med. J. 2004, 80, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Niu, Z.; Zou, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Gu, X.; Lu, H.; Tian, H.; Jha, R. Corrigendum to “Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics regulate the intestinal microbiota differentially and restore the relative abundance of specific gut microorganisms”. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 5816–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Fan, S.-T.; Huang, D.; Xiong, T.; Nie, S.; Xie, M.-Y. Polysaccharides from fermented Asparagus officinalis with Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116 alleviated liver injury via modulation of glutathione homeostasis, bile acid metabolism, and SCFA production. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 7681–7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, R.L.; Holscher, H.D. Fueling Gut Microbes: A Review of the Interaction between Diet, Exercise, and the Gut Microbiota in Athletes. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2021, 12, 2190–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi-Rad, F.; Behrouzi, A.; Mazaheri, H.; Katebi, A.; Ajdary, S. Impact of gut microbiota on immune system. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2021, 68, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, F.; Sun, M.; Song, Y.; Xu, D.; Mu, G.; Tuo, Y. Lactobacillus plantarum Y44 alleviates oxidative stress by regulating gut microbiota and colonic barrier function in Balb/C mice with subcutaneous d-galactose injection. Food Funct. 2020, 12, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Luo, Q.; Nie, R.; Yang, X.; Tang, Z.; Chen, H. Potential implications of polyphenols on aging considering oxidative stress, inflammation, autophagy, and gut microbiota. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2175–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayacan, Y.; Çetinkaya, A.; Yazar, H.; Makaracı, Y. Oxidative stress response to different exercise intensity with an automated assay: Thiol/disulphide homeostasis. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 127, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayacan, Y.; Yazar, H.; Cerit, G.; Ghojebeigloo, B.E. A new oxidative stress indicator: Effect of 5-hydroxytryptophan on thiol-disulfide homeostasis in exercise. Nutrition 2019, 63–64, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, M.A.; Koyuncu, I.; Incebıyık, H.; Karakaş, H.; Erel, Ö.; Sabuncu, T. The evaluation of thiol/disulphide homeostasis in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 148, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayacan, Y.; Yazar, H.; Kisa, E.C.; Ghojebeigloo, B.E. A novel biomarker explaining the role of oxidative stress in exercise and l-tyrosine supplementation: Thiol/disulphide homeostasis. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagarolli, R.A.; Tobar, N.; Oliveira, A.G.; Araújo, T.G.; Carvalho, B.M.; Rocha, G.Z.; Vecina, J.F.; Calisto, K.; Guadagnini, D.; Prada, P.D.O.; et al. Probiotics modulate gut microbiota and improve insulin sensitivity in DIO mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 50, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erel, O.; Neselioglu, S. A novel and automated assay for thiol/disulphide homeostasis. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 47, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asemi, Z.; Zare, Z.; Shakeri, H.; Sabihi, S.-S.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Effect of Multispecies Probiotic Supplements on Metabolic Profiles, hs-CRP, and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrabadi, S.; Sadr, S.S. Assessment of Probiotics Mixture on Memory Function, Inflammation Markers, and Oxidative Stress in an Alzheimer’s Disease Model of Rats. Iran. Biomed. J. 2020, 24, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, B.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Vaghef-Mehrabany, E.; Sharif, S.K.; Vaghef-Mehrabany, L.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Nakhjavani, M.R.; Mohtadi-Nia, J. Effects ofLactobacillus caseisupplementation on disease activity and inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis patients: A randomized double-blind clinical trial. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 17, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez-Lara, M.J.; Robles-Sanchez, C.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Gil, A. Effects of Probiotics and Synbiotics on Obesity, Insulin Resistance Syndrome, Type 2 Diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Review of Human Clinical Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccotti, G.; Meneghin, F.; Raimondi, C.; Dilillo, D.; Agostoni, C.; Riva, E.; Giovannini, M. Probiotics in Clinical Practice: An Overview. J. Int. Med. Res. 2008, 36, 1A–53A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Prasad, D. Application of in vitro methods for selection of Lactobacillus casei strains as potential probiotics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 103, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullisaar, T.; Zilmer, M.; Mikelsaar, M.; Vihalemm, T.; Annuk, H.; Kairane, C.; Kilk, A. Two antioxidative lactobacilli strains as promising probiotics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 72, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-G.; Xu, H.-B.; Xu, F.; Zeng, Z.-L.; Wei, H. Efficacy of oral Bifidobacterium bifidum ATCC 29521 on microflora and antioxidant in mice. Can. J. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkasheh, G.; Kashani-Poor, Z.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Jafari, P.; Akbari, H.; Taghizadeh, M.; Memarzadeh, M.R.; Asemi, Z.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Clinical and metabolic response to probiotic administration in patients with major depressive disorder: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrition 2016, 32, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, B.; Sheikhi, A.; Namazi, N.; Larijani, B.; Azadbakht, L. The Effects of Supplementation with Probiotic on Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Adult Subjects: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Trials. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avloniti, A.; Chatzinikolaou, A.; Deli, C.K.; Vlachopoulos, D.; Gracia-Marco, L.; Leontsini, D.; Draganidis, D.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Mastorakos, G.; Fatouros, I.G. Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress Responses in the Pediatric Population. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschalis, V.; Theodorou, A.A.; Margaritelis, N.V.; Kyparos, A.; Nikolaidis, M.G. N-acetylcysteine supplementation increases exercise performance and reduces oxidative stress only in individuals with low levels of glutathione. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 115, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, A.; Annis, S.; Kraytsberg, Y.; Laverack, C.; Saleem, A.; Popadin, K.; Woods, D.C.; Tilly, J.L.; Khrapko, K. Amelioration of premature aging in mtDNA mutator mouse by exercise: The interplay of oxidative stress, PGC-1α, p53, and DNA damage. A hypothesis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2016, 38, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.W.; Omaye, S.T. Use of Saliva Biomarkers to Monitor Efficacy of Vitamin C in Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radak, Z.; Taylor, A.W.; Ohno, H.; Goto, S. Adaptation to exercise-induced oxidative stress: From muscle to brain. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2001, 7, 90–107. [Google Scholar]
- Zwetsloot, K.A.; Nieman, D.C.; Knab, A.; John, C.S.; Lomiwes, D.D.; Hurst, R.D.; Gillitt, N.D.; Lila, M.A. Effect of 4 weeks of high-intensity interval training on exercise performance and markers of inflammation and oxidative stress. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 839-1. [Google Scholar]
- Radak, Z.; Ishihara, K.; Tekus, E.; Varga, C.; Posa, A.; Balogh, L.; Boldogh, I.; Koltai, E. Exercise, oxidants, and antioxidants change the shape of the bell-shaped hormesis curve. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martarelli, D.; Verdenelli, M.C.; Scuri, S.; Cocchioni, M.; Silvi, S.; Cecchini, C.; Pompei, P. Effect of a Probiotic Intake on Oxidant and Antioxidant Parameters in Plasma of Athletes During Intense Exercise Training. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalickova, D.; Kotur-Stevuljevic, J.; Miljkovic, M.; Dikic, N.; Kostic-Vucicevic, M.; Andjelkovic, M.; Koricanac, V.; Djordjevic, B. Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Selected Parameters of Blood Prooxidant-Antioxidant Balance in Elite Athletes: A Double-Blind Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Hum. Kinet. 2018, 64, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprecht, M.; Bogner, S.; Schippinger, G.; Steinbauer, K.; Fankhauser, F.; Hallstroem, S.; Schuetz, B.; Greilberger, J.F. Probiotic supplementation affects markers of intestinal barrier, oxidation, and inflammation in trained men; a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2012, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibel, E.R.; Hoppeler, H. Exercise-induced maximal metabolic rate scales with muscle aerobic capacity. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Østlie, H.M.; Helland, M.H.; Narvhus, J.A. Growth and metabolism of selected strains of probiotic bacteria in milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 87, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

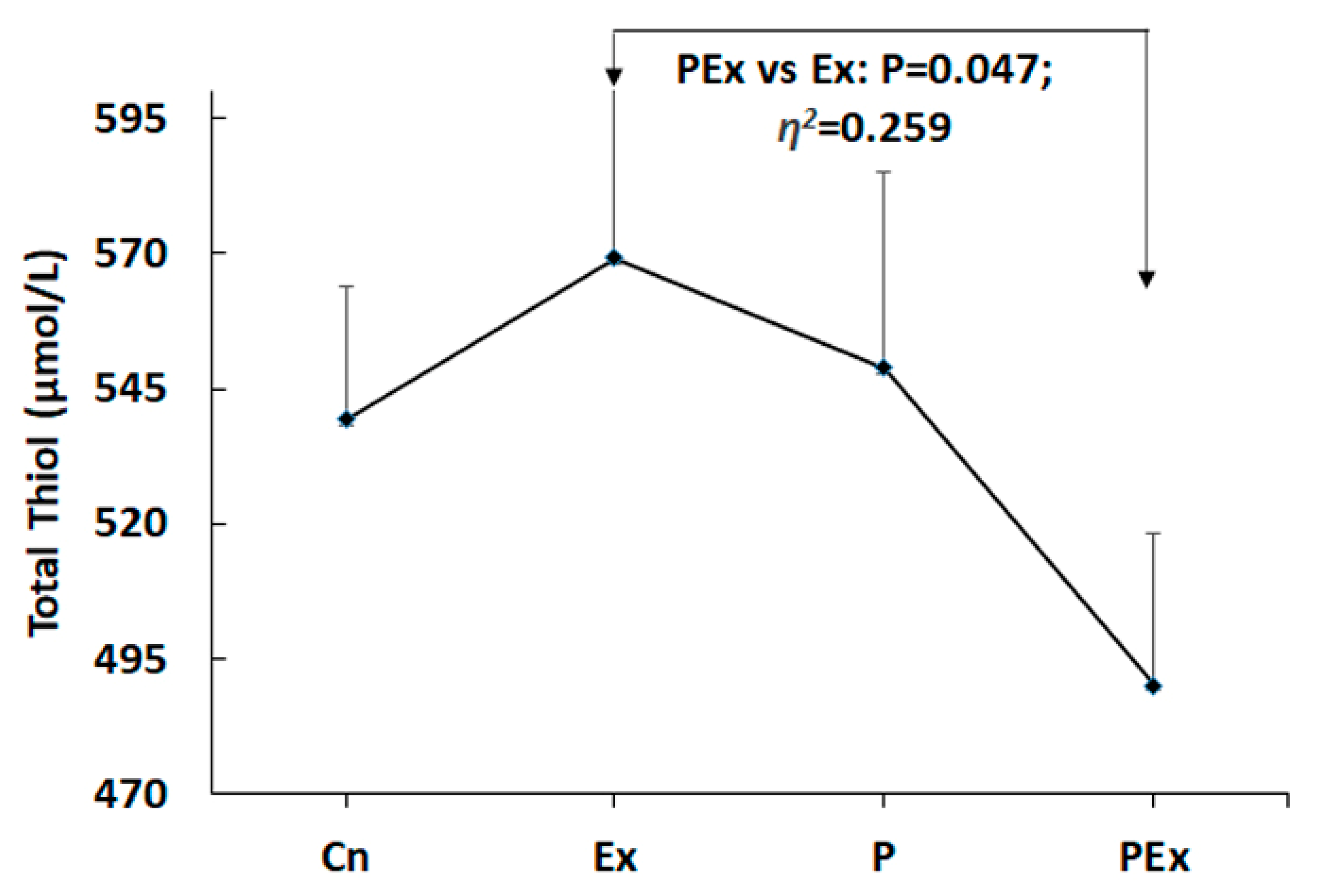
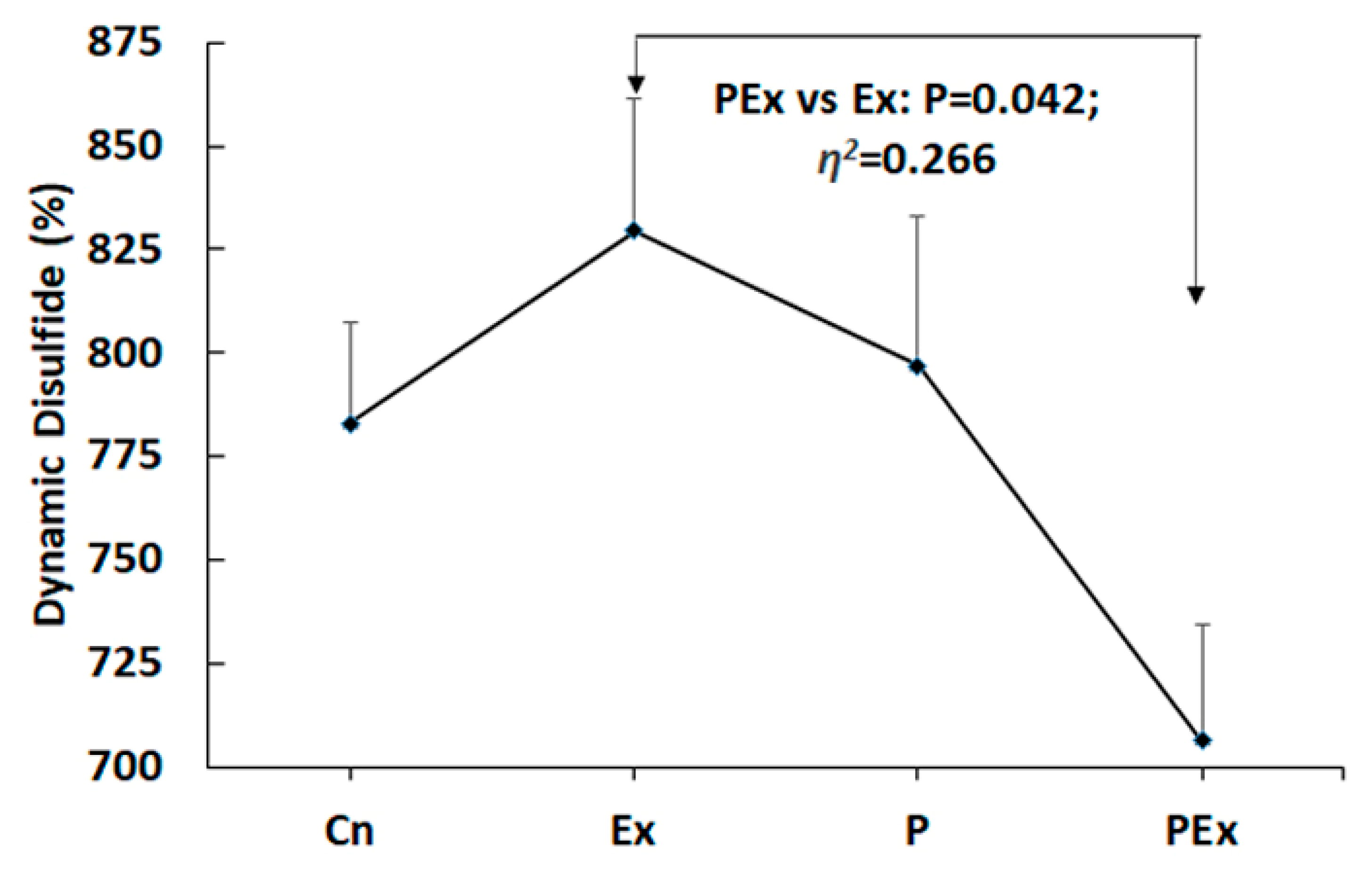
| Parameters | Group | Mean | Std.D. | SEM | Eta Squared (η2) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT (μmol/L) | Cn | 147.86 | 13.171 | 4.978 | 0.228 | NS |
| Ex | 154.57 | 9.947 | 3.760 | |||
| P | 150.43 | 17.587 | 6.647 | |||
| PEx | 137.00 | 10.893 | 4.117 | |||
| TT (μmol/L) | Cn | 539.29 | 45.474 | 17.188 | 0.259 | 0.047 |
| Ex | 569.29 | 52.261 | 19.753 | |||
| P | 548.86 | 65.162 | 24.629 | |||
| PEx | 490.14 | 47.291 | 17.874 | |||
| DD (%) | Cn | 782.86 | 65.522 | 24.765 | 0.266 | 0.042 |
| Ex | 829.43 | 85.094 | 32.162 | |||
| P | 796.86 | 96.020 | 36.292 | |||
| PEx | 706.29 | 74.220 | 28.052 | |||
| RT (%) | Cn | 27.43 | 0.535 | 0.202 | 0.129 | NS |
| Ex | 27.14 | 0.900 | 0.340 | |||
| P | 27.43 | 0.976 | 0.369 | |||
| PEx | 28.00 | 1.000 | 0.378 | |||
| OT (%) | Cn | 145.14 | 1.215 | 0.459 | 0.187 | NS |
| Ex | 145.71 | 1.890 | 0.714 | |||
| P | 145.00 | 1.291 | 0.488 | |||
| PEx | 143.86 | 1.574 | 0.595 | |||
| TOR (%) | Cn | 18.86 | 0.690 | 0.261 | 0.074 | NS |
| Ex | 18.86 | 0.690 | 0.261 | |||
| P | 18.86 | 0.690 | 0.261 | |||
| PEx | 19.29 | 0.756 | 0.286 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kayacan, Y.; Kola, A.Z.; Guandalini, S.; Yazar, H.; Söğüt, M.Ü. The Use of Probiotics Combined with Exercise Affects Thiol/Disulfide Homeostasis, an Oxidative Stress Parameter. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173555
Kayacan Y, Kola AZ, Guandalini S, Yazar H, Söğüt MÜ. The Use of Probiotics Combined with Exercise Affects Thiol/Disulfide Homeostasis, an Oxidative Stress Parameter. Nutrients. 2022; 14(17):3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173555
Chicago/Turabian StyleKayacan, Yıldırım, Aybike Zeynep Kola, Stefano Guandalini, Hayrullah Yazar, and Mehtap Ünlü Söğüt. 2022. "The Use of Probiotics Combined with Exercise Affects Thiol/Disulfide Homeostasis, an Oxidative Stress Parameter" Nutrients 14, no. 17: 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173555
APA StyleKayacan, Y., Kola, A. Z., Guandalini, S., Yazar, H., & Söğüt, M. Ü. (2022). The Use of Probiotics Combined with Exercise Affects Thiol/Disulfide Homeostasis, an Oxidative Stress Parameter. Nutrients, 14(17), 3555. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173555







