Role of Vitamin K in Selected Malignant Neoplasms in Women
Abstract
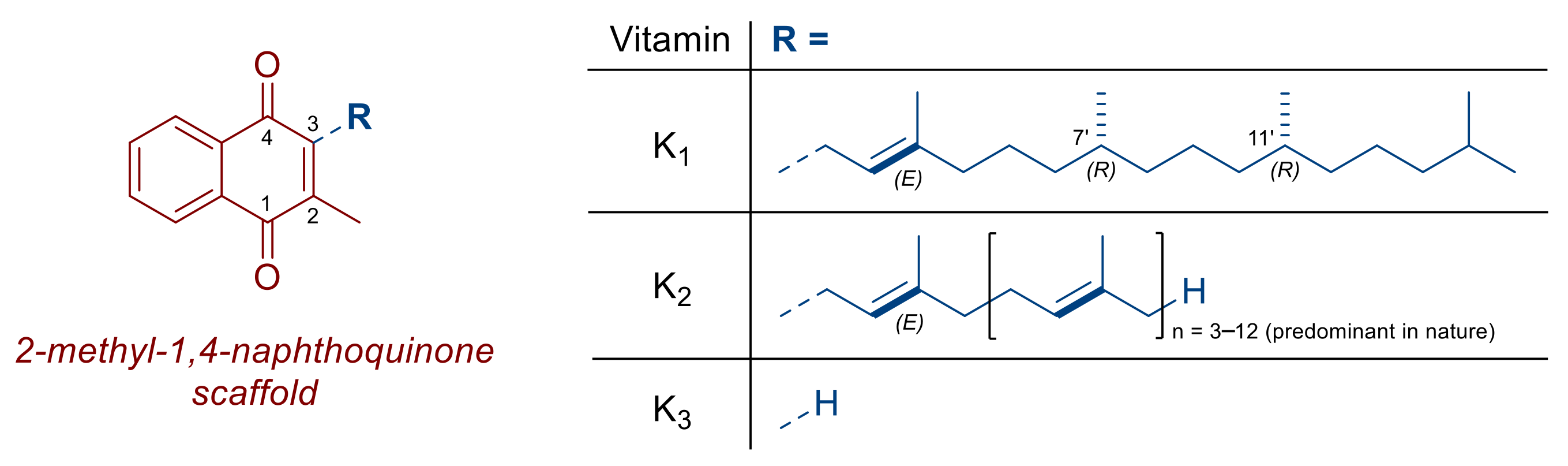
:1. Introduction
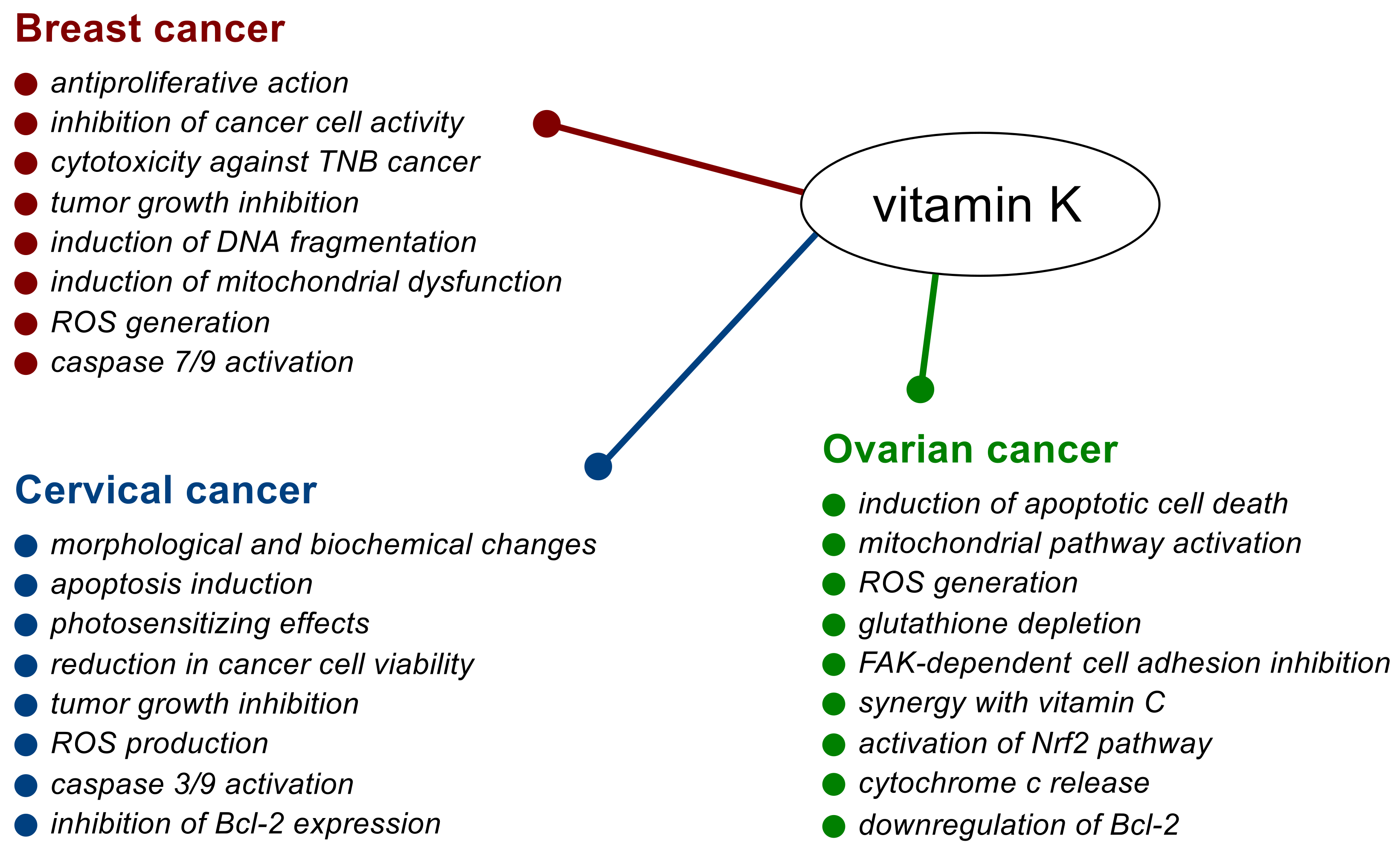
Anticancer Mechanism of Action
| Cancer Type | Active Form of Vitamin K | Cancer Cell Lines Sensitive to the Action of Vitamin K | Optimal Concentration | Combination Treatment/In Vivo Studies | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast cancer | K2 | Hs578T, SUM159PT | 5 μg mL−1 (supplemented medium) | [30] | |
| K2 (MK-4) | BT-474, MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-468 | 10–25 μM (supplemented medium) | [31] | ||
| K2 (MK-4) | MDA-MB-231 | 124.4 µM (IC50) | low-glucose medium (5.5 mM) | [32] | |
| K3 | BT-474, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, SK-BR3 | 11.3–25.1 µM (IC50) | in vivo studies | [33] | |
| K3 | MCF-7 | 14.2 μM (IC50) | [34] | ||
| Cervical cancer | K3 | SiHa (HPV-16 positive) | 10.8 µM (IC50) 21.7 µM (IC90) | [35] | |
| K3 | HeLa, SiHa | ultraviolet radiation A + in vivo studies | [36] | ||
| Ovarian cancer | K2 (MK-4) | PA-1, TYK-nu | 5.0–73.0 µM (IC50) | [37] | |
| K2 (MK-4) | TYK-nu | 73.0 µM (IC50) | [38] | ||
| K3 | OVCAR-3, SK-OV-3 | 7.5 µM (~59% cell death) | [39] | ||
| K3 (menadione bisulfite) | MDAH 2774, CAOV-3, ES-2 | 22.0–41.8 µM (CD50) | vitamin C | [40] | |
| K3 (menadione bisulfite) | MDAH 2774 | 20.3 µM (supplemented medium) | vitamin C | [41] | |
| K3 | SK-OV-3 | 20.0 µM (80% inhibition rate) | [42] |
2. Breast Cancer
2.1. In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
2.2. Effects in Cancer Patients
3. Cervical Cancer
3.1. In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
3.2. Effects in Cancer Patients
4. Ovarian Cancer
In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ball, G.F.M. Vitamins: Their Role in the Human Body, 1st ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sakano, T.; Notsumoto, S.; Nagaoka, T.; Morimoto, A.; Fujimoto, K.; Masuda, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Hirauchi, K. Measurement of K vitamins in food by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorometric detection. Vitamins 1988, 62, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirauchi, K.; Sakano, T.; Notsumoto, S.; Nagaoka, T.; Morimoto, A.; Fujimoto, K.; Masuda, S.; Suzuki, Y. Measurement of K vitamins in foods by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorometric detection. Vitamins 1989, 63, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, M.J.; Bach, A.; Kohlmeier, M. Chemistry, nutritional sources, tissue distribution and metabolism of vitamin K with special reference to bone health. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 1181S–1186S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gröber, U.; Reichrath, J.; Holick, M.; Kisters, K. Vitamin K: An old vitamin in a new perspective. Dermato-Endocrinology 2014, 6, e968490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalfenberg, G.K. Vitamins K1 and K2: The emerging group of vitamins required for human health. J. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 2017, 6254836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbulut, A.C.; Pavlic, A.; Petsophonsakul, P.; Halder, M.; Maresz, K.; Kramann, R.; Schurgers, L. Vitamin K2 needs an RDI separate from vitamin K1. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlberg, S.; Ede, J.; Schött, U. Vitamin K and cancer. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2017, 77, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, M.; Petsophonsakul, P.; Akbulut, A.; Pavlic, A.; Bohan, F.; Anderson, E.; Maresz, K.; Kramann, R.; Schurgers, L. Vitamin K: Double bonds beyond coagulation insights into differences between vitamin K1 and K2 in health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, Q.; Li, Z.; Reger, M.K.; Xiong, Y.; Zhong, G.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Foukakis, T.; et al. Vitamin K intake and breast cancer incidence and death: Results from a prospective cohort study. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3370–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C.R.; Bellinge, J.W.; Dalgaard, F.; Sim, M.; Murray, K.; Connolly, E.; Blekkenhorst, L.C.; Bondonno, C.P.; Croft, K.D.; Gislason, G.; et al. Association between vitamin K1 intake and mortality in the Danish Diet, Cancer, and Health cohort. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 36, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.W.; Li, Q.J.; Cheng, L.; Yang, P.F.; Sun, W.P.; Peng, Y.; Hu, J.J.; Wu, J.J.; Gong, J.P.; Zhong, G.C. Dietary vitamin K intake and the risk of pancreatic cancer: A prospective study of 101,695 American adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 190, 2029–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimptsch, K.; Rohrmann, S.; Kaaks, R.; Linseisen, J. Dietary vitamin K intake in relation to cancer incidence and mortality: Results from the Heidelberg cohort of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC-Heidelberg). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, M.; Reger, M.; Marley, A.; Fan, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J. Vitamin K intake and prostate cancer risk in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer (PLCO) Screening Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruna, Y.; Yakushijin, T.; Kawamoto, S. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib plus vitamin K treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase II, randomized study. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibayama-Imazu, T.; Aiuchi, T.; Nakaya, K. Vitamin K2-mediated apoptosis in cancer cells: Role of mitochondrial transmembrane potential. Vitam. Horm. 2008, 78, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xv, F.; Chen, J.; Duan, L.; Li, S. Research progress on the anticancer effects of Vitamin K2. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 8926–8934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Samy, A.L.P.A.; Kajdacsy-Balla, A.; Bosland, M.C.; Munirathinam, G. Vitamin K2, a menaquinone present in dairy products targets castration-resistant prostate cancer cell-line by activating apoptosis signaling. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 115, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, C.; Sundaram, S.; Karunagaran, D. Vitamin K3 (menadione) suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal-transition and Wnt signaling pathway in human colorectal cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 309, 108725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasawa, S.; Azuma, M.; Kasama, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Kabe, Y.; Imai, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Miyazawa, K.; Handa, H. Vitamin K2 covalently binds to Bak and induces Bak-mediated apoptosis. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 83, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibayama-Imazu, T.; Sonoda, I.; Sakairi, S.; Aiuchi, T.; Ann, W.; Nakajo, S.; Itabe, H.; Nakaya, K. Production of superoxide and dissipation of mitochondrial transmembrane potential by vitamin K2 trigger apoptosis in human ovarian cancer TYK-nu cells. Apoptosis 2006, 11, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujioka, T.; Miura, Y.; Otsuki, T.; Nishimura, Y.; Hyodoh, F.; Wada, H.; Sugihara, T. The mechanisms of vitamin K2-induced apoptosis of myeloma cells. Haematologica 2006, 91, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, I.; Zhang, H.; Mizuta, T.; Ide, Y.; Eguchi, Y.; Yasutake, T.; Sakamaki, T.; Pestell, R.G.; Yamamoto, K. Menatetrenone, a vitamin K2 analogue, inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth by suppressing cyclin D1 expression through inhibition of nuclear factor κB activation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2236–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amalia, H.; Sasaki, R.; Suzuki, Y.; Demizu, Y.; Bito, T.; Nishimura, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Miyawaki, D.; Kawabe, T.; et al. Vitamin K2-derived compounds induce growth inhibition in radioresistant cancer cells. Kobe J. Med. Sci. 2010, 56, E38–E49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duan, F.; Mei, C.; Yang, L.; Zheng, J.; Lu, H.; Xia, Y.; Hsu, S.; Liang, H.; Hong, L. Vitamin K2 promotes PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α-mediated glycolysis that leads to AMPK-dependent autophagic cell death in bladder cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Ma, P.; Kong, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L. Vitamin K2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by binding to 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 4. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 757603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowska, A.; Antoszczak, M.; Kojs, Z.; Bednarek, W.; Markowska, J.; Huczyński, A. Role of vitamin D3 in selected malignant neoplasms. Nutrition 2020, 79–80, 110964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowska, A.; Antoszczak, M.; Markowska, J.; Huczyński, A. Role of vitamin E in selected malignant neoplasms in women. Nutr. Cancer 2022, 74, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowska, A.; Antoszczak, M.; Markowska, J.; Huczyński, A. Role of vitamin C in selected malignant neoplasms in women. Nutrients 2022, 14, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudin, S.; Kokabee, L.; Welsh, J. Divergent effects of vitamins K1 and K2 on triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2292–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazawa, S.; Moriya, S.; Kokuba, H.; Hino, H.; Takano, N.; Miyazawa, K. Vitamin K2 induces non-apoptotic cell death along with autophagosome formation in breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer 2020, 27, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiely, M.; Hodgins, S.J.; Merrigan, B.A.; Tormey, S.; Kiely, P.A.; O’Connor, E.M. Real-time cell analysis of the inhibitory effect of vitamin K2 on adhesion and proliferation of breast cancer cells. Nutr. Res. 2015, 35, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, A.; Osada, S.; Tanahashi, T.; Matsui, S.; Sasaki, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Okumura, N.; Matsuhashi, N.; Takahashi, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; et al. Novel therapy for locally advanced triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyoshi, T.; Matzno, S.; Sakai, M.; Okamura, N.; Matsuyama, K. The potential of vitamin K3 as an anticancer agent against breast cancer that acts via the mitochondria-related apoptotic pathway. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2009, 65, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho Scharf Santana, N.; Lima, N.A.; Desoti, V.C.; Bidóia, D.L.; de Souza Bonfim Mendonça, P.; Ratti, B.A.; Nakamura, T.U.; Nakamura, C.V.; Consolaro, M.E.L.; Ximenes, V.F.; et al. Vitamin K3 induces antiproliferative effect in cervical epithelial cells transformed by HPV 16 (SiHa cells) through the increase in reactive oxygen species production. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2016, 294, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Guo, W.; Yang, C.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, G. Photodynamic effects of vitamin K3 on cervical carcinoma cells activating mitochondrial apoptosis pathways. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 21, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibayama-Imazu, T.; Fujisawa, Y.; Masuda, Y.; Aiuchi, T.; Nakajo, S.; Itabe, H.; Nakaya, K. Induction of apoptosis in PA-1 ovarian cancer cells by vitamin K2 is associated with an increase in the level of TR3/Nur77 and its accumulation in mitochondria and nuclei. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 134, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibayama-Imazu, T.; Sakairi, S.; Watanabe, A.; Aiuchi, T.; Nakajo, S.; Nakaya, K. Vitamin K2 selectively induced apoptosis in ovarian TYK-nu and pancreatic MIA PaCa-2 cells out of eight solid tumor cell lines through a mechanism different from geranylgeraniol. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 129, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Shin, Y.K.; Sohn, D.S.; Lee, C.S. Menadione induces the formation of reactive oxygen species and depletion of GSH-mediated apoptosis and inhibits the FAK-mediated cell invasion. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2014, 387, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Gruenigen, V.E.; Jamison, J.M.; Gilloteaux, J.; Lorimer, H.E.; Summers, M.; Pollard, R.R.; Gwin, C.A.; Summers, J.L. The in vitro antitumor activity of vitamins C and K3 against ovarian carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2003, 23, 3279–3287. [Google Scholar]
- Gilloteaux, J.; Jamison, J.M.; Arnold, D.; Taper, H.S.; von Gruenigen, V.E.; Summers, J.L. Microscopic aspects of autoschizic cell death in human ovarian carcinoma (2774) cells following vitamin C, vitamin K3 or vitamin C: K3 treatment. Microsc. Microanal. 2003, 9, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Yan, X.; Zhou, L.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Yi, H.; Su, J. P62 suppressed VK3-induced oxidative damage through Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in human ovarian cancer cells. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.R.; Liao, W.S.; Wu, Y.H.; Murugan, K.; Chen, C.; Chao, J.I. CR108, a novel vitamin K3 derivative induces apoptosis and breast tumor inhibition by reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial dysfunction. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 273, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellington, K.W.; Hlatshwayo, V.; Kolesnikova, N.I.; Saha, S.T.; Kaur, M.; Motadi, L.R. Anticancer activities of vitamin K3 analogues. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Carr, B.I. Growth inhibition and protein tyrosine phosphorylation in MCF 7 breast cancer cells by a novel K vitamin. J. Cell. Physiol. 2000, 185, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrad Nasab, M.; Afsharfar, M.; Ahmadzadeh, M.; Vahid, F.; Gholamalizadeh, M.; Abbastorki, S.; Davoodi, S.H.; Majidi, N.; Akbari, M.E.; Doaei, S. Comparison of the index of nutritional quality in breast cancer patients with healthy women. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 811827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbyn, M.; Weiderpass, E.; Bruni, L.; de Sanjosé, S.; Saraiya, M.; Ferlay, J.; Bray, F. Estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: A worldwide analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e191–e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, A.; Koshiyama, M.; Nakagawa, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Ikuta, E.; Seki, K.; Oowaki, M. The preventive effect of dietary antioxidants on cervical cancer development. Medicina 2020, 56, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, A.; Yang, J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Song, J.; Li, L.; Lv, W.; et al. Dietary nutrient intake related to higher grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia risk: A Chinese population-based study. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 17, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.K.; Alvarez, R.D.; Bakkum-Gamez, J.N.; Barroilhet, L.; Behbakht, K.; Berchuck, A.; Chen, L.; Cristea, M.; DeRosa, M.; Eisenhauer, E.L.; et al. Ovarian Cancer, Version 2.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 191–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nagell, J.R.; Burgess, B.T.; Miller, R.W.; Baldwin, L.; DeSimone, C.P.; Ueland, F.R.; Huang, B.; Chen, Q.; Kryscio, R.J.; Pavlik, E.J. Survival of women with type I and II epithelial ovarian cancer detected by ultrasound screening. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 132, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tossetta, G.; Marzioni, D. Natural and synthetic compounds in ovarian cancer: A focus on NRF2/KEAP1 pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 183, 106365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.L.; Fu, X.; Karl, J.P.; Hernandez, C.J.; Mason, J.B.; DeBose-Boyd, R.A.; Booth, S.L. Multiple dietary vitamin K forms are converted to tissue menaquinone-4 in mice. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markowska, A.; Antoszczak, M.; Markowska, J.; Huczyński, A. Role of Vitamin K in Selected Malignant Neoplasms in Women. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3401. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163401
Markowska A, Antoszczak M, Markowska J, Huczyński A. Role of Vitamin K in Selected Malignant Neoplasms in Women. Nutrients. 2022; 14(16):3401. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163401
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkowska, Anna, Michał Antoszczak, Janina Markowska, and Adam Huczyński. 2022. "Role of Vitamin K in Selected Malignant Neoplasms in Women" Nutrients 14, no. 16: 3401. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163401
APA StyleMarkowska, A., Antoszczak, M., Markowska, J., & Huczyński, A. (2022). Role of Vitamin K in Selected Malignant Neoplasms in Women. Nutrients, 14(16), 3401. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163401








