Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and High Triglyceride Levels Mediate the Association between Pre-Pregnancy Overweight/Obesity and Macrosomia: A Prospective Cohort Study in Central China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
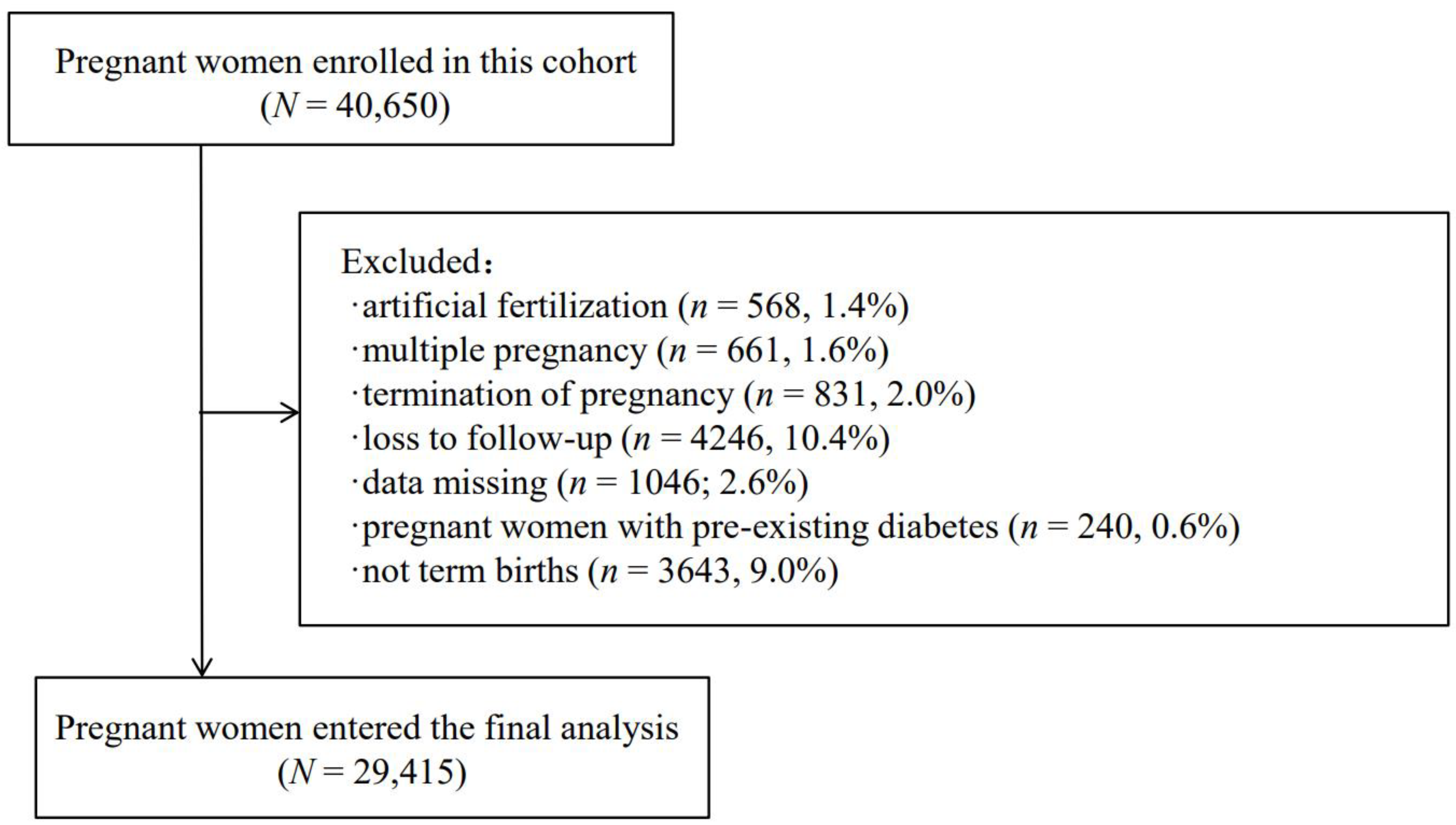
2.1. Research Design and Study Population
2.2. Exposure
2.3. Outcome
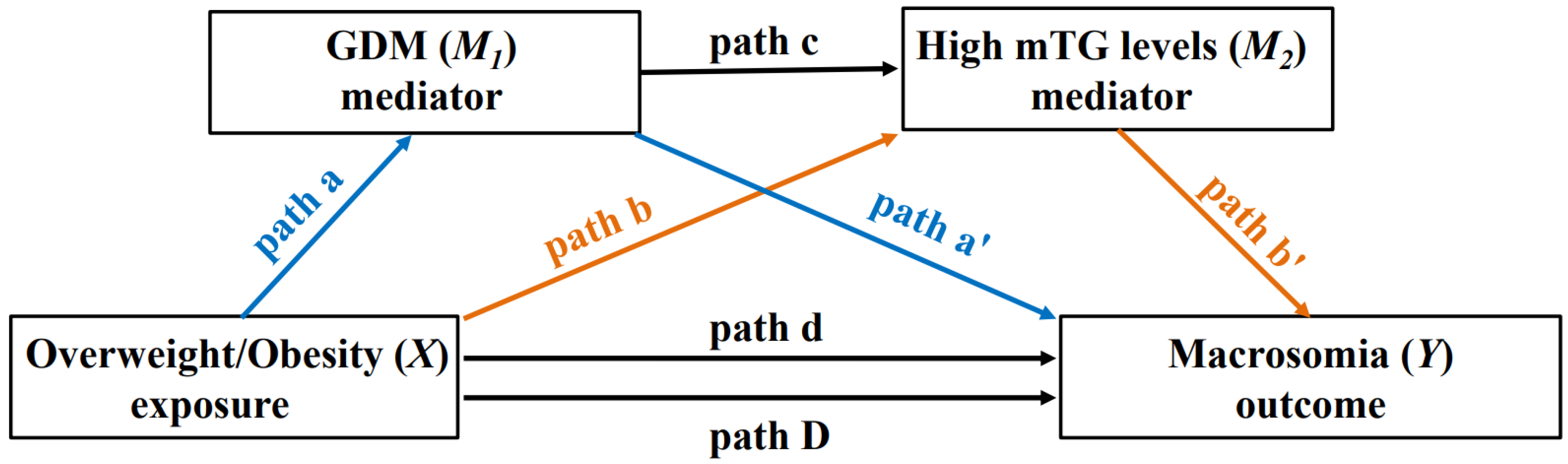
2.4. Mediator
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Prevalence of High mTG Levels, GDM and Fetal Macrosomia in Each BMI Group
3.3. The Testing for Significance of Paths a, a′, b, b′, c, and D
3.4. Mediation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Category | Total Effect (95% CI) | Direct Effect (95% CI) | Indirect Effect (95% CI) | Mediated Proportion, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overweight | 0.009 (0.005–0.013) *** | 0.008 (0.004, 0.012) *** | 0.001 (0.001, 0.002) *** | 11.1 |
| Obese | 0.038 (0.030–0.046) *** | 0.037 (0.028–0.045) *** | 0.002 (0.001–0.002) *** | 5.3 |
References
- Wang, L.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z.; et al. Body-mass index and obesity in urban and rural China: Findings from consecutive nationally representative surveys during 2004–18. Lancet 2021, 398, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.E.; Lowe, L.P.; Dyer, A.R.; Trimble, E.R.; Chaovarindr, U.; Coustan, D.R.; Hadden, D.R.; McCance, D.R.; Hod, M.; McIntyre, H.D.; et al. Hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vidakovic, A.J.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Gishti, O.; Felix, J.F.; Williams, M.A.; Hofman, A.; Demmelmair, H.; Koletzko, B.; Tiemeier, H.; Gaillard, R. Body mass index, gestational weight gain and fatty acid concentrations during pregnancy: The Generation R Study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 30, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Moore, D.; Subramanian, A.; Cheng, K.K.; Toulis, K.A.; Qiu, X.; Saravanan, P.; Price, M.J.; Nirantharakumar, K. Gestational dyslipidaemia and adverse birthweight outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cnattingius, S.; Villamor, E.; Lagerros, Y.T.; Wikström, A.K.; Granath, F. High birth weight and obesity—A vicious circle across generations. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 1320–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxley, R.; Owen, C.G.; Whincup, P.H.; Cook, D.G.; Rich-Edwards, J.; Smith, G.D.; Collins, R. Is birth weight a risk factor for ischemic heart disease in later life? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoet, J.J.; Hanson, M.A. Intrauterine nutrition: Its importance during critical periods for cardiovascular and endocrine development. J. Physiol. 1999, 514 Pt 3, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, L.A.; Hernandez, T.L. Maternal Lipids and Fetal Overgrowth: Making Fat from Fat. Clin. Ther. 2018, 40, 1638–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, R.H.; Magee, M.S.; Walden, C.E.; Bonet, B.; Benedetti, T.J. Prediction of infant birth weight by GDM screening tests. Importance of plasma triglyceride. Diabetes Care 1992, 15, 1605–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, C.J.; Riley, S.F.; Sheedy, M.T.; Walstab, J.E.; Beischer, N.A. Maternal serum triglyceride, glucose tolerance, and neonatal birth weight ratio in pregnancy. Diabetes Care 1995, 18, 1550–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freinkel, N. Banting Lecture 1980: Of pregnancy and progeny. Diabetes 1980, 29, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondracki, A.J.; Valente, M.J.; Ibrahimou, B.; Bursac, Z. Risk of large for gestational age births at early, full and late term in relation to pre-pregnancy body mass index: Mediation by gestational diabetes status. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2022, 36, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Fu, Y.; Wu, Y.Y.; Mao, A.F.; Xu, M.Y.; Zheng, G.; Cai, F.C.; Wang, X.H.; Shi, M.Q.; Hu, W.S. Mediating Effects of Maternal Blood Triglycerides on the Relationship between Prepregnancy Body Mass Index and Fetal Macrosomia. J. Pediatr. 2020, 226, 118–122.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryckman, K.K.; Spracklen, C.N.; Smith, C.J.; Robinson, J.G.; Saftlas, A.F. Maternal lipid levels during pregnancy and gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG 2015, 122, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ACOG Practice Bulletin. Clinical management guidelines for obstetrician-gynecologists. Number 30, September 2001 (replaces Technical Bulletin Number 200, December 1994). Gestational diabetes. Obstet. Gynecol. 2001, 98, 525–538. [Google Scholar]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Criteria of Weight for Adults. 2013. Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/ewebeditor/uploadfile/2013/08/20130808135715967 (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- ACOG Committee opinion no. 549: Obesity in pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 121, 213–217.
- Committee Opinion No 700: Methods for Estimating the Due Date. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 129, e150–e154. [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.E.; Gabbe, S.G.; Persson, B.; Buchanan, T.A.; Catalano, P.A.; Damm, P.; Dyer, A.R.; Leiva, A.; Hod, M.; Kitzmiler, J.L.; et al. International association of diabetes and pregnancy study groups recommendations on the diagnosis and classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.F.; Wang, H.; Wu, D.D.; Zhang, J.L.; Gao, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.X. The Impact of Gestational Weight Gain on the Risks of Adverse Maternal and Infant Outcomes among Normal BMI Women with High Triglyceride Levels during Early Pregnancy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.H.; Wu, D.D.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.J.; Gao, L.; Lass, G.; Zhang, J.; Tian, S.; Ivanova, D.; Tang, L.; et al. Maternal High Triglyceride Levels During Early Pregnancy and Risk of Preterm Delivery: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, R.X.; He, X.J.; Hu, C.L. The Association between Advanced Maternal Age and Macrosomia: A Meta-Analysis. Child. Obes. 2019, 15, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Farsi, Y.M.; Brooks, D.R.; Werler, M.M.; Cabral, H.J.; Al-Shafaee, M.A.; Wallenburg, H.C. Effect of high parity on occurrence of some fetal growth indices: A cohort study. Int. J. Women’s Health 2012, 4, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.K.; Rai, M.; Rehkopf, D.H.; Abrams, B. Educational attainment and obesity: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 989–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Uitert, E.M.; van der Elst-Otte, N.; Wilbers, J.J.; Exalto, N.; Willemsen, S.P.; Eilers, P.H.; Koning, A.H.; Steegers, E.A.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P. Periconception maternal characteristics and embryonic growth trajectories: The Rotterdam Predict study. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 3188–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.F.; Abell, S.K.; Ranasinha, S.; Misso, M.; Boyle, J.A.; Black, M.H.; Li, N.; Hu, G.; Corrado, F.; Rode, L.; et al. Association of Gestational Weight Gain With Maternal and Infant Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA 2017, 317, 2207–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, R.F.; Abell, S.K.; Ranasinha, S.; Misso, M.L.; Boyle, J.A.; Harrison, C.L.; Black, M.H.; Li, N.; Hu, G.; Corrado, F.; et al. Gestational weight gain across continents and ethnicity: Systematic review and meta-analysis of maternal and infant outcomes in more than one million women. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.M.; McAuliffe, F.M. Prediction and prevention of the macrosomic fetus. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2012, 162, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.M.; Kenny, D.A. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1986, 51, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeri, L.; Vanderweele, T.J. Mediation analysis allowing for exposure-mediator interactions and causal interpretation: Theoretical assumptions and implementation with SAS and SPSS macros. Psychol. Methods 2013, 18, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhnke, J.R. Explanation in causal inference: Methods for mediation and interaction. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2016, 69, 1243–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z. Monte Carlo based statistical power analysis for mediation models: Methods and software. Behav. Res. Methods 2014, 46, 1184–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, E.; Ortega-Senovilla, H. Disturbances in lipid metabolism in diabetic pregnancy—Are these the cause of the problem? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 24, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiefari, E.; Arcidiacono, B.; Foti, D.; Brunetti, A. Gestational diabetes mellitus: An updated overview. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, J. Weight and length at birth of infants of diabetic mothers. Acta Endocrinol. 1954, 16, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Shu, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Diao, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wei, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, M.; et al. Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index and Risk of Macrosomia and Large for Gestational Age Births with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus as a Mediator: A Prospective Cohort Study in Central China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, K.S.; Stetzer, B.; Catalano, P.M.; Myers, S.A. Comparison of 2- and 3-Dimensional Sonography for Estimation of Birth Weight and Neonatal Adiposity in the Setting of Suspected Fetal Macrosomia. J. Ultrasound Med. 2016, 35, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Poppel, M.N.; Desoye, G. Growing fat in utero: Timing is everything. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, G.R.; Deepa, R. Do Gestational Obesity and Gestational Diabetes Have an Independent Effect on Neonatal Adiposity? Results of Mediation Analysis from a Cohort Study in South India. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poprzeczny, A.J.; Louise, J.; Deussen, A.R.; Dodd, J.M. The mediating effects of gestational diabetes on fetal growth and adiposity in women who are overweight and obese: Secondary analysis of the LIMIT randomised trial. BJOG 2018, 125, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, C.A.; Hiller, J.E.; Moss, J.R.; McPhee, A.J.; Jeffries, W.S.; Robinson, J.S. Effect of treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus on pregnancy outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 2477–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landon, M.B.; Spong, C.Y.; Thom, E.; Carpenter, M.W.; Ramin, S.M.; Casey, B.; Wapner, R.J.; Varner, M.W.; Rouse, D.J.; Thorp, J.M., Jr.; et al. A multicenter, randomized trial of treatment for mild gestational diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Hinkle, S.N.; Grantz, K.L.; Kim, S.; Grewal, J.; Grobman, W.A.; Skupski, D.W.; Newman, R.B.; Chien, E.K.; Sciscione, A.; et al. Glycaemic status during pregnancy and longitudinal measures of fetal growth in a multi-racial US population: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovio, U.; Murphy, H.R.; Smith, G.C. Accelerated Fetal Growth Prior to Diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Prospective Cohort Study of Nulliparous Women. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiefari, E.; Quaresima, P.; Visconti, F.; Mirabelli, M.; Brunetti, A. Gestational diabetes and fetal overgrowth: Time to rethink screening guidelines. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 561–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.R.; Kumaran, K.; Rao, S.R.; Chougule, S.D.; Deokar, T.M.; Bhalerao, A.J.; Solat, V.A.; Bhat, D.S.; Fall, C.H.; Yajnik, C.S. Maternal lipids are as important as glucose for fetal growth: Findings from the Pune Maternal Nutrition Study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2706–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Sun, M.; Shu, J.; Wang, T.; Qin, J. High Maternal Triglyceride Levels Mediate the Association between Pre-Pregnancy Overweight/Obesity and Macrosomia among Singleton Term Non-Diabetic Pregnancies: A Prospective Cohort Study in Central China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.J.; Montelongo, A.; Iglesias, A.; Lasunción, M.A.; Herrera, E. Longitudinal study on lipoprotein profile, high density lipoprotein subclass, and postheparin lipases during gestation in women. J. Lipid Res. 1996, 37, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duttaroy, A.K. Transport of fatty acids across the human placenta: A review. Prog. Lipid Res. 2009, 48, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos, P.R.; Rigotti, A.; Busso, D.; Berkowitz, L.; Santos, J.L.; Borzone, G.R.; Poblete, J.A.; Vera, C.; Belmar, C.; Goldenberg, D.; et al. Maternal hypertriglyceridemia: A link between maternal overweight-obesity and macrosomia in gestational diabetes. Obesity 2014, 22, 2156–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Woestijne, A.P.; Monajemi, H.; Kalkhoven, E.; Visseren, F.L. Adipose tissue dysfunction and hypertriglyceridemia: Mechanisms and management. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total Births n (%) | GDM n (%) | High mTG n (%) | Macrosomia n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 29,415 | 4685 (15.9) | 3008 (10.2) | 1271 (4.3) | |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | ||||
| Underweight (<18.5) | 4153 (14.1) | 372 (7.9) | 318 (10.6) | 117 (9.2) |
| Normal (18.5–23.9) | 20,785 (70.7) | 3192 (68.1) | 2098 (69.7) | 816 (64.2) |
| Overweight (24.0–27.9) | 3699 (12.6) | 877 (18.7) | 478 (15.9) | 217 (17.1) |
| Obese (≥28.0) | 778 (2.6) | 244 (5.2) | 114 (3.8) | 121 (9.5) |
| Age at pregnancy onset (year) | ||||
| <25 | 1451 (4.9) | 100 (2.1) | 142 (4.7) | 68 (5.4) |
| 25–29 | 10,335 (35.1) | 1232 (26.3) | 839 (27.9) | 445 (35.0) |
| 30–34 | 11,145 (37.9) | 1897 (40.5) | 1123 (37.3) | 490 (38.6) |
| ≥35 | 6484 (22.0) | 1456 (31.1) | 904 (30.1) | 268 (21.1) |
| Education | ||||
| High school or less | 10,179 (34.6) | 1554 (33.2) | 1108 (36.8) | 436 (34.3) |
| Some college | 15,202 (51.7) | 2515 (53.7) | 1579 (52.5) | 668 (52.6) |
| Bachelor’s or higher | 4034 (13.7) | 616 (13.1) | 321 (10.7) | 167 (13.1) |
| Smoke | ||||
| No | 29,124 (99.0) | 4648 (99.2) | 2981 (99.1) | 1257 (98.9) |
| Yes | 291 (1.0) | 37 (0.8) | 27 (0.9) | 14 (1.1) |
| Drink | ||||
| No | 28,958 (98.4) | 4605 (98.3) | 2950 (98.1) | 1253 (98.6) |
| Yes | 457 (1.6) | 80 (1.7) | 58 (1.9) | 18 (1.4) |
| Parity | ||||
| Primipara | 14,236 (48.4) | 2148 (45.8) | 1388 (46.1) | 600 (47.2) |
| Multipara | 15,179 (51.6) | 2537 (54.2) | 1620 (53.9) | 671 (52.8) |
| Infant sex | ||||
| Male | 15,582 (53.0) | 2398 (51.2) | 1609 (53.5) | 822 (64.7) |
| Female | 13,833 (47.0) | 2287 (48.8) | 1399 (46.5) | 449 (35.3) |
| Gestational weight gain (kg) | ||||
| <10 | 4478 (15.2) | 1105 (23.6) | 506 (16.8) | 120 (9.4) |
| 10–20 | 21,630 (73.5) | 3277 (69.9) | 2134 (70.9) | 907 (71.4) |
| ≥20 | 3307 (11.2) | 303 (6.5) | 368 (12.2) | 244 (19.2) |
| Gestational hypertension | ||||
| No | 28,473 (96.8) | 4523 (96.5) | 2916 (96.9) | 1243 (97.8) |
| Yes | 942 (3.2) | 162 (3.5) | 92 (3.1) | 28 (2.2) |
| Category | GDM % (95% CI) | High mTG % (95% CI) | Macrosomia % (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Underweight (<18.5) | 9.0 (0.81–0.98) | 7.7 (6.8–8.5) | 2.8 (2.3–3.3) |
| Normal (18.5–23.9) | 15.4 (14.9–15.8) | 10.1 (9.7–10.5) | 3.9 (3.7–4.2) |
| Overweight (24.0–27.9) | 23.7 (22.3–25.1) | 12.9 (11.8–14.0) | 5.9 (5.1–6.6) |
| Obese (≥28.0) | 31.4 (28.1–34.6) | 14.7 (12.2–17.1) | 15.6 (13.0–18.1) |
| Category | Path a aRR (95%CI) a | Path a′ aRR (95%CI) b | Path b aRR (95%CI) c | Path b′ aRR (95%CI) d | Path c aRR (95%CI) e | Path D aRR (95%CI) f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overweight | 1.56 (1.43–1.70) | 1.66 (1.42–1.93) | 1.20 (1.08–1.34) | 2.93 (2.52–3.41) | 1.89 (1.71–2.08) | 1.56 (1.33–1.83) |
| Obese | 2.09 (1.78–2.45) | 1.79 (1.53–2.10) | 1.32 (1.07–1.62) | 2.46 (2.08–2.90) | 1.94 (1.74–2.15) | 5.19 (4.17–6.46) |
| Category | Total Effect (95% CI) | Direct Effect (95% CI) | Indirect Effect (95% CI) | Mediated Proportion, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overweight | 0.009 (0.006–0.013) *** | 0.008 (0.004–0.012) *** | 0.001 (0.001–0.002) *** | 11.1 |
| Obese | 0.038 (0.030–0.047) *** | 0.037 (0.028–0.045) *** | 0.002 (0.001–0.002) *** | 5.3 |
| Category | X_M1_Y (95% CI) | X_M2_Y (95% CI) | X_M1_M2_Y (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overweight | 0.001 (0.000, 0.001) *** | 0.001 (0.000, 0.001) *** | 0.000 (0.000, 0.000) ** |
| Obese | 0.001 (0.001, 0.002) *** | 0.001 (0.000, 0.001) ** | 0.000 (0.000, 0.000) * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Wang, T.; Qin, J. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and High Triglyceride Levels Mediate the Association between Pre-Pregnancy Overweight/Obesity and Macrosomia: A Prospective Cohort Study in Central China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163347
Song X, Chen L, Zhang S, Liu Y, Wei J, Wang T, Qin J. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and High Triglyceride Levels Mediate the Association between Pre-Pregnancy Overweight/Obesity and Macrosomia: A Prospective Cohort Study in Central China. Nutrients. 2022; 14(16):3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163347
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Xinli, Letao Chen, Senmao Zhang, Yiping Liu, Jianhui Wei, Tingting Wang, and Jiabi Qin. 2022. "Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and High Triglyceride Levels Mediate the Association between Pre-Pregnancy Overweight/Obesity and Macrosomia: A Prospective Cohort Study in Central China" Nutrients 14, no. 16: 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163347
APA StyleSong, X., Chen, L., Zhang, S., Liu, Y., Wei, J., Wang, T., & Qin, J. (2022). Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and High Triglyceride Levels Mediate the Association between Pre-Pregnancy Overweight/Obesity and Macrosomia: A Prospective Cohort Study in Central China. Nutrients, 14(16), 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163347






