Metagenomic Changes of Gut Microbiota following Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection with a Simplified Low-Dose Quadruple Therapy with Bismuth or Lactobacillus reuteri
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
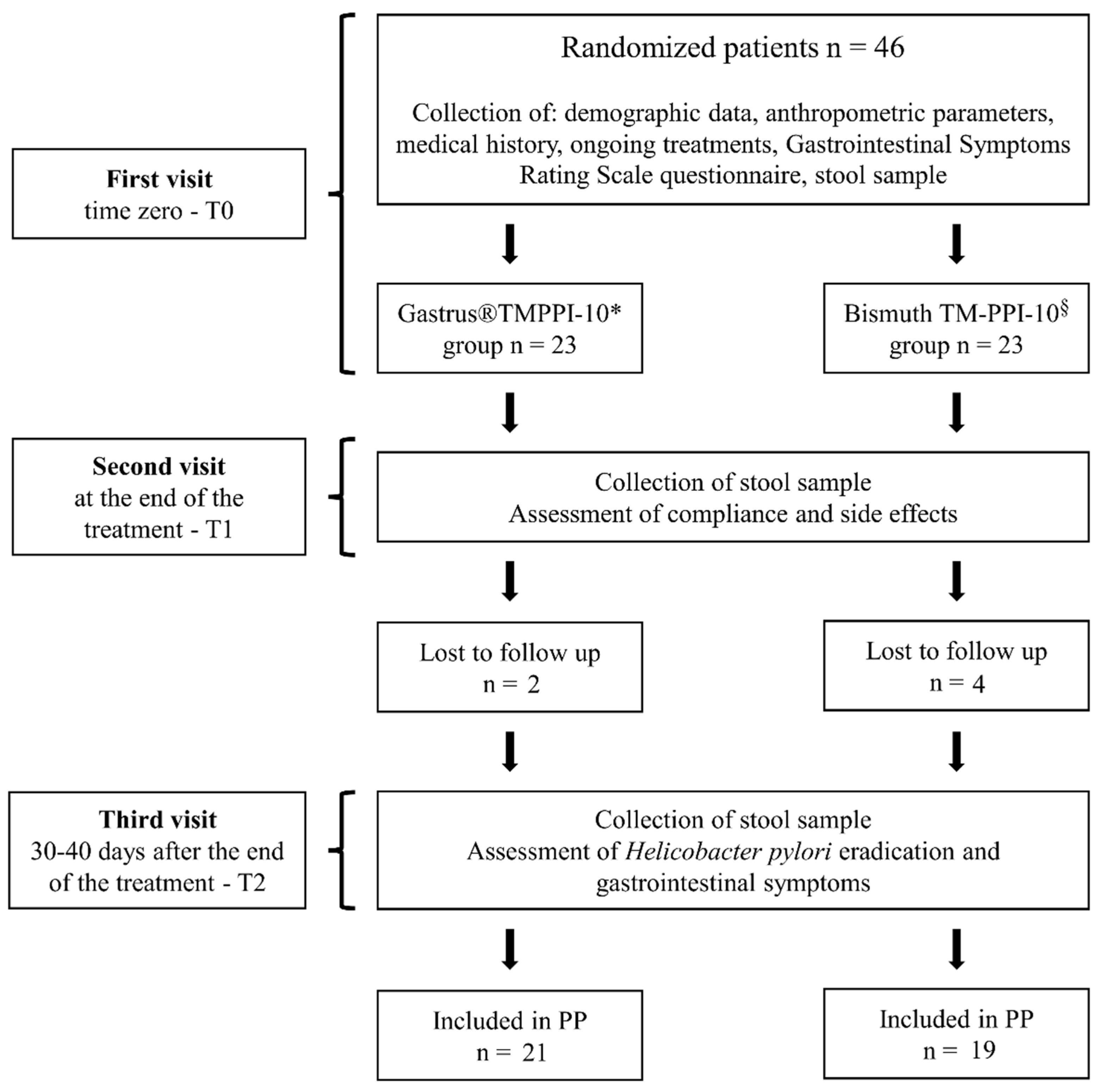
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patient Eligibility
2.3. Ethical Issues
2.4. Exclusion Criteria
2.5. H. pylori Status
2.6. Medication
2.7. Patients’ Compliance and Side Effects
2.8. Characterization of the Gut Microbiota
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Eradication Rate
3.2. Compliance and Side Effects
3.3. Gut Microbiota Changes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kikuchi, S.; Dore, M.P. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Helicobacter 2005, 10 (Suppl. S1), 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Graham, D.Y. The eradication of Helicobacter pylori to prevent gastric cancer: A critical appraisal. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Dore, M.P.; Graham, D.Y. Diagnosis and Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, M.P.; Marras, L.; Maragkoudakis, E.; Nieddu, S.; Manca, A.; Graham, D.Y.; Realdi, G. Salvage therapy after two or more prior Helicobacter pylori treatment failures: The super salvage regimen. Helicobacter 2003, 8, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiotani, A.; Lu, H.; Dore, M.P.; Graham, D.Y. Treating Helicobacter pylori effectively while minimizing misuse of antibiotics. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2017, 84, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imhann, F.; Bonder, M.J.; Vich Vila, A.; Fu, J.; Mujagic, Z.; Vork, L.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Jankipersadsing, S.A.; Cenit, M.C.; Harmsen, H.J.; et al. Proton pump inhibitors affect the gut microbiome. Gut 2016, 65, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dore, M.P.; Bibbo, S.; Pes, G.M.; Francavilla, R.; Graham, D.Y. Role of Probiotics in Helicobacter pylori Eradication: Lessons from a Study of Lactobacillus reuteri Strains DSM 17938 and ATCC PTA 6475 (Gastrus(R)) and a Proton-Pump Inhibitor. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 2019, 3409820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dore, M.P.; Goni, E.; Di Mario, F. Is There a Role for Probiotics in Helicobacter pylori Therapy? Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 2015, 44, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.R.; Zhang, G.Q.; Cheng, J.Y.; Li, Z.Y. Efficacy of Lactobacillus-supplemented triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection in children: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2019, 178, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, J.; Mo, L.; Shi, J.; Qin, M.; Huang, X. Efficacy and safety of probiotics in eradicating Helicobacter pylori: A network meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e15180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.B.; Lan, Y.; Qiao, L. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of bismuth-containing quadruple therapy combined with probiotic supplement for eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2017, 56, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, R.; Ni, P.; Chen, S.; Duan, G. Efficacy of Lactobacillus-supplemented triple therapy for H. pylori eradication: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of probiotic-supplemented therapy on the eradication of H. pylori and incidence of therapy-associated side effects. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olekhnovich, E.I.; Manolov, A.I.; Samoilov, A.E.; Prianichnikov, N.A.; Malakhova, M.V.; Tyakht, A.V.; Pavlenko, A.V.; Babenko, V.V.; Larin, A.K.; Kovarsky, B.A.; et al. Shifts in the Human Gut Microbiota Structure Caused by Quadruple Helicobacter pylori Eradication Therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Liang, L.; Lv, P.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y. Effects of non-viable Lactobacillus reuteri combining with 14-day standard triple therapy on Helicobacter pylori eradication: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Tang, L.; Huang, C.; Tian, C.; Chen, L.; He, Z.; Yang, G.; Zuo, L.; Zhao, G.; Liu, E.; et al. The Effect of Probiotics Supplementation on Gut Microbiota after Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Peng, C.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Shu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N. The eradication of Helicobacter pylori restores rather than disturbs the gastrointestinal microbiota in asymptomatic young adults. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, M.P.; Bibbo, S.; Loria, M.; Salis, R.; Manca, A.; Pes, G.M.; Graham, D.Y. Twice-a-day PPI, tetracycline, metronidazole quadruple therapy with Pylera(R) or Lactobacillus reuteri for treatment naive or for retreatment of Helicobacter pylori. Two randomized pilot studies. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GraphPad Software, S.D., California USA. Available online: http://www.graphpad.com/quickcalcs/randomize2/ (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Bibbo, S.; Abbondio, M.; Sau, R.; Tanca, A.; Pira, G.; Errigo, A.; Manetti, R.; Pes, G.M.; Dore, M.P.; Uzzau, S. Fecal Microbiota Signatures in Celiac Disease Patients With Poly-Autoimmunity. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lozupone, C.; Lladser, M.E.; Knights, D.; Stombaugh, J.; Knight, R. UniFrac: An effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME J. 2011, 5, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boekel, J.; Chilton, J.M.; Cooke, I.R.; Horvatovich, P.L.; Jagtap, P.D.; Kall, L.; Lehtio, J.; Lukasse, P.; Moerland, P.D.; Griffin, T.J. Multi-omic data analysis using Galaxy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Holik, A.Z.; Su, S.; Jansz, N.; Chen, K.; Leong, H.S.; Blewitt, M.E.; Asselin-Labat, M.L.; Smyth, G.K.; Ritchie, M.E. Why weight? Modelling sample and observational level variability improves power in RNA-seq analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galaxy/Proteomics. Available online: https://proteomics.usegalaxy.eu (accessed on 2 December 2021).
- Robinson, M.D.; Oshlack, A. A scaling normalization method for differential expression analysis of RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benjamini, Y.; Drai, D.; Elmer, G.; Kafkafi, N.; Golani, I. Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior genetics research. Behav. Brain Res. 2001, 125, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.L.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, H.H.; Szoecs, E.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Mukai, T.; Asasaka, T.; Sato, E.; Mori, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Ohori, H. Inhibition of binding of Helicobacter pylori to the glycolipid receptors by probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 32, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, T.C.; Axelsson, L.; Lindgren, S.E.; Dobrogosz, W.J. In Vitro Studies on Reuterin Synthesis by Lactobacillus reuteri. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 1989, 2, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, X.; Xiao, S.; Zhou, L. Integrative proteomic and metabolomic analyses reveal the mechanism by which bismuth enables Helicobacter pylori eradication. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyssen, O.P.; Perez-Aisa, A.; Castro-Fernandez, M.; Pellicano, R.; Huguet, J.M.; Rodrigo, L.; Ortun, J.; Gomez-Rodriguez, B.J.; Pinto, R.M.; Areia, M.; et al. European Registry on Helicobacter pylori management: Single-capsule bismuth quadruple therapy is effective in real-world clinical practice. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2021, 9, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, D.; Desseyn, J.L.; Gouyer, V.; Plet, S.; Tims, S.; Renes, I.; Mischke, M.; Gottrand, F. Early life nutrition influences susceptibility to chronic inflammatory colitis in later life. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandy, A. Ringing bells: Morganella morganii fights for recognition. Public Health 2020, 182, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Cui, B.; Chen, X. Antibiotic Disruption of the Gut Microbiota Enhances the Murine Hepatic Dysfunction Associated With a High-Salt Diet. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 829686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waite, D.W.; Chuvochina, M.; Pelikan, C.; Parks, D.H.; Yilmaz, P.; Wagner, M.; Loy, A.; Naganuma, T.; Nakai, R.; Whitman, W.B.; et al. Proposal to reclassify the proteobacterial classes Deltaproteobacteria and Oligoflexia, and the phylum Thermodesulfobacteria into four phyla reflecting major functional capabilities. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5972–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ye, Z.; Lu, J.; Miao, S.; Lu, X.; Sun, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y. Long-term changes in the gut microbiota after 14-day bismuth quadruple therapy in penicillin-allergic children. Helicobacter 2020, 25, e12721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.J.Y.; Coker, O.O.; Chu, E.; Szeto, C.H.; Luk, S.T.Y.; Lau, H.C.H.; Yu, J. Gastric microbes associated with gastric inflammation, atrophy and intestinal metaplasia 1 year after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Gut 2020, 69, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holloway, V.; Jacob, G.; Hayes, N. Challenges in the diagnosis and management of Granulicatella elegans endocarditis in a 9-year-old child. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e240079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.Y.; Li, S.Z.; Shi, Y.Y.; Xue, Y. Effect of gastric microbiota on quadruple Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy containing bismuth. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3913–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Xiao, S.; Li, S.; Suo, B.; Wang, Y.; Meng, L.; Liu, Z.; Yin, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, L. The impact of Helicobacter pylori infection, eradication therapy, and probiotics intervention on gastric microbiota in young adults. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.I.; Pan, C.Y.; Kao, J.Y.; Tsay, F.W.; Peng, N.J.; Kao, S.S.; Wang, H.M.; Tsai, T.J.; Wu, D.C.; Chen, C.L.; et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication with bismuth quadruple therapy leads to dysbiosis of gut microbiota with an increased relative abundance of Proteobacteria and decreased relative abundances of Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria. Helicobacter 2018, 23, e12498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, S.S.; Yalinay, M.; Karakan, T. Bismuth-based quadruple Helicobacter pylori eradication regimen alters the composition of gut microbiota. Infez Med. 2018, 26, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Macchione, I.G.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Ianiro, G.; Napoli, M.; Gibiino, G.; Rizzatti, G.; Petito, V.; Gasbarrini, A.; Scaldaferri, F. Akkermansia muciniphila: Key player in metabolic and gastrointestinal disorders. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 8075–8083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilinski, J.; Grzesiowski, P.; Sorensen, N.; Madry, K.; Muszynski, J.; Robak, K.; Wroblewska, M.; Dzieciatkowski, T.; Dulny, G.; Dwilewicz-Trojaczek, J.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Patients With Blood Disorders Inhibits Gut Colonization With Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: Results of a Prospective, Single-Center Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butera, A.; Di Paola, M.; Pavarini, L.; Strati, F.; Pindo, M.; Sanchez, M.; Cavalieri, D.; Boirivant, M.; De Filippo, C. Nod2 Deficiency in mice is Associated with Microbiota Variation Favouring the Expansion of mucosal CD4+ LAP+ Regulatory Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, B.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, J.S.; Koh, S.J.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, K.L.; Chun, J. The Effect of Probiotics on Gut Microbiota during the Helicobacter pylori Eradication: Randomized Controlled Trial. Helicobacter 2016, 21, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Feng, J.; Chen, P.; Liu, X.; Ma, M.; Zhou, R.; Chang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q. Probiotics in Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2017, 41, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gastrus® Group | Bismuth Group |
|---|---|
| Rabeprazole 20 mg 1 cp | Rabeprazole 20 mg 1 cp |
| Metronidazole 250 mg 2 cp | Metronidazole 250 mg 1 cp |
| Tetracycline 250 mg 2 cp | Tetracycline 250 mg 1 cp |
| (b.i.d.: midday and evening meals) | Pylera® 140 mg/125 mg/125 mg 2 cp |
| for 10 days | (b.i.d.: midday and evening meals) |
| Gastrus® 1 tablet in the morning and 1 tablet in the afternoon for 27 days | for 10 days |
| Status | Gastrus® Group 1 | Bismuth Group 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Received intervention | 23 | 23 |
| Lost to follow-up | 2 | 4 |
| Completed trial | 21 | 19 |
| Intervention ineffective | 3 | 1 |
| Cure Rate ITT 2 | 78.3% (18/23) | 78.3% (18/23) |
| 95% CI 4-ITT | 61.4–95.1 | 61.4–95.1 |
| Cure Rate PP 3 | 85.7% (18/21) | 94.7% (18/19) |
| 95% CI 4-PP | 71.4–100 | 85.6–100 |
| Taxonomic Level | Taxa | Time T1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| logFC (Gastrus®/Bismuth) 1 | FDR 1 | ||
| Phylum | Verrucomicrobiota | −7.24 | 0.02329 |
| Family | Akkermansiaceae | −9.30 | 0.02715 |
| Acidaminococcaceae | −11.14 | 0.02182 | |
| Genus | Gastrus® Group | Bismuth Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 < T0 | T2 < T0 | T1 < T0 | T2 < T0 | |||||
| logFC (T1/T0) | FDR | logFC (T2/T0) | FDR | logFC (T1/T0) | FDR | logFC (T2/T0) | FDR | |
| Adlercreutzia | −6.60 | 0.03803 | ||||||
| Akkermansia | −11.37 | 0.00730 | ||||||
| Alistipes | −12.18 | 0.00548 | ||||||
| Anaerostipes | −5.74 | 0.02256 | ||||||
| Barnesiella | −13.47 | 0.00280 | −12.18 | 0.01277 | −6.94 | 0.00996 | ||
| Bilophila | −8.20 | 0.00962 | ||||||
| Butyricimonas | −8.33 | 0.00962 | ||||||
| Collinsella | −8.05 | 0.00960 | ||||||
| Coprococcus | −9.70 | 0.04882 | ||||||
| Flavonifractor | −7.23 | 0.04680 | ||||||
| Fusicatenibacter | −8.80 | 0.00102 | ||||||
| Intestinimonas | −7.42 | 0.00962 | ||||||
| Lachnoclostridium | −7.06 | 0.00962 | ||||||
| Megasphaera | −10.41 | 0.00962 | ||||||
| Monoglobus | −11.23 | 0.00548 | −8.52 | 0.00167 | ||||
| Odoribacter | −10.65 | 0.03474 | −9.56 | 0.00088 | ||||
| Oscillibacter | −7.38 | 0.03803 | ||||||
| Parabacteroides | −9.44 | 0.04882 | ||||||
| Parasutterella | −6.63 | 0.00996 | ||||||
| Romboutsia | −7.80 | 0.00962 | ||||||
| Roseburia | −9.08 | 0.00167 | ||||||
| Ruminococcus | −8.07 | 0.04882 | −9.23 | 0.00167 | ||||
| Subdoligranulum | −11.22 | 0.03586 | ||||||
| Genus | T1 > T0 | T2 > T0 | T1 > T0 | T2 > T0 | ||||
| logFC (T1/T0) | FDR | logFC (T2/T0) | FDR | logFC (T1/T0) | FDR | logFC (T2/T0) | FDR | |
| Enterococcus | 10.98 | 0.00548 | 12.81 | 0.00276 | ||||
| Granulicatella | 5.56 | 0.04680 | ||||||
| Lactobacillus | 7.32 | 0.04909 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dore, M.P.; Sau, R.; Niolu, C.; Abbondio, M.; Tanca, A.; Bibbò, S.; Loria, M.; Pes, G.M.; Uzzau, S. Metagenomic Changes of Gut Microbiota following Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection with a Simplified Low-Dose Quadruple Therapy with Bismuth or Lactobacillus reuteri. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142789
Dore MP, Sau R, Niolu C, Abbondio M, Tanca A, Bibbò S, Loria M, Pes GM, Uzzau S. Metagenomic Changes of Gut Microbiota following Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection with a Simplified Low-Dose Quadruple Therapy with Bismuth or Lactobacillus reuteri. Nutrients. 2022; 14(14):2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142789
Chicago/Turabian StyleDore, Maria Pina, Rosangela Sau, Caterina Niolu, Marcello Abbondio, Alessandro Tanca, Stefano Bibbò, Mariafrancesca Loria, Giovanni Mario Pes, and Sergio Uzzau. 2022. "Metagenomic Changes of Gut Microbiota following Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection with a Simplified Low-Dose Quadruple Therapy with Bismuth or Lactobacillus reuteri" Nutrients 14, no. 14: 2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142789
APA StyleDore, M. P., Sau, R., Niolu, C., Abbondio, M., Tanca, A., Bibbò, S., Loria, M., Pes, G. M., & Uzzau, S. (2022). Metagenomic Changes of Gut Microbiota following Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection with a Simplified Low-Dose Quadruple Therapy with Bismuth or Lactobacillus reuteri. Nutrients, 14(14), 2789. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142789










