Abnormal Micronutrient Intake Is Associated with the Risk of Periodontitis: A Dose–response Association Study Based on NHANES 2009–2014
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Periodontal Examination
- ≥2 Interproximal sites with a clinical attachment loss (CAL) of ≥4 mm;
- ≥2 Interproximal sites with a periodontal probing depth of ≥5 mm.
2.3. Micronutrient Intake
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Descriptive Characteristics and Periodontal Disease
3.3. Description of the Four Models Using Logistic Regression and PSM
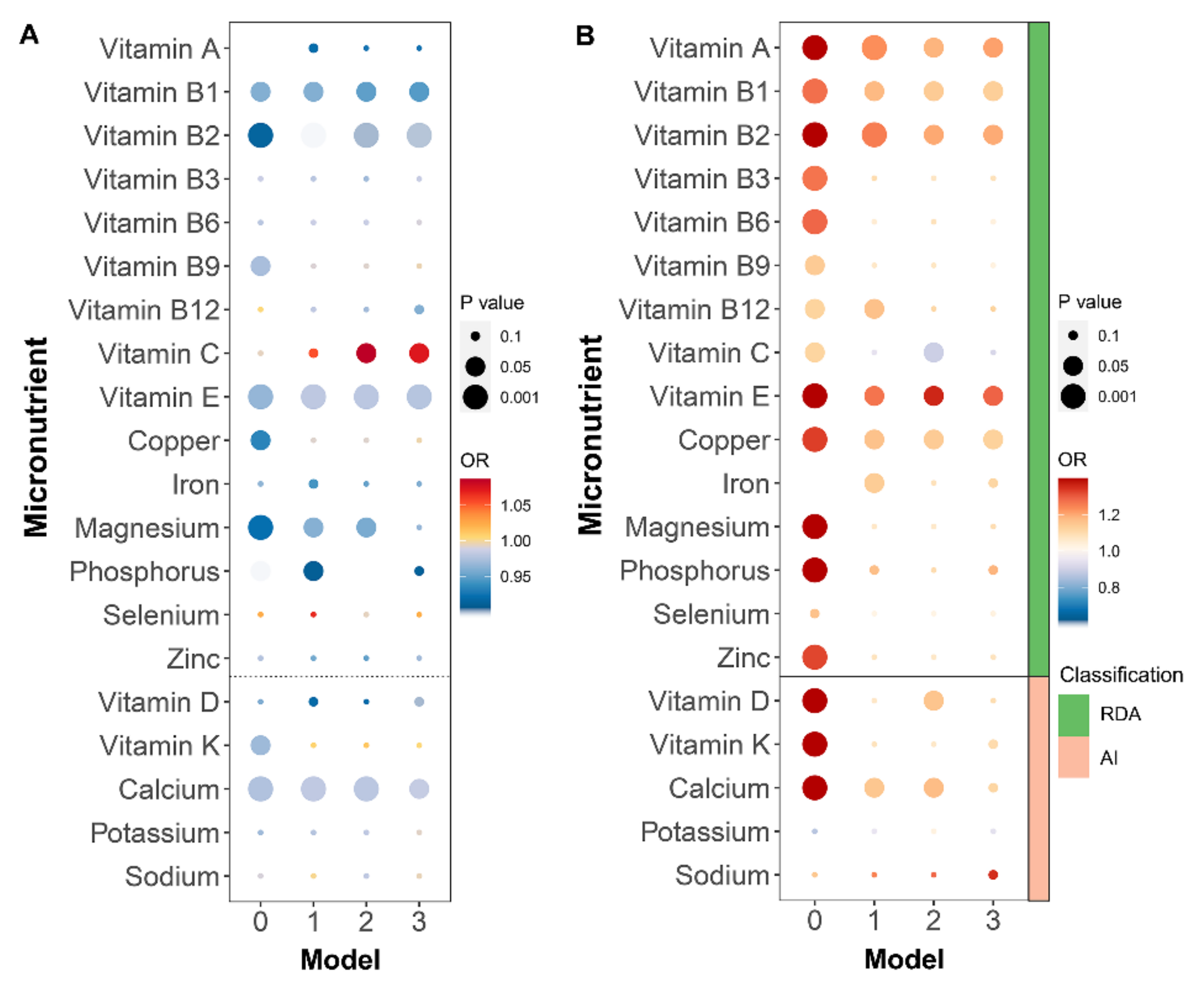
3.4. Characteristics of Micronutrients
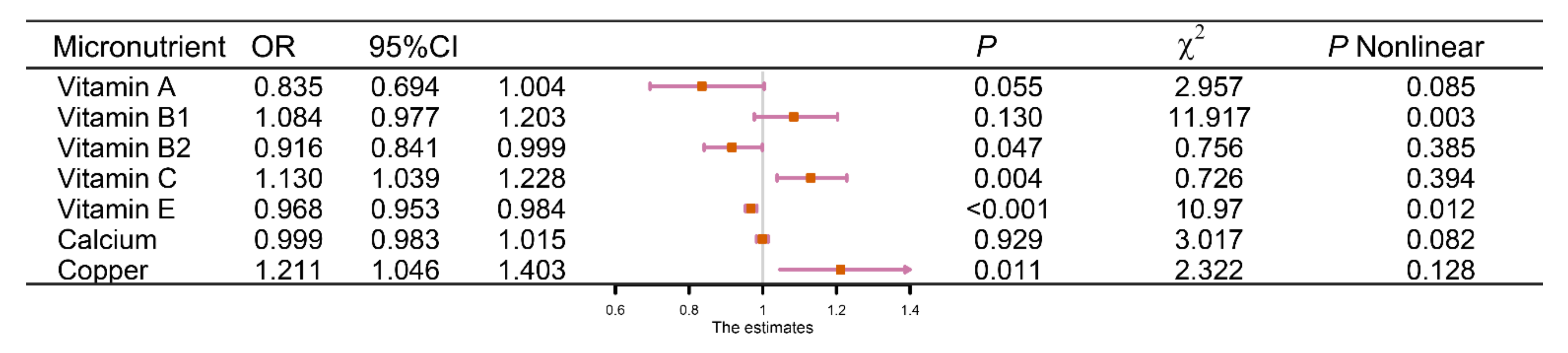
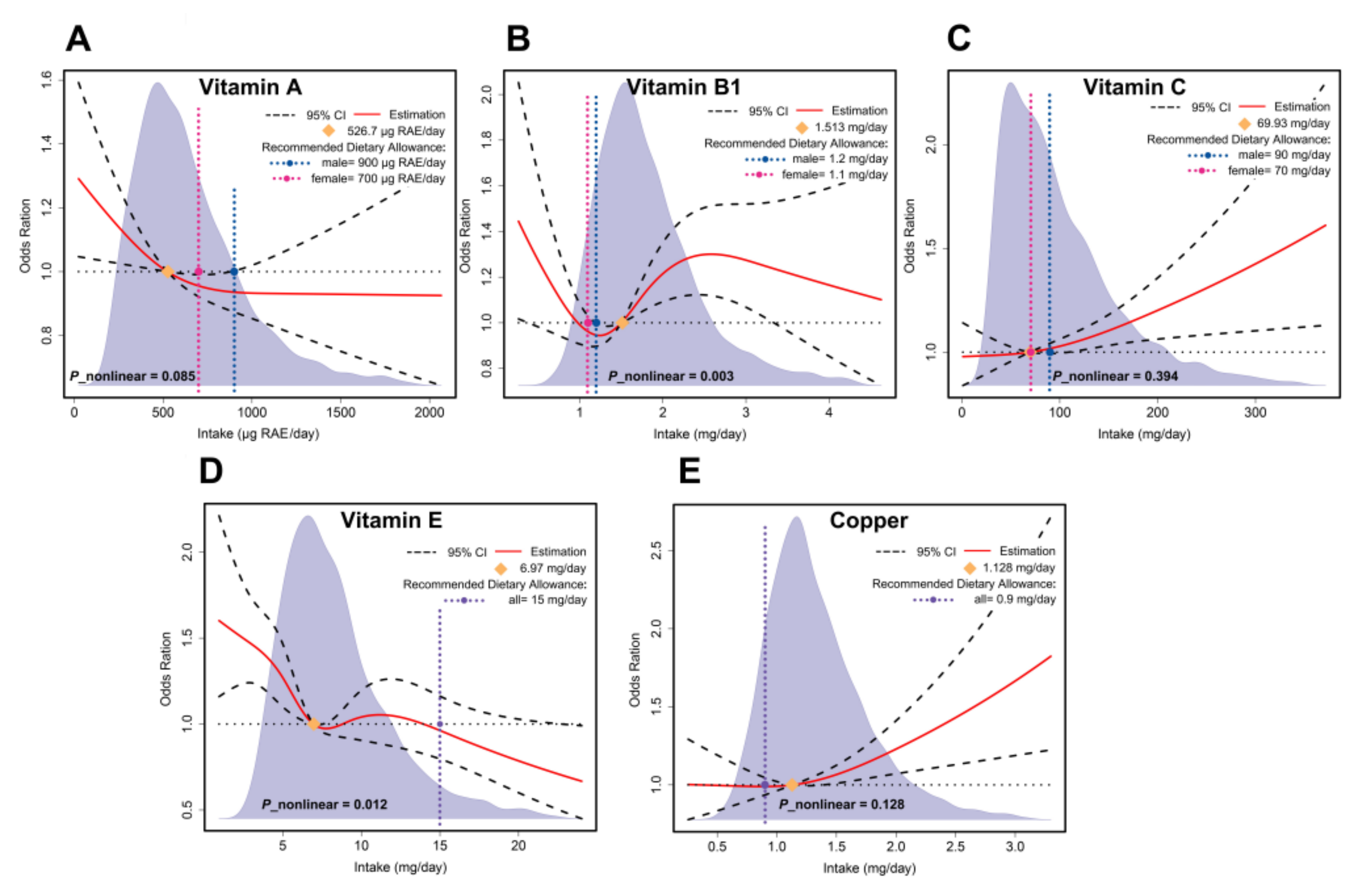
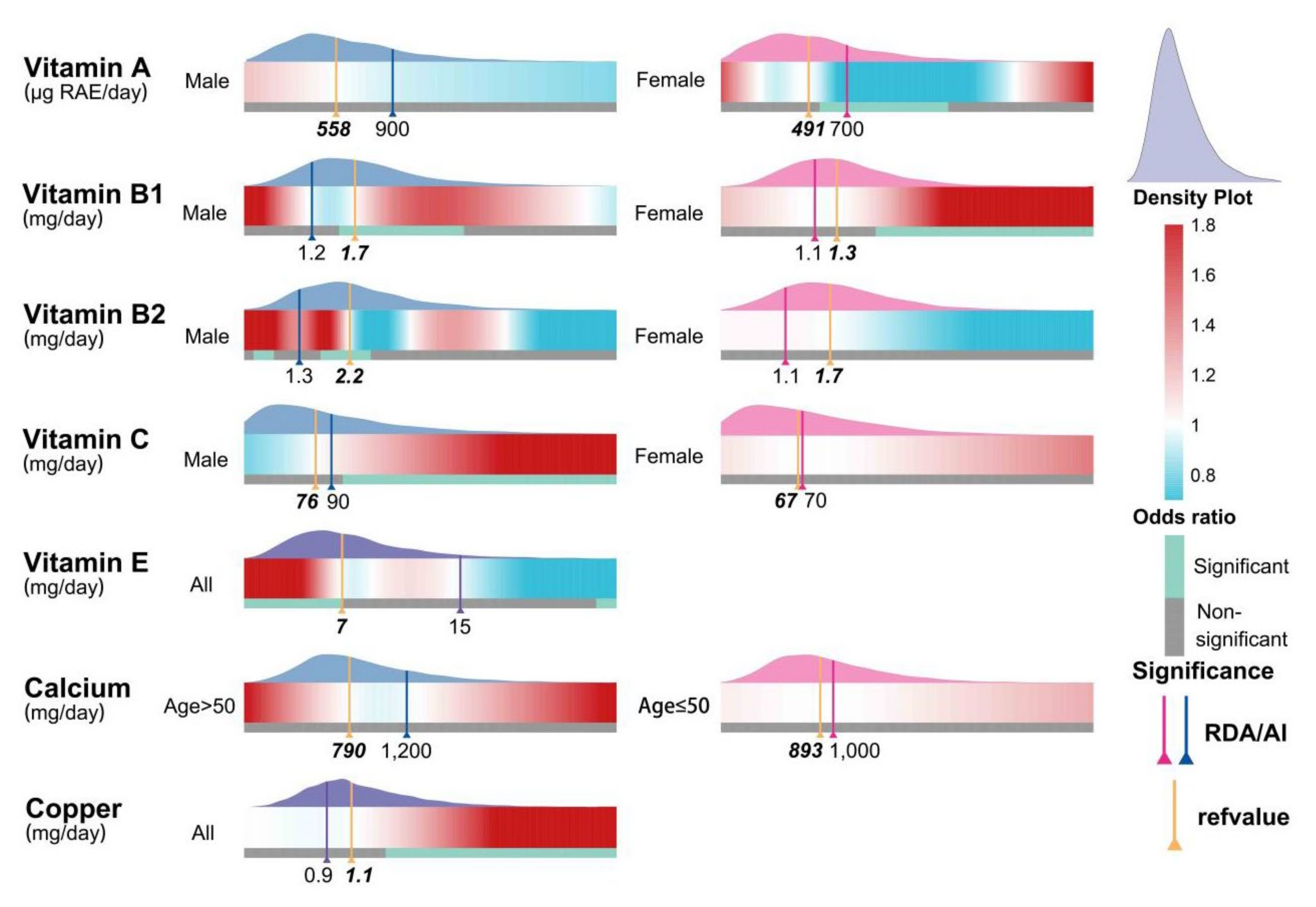
3.5. Dose–Response Effect Examination
3.6. Subgroup Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almoshari, Y.; Ren, R.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Z.; Wei, X.; Chen, N.; Li, G.; Ryu, S.; Lele, S.M.; Reinhardt, R.A.; et al. GSK3 inhibitor-loaded osteotropic Pluronic hydrogel effectively mitigates periodontal tissue damage associated with experimental periodontitis. Biomaterials 2020, 261, 120293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Lin, L. Is periodontal disease a risk indicator for colorectal cancer? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, C.; Garcia, M.P.; Polanco, A.F.; Gonzalez-Osuna, L.; Sierra-Cristancho, A.; Melgar-Rodriguez, S.; Cafferata, E.A.; Vernal, R. Humanized Mouse Models for the Study of Periodontitis: An Opportunity to Elucidate Unresolved Aspects of Its Immunopathogenesis and Analyze New Immunotherapeutic Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 663328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.X.; Zhong, Y.J.; Dong, Q.Q.; Wong, H.M.; Wen, Y.F. Global, regional, and national burden of severe periodontitis, 1990-2019: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, S.A.; Anto, F.; Blankson, P.K.; Tormeti, D.; Ayettey-Adamafio, M.; Bayitse, P.; Danso-Appiah, T.; Amoah, A.G. Periodontitis prevalence and severity in an African population: A cross-sectional study in the Greater Accra Region of Ghana. J. Periodontol. 2021, 93, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shungin, D.; Haworth, S.; Divaris, K.; Agler, C.S.; Kamatani, Y.; Keun Lee, M.; Grinde, K.; Hindy, G.; Alaraudanjoki, V.; Pesonen, P.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of dental caries and periodontitis combining clinical and self-reported data. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietrich, T.; Jimenez, M.; Krall Kaye, E.A.; Vokonas, P.S.; Garcia, R.I. Age-dependent associations between chronic periodontitis/edentulism and risk of coronary heart disease. Circulation 2008, 117, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.K.; Wu, Q.L.; Peng, Y.W.; Liang, F.Y.; You, H.J.; Feng, Y.W.; Li, G.; Li, X.J.; Liu, S.H.; Li, Y.C.; et al. Oral P. gingivalis impairs gut permeability and mediates immune responses associated with neurodegeneration in LRRK2 R1441G mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norhammar, A.; Kjellstrom, B.; Habib, N.; Gustafsson, A.; Klinge, B.; Nygren, A.; Nasman, P.; Svenungsson, E.; Ryden, L. Undetected Dysglycemia Is an Important Risk Factor for Two Common Diseases, Myocardial Infarction and Periodontitis: A Report from the PAROKRANK Study. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1504–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punthakee, Z. In type 2 diabetes with periodontitis, intensive periodontitis treatment improved glycemic control at 1 year. Ann. Intern. Med 2019, 170, JC40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwahn, C.; Frenzel, S.; Holtfreter, B.; Van der Auwera, S.; Pink, C.; Bulow, R.; Friedrich, N.; Volzke, H.; Biffar, R.; Kocher, T.; et al. Effect of periodontal treatment on preclinical Alzheimer’s disease-Results of a trial emulation approach. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 18, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinane, D.F.; Stathopoulou, P.G.; Papapanou, P.N. Periodontal diseases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, C.; Zhou, J.; Kong, N.; Bian, T.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, W.; Yan, F. Gold nanoparticles modulate the crosstalk between macrophages and periodontal ligament cells for periodontitis treatment. Biomaterials 2019, 206, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, S. Impact of calorie restriction and intermittent fasting on periodontal health. Periodontol. 2000 2021, 87, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genco, R.J.; Borgnakke, W.S. Risk factors for periodontal disease. Periodontol. 2000 2013, 62, 59–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz Aguilera, E.; Suvan, J.; Orlandi, M.; Miro Catalina, Q.; Nart, J.; D’Aiuto, F. Association between Periodontitis and Blood Pressure Highlighted in Systemically Healthy Individuals: Results from a Nested Case-Control Study. Hypertension 2021, 77, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopidis, K.; Witard, O.C. Understanding the role of smoking and chronic excess alcohol consumption on reduced caloric intake and the development of sarcopenia. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, A.; Slade, G. State cigarette excise tax, secondhand smoke exposure, and periodontitis in US nonsmokers. Am. J. Public Health 2013, 103, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, D.V.; Viafara, J.A.S.; Zangeronimo, M.G.; Ribeiro Lima, R.; Marques, L.S.; Pereira, L.J. n-3 Ingestion may modulate the severity of periodontal disease? Systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1937–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasco-Baque, V.; Garidou, L.; Pomie, C.; Escoula, Q.; Loubieres, P.; Le Gall-David, S.; Lemaitre, M.; Nicolas, S.; Klopp, P.; Waget, A.; et al. Periodontitis induced by Porphyromonas gingivalis drives periodontal microbiota dysbiosis and insulin resistance via an impaired adaptive immune response. Gut 2017, 66, 872–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decker, A.M.; Kapila, Y.L.; Wang, H.L. The psychobiological links between chronic stress-related diseases, periodontal/peri-implant diseases, and wound healing. Periodontol. 2000 2021, 87, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Lamont, R.J. Polymicrobial communities in periodontal disease: Their quasi-organismal nature and dialogue with the host. Periodontol. 2000 2021, 86, 210–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, M.; Usui, M.; Ariyoshi, W.; Nakashima, K.; Nagai-Yoshioka, Y.; Inoue, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Nishihara, T. Sleep duration and severe periodontitis in middle-aged Japanese workers. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2022, 49, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannsen, A.; Asberg, M.; Soder, P.O.; Soder, B. Anxiety, gingival inflammation and periodontal disease in non-smokers and smokers—An epidemiological study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2005, 32, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Kang, X.N.; Cao, Y.; Zheng, D.X.; Lu, Y.M.; Pang, C.F.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, B.; Peng, Y. Porphyromonas gingivalis induces depression via downregulating p75NTR-mediated BDNF maturation in astrocytes. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 81, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Xu, H. Association of short sleep with risk of periodontal disease: A meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.L.; Fulgoni, V.L.; Taylor, C.L.; Pfeiffer, C.M.; Thuppal, S.V.; McCabe, G.P.; Yetley, E.A. Correspondence of folate dietary intake and biomarker data. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berryman, C.E.; Lieberman, H.R.; Fulgoni, V.L., III; Pasiakos, S.M. Protein intake trends and conformity with the Dietary Reference Intakes in the United States: Analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2001–2014. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.R.; Lazo, M.; Appel, L.J.; Gutierrez, O.M.; Grams, M.E. High dietary phosphorus intake is associated with all-cause mortality: Results from NHANES III. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Du, M.; Blumberg, J.B.; Ho Chui, K.K.; Ruan, M.; Rogers, G.; Shan, Z.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, F.F. Association Among Dietary Supplement Use, Nutrient Intake, and Mortality Among U.S. Adults: A Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, J.; Murphy, K.G.; Frost, G.; Chambers, E.S. Higher dietary fibre intake is associated with increased skeletal muscle mass and strength in adults aged 40 years and older. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 2134–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Tucker, K.L. Dietary quality of the US child and adolescent population: Trends from 1999 to 2012 and associations with the use of federal nutrition assistance programs. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.Y.; Forno, E.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hebert, J.R.; Celedon, J.C. The Dietary Inflammatory Index and Current Wheeze Among Children and Adults in the United States. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, T.; Liu, B.; Bao, W.; Thorne, P.S. BMI modifies the association between dietary intake and serum levels of PCBs. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazidi, M.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Sattar, N.; Toth, P.P.; Judd, S.; Blaha, M.J.; Hernandez, A.V.; Penson, P.E.; Banach, M.; International Lipid Expert, P.; et al. Association of types of dietary fats and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: A prospective cohort study and meta-analysis of prospective studies with 1,164,029 participants. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3677–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Gao, J.; Li, N.; Han, S.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, T.; Shan, R.; Li, Y.; Sun, C.; et al. Dietary iron and vitamins in association with mortality. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2401–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumpitsch, C.; Fischmeister, F.P.S.; Mahnert, A.; Lackner, S.; Wilding, M.; Sturm, C.; Springer, A.; Madl, T.; Holasek, S.; Hogenauer, C.; et al. Reduced B12 uptake and increased gastrointestinal formate are associated with archaeome-mediated breath methane emission in humans. Microbiome 2021, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogire, R.M.; Mutua, A.; Kimita, W.; Kamau, A.; Bejon, P.; Pettifor, J.M.; Adeyemo, A.; Williams, T.N.; Atkinson, S.H. Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e134–e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Finn, F.; Carr, B.I. The growth inhibitory effects of vitamins K and their actions on gene expression. Hepatology 1995, 22, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessi, M.; Paul, T.; Scaiano, J.C.; Ingold, K.U. The contrasting kinetics of peroxidation of vitamin E-containing phospholipid unilamellar vesicles and human low-density lipoprotein. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 6957–6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas-Wallscheid, N.; Buettner, F.; Sommerkamp, P.; Klimmeck, D.; Ladel, L.; Thalheimer, F.B.; Pastor-Flores, D.; Roma, L.P.; Renders, S.; Zeisberger, P.; et al. Vitamin A-Retinoic Acid Signaling Regulates Hematopoietic Stem Cell Dormancy. Cell 2017, 169, 807–823.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ford, A.H.; Flicker, L.; Alfonso, H.; Thomas, J.; Clarnette, R.; Martins, R.; Almeida, O.P. Vitamins B(12), B(6), and folic acid for cognition in older men. Neurology 2010, 75, 1540–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Messa, P.; Vallone, C.; Mioni, G.; Geatti, O.; Turrin, D.; Passoni, N.; Cruciatti, A. Direct in vivo assessment of parathyroid hormone-calcium relationship curve in renal patients. Kidney Int. 1994, 46, 1713–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, P.P.; Xu, H.S.; Chen, Y.W.; Wu, S.P. Periodontal disease severity is associated with micronutrient intake. Aust. Dent. J. 2018, 63, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, M.; Grossi, S.G.; Dunford, R.G.; Ho, A.W.; Trevisan, M.; Genco, R.J. Calcium and the risk for periodontal disease. J. Periodontol. 2000, 71, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegboye, A.; Boucher, B.; Kongstad, J.; Fiehn, N.; Christensen, L.; Heitmann, B. Calcium, vitamin D, casein and whey protein intakes and periodontitis among Danish adults. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 19, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapple, I.L.; Bouchard, P.; Cagetti, M.G.; Campus, G.; Carra, M.C.; Cocco, F.; Nibali, L.; Hujoel, P.; Laine, M.L.; Lingstrom, P.; et al. Interaction of lifestyle, behaviour or systemic diseases with dental caries and periodontal diseases: Consensus report of group 2 of the joint EFP/ORCA workshop on the boundaries between caries and periodontal diseases. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44 (Suppl. S18), S39–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dommisch, H.; Kuzmanova, D.; Jonsson, D.; Grant, M.; Chapple, I. Effect of micronutrient malnutrition on periodontal disease and periodontal therapy. Periodontol. 2000 2018, 78, 129–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpinar, A.; Karakan, N.C.; Alpan, A.L.; Dogan, S.S.A.; Goze, F.; Poyraz, O. Comparative effects of riboflavin, nicotinamide and folic acid on alveolar bone loss: A morphometric and histopathologic study in rats. Srp. Arh. Celok. Lek. 2016, 144, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoloi, J.; Dihingia, A.; Kalita, J.; Manna, P. Implication of a novel vitamin K dependent protein, GRP/Ucma in the pathophysiological conditions associated with vascular and soft tissue calcification, osteoarthritis, inflammation, and carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebersole, J.L.; Lambert, J.; Bush, H.; Huja, P.E.; Basu, A. Serum Nutrient Levels and Aging Effects on Periodontitis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwasaki, M.; Moynihan, P.; Manz, M.C.; Taylor, G.W.; Yoshihara, A.; Muramatsu, K.; Watanabe, R.; Miyazaki, H. Dietary antioxidants and periodontal disease in community-based older Japanese: A 2-year follow-up study. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kunz, D.; Wirth, J.; Sculean, A.; Eick, S. In-vitro-activity of additive application of hydrogen peroxide in antimicrobial photodynamic therapy using LED in the blue spectrum against bacteria and biofilm associated with periodontal disease. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 26, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willershausen, B.; Ross, A.; Forsch, M.; Willershausen, I.; Mohaupt, P.; Callaway, A. The influence of micronutrients on oral and general health. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2011, 16, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Hou, Y.; He, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, R.; Wang, X.; Gong, T.; Jiang, W. Synthetic vitamin K analogs inhibit inflammation by targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2422–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhassani, A.A.; Hu, F.B.; Rimm, E.B.; Li, Y.; Rosner, B.A.; Willett, W.C.; Joshipura, K.J. Dietary flavonoid intake and risk of periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2020, 91, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.Y.; Jang, J.H.; Park, J.E. Association between Healthy Lifestyle (Diet Quality, Physical Activity, Normal Body Weight) and Periodontal Diseases in Korean Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartha, V.; Exner, L.; Meyer, A.L.; Basrai, M.; Schweikert, D.; Adolph, M.; Bruckner, T.; Meller, C.; Woelber, J.P.; Wolff, D. How to Measure Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet in Dental Studies: Is a Short Adherence Screener Enough? A Comparative Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.; Woodside, J.V.; Winning, L.; Wright, D.M.; Srinivasan, M.; McKenna, G. Associations between self-reported periodontal disease and nutrient intakes and nutrient-based dietary patterns in the UK Biobank. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2022, 49, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, J.; Ruiz, K.; Tan, J.; Jayasinghe, T.; Khan, S.; Eroglu, E.; Adler, C.; Simpson, S.; Le Couteur, D.; Raubenheimer, D.; et al. A randomized clinical trial to investigate the effect of dietary protein sources on periodontal health. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2022, 49, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondonno, N.P.; Murray, K.; Cassidy, A.; Bondonno, C.P.; Lewis, J.R.; Croft, K.D.; Kyro, C.; Gislason, G.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Scalbert, A.; et al. Higher habitual flavonoid intakes are associated with a lower risk of peripheral artery disease hospitalizations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 113, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.; Hankinson, S.E.; Rosner, B.; Willett, W.C.; Colditz, G.A. Prospective study of lutein/zeaxanthin intake and risk of age-related macular degeneration. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1837–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayedi, A.; Rashidy-Pour, A.; Parohan, M.; Zargar, M.S.; Shab-Bidar, S. Dietary Antioxidants, Circulating Antioxidant Concentrations, Total Antioxidant Capacity, and Risk of All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Observational Studies. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 701–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jayedi, A.; Zargar, M.S. Intake of vitamin B6, folate, and vitamin B12 and risk of coronary heart disease: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2697–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; He, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Qin, X. Inverse Association Between Riboflavin Intake and New-Onset Hypertension: A Nationwide Cohort Study in China. Hypertension 2020, 76, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareba, P.; Colaci, D.S.; Afeiche, M.; Gaskins, A.J.; Jorgensen, N.; Mendiola, J.; Swan, S.H.; Chavarro, J.E. Semen quality in relation to antioxidant intake in a healthy male population. Fertil. Steril. 2013, 100, 1572–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zittermann, A.; Ernst, J.B.; Prokop, S.; Fuchs, U.; Dreier, J.; Kuhn, J.; Knabbe, C.; Birschmann, I.; Schulz, U.; Berthold, H.K.; et al. Effect of vitamin D on all-cause mortality in heart failure (EVITA): A 3-year randomized clinical trial with 4000 IU vitamin D daily. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, K.; Tsugawa, Y.; Mangione, C.M.; Duru, O.K. Association between industry payments and prescriptions of long-acting insulin: An observational study with propensity score matching. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Initiative, S. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dye, B.A.; Afful, J.; Thornton-Evans, G.; Iafolla, T. Overview and quality assurance for the oral health component of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 2011–2014. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eke, P.I.; Borgnakke, W.S.; Genco, R.J. Recent epidemiologic trends in periodontitis in the USA. Periodontol. 2000 2020, 82, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eke, P.I.; Dye, B.A.; Wei, L.; Slade, G.D.; Thornton-Evans, G.O.; Borgnakke, W.S.; Taylor, G.W.; Page, R.C.; Beck, J.D.; Genco, R.J. Update on Prevalence of Periodontitis in Adults in the United States: NHANES 2009 to 2012. J. Periodontol. 2015, 86, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tran, D.T.; Gay, I.; Du, X.L.; Fu, Y.; Bebermeyer, R.D.; Neumann, A.S.; Streckfus, C.; Chan, W.; Walji, M.F. Assessment of partial-mouth periodontal examination protocols for periodontitis surveillance. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2014, 41, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Machado, V.; Botelho, J.; Viana, J.; Pereira, P.; Lopes, L.B.; Proenca, L.; Delgado, A.S.; Mendes, J.J. Association between Dietary Inflammatory Index and Periodontitis: A Cross-Sectional and Mediation Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.M.; McKenna, G.; Nugent, A.; Winning, L.; Linden, G.J.; Woodside, J.V. Association between diet and periodontitis: A cross-sectional study of 10,000 NHANES participants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; p. 1344. [Google Scholar]
- Bidinotto, A.B.; Martinez-Steele, E.; Thomson, W.M.; Hugo, F.N.; Hilgert, J.B. Investigation of direct and indirect association of ultra-processed food intake and periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2021, 93, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.; Weuve, J.; Schwartz, J.; Wright, R.O. Association of environmental cadmium exposure with periodontal disease in U.S. adults. Environ. Health Perspect 2009, 117, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brook, R.D.; Rajagopalan, S. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults. A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2018, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herxenberg, L.A.; Moore, W.A.; De Rosa, S.C. Estimation of missing values. Lancet 1999, 354, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.M.; Dunson, D.B. Bayesian multivariate logistic regression. Biometrics 2004, 60, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhan, C.; Wang, Q. Using Propensity Score Matching to Balance the Baseline Characteristics. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, e45–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, D.; Bevilacqua, V.; Colantonio, D.A.; Pasic, M.D.; Perumal, N.; Chan, M.K.; Adeli, K. Pediatric within-day biological variation and quality specifications for 38 biochemical markers in the CALIPER cohort. Clin. Chem. 2014, 60, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hickman, P.E.; Koerbin, G.; Potter, J.M.; Glasgow, N.; Cavanaugh, J.A.; Abhayaratna, W.P.; West, N.P.; Glasziou, P. Choice of Statistical Tools for Outlier Removal Causes Substantial Changes in Analyte Reference Intervals in Healthy Populations. Clin. Chem. 2020, 66, 1558–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
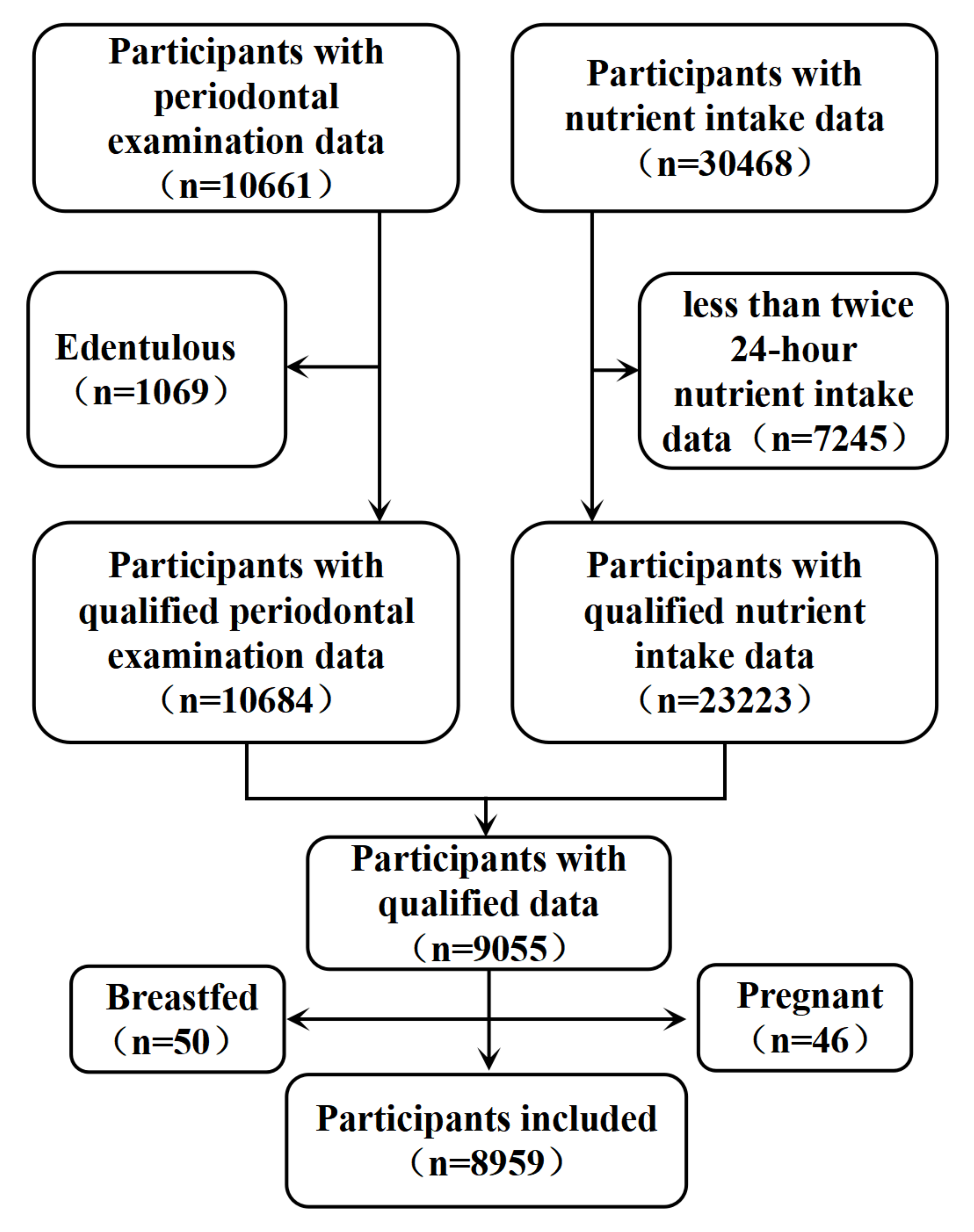
| Level | Overall a | Periodontitis | No Periodontitis a | χ2 | p b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | 8959 | 3994 | 4965 | |||
| Age (mean (SD)) | 52.36 (14.16) | 56.75 (13.63) | 48.82 (13.59) | / | <0.001 | |
| Gender (%) | Female | 4585 (51.2) | 1681 (42.1) | 2904 (58.5) | 237.64 | <0.001 |
| Male | 4374 (48.8) | 2313 (57.9) | 2061 (41.5) | |||
| Edu (%) | <High school graduate | 1950 (21.8) | 1209 (30.3) | 741 (14.9) | 551.05 | <0.001 |
| College | 2576 (28.8) | 1053 (26.4) | 1523 (30.7) | |||
| College graduate | 2490 (27.8) | 717 (18.0) | 1773 (35.7) | |||
| High school graduate | 1943 (21.7) | 1015 (25.4) | 928 (18.7) | |||
| Income (%) | High | 3106 (34.7) | 1002 (25.1) | 2104 (42.4) | 314.75 | <0.001 |
| Low | 2600 (29.0) | 1419 (35.5) | 1181 (23.8) | |||
| Middle | 3253 (36.3) | 1573 (39.4) | 1680 (33.8) | |||
| BMI (mean (SD)) | 29.48 (6.74) | 29.65 (6.73) | 29.35 (6.74) | / | 0.037 | |
| Diabetes (%) | Diabetes | 1399 (15.6) | 845 (21.2) | 554 (11.2) | 167.17 | <0.001 |
| No diabetes | 7560 (84.4) | 3149 (78.8) | 4411 (88.8) | |||
| Alcohol (%) | Drinkers | 6604 (73.7) | 2936 (73.5) | 3668 (73.9) | 0.1354 | 0.713 |
| Nondrinkers | 2355 (26.3) | 1058 (26.5) | 1297 (26.1) | |||
| HPL (%) | Hyperlipidemia | 4077 (45.5) | 1939 (48.5) | 2138 (43.1) | 26.646 | <0.001 |
| No hyperlipidemia | 4882 (54.5) | 2055 (51.5) | 2827 (56.9) | |||
| HTN (%) | Hypertension | 5113 (57.1) | 2612 (65.4) | 2501 (50.4) | 203.35 | <0.001 |
| No hypertension | 3846 (42.9) | 1382 (34.6) | 2464 (49.6) | |||
| Phy (%) | No physical activity | 2866 (32.0) | 1406 (35.2) | 1460 (29.4) | 33.923 | <0.001 |
| Physical activity | 6093 (68.0) | 2588 (64.8) | 3505 (70.6) | |||
| Smoke (%) | Active smoker | 1598 (17.8) | 970 (24.3) | 628 (12.6) | 334.72 | <0.001 |
| Former smoker | 2322 (25.9) | 1180 (29.5) | 1142 (23.0) | |||
| Never smoker | 5039 (56.2) | 1844 (46.2) | 3195 (64.4) | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Shang, Q.; Yang, D.; Peng, J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, H.; Chen, Q. Abnormal Micronutrient Intake Is Associated with the Risk of Periodontitis: A Dose–response Association Study Based on NHANES 2009–2014. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122466
Li W, Shang Q, Yang D, Peng J, Zhao H, Xu H, Chen Q. Abnormal Micronutrient Intake Is Associated with the Risk of Periodontitis: A Dose–response Association Study Based on NHANES 2009–2014. Nutrients. 2022; 14(12):2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122466
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Weiqi, Qianhui Shang, Dan Yang, Jiakuan Peng, Hang Zhao, Hao Xu, and Qianming Chen. 2022. "Abnormal Micronutrient Intake Is Associated with the Risk of Periodontitis: A Dose–response Association Study Based on NHANES 2009–2014" Nutrients 14, no. 12: 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122466
APA StyleLi, W., Shang, Q., Yang, D., Peng, J., Zhao, H., Xu, H., & Chen, Q. (2022). Abnormal Micronutrient Intake Is Associated with the Risk of Periodontitis: A Dose–response Association Study Based on NHANES 2009–2014. Nutrients, 14(12), 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122466






