Integrated Evaluation of the Multifunctional DPP-IV and ACE Inhibitory Effect of Soybean and Pea Protein Hydrolysates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
SH and PH Samples Description
2.2. SH and PH Ultrafiltration
2.3. Mass Spectrometry Analysis (HPLC Chip ESI-MS/MS)
2.4. Biochemical Investigation of DPP-IV and ACE Inhibitory Activity of SH and PH Peptides
2.4.1. In Vitro DPP-IV Activity Assay
2.4.2. In Vitro Measurement of ACE Inhibitory Activity
2.5. Cellular Measurement of SH and PH Inhibitory Effect of DPP-IV and ACE Activities
2.5.1. Cell Culture Conditions
2.5.2. Evaluation of Caco-2 Cell Viability by MTT Experiments
2.5.3. Evaluation of the Inhibitory Effect of SH and PH on Cellular DPP-IV Activity
2.5.4. Evaluation of the Inhibitory Effect of SH and PH on Cellular ACE1 Activity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Peptidomic Characterization of SH and PH
3.2. SH and PH Peptides: Biochemical Investigation of DPP-IV and ACE Inhibitory Activities
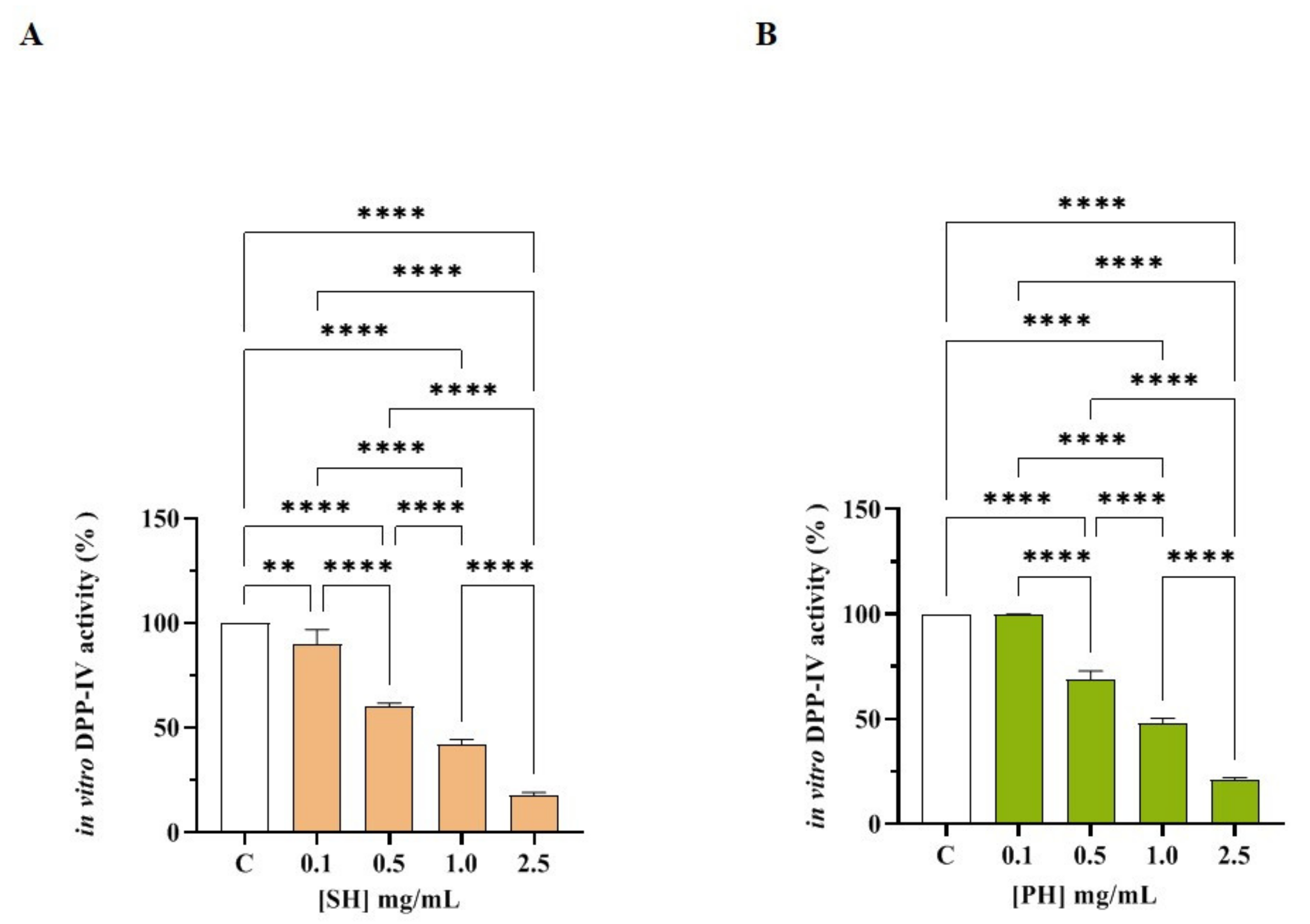
3.2.1. SH and PH Inhibit In Vitro DPP-IV Activity
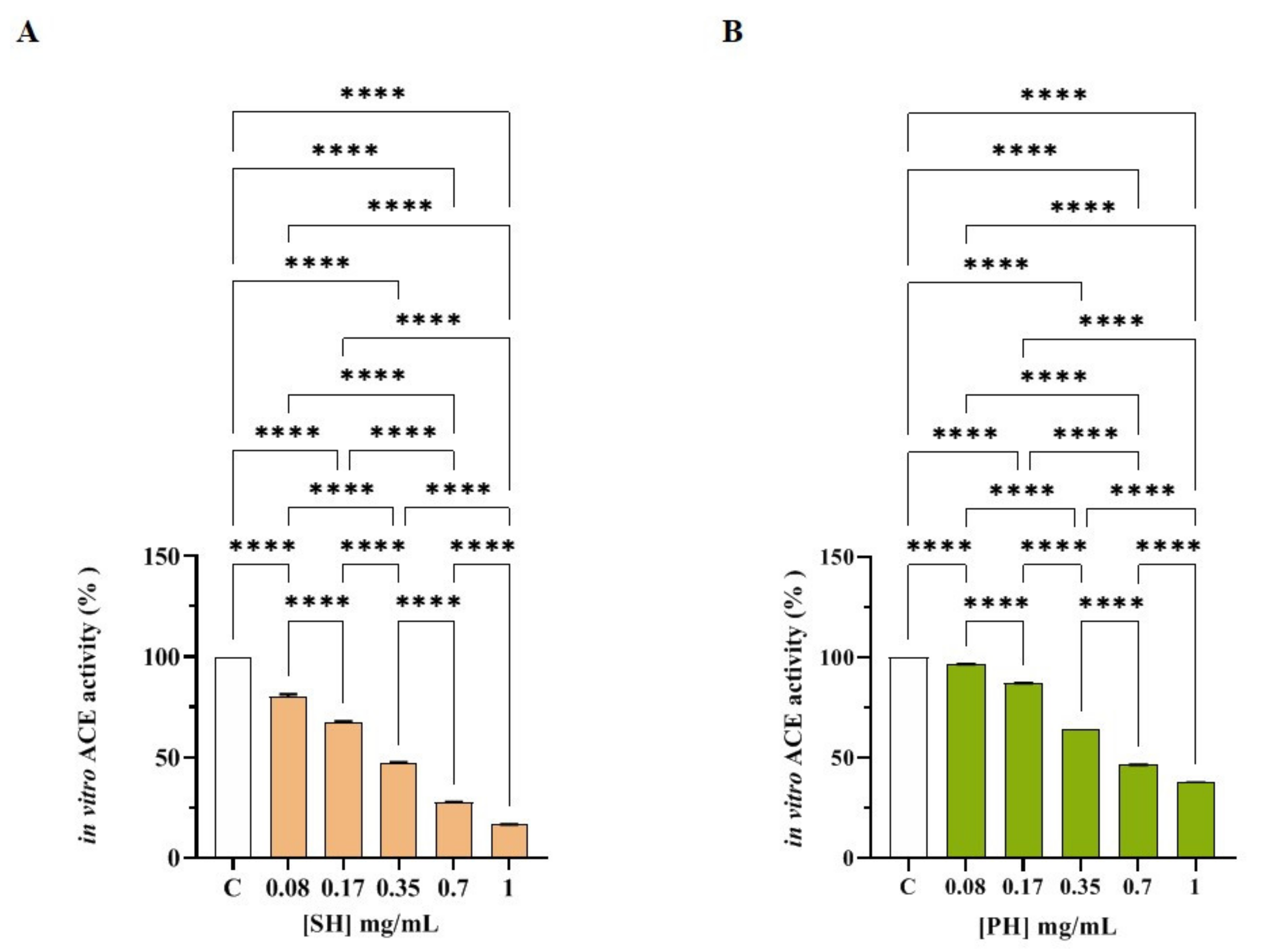
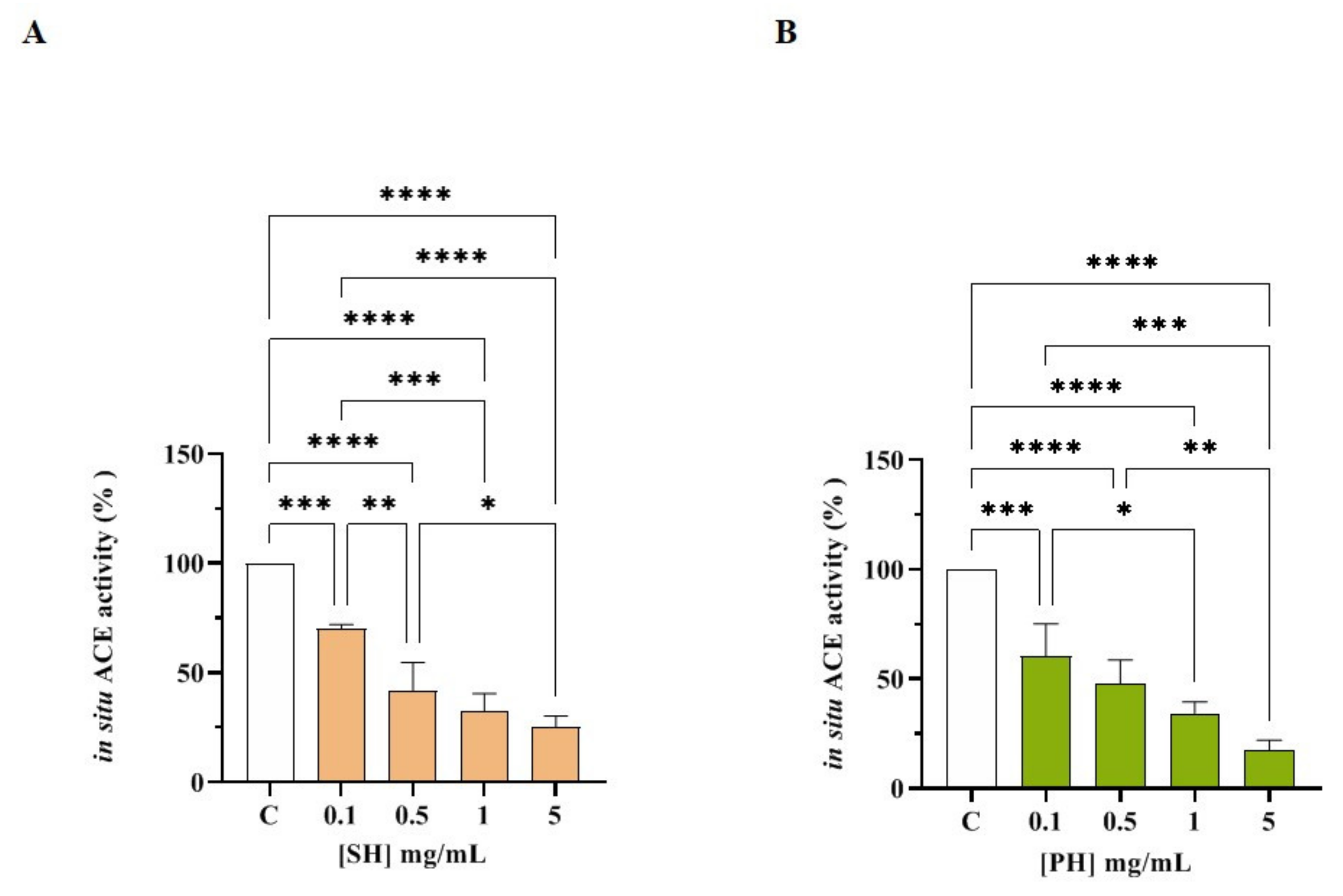
3.2.2. SH and PH Peptides Inhibit In Vitro ACE Activity
3.3. Cellular Assessment of DPP-IV and ACE Inhibition by SH and PH Peptides
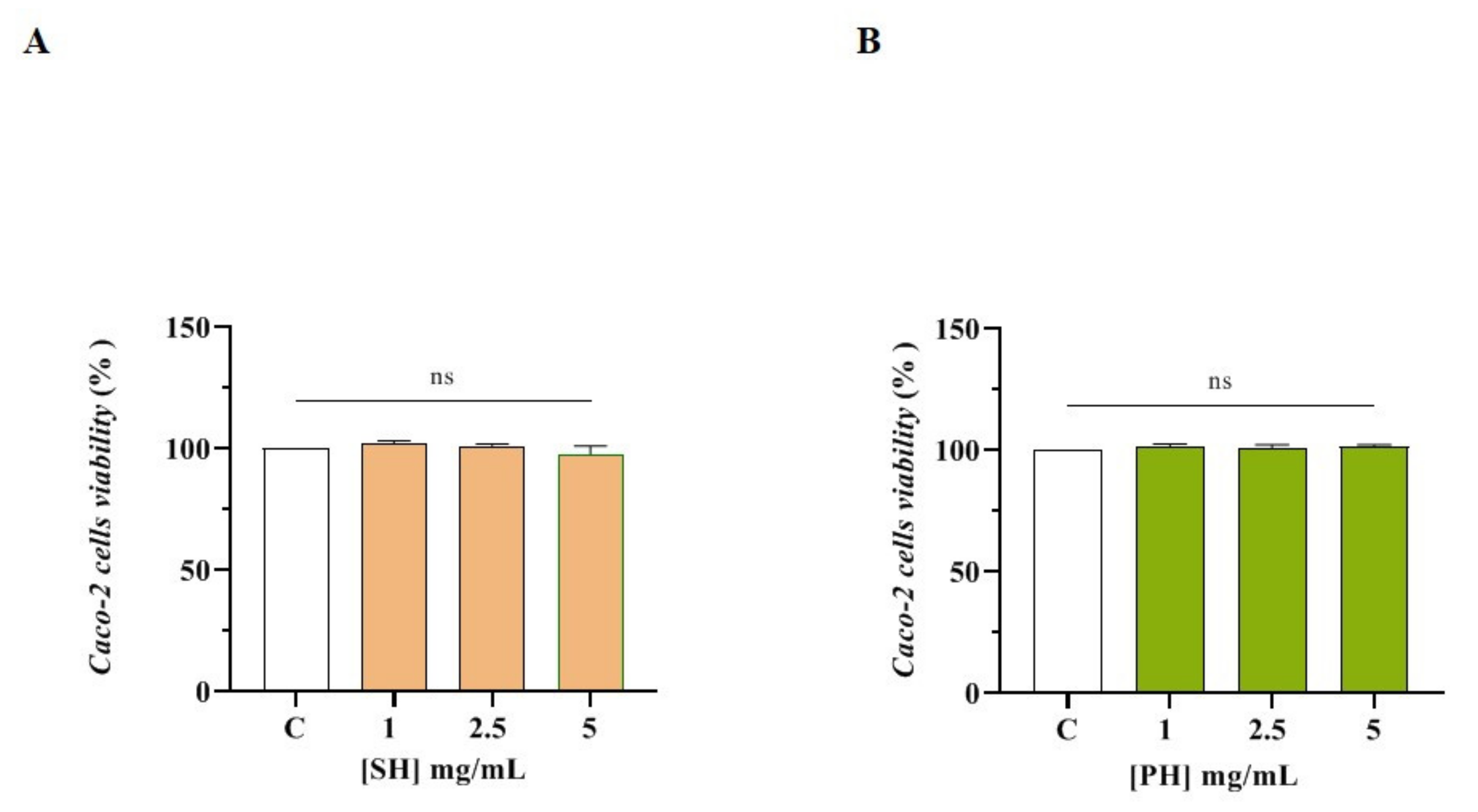
3.3.1. Effect of SH and PH Peptides on Caco-2 Cell Viability
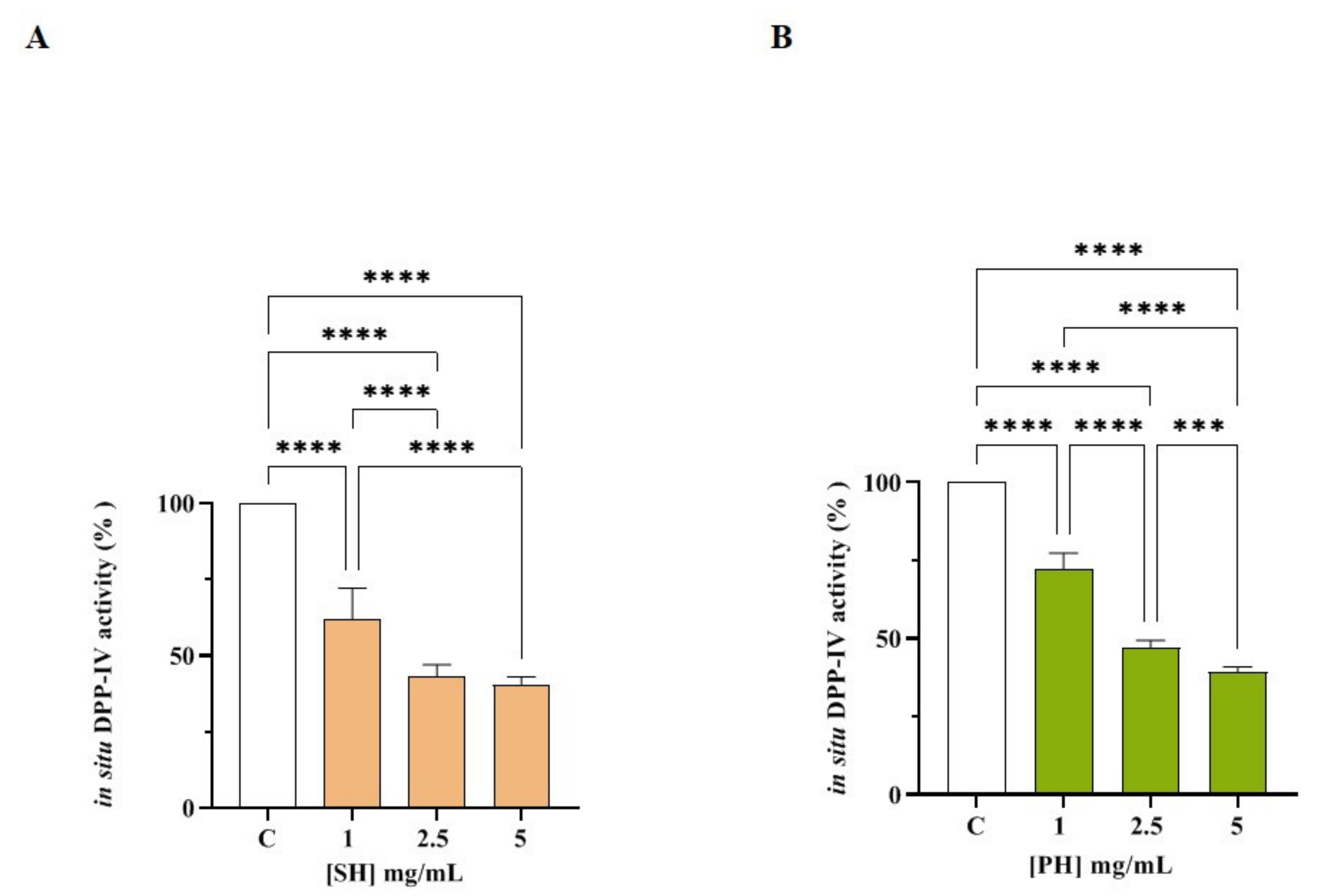
3.3.2. SH and PH Inhibit ACE Activity Expressed on Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lammi, C.; Aiello, G.; Boschin, G.; Arnoldi, A. Multifunctional Peptides for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A New Concept in the Area of Bioactive Food-Derived Peptides. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 55, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarian, M.; Khani, A.; Eghbalpour, S.; Uversky, V.N. Bioactive Peptides: Synthesis, Sources, Applications, and Proposed Mechanisms of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, K.; Tachibana, N.; Wanezaki, S.; Tsuzaki, S.; Takamatsu, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Shimoda, T. Isoflavone-Free Soy Protein Prepared by Column Chromatography Reduces Plasma Cholesterol in Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5717–5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Santos-Sánchez, G.; Bollati, C.; Bartolomei, M.; Li, J.; Arnoldi, A.; Lammi, C. Hempseed (Cannabis Sativa) Peptides WVSPLAGRT and IGFLIIWV Exert Anti-Inflammatory Activity in the LPS-Stimulated Human Hepatic Cell Line. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udenigwe, C.C.; Aluko, R.E. Food Protein-Derived Bioactive Peptides: Production, Processing, and Potential Health Benefits. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, R11–R24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguchem, R.N.; Okagu, I.U.; Okagu, O.D.; Ndefo, J.C.; Udenigwe, C.C. A Review on the Techno-Functional, Biological, and Health-Promoting Properties of Hempseed-Derived Proteins and Peptides. J. Food Biochem. 2022, e14127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoldi, A.; Zanoni, C.; Lammi, C.; Boschin, G. The Role of Grain Legumes in the Prevention of Hypercholesterolemia and Hypertension. CRC Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2015, 34, 144–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-M.; Ho, S.C.; Chen, Y.-M.; Ho, S.; To, K.; Tomlinson, B.; Woo, J. Whole Soy, but Not Purified Daidzein, Had a Favorable Effect on Improvement of Cardiovascular Risks: A 6-Month Randomized, Double-Blind, and Placebo-Controlled Trial in Equol-Producing Postmenopausal Women. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammi, C.; Zanoni, C.; Arnoldi, A. Three Peptides from Soy Glycinin Modulate Glucose Metabolism in Human Hepatic HepG2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 27362–27370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.D.; Arntfield, S.D. Gelation Properties of Salt-Extracted Pea Protein Isolate Catalyzed by Microbial Transglutaminase Cross-Linking. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Sun, C.X.; Corke, H.; Gul, K.; Gan, R.Y.; Fang, Y. The Health Benefits, Functional Properties, Modifications, and Applications of Pea (Pisum Sativum L.) Protein: Current Status, Challenges, and Perspectives. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1835–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluko, R.E.; Girgih, A.T.; He, R.; Malomo, S.; Li, H.; Offengenden, M.; Wu, J. Structural and Functional Characterization of Yellow Field Pea Seed (Pisum Sativum L.) Protein-Derived Antihypertensive Peptides. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Aluko, R.E. Identification and Inhibitory Properties of Multifunctional Peptides from Pea Protein Hydrolysate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11471–11476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Prairie, N.; Udenigwe, C.C.; Adebiyi, A.P.; Tappia, P.S.; Aukema, H.M.; Jones, P.J.H.; Aluko, R.E. Blood Pressure Lowering Effect of a Pea Protein Hydrolysate in Hypertensive Rats and Humans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 9854–9860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammi, C.; Aiello, G.; Dellafiora, L.; Bollati, C.; Boschin, G.; Ranaldi, G.; Ferruzza, S.; Sambuy, Y.; Galaverna, G.; Arnoldi, A. Assessment of the Multifunctional Behavior of Lupin Peptide P7 and Its Metabolite Using an Integrated Strategy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13179–13188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammi, C.; Zanoni, C.; Ferruzza, S.; Ranaldi, G.; Sambuy, Y.; Arnoldi, A. Hypocholesterolaemic Activity of Lupin Peptides: Investigation on the Crosstalk between Human Enterocytes and Hepatocytes Using a Co-Culture System Including Caco-2 and HepG2 Cells. Nutrients 2016, 8, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bollati, C.; Cruz-Chamorro, I.; Aiello, G.; Li, J.; Bartolomei, M.; Santos-Sánchez, G.; Ranaldi, G.; Ferruzza, S.; Sambuy, Y.; Arnoldi, A.; et al. Investigation of the Intestinal Trans-Epithelial Transport and Antioxidant Activity of Two Hempseed Peptides WVSPLAGRT (H2) and IGFLIIWV (H3). Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 110720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammi, C.; Arnoldi, A.; Aiello, G. Soybean Peptides Exert Multifunctional Bioactivity Modulating 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-CoA Reductase and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Targets in Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4824–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Guha, S.; Majumder, K. Food-Derived Bioactive Peptides in Human Health: Challenges and Opportunities. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lammi, C.; Zanoni, C.; Arnoldi, A.; Vistoli, G. Peptides Derived from Soy and Lupin Protein as Dipeptidyl-Peptidase IV Inhibitors: In Vitro Biochemical Screening and in Silico Molecular Modeling Study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 9601–9606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boschin, G.; Scigliuolo, G.M.; Resta, D.; Arnoldi, A. Optimization of the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Lupin (Lupinus) Proteins for Producing ACE-Inhibitory Peptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1846–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschin, G.; Scigliuolo, G.M.; Resta, D.; Arnoldi, A. ACE-Inhibitory Activity of Enzymatic Protein Hydrolysates from Lupin and Other Legumes. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammi, C.; Bollati, C.; Gelain, F.; Arnoldi, A.; Pugliese, R. Enhancement of the Stability and Anti-DPPIV Activity of Hempseed Hydrolysates through Self-Assembling Peptide-Based Hydrogels. Front. Chem. 2019, 6, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daskaya-Dikmen, C.; Yucetepe, A.; Karbancioglu-Guler, F.; Daskaya, H.; Ozcelik, B. Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides from Plants. Nutrients 2017, 9, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Features of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-IV) Inhibitory Peptides from Dietary Proteins. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aiello, G.; Lammi, C.; Boschin, G.; Zanoni, C.; Arnoldi, A. Exploration of Potentially Bioactive Peptides Generated from the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Hempseed Proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10174–10184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoni, C.; Aiello, G.; Arnoldi, A.; Lammi, C. Hempseed Peptides Exert Hypocholesterolemic Effects with a Statin-Like Mechanism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8829–8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Investigation of the Potential of Hemp, Pea, Rice and Soy Protein Hydrolysates as a Source of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-IV) Inhibitory Peptides. Food Dig. 2015, 6, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Montoya, M.; Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Mora-Escobedo, R.; Martínez-Villaluenga, C. Bioactive Peptides from Germinated Soybean with Anti-Diabetic Potential by Inhibition of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV, α-Amylase, and α-Glucosidase Enzymes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howell, S.; Kenny, A.J.; Turner, A.J. A Survey of Membrane Peptidases in Two Human Colonic Cell Lines, Caco-2 and HT-29. Biochem. J. 1992, 284, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mentlein, R. Cell-Surface Peptidases. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2004, 235, 165–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Aiello, G.; Fassi, E.M.A.; Boschin, G.; Bartolomei, M.; Bollati, C.; Roda, G.; Arnoldi, A.; Grazioso, G.; Lammi, C. Investigation of Chlorella Pyrenoidosa Protein as a Source of Novel Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (Ace) and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-Iv (Dpp-Iv) Inhibitory Peptides. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammi, C.; Boschin, G.; Bollati, C.; Arnoldi, A.; Galaverna, G.; Dellafiora, L. A Heuristic, Computer-Driven and Top-down Approach to Identify Novel Bioactive Peptides: A Proof-of-Principle on Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, G.; Li, Y.; Boschin, G.; Bollati, C.; Arnoldi, A.; Lammi, C. Chemical and Biological Characterization of Spirulina Protein Hydrolysates: Focus on ACE and DPP-IV Activities Modulation. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 63, 103592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Aiello, G.; Bollati, C.; Bartolomei, M.; Arnoldi, A.; Lammi, C. Phycobiliproteins from Arthrospira Platensis (Spirulina): A New Source of Peptides with Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitory Activity. Nutrients 2020, 12, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
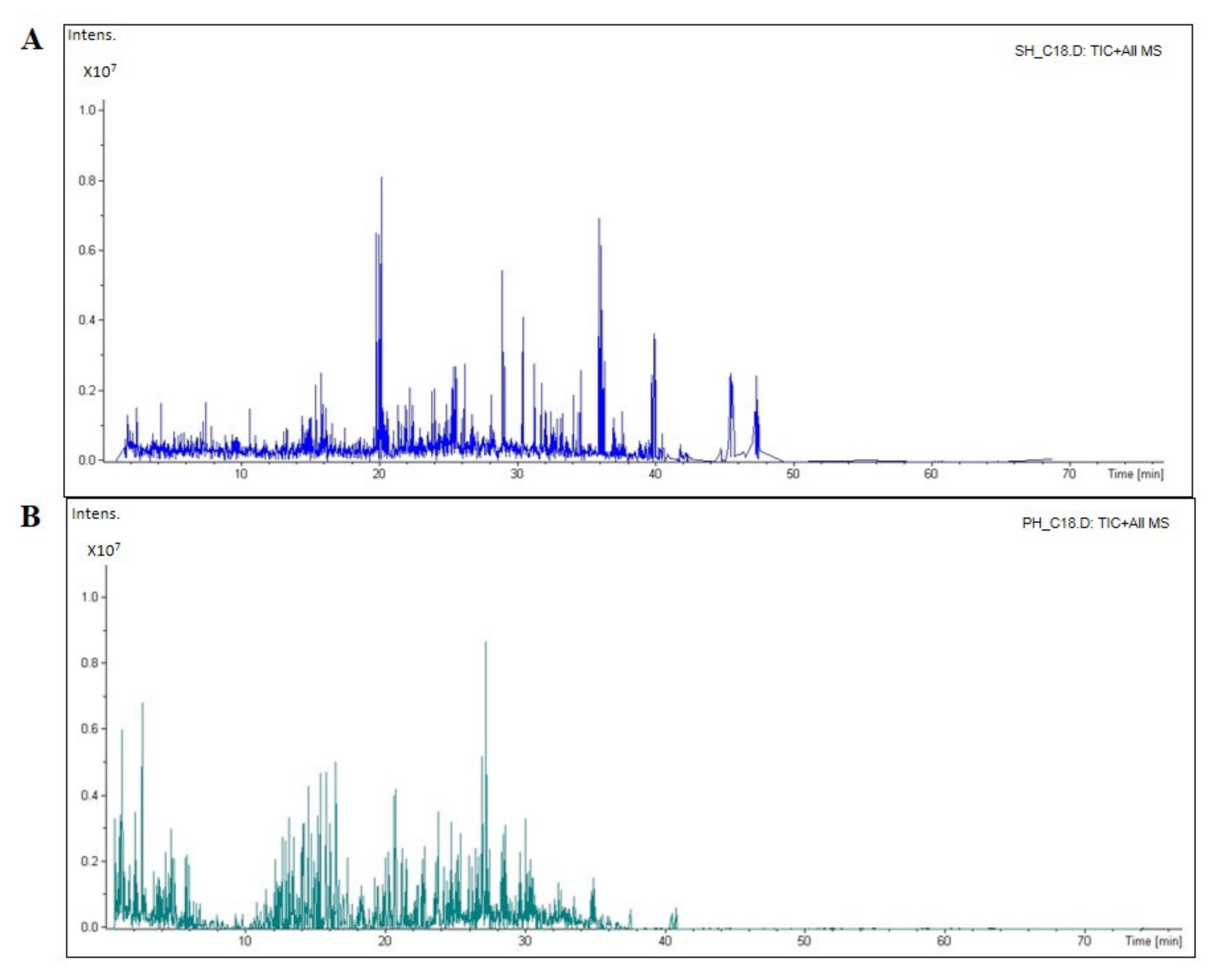
| Hydrolysate | MW > 3 kDa (%) | MW < 3 kDa (%) |
|---|---|---|
| SH | 53.6 | 46.4 |
| PH | 57.15 | 42.85 |
| Hydrolysate | Protein Name | Peptide Sequence | Intensity | ACE Inhibitor Sequence a | DPP-IV Inhibitor Sequence a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH | Ankyrin repeat domain-containing protein 52 | IRSWIVQVMS | 5.11 × 107 | IVQ, VQV, VM | WI, IR, QV, SW, VM, VQ |
| Glycinin G1 | VSIIDTNSLENQLDQ | 4.56 × 107 | SL, DQ, II, NQ, QL, SI, TN, VS | ||
| IIDTNSLENQLDQMPR | 2.07 × 107 | PR | MP, SL, DQ, II, NQ, QL TN | ||
| ANSLLNALPEEVIQ | 1.75 × 107 | EV, LN, ALP, LP | LP, LL, AL, SL, EV, IQ, LN, NA, VI | ||
| Hydrolase_4 domain-containing protein | AAEGGGFSDPAPAPPRLAIPEV | 1.45 × 107 | PR, AIP, IP, AP, LA, AA, GF, GG, AI, EG, PAP, EV, PP | PP, LA, AP PA, IP, AA AE, DP, EG EV, GF, GG, RL | |
| DNA-directed RNA polymerase (fragment) | FDIYRVMRPGEPPTMDSAEAMFNA | 1.48 × 107 | IY, MF, GEP, RP, GE, EA, PG, PT, PP, VM | PP, RP, EP, AE, FN, GE, MF, MR, NA, PG, PT, TM, VM, YR | |
| PH | Vicilin 47k | EITPEKNQQLQDLDIFVN | 2.26 × 107 | IF, EI, LQ EK, TP | TP, EK, EI NQ, QD, QL, QQ, VN |
| NQQLQDLDIFVN | 2.80 × 107 | IF, LQ | NQ, QD, QL, QQ, VN | ||
| KNQQLQDLDIFVN | 7.09 × 107 | IF, LQ | NQ, QD, QL, QQ VN | ||
| Vicilin | ITPEKNPQLQDLDIFVN | 1.58 × 107 | IF, LQ PQ, EK, TP | TP, NP, EK PQ, QD, QL, VN | |
| KNPQLQDLDIFVN | 5.13 × 107 | IF, LQ PQ | NP, PQ, QD QL, VN | ||
| AsmA family protein | GGLSFDRKAAKTTASGGLTLSKADA | 2.73 × 107 | AA, GL, DA, GG, SG, SF, KA, TLS, DR | KA, TA, TT GL, AA, AD AS, DR, GG KT, LT, RK SF, SK, TL | |
| Legumin A2 | LFGQAGLDPLPVDVGA-NGRL | 1.80 × 107 | PLP, RL LF, PL, VG GA, GL, AG GR, FG, GQ NG, LP | LP, GA, GL PL, AG, DP NG, PV, QA RL, VD, VG | |
| ALEPDNRIE | 1.53× 107 | IE, ALEP | EP, AL, DN NR, RI | ||
| SVINNLPLDVVA | 4.96 × 107 | PL, LPL, LP | VA, LP, VV LPL, PL, IN NL, NN, SV, VI |
| IC50 (mg/mL) DPP-IV | IC50 (mg/mL) ACE | |
|---|---|---|
| SH | 1.15 ± 0.004 | 0.33 ± 0.01 |
| PH | 1.33 ± 0.004 | 0.61 ± 0.05 |
| SH <3 kDa (F3) | 0.82 ± 0.01 | 0.40 ± 0.01 |
| PH <3 kDa (F3) | 1.0 ± 0.003 | 0.43 ± 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bollati, C.; Xu, R.; Boschin, G.; Bartolomei, M.; Rivardo, F.; Li, J.; Arnoldi, A.; Lammi, C. Integrated Evaluation of the Multifunctional DPP-IV and ACE Inhibitory Effect of Soybean and Pea Protein Hydrolysates. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122379
Bollati C, Xu R, Boschin G, Bartolomei M, Rivardo F, Li J, Arnoldi A, Lammi C. Integrated Evaluation of the Multifunctional DPP-IV and ACE Inhibitory Effect of Soybean and Pea Protein Hydrolysates. Nutrients. 2022; 14(12):2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122379
Chicago/Turabian StyleBollati, Carlotta, Ruoxian Xu, Giovanna Boschin, Martina Bartolomei, Fabrizio Rivardo, Jianqiang Li, Anna Arnoldi, and Carmen Lammi. 2022. "Integrated Evaluation of the Multifunctional DPP-IV and ACE Inhibitory Effect of Soybean and Pea Protein Hydrolysates" Nutrients 14, no. 12: 2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122379
APA StyleBollati, C., Xu, R., Boschin, G., Bartolomei, M., Rivardo, F., Li, J., Arnoldi, A., & Lammi, C. (2022). Integrated Evaluation of the Multifunctional DPP-IV and ACE Inhibitory Effect of Soybean and Pea Protein Hydrolysates. Nutrients, 14(12), 2379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122379









