Oxidative Stress Protection by Canary Seed (Phalaris canariensis L.) Peptides in Caco-2 Cells and Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Canary Seed Peptide Fraction (CSPF)
2.3. Proximate Composition
2.4. Total Amino Acid Analysis
2.5. Cellular Viability Test
2.6. Cellular Antioxidant Activity (CAA)
2.7. Caenorhabditis Elegans Growth and Maintenance
2.8. Chronic and Acute Oxidative Stress Using C. elegans Model
2.9. Quantitative Analysis of the Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
2.10. Gene Expression by Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximal Composition and Amino Acid Analysis
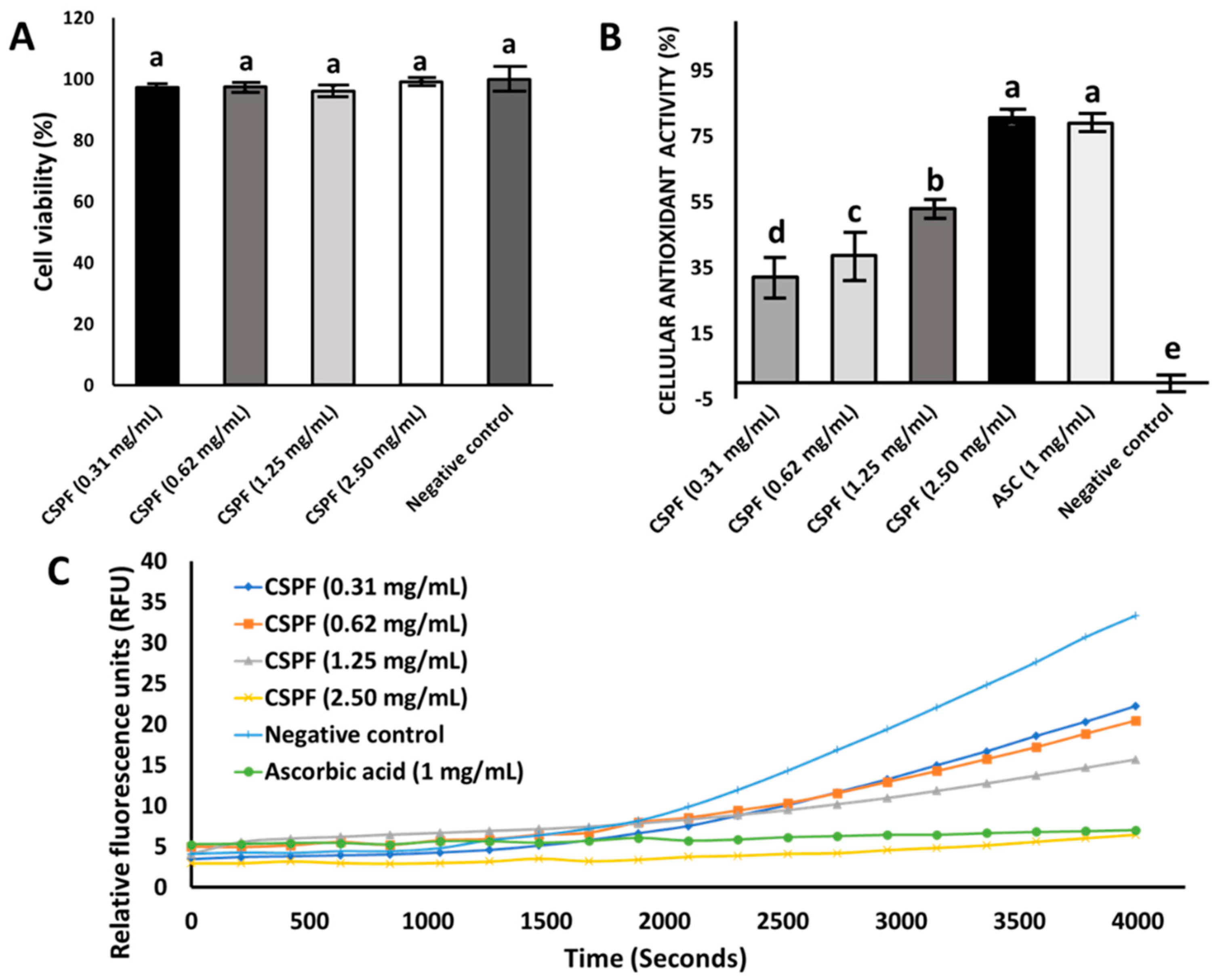
3.2. Effect of Canary Seed Peptides on Cellular Viability and Oxidative Stress
3.3. Antioxidant Properties of Canary Seed Peptides against Chronic and Acute Oxidative Stress
3.4. Expression of Antioxidant-Related Genes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mason, E.; L’Hocine, L.; Achouri, A.; Karboune, S. Hairless Canaryseed: A Novel Cereal with Health Promoting Potential. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M. Nutritional and functional attributes of hairless canary seed groats and components and their potential as functional ingredients. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novas, M.; Jiménez, A.; Asuero, A. Determination of Antioxidant Activity of Canary Seed Infusions by Chemiluminescence1. J. Anal. Chem. 2004, 59, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, L.; Wang, X.; Gu, Z.; Beta, T. Changes of phenolic profiles and antioxidant activity in canaryseed (Phalaris canariensis L.) during germination. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, E.; L’Hocine, L.; Achouri, A.; Pitre, M.; Karboune, S. Health Promoting Bioactive Properties of Novel Hairless Canary Seed Flour after In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion. Foods 2020, 9, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbizo-Reyes, U.; Aguilar-Toalá, J.; Liceaga, A. Hairless canary seeds (Phalaris canariensis L.) as a potential source of antioxidant, antihypertensive, antidiabetic, and antiobesity biopeptides. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2021, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, M.E.; Orona-Tamayo, D.; Nieto-Rendón, B.; Paredes-López, O. Antioxidant and antihypertensive potential of protein fractions from flour and milk substitutes from canary seeds (Phalaris canariensis L.). Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2017, 72, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketnawa, S.; Liceaga, A.M. Effect of microwave treatments on antioxidant activity and antigenicity of fish frame protein hydrolysates. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbizo-Reyes, U.; San Martin-González, M.F.; Garcia-Bravo, J.; López-Malo Vigil, A.; Liceaga, A.M. Physicochemical characteristics of chia seed (Salvia hispanica) protein hydrolysates produced using ultrasonication followed by microwave-assisted hydrolysis. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mares-Mares, E.; Aguilar-Bravo, C.; Herrera-Castillo, F.L.M.; Sosa-Morales, M.C.E.; Del Rincón-Castro, M.C.; León-Galván, M.F. Antihypertensive and antioxidant capacity of a high protein beverage (walnut-sesame seeds- oat-soybean). In Proceedings of the 2017 ASABE Annual International Meeting, Spokane, WA, USA, 16–19 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, F.; Liceaga, A. Effect of microwave-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis of cricket (Gryllodes sigillatus) protein on ACE and DPP-IV inhibition and tropomyosin-IgG binding. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, R.J.; Kellerby, S.S.; Decker, E.A. Antioxidant activity of proteins and peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapakse, N.; Mendis, E.; Jung, W.-K.; Je, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-K. Purification of a radical scavenging peptide from fermented mussel sauce and its antioxidant properties. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmadi, B.H.; Ismail, A.J.P. Antioxidative peptides from food proteins: A review. Peptides 2010, 31, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebiyi, A.P.; Adebiyi, A.O.; Yamashita, J.; Ogawa, T.; Muramoto, K. Purification and characterization of antioxidative peptides derived from rice bran protein hydrolysates. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 228, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzadehpanah, H.; Asoodeh, A.; Chamani, J. An antioxidant peptide derived from Ostrich (Struthio camelus) egg white protein hydrolysates. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, V.; Patil, A.; Phatak, A.; Chandra, N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, W.; Kong, X.; Hua, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y. Antioxidant and antibacterial activity and in vitro digestion stability of cottonseed protein hydrolysates. LWT 2020, 118, 108724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Zheng, X. Protective effect of mulberry fruit anthocyanin on human hepatocyte cells (LO2) and Caenorhabditis elegans under hyperglycemic conditions. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Peng, Q.; Su, L.; Yu, X.; Ma, C.W.; Liang, M.; Yin, X.; Zou, Y.; Huang, Z. Novel bioactive peptides from Meretrix meretrix protect Caenorhabditis elegans against free radical-induced oxidative stress through the stress response factor DAF-16/FOXO. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Arriola, E.; Cárdenas-Rodríguez, N.; Coballase-Urrutia, E.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Carmona-Aparicio, L.; Ortega-Cuellar, D. Caenorhabditis elegans: A useful model for studying metabolic disorders in which oxidative stress is a contributing factor. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 705253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, L.; Zhao, M.; Regenstein, J.M.; Ren, J. Changes in the antioxidant activity of loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) protein hydrolysates during a simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaswad, A.A.; Song, B.; Oehrle, N.W.; Wiebold, W.J.; Mawhinney, T.P.; Krishnan, H.B. Development of soybean experimental lines with enhanced protein and sulfur amino acid content. Plant Sci. 2021, 308, 110912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Er, S.; Koparal, A.T.; Kivanc, M. Cytotoxic effects of various lactic acid bacteria on Caco-2 cells. Turk. J. Biol. 2015, 39, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaypally, S.P.; Liceaga, A.M.; Kim, K.-H.; Ferruzzi, M.; Martin, F.S.; Goforth, R.R. Influence of molecular weight on intracellular antioxidant activity of invasive silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) protein hydrolysates. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Farias-Pereira, R.; Zhang, Y.; Jang, M.; Park, Y.; Kim, K.-H. C. elegans ACAT regulates lipolysis and its related lifespan in fasting through modulation of the genes in lipolysis and insulin/IGF-1 signaling. BioFactors 2020, 46, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solis, G.M.; Petrascheck, M. Measuring Caenorhabditis elegans life span in 96 well microtiter plates. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 49, e2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Cheng, Q.; Peng, Q.; Yu, X.; Yin, X.; Liang, M.; Ma, C.W.; Huang, Z.; Jia, W. Antioxidant peptides derived from the hydrolyzate of purple sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus nudus) gonad alleviate oxidative stress in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasija, S.; Norman, K.R. Measurement of ROS in Caenorhabditis elegans using a reduced form of fluorescein. Bio-Protocol 2018, 8, e2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J. Total RNA extraction from Caenorhabditis elegans. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Kodera, Y.; Hirata, D.; Blackwell, T.K.; Mizunuma, M. Natural thioallyl compounds increase oxidative stress resistance and lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans by modulating SKN-1/Nrf. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, R.K.; Welch, R.W. Cereal Grains, in Encyclopedia of Human Nutrition, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 307–316. [Google Scholar]
- Urbizo-Reyes, U.; Liceaga, A.M.; Reddivari, L.; Kim, K.-H.; Anderson, J.M. Enzyme kinetics, molecular docking, and in silico characterization of canary seed (Phalaris canariensis L.) peptides with ACE and pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 88, 104892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellett, M.E.; Greenspan, P.; Pegg, R.B. Modification of the cellular antioxidant activity (CAA) assay to study phenolic antioxidants in a Caco-2 cell line. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Liu, D.; Yu, X.; Sun, H.; Li, Y. A Caco-2 cell-based quantitative antioxidant activity assay for antioxidants. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Nagarajan, A.; Uchil, P.D. Analysis of cell viability by the MTT assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, B.A.; Patterson, C.A.; Hucl, P.; Newkirk, R.W.; Ram, J.I.; Classen, H.L. Safety assessment of consumption of glabrous canary seed (Phalaris canariensis L.) in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 63, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-Y.; Zhang, J.-T.; Miyakawa, T.; Li, G.-M.; Gu, R.-Z.; Tanokura, M. Antioxidant properties and inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme by highly active peptides from wheat gluten. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülseren, İ.; Vahapoglu, B. The Stability of Food Bioactive Peptides in Blood: An Overview. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2022, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Hao, X.; Tan, J.; Wang, W.; Yu, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of the Enzymatic hydrolysates from Chlorella vulgaris protein and assessment of their antioxidant potential using Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Biotechnol. 2021, 63, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Ma, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Zou, C.-G. Antioxidant response is a protective mechanism against nutrient deprivation in C. elegans. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masella, R.; Di Benedetto, R.; Varì, R.; Filesi, C.; Giovannini, C. Novel mechanisms of natural antioxidant compounds in biological systems: Involvement of glutathione and glutathione-related enzymes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, F.; Teixeira-Castro, A.; Costa, M.D.; Lindsay, V.; Fiúza-Fernandes, J.; Goua, M.; Bermano, G.; Russell, W.; Maciel, P.; Kong Thoo Lin, P. GST-4-dependent suppression of neurodegeneration in C. elegans models of Parkinson’s and Machado-Joseph disease by rapeseed pomace extract supplementation. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Cui, X.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Wang, Z. Peptides from sesame cake reduce oxidative stress and amyloid-β-induced toxicity by upregulation of SKN-1 in a transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 39, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calahorra Garcia-Moreno, J.; Porta de la Riva, M.; Martínez-Lara, E.; Siles, E.; Cañuelo, A. Tyrosol, a simple phenol from EVOO, targets multiple pathogenic mechanisms of neurodegeneration in a C. elegans model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 82, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Rubio, M.A.; Hernández-García, S.; García-Carmona, F.; Gandía-Herrero, F. Flavonoids’ Effects on Caenorhabditis elegans’ Longevity, Fat Accumulation, Stress Resistance and Gene Modulation Involve mTOR, SKN-1 and DAF-16. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ijomone, O.M.; Miah, M.R.; Akingbade, G.T.; Bucinca, H.; Aschner, M. Nickel-induced developmental neurotoxicity in C. elegans includes cholinergic, dopaminergic and GABAergic degeneration, altered behaviour, and increased SKN-1 activity. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 37, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detienne, G.; Van de Walle, P.; De Haes, W.; Schoofs, L.; Temmerman, L. SKN-1-independent transcriptional activation of glutathione S-transferase 4 (GST-4) by EGF signaling. In Worm; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mohankumar, A.; Kalaiselvi, D.; Thiruppathi, G.; Muthusaravanan, S.; Nivitha, S.; Levenson, C.; Tawata, S.; Sundararaj, P. α-and β-santalols delay aging in Caenorhabditis elegans via preventing oxidative stress and protein aggregation. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 32641–32654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Amino Acids | Relative Content (g/100 g) |
|---|---|
| Taurine § | 0.10 |
| Aspartic Acid | 4.79 |
| Threonine | 2.50 |
| Serine | 3.98 |
| Glutamic Acid | 30.72 |
| Proline | 6.34 |
| Lanthionine § | 0.19 |
| Glycine | 3.21 |
| Alanine | 4.44 |
| Cysteine | 2.50 |
| Valine | 4.55 |
| Methionine | 1.37 |
| Isoleucine | 4.31 |
| Leucine | 7.56 |
| Tyrosine | 3.46 |
| Phenylalanine | 6.34 |
| Hydroxylysine | 0.30 |
| Ornithine § | 0.07 |
| Lysine | 2.00 |
| Histidine | 2.02 |
| Arginine | 6.27 |
| Tryptophan | 2.98 |
| AAA | 12.78 |
| PCAA | 10.29 |
| SAA | 3.88 |
| HAA | 41.08 |
| EAA/NEAA | 0.51 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urbizo-Reyes, U.; Kim, K.-H.; Reddivari, L.; Anderson, J.M.; Liceaga, A.M. Oxidative Stress Protection by Canary Seed (Phalaris canariensis L.) Peptides in Caco-2 Cells and Caenorhabditis elegans. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122415
Urbizo-Reyes U, Kim K-H, Reddivari L, Anderson JM, Liceaga AM. Oxidative Stress Protection by Canary Seed (Phalaris canariensis L.) Peptides in Caco-2 Cells and Caenorhabditis elegans. Nutrients. 2022; 14(12):2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122415
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrbizo-Reyes, Uriel, Kee-Hong Kim, Lavanya Reddivari, Joseph M. Anderson, and Andrea M. Liceaga. 2022. "Oxidative Stress Protection by Canary Seed (Phalaris canariensis L.) Peptides in Caco-2 Cells and Caenorhabditis elegans" Nutrients 14, no. 12: 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122415
APA StyleUrbizo-Reyes, U., Kim, K.-H., Reddivari, L., Anderson, J. M., & Liceaga, A. M. (2022). Oxidative Stress Protection by Canary Seed (Phalaris canariensis L.) Peptides in Caco-2 Cells and Caenorhabditis elegans. Nutrients, 14(12), 2415. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14122415