Bioactive Foods Decrease Liver and Brain Alterations Induced by a High-Fat-Sucrose Diet through Restoration of Gut Microbiota and Antioxidant Enzymes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Serum Biochemical Parameters
2.3. Energy Expenditure
2.4. Intraperitoneal Glucose Tolerance Test
2.5. Behavioral Evaluation
2.6. Body Composition
2.7. Gene Expression Analysis
2.8. Microbiota Analysis
2.9. Brain Tissue Preparation
2.10. Western-Blot Analysis
2.11. Diolistic Labelling
2.12. Immunohistochemistry
2.13. Image Acquisition and Morphometry
2.14. Statistical Analysis
2.15. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.16. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3. Results
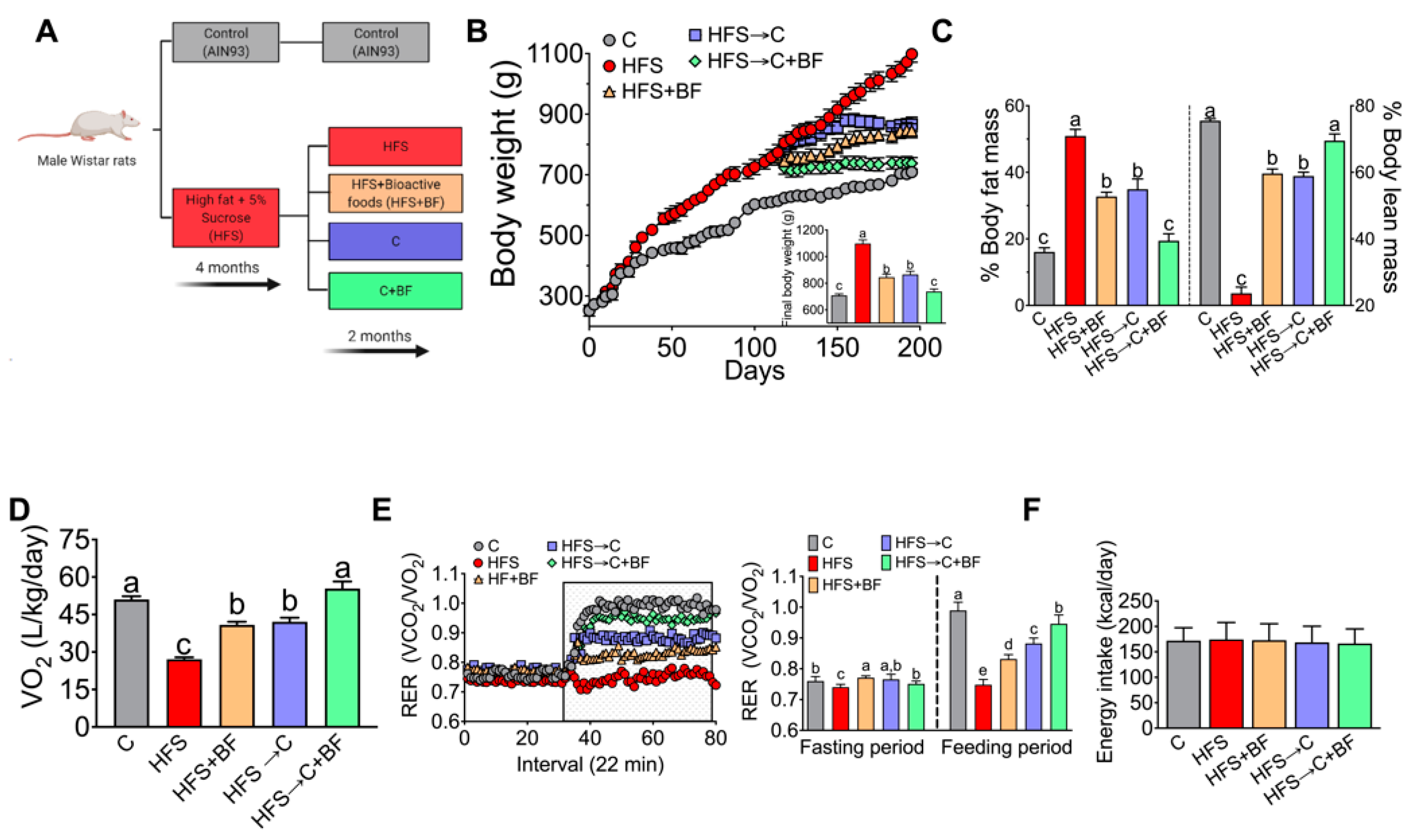
3.1. Body Weight, Body Composition, and Energy Expenditure
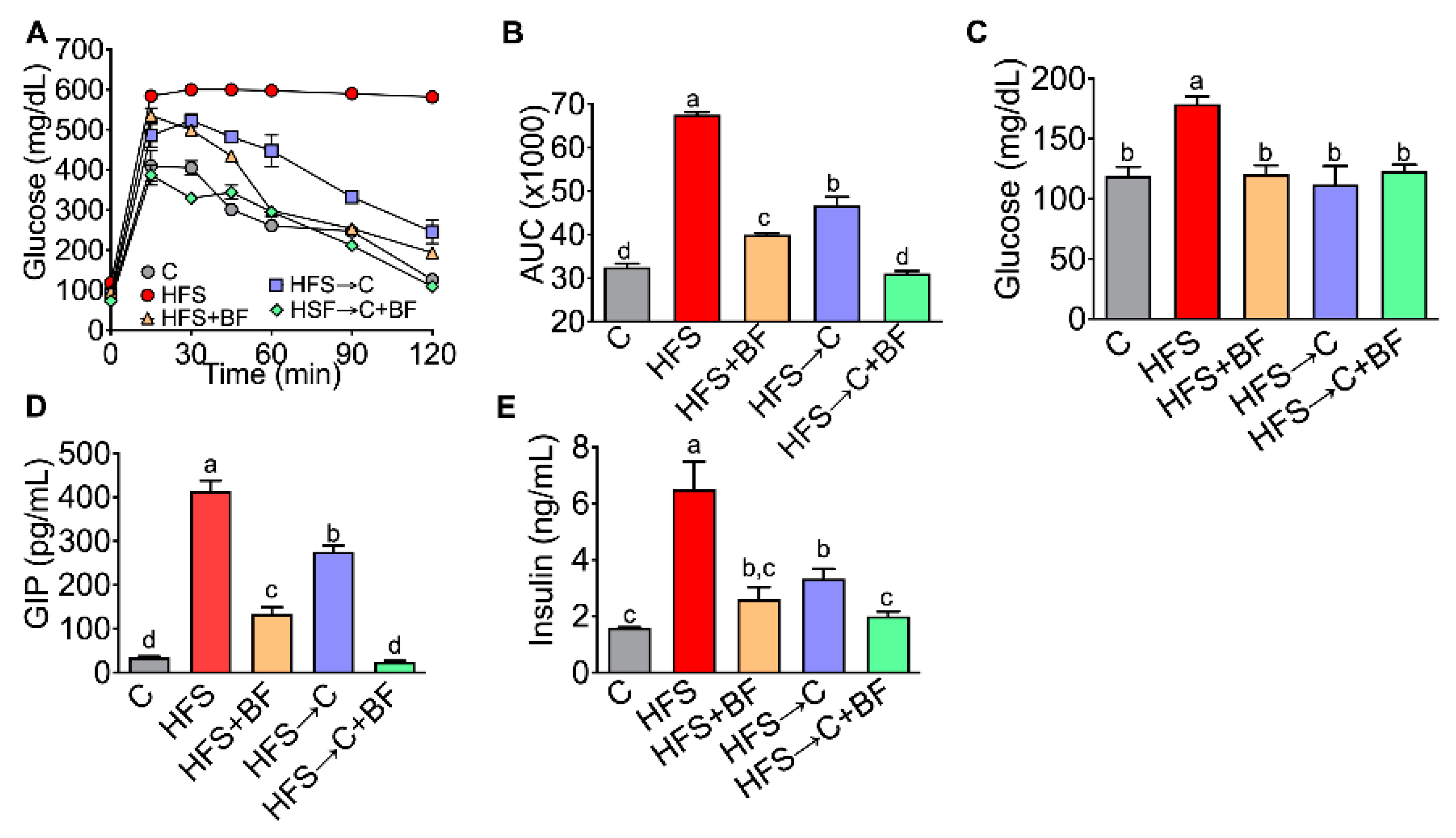
3.2. Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Sensitivity
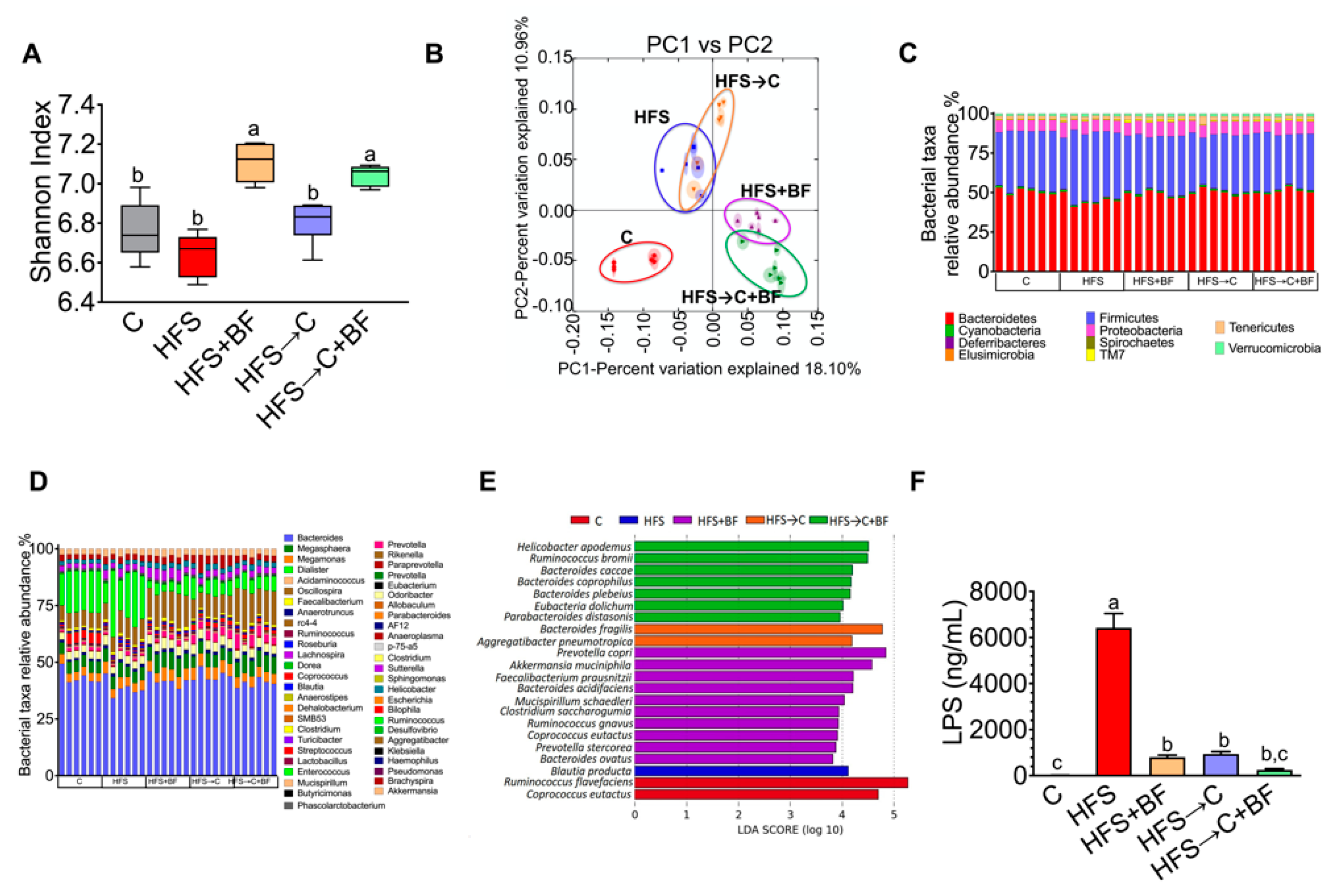
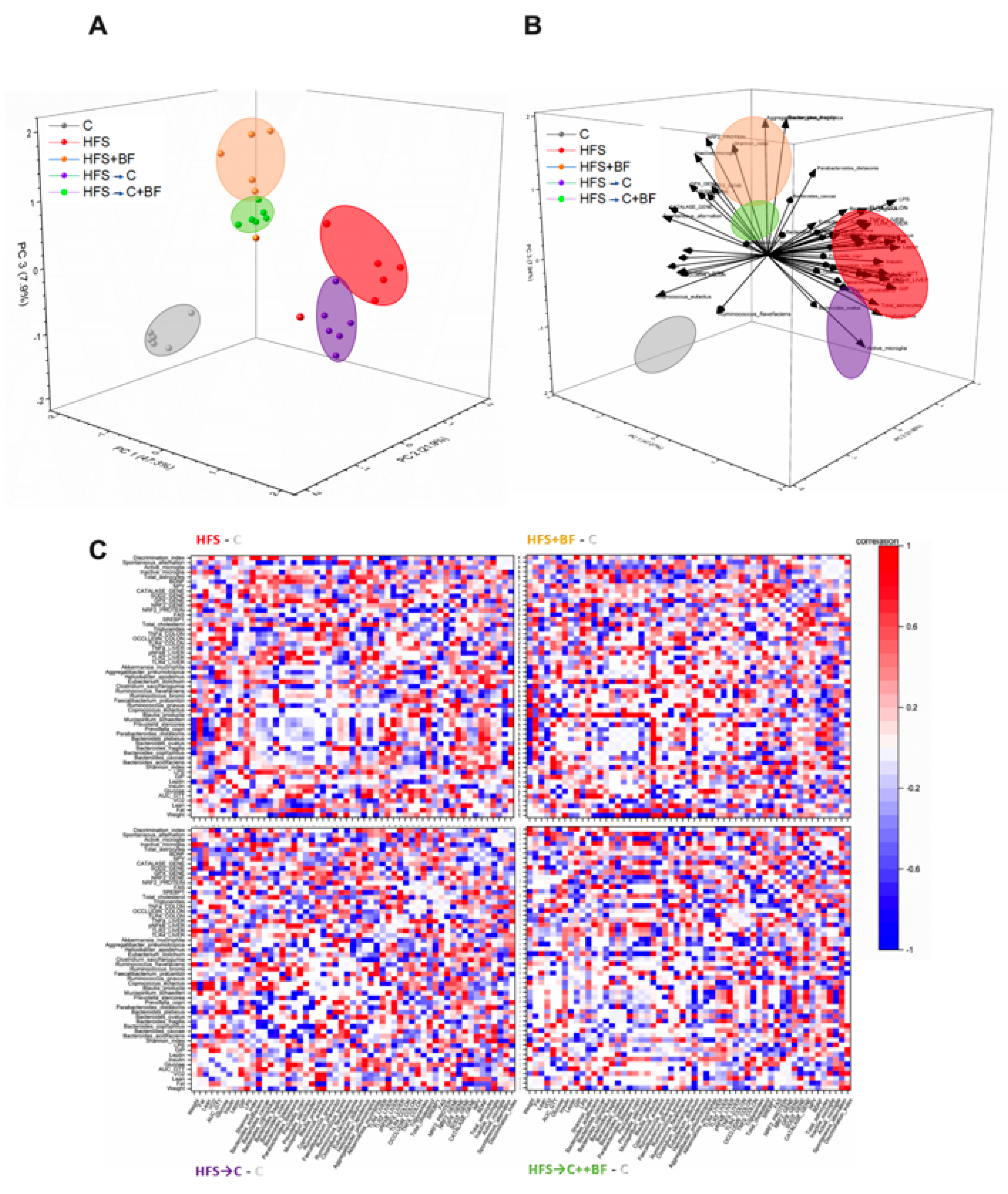
3.3. Gut Microbiota and Microbial α-Diversity
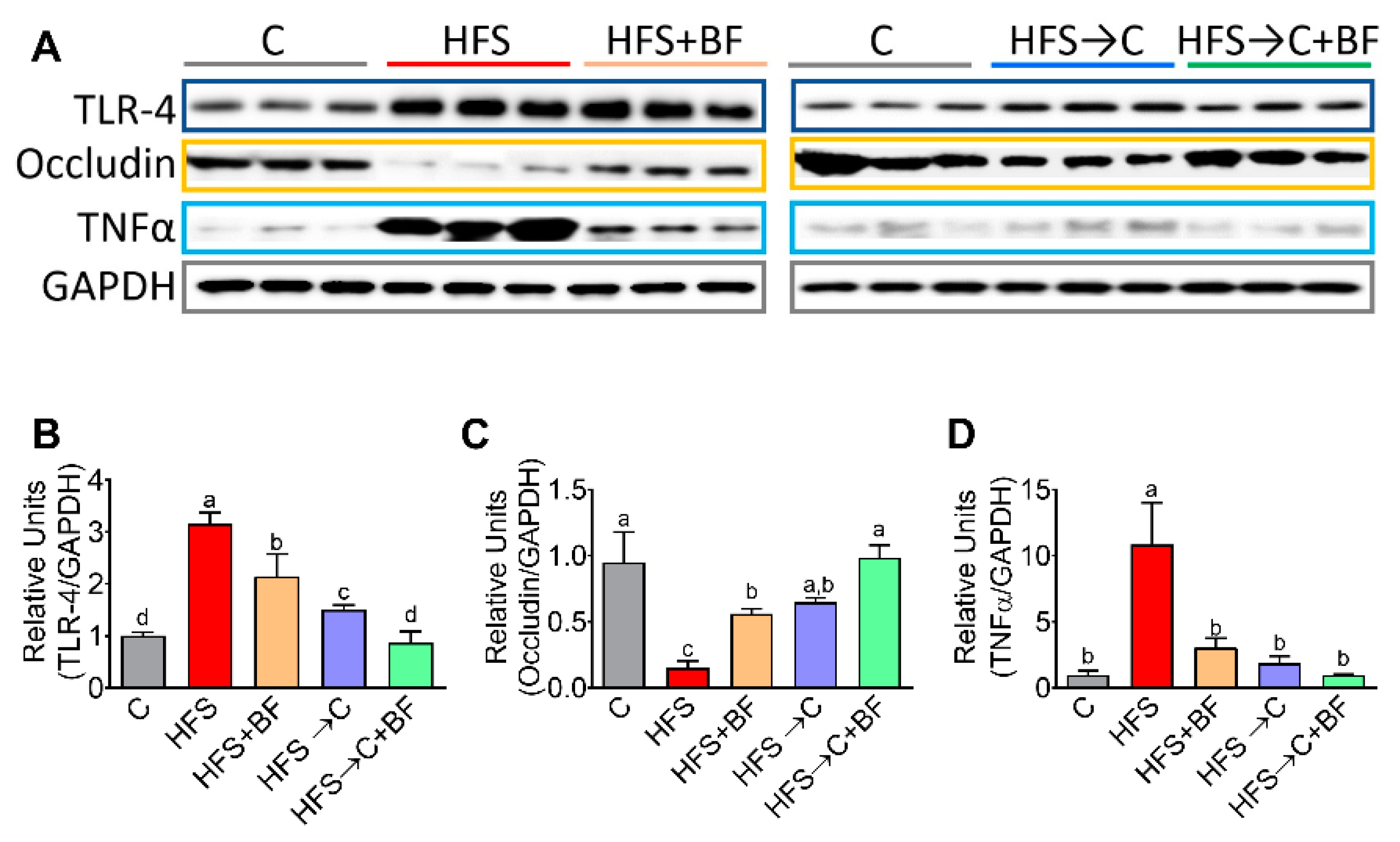
3.4. TNFα Production and Occludin Abundance in the Colon
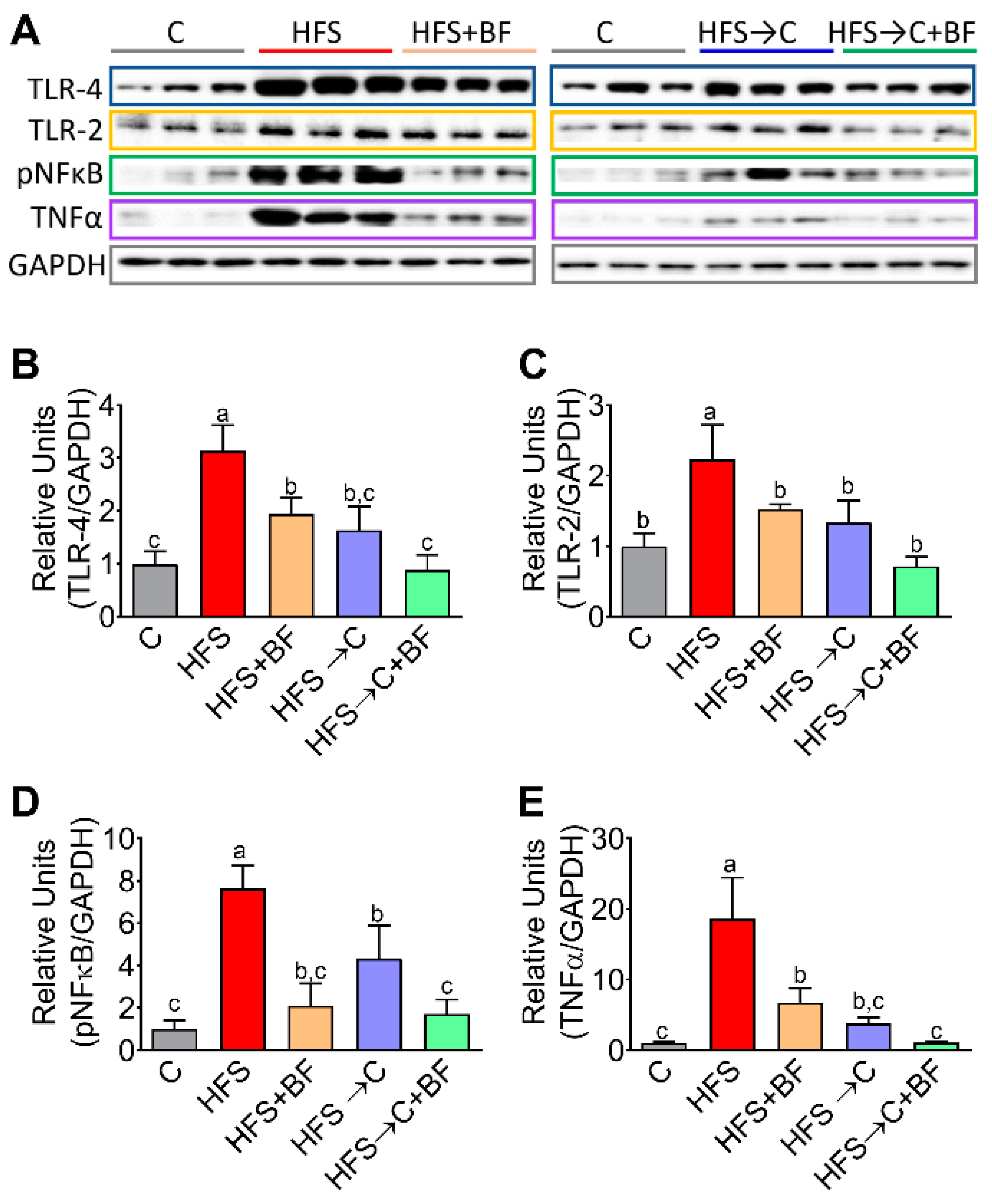
3.5. TNFα Release Mediated by TLR4 and pNF−κB
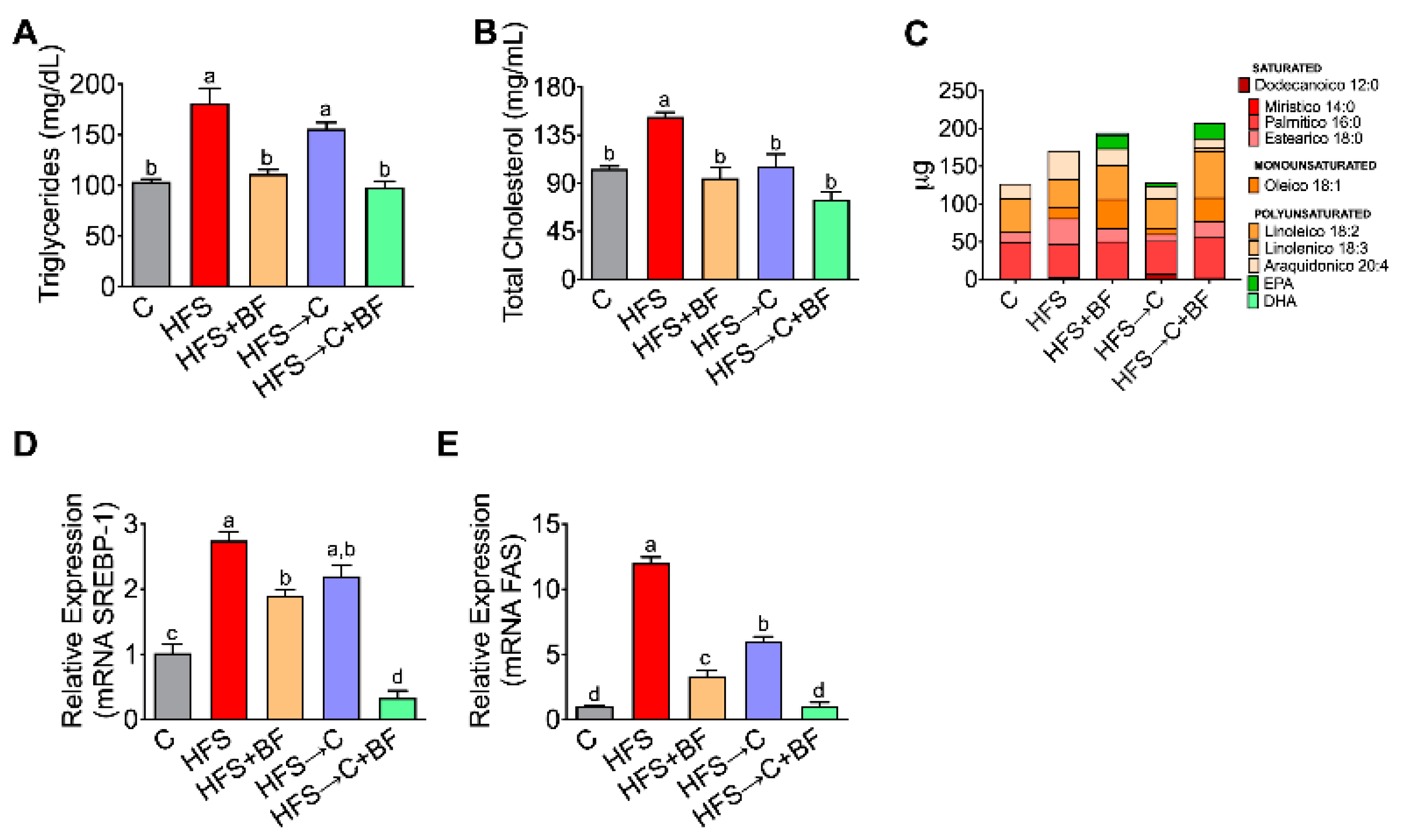
3.6. Expression of Lipogenic Genes
3.7. Hepatic Antioxidant System
3.8. Working Memory and Object Recognition
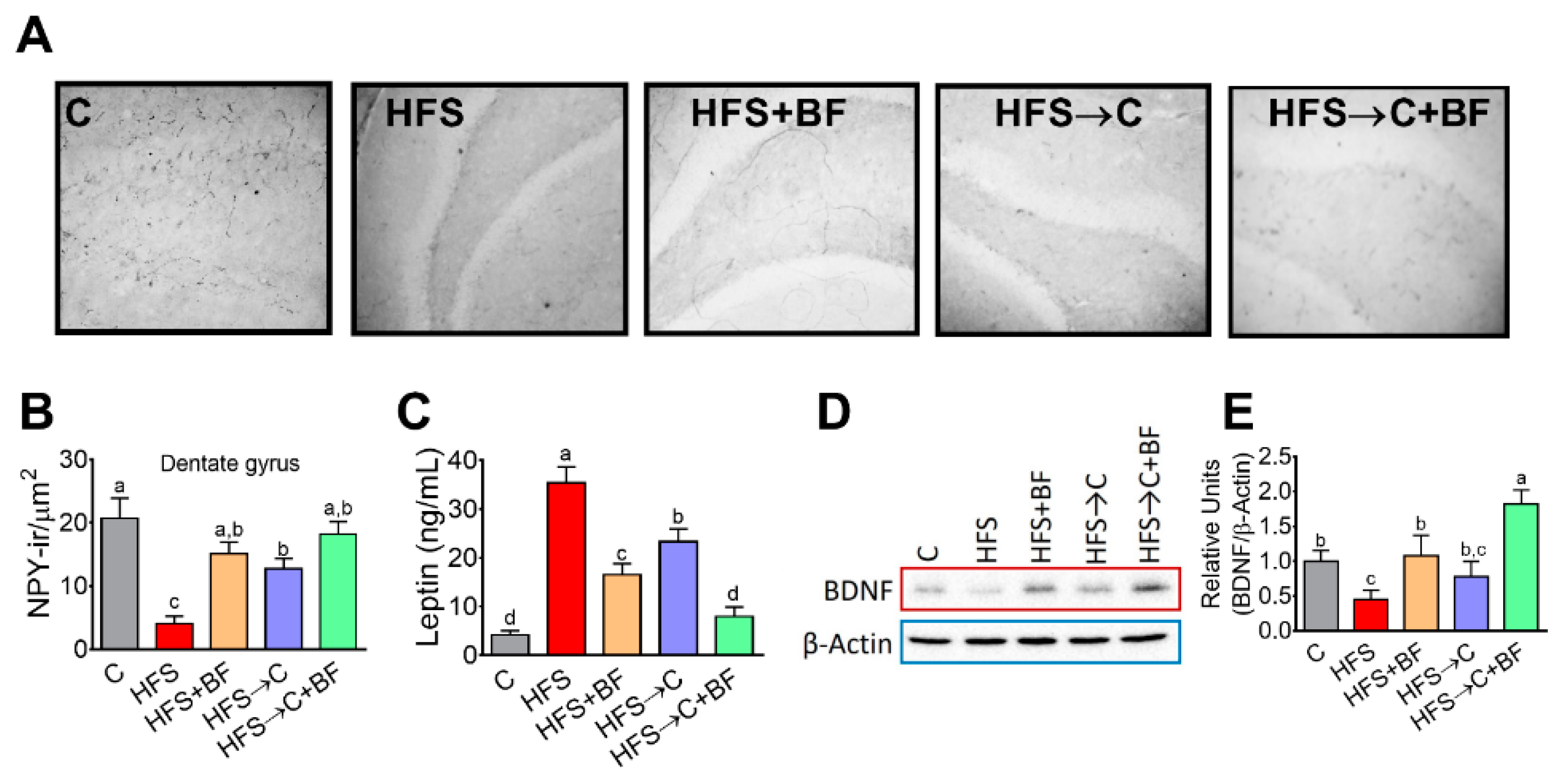
3.9. Number of NYP-Positive Cells in Dentate Gyrus and BDFN Levels in the PFC
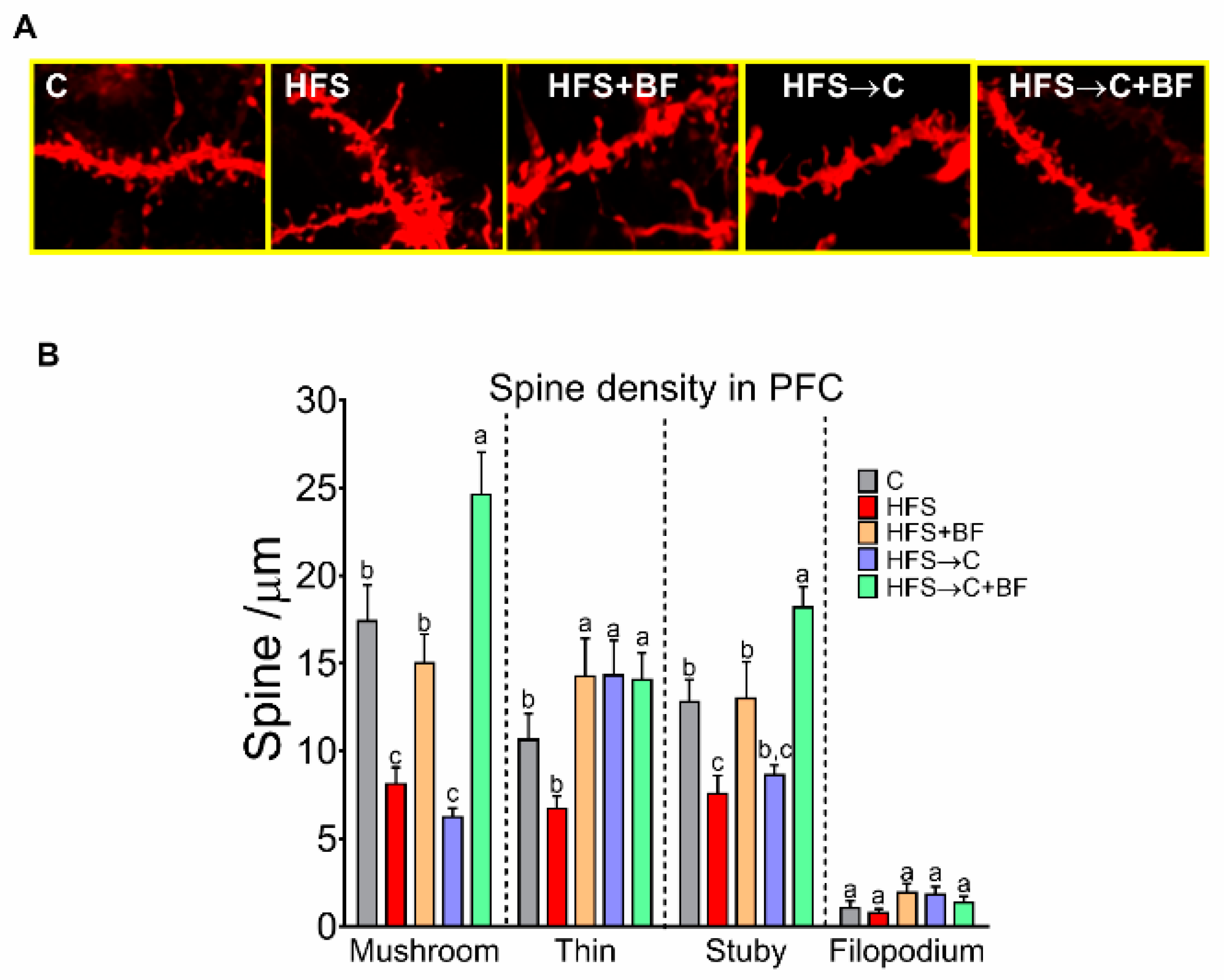
3.10. Number of Dendritic Spines in the PFC
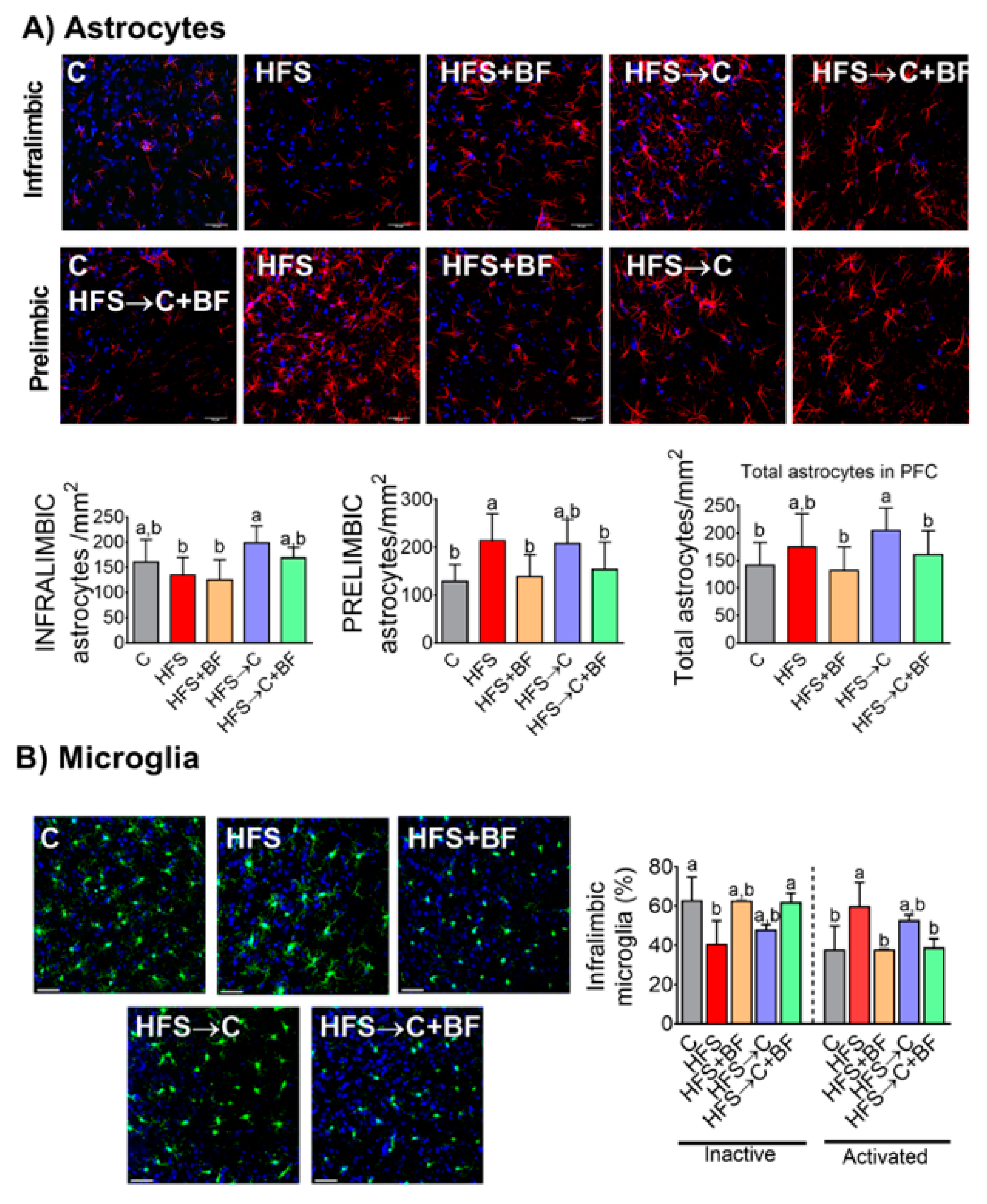
3.11. Neuroinflammation in the PFC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Ingredients (%) | C | HF | HF-C | HF + BF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cornstarch | 39.77 | 23.90 | 39.77 | 38.7 |
| Casein (<85% protein) | 20.00 | 24.00 | 20.00 | 24.00 |
| Dextrinized cornstarch | 13.20 | 10.27 | 13.20 | 10.27 |
| Sucrose | 10.00 | 7.78 | 10.00 | 7.78 |
| Soybean oil | 10.00 | 7.00 | 10.00 | 7.00 |
| Fiber celluose | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | - |
| Mineral mix (AIN-93MX) | 3.50 | 3.50 | 3.50 | 3.50 |
| Vitamin mix (AIN-93-VX) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| L-Cystine | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| Choline bitartrate (41.1% coline) | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Tert-butylhydroquinone | 0.0014 | 0.0014 | 0.0014 | 0.0014 |
| Lard | - | 17 | - | 17 |
| Chia oil | - | - | - | 3 |
| Nopal | - | - | - | 5 |
| Soy protein | - | - | - | 20 |
| Turmeric | - | - | - | 1 |
References
- Nguyen, J.C.; Killcross, A.S.; Jenkins, T.A. Obesity and cognitive decline: Role of inflammation and vascular changes. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas-Villegas, A.; Sanchez-Tapia, M.; Avila-Nava, A.; Ramirez, V.; Tovar, A.R.; Torres, N. Differential Effect of Sucrose and Fructose in Combination with a High Fat Diet on Intestinal Microbiota and Kidney Oxidative Stress. Nutrients 2017, 9, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroni, L.; Sarni, A.R.; Zuliani, C. Plant Foods Rich in Antioxidants and Human Cognition: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, P.G.; Nielsen, F.H.; Fahey, G.C., Jr. AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: Final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Salazar, V.; Tapia, M.S.; Tobon-Cornejo, S.; Diaz, D.; Aleman-Escondrillas, G.; Granados-Portillo, O.; Noriega, L.; Tovar, A.R.; Torres, N. Consumption of soybean or olive oil at recommended concentrations increased the intestinal microbiota diversity and insulin sensitivity and prevented fatty liver compared to the effects of coconut oil. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 94, 108751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Tapia, M.; Miller, A.W.; Granados-Portillo, O.; Tovar, A.R.; Torres, N. The development of metabolic endotoxemia is dependent on the type of sweetener and the presence of saturated fat in the diet. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1801301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuervo-Zanatta, D.; Garcia-Mena, J.; Perez-Cruz, C. Gut Microbiota Alterations and Cognitive Impairment Are Sexually Dissociated in a Transgenic Mice Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 82, S195–S214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeda, T.; Sanchez-Tapia, M.; Pinedo-Vargas, L.; Granados, O.; Cuervo-Zanatta, D.; Rojas-Santiago, E.; Diaz-Cintra, S.A.; Torres, N.; Perez-Cruz, C. Bioactive Food Abates Metabolic and Synaptic Alterations by Modulation of Gut Microbiota in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 66, 1657–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar, A.R.; Diaz-Villasenor, A.; Cruz-Salazar, N.; Ordaz, G.; Granados, O.; Palacios-Gonzalez, B.; Tovar-Palacio, C.; Lopez, P.; Torres, N. Dietary type and amount of fat modulate lipid metabolism gene expression in liver and in adipose tissue in high-fat diet-fed rats. Arch. Med. Res. 2011, 42, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Cruz, C.; Nolte, M.W.; van Gaalen, M.M.; Rustay, N.R.; Termont, A.; Tanghe, A.; Kirchhoff, F.; Ebert, U. Reduced spine density in specific regions of CA1 pyramidal neurons in two transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 3926–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Tapia, M.; Aguilar-Lopez, M.; Perez-Cruz, C.; Pichardo-Ontiveros, E.; Wang, M.; Donovan, S.M.; Tovar, A.R.; Torres, N. Nopal (Opuntia ficus indica) protects from metabolic endotoxemia by modifying gut microbiota in obese rats fed high fat/sucrose diet. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Callejas, J.D.; Fuchs, E.; Perez-Cruz, C. Evidence of Tau Hyperphosphorylation and Dystrophic Microglia in the Common Marmoset. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Callejas, J.D.; Cuervo-Zanatta, D.; Rosas-Arellano, A.; Fonta, C.; Fuchs, E.; Perez-Cruz, C. Loss of ferritin-positive microglia relates to increased iron, RNA oxidation, and dystrophic microglia in the brains of aged male marmosets. Am. J. Primatol. 2019, 81, e22956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Kaneko, K.; Lin, H.Y.; Mo, Q.; Xu, Y.; Suganami, T.; Ravn, P.; Fukuda, M. Gut Hormone GIP Induces Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in the Hypothalamus. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqaa102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Vianna, C.R.; Fukuda, M.; Berglund, E.D.; Liu, C.; Tao, C.; Sun, K.; Liu, T.; Harper, M.J.; Lee, C.E.; et al. Hepatocyte Toll-like receptor 4 regulates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, J.H.; Jin, Z.; Yang, X.X.; Lou, J.; Shan, W.X.; Hu, Y.X.; Du, Q.; Liao, Q.S.; Xie, R.; Xu, J.Y. Role of gut microbiota via the gut-liver-brain axis in digestive diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 6141–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabia, S.; Kivimaki, M.; Shipley, M.J.; Marmot, M.G.; Singh-Manoux, A. Body mass index over the adult life course and cognition in late midlife: The Whitehall II Cohort Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Tapia, M.; Moreno-Vicencio, D.; Ordaz-Nava, G.; Guevara-Cruz, M.; Granados-Portillo, O.; Vargas-Castillo, A.; Torres, N.; Tovar, A.R. Antibiotic Treatment Reduces the Health Benefits of Soy Protein. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, e2000532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Mechanisms of action of (n-3) fatty acids. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 592S–599S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, A.; Ying, Z.; Gomez-Pinilla, F. Dietary curcumin counteracts the outcome of traumatic brain injury on oxidative stress, synaptic plasticity, and cognition. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 197, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Key Molecule for Memory in the Healthy and the Pathological Brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozato, N.; Saito, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Katashima, M.; Tokuda, I.; Sawada, K.; Katsuragi, Y.; Kakuta, M.; Imoto, S.; Ihara, K.; et al. Blautia genus associated with visceral fat accumulation in adults 20–76 years of age. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2019, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodpaster, B.H.; Sparks, L.M. Metabolic Flexibility in Health and Disease. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreira, A.P.; Texeira, T.F.; Ferreira, A.B.; Peluzio Mdo, C.; Alfenas Rde, C. Influence of a high-fat diet on gut microbiota, intestinal permeability and metabolic endotoxaemia. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Murray, D.L.; Choy, L.N.; Spiegelman, B.M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits signaling from the insulin receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4854–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habbas, S.; Santello, M.; Becker, D.; Stubbe, H.; Zappia, G.; Liaudet, N.; Klaus, F.R.; Kollias, G.; Fontana, A.; Pryce, C.R.; et al. Neuroinflammatory TNFalpha Impairs Memory via Astrocyte Signaling. Cell 2015, 163, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ley, R.E. Gut microbiota in 2015: Prevotella in the gut: Choose carefully. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, D. Role of Natural Antioxidants on Neuroprotection and Neuroinflammation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; de Vos, W.M. Next-Generation Beneficial Microbes: The Case of Akkermansia muciniphila. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miquel, S.; Martin, R.; Rossi, O.; Bermudez-Humaran, L.G.; Chatel, J.M.; Sokol, H.; Thomas, M.; Wells, J.M.; Langella, P. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and human intestinal health. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Ryu, S.; Fukuda, S.; Hase, K.; Yang, C.S.; Lim, H.S.; Kim, M.S.; et al. Gut commensal Bacteroides acidifaciens prevents obesity and improves insulin sensitivity in mice. Mucosal. Immunol. 2017, 10, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerdiles, O.; Layé, S.; Calon, F. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and brain health: Preclinical evidence for the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samieri, C.; Maillard, P.; Crivello, F.; Proust-Lima, C.; Peuchant, E.; Helmer, C.; Amieva, H.; Allard, M.; Dartigues, J.F.; Cunnane, S.C.; et al. Plasma long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and atrophy of the medial temporal lobe. Neurology 2012, 79, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Loh, K.H.; Wu, M.; Morgan, D.A.; Schneeberger, M.; Yu, X.; Chi, J.; Kosse, C.; Kim, D.; Rahmouni, K.; et al. A leptin-BDNF pathway regulating sympathetic innervation of adipose tissue. Nature 2020, 583, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliari, B.; Scherer, E.B.; Machado, F.R.; Ferreira, A.G.; Dalmaz, C.; Wyse, A.T. Antioxidants prevent memory deficits provoked by chronic variable stress in rats. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Syeda, T.; Sánchez-Tapia, M.; Orta, I.; Granados-Portillo, O.; Pérez-Jimenez, L.; Rodríguez-Callejas, J.-d.-D.; Toribio, S.; Silva-Lucero, M.-d.-C.; Rivera, A.-L.; Tovar, A.R.; et al. Bioactive Foods Decrease Liver and Brain Alterations Induced by a High-Fat-Sucrose Diet through Restoration of Gut Microbiota and Antioxidant Enzymes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010022
Syeda T, Sánchez-Tapia M, Orta I, Granados-Portillo O, Pérez-Jimenez L, Rodríguez-Callejas J-d-D, Toribio S, Silva-Lucero M-d-C, Rivera A-L, Tovar AR, et al. Bioactive Foods Decrease Liver and Brain Alterations Induced by a High-Fat-Sucrose Diet through Restoration of Gut Microbiota and Antioxidant Enzymes. Nutrients. 2022; 14(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleSyeda, Tauqeerunnisa, Mónica Sánchez-Tapia, Itzel Orta, Omar Granados-Portillo, Lizbeth Pérez-Jimenez, Juan-de-Dios Rodríguez-Callejas, Samuel Toribio, Maria-del-Carmen Silva-Lucero, Ana-Leonor Rivera, Armando R. Tovar, and et al. 2022. "Bioactive Foods Decrease Liver and Brain Alterations Induced by a High-Fat-Sucrose Diet through Restoration of Gut Microbiota and Antioxidant Enzymes" Nutrients 14, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010022
APA StyleSyeda, T., Sánchez-Tapia, M., Orta, I., Granados-Portillo, O., Pérez-Jimenez, L., Rodríguez-Callejas, J.-d.-D., Toribio, S., Silva-Lucero, M.-d.-C., Rivera, A.-L., Tovar, A. R., Torres, N., & Perez-Cruz, C. (2022). Bioactive Foods Decrease Liver and Brain Alterations Induced by a High-Fat-Sucrose Diet through Restoration of Gut Microbiota and Antioxidant Enzymes. Nutrients, 14(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010022










