DW2009 Elevates the Efficacy of Donepezil against Cognitive Impairment in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Culture of Lactobacillus Plantarum C29
2.3. Animals
2.4. Preparation of Mice with Cognitive Impairment
2.5. Behavioral Tasks
2.6. Myeloperoxidase Activity Assay, Immunblotting, and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.8. Microbiota Composition Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
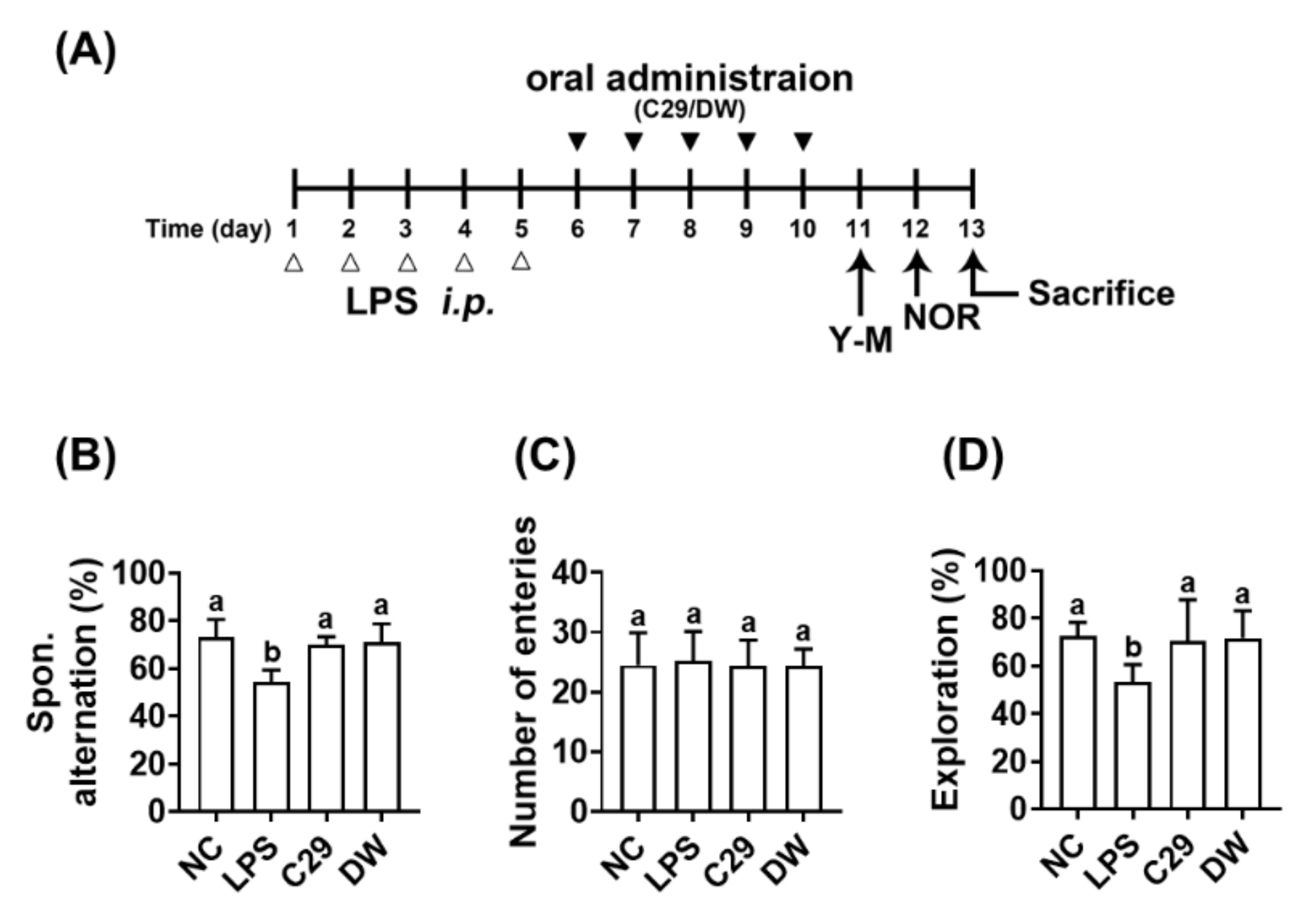
3.1. Effects of C29 and DW2009 in the LPS-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Mice
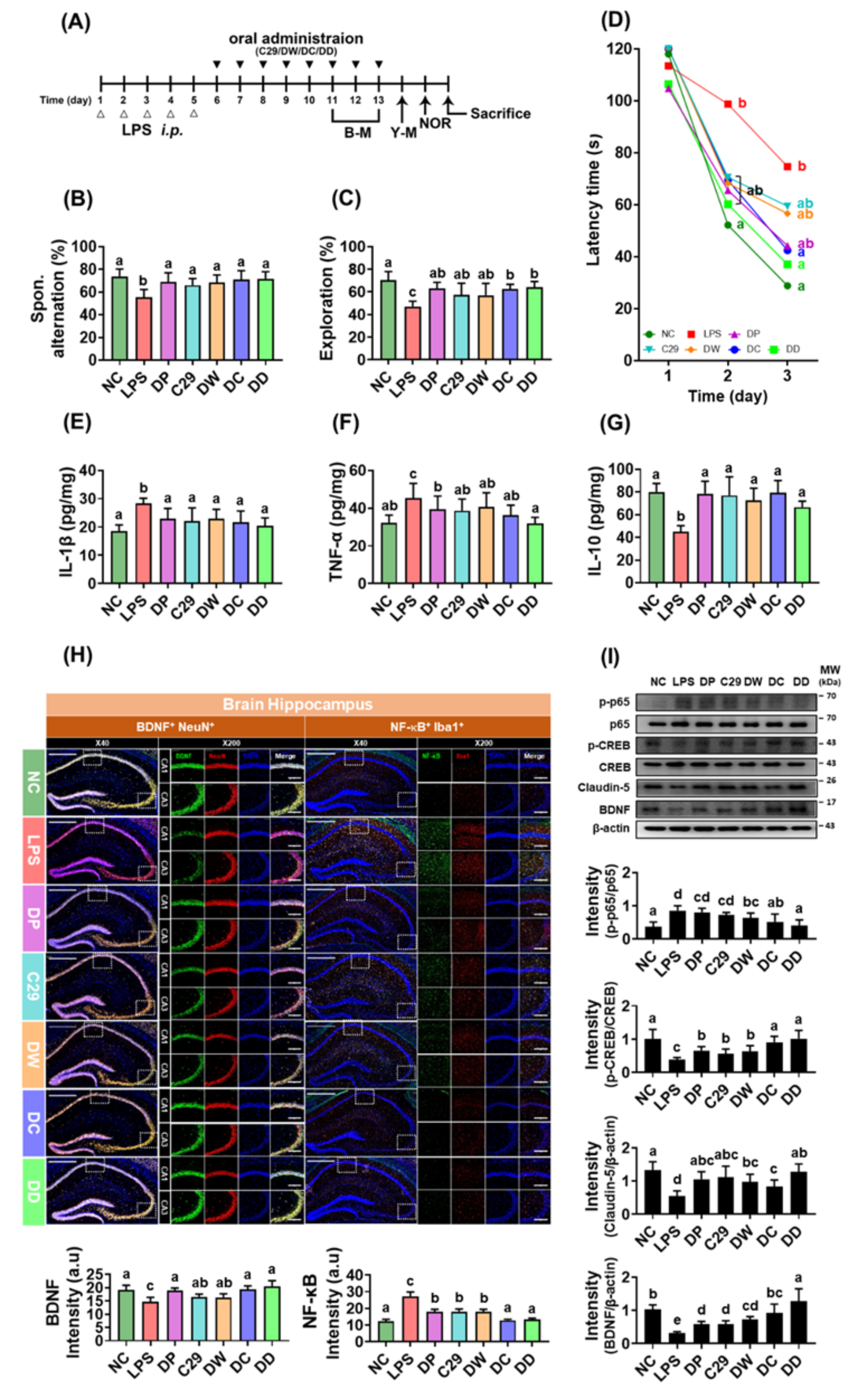
3.2. C29 and DW2009 Increased the Efficacy of Donepezil on LPS-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Mice
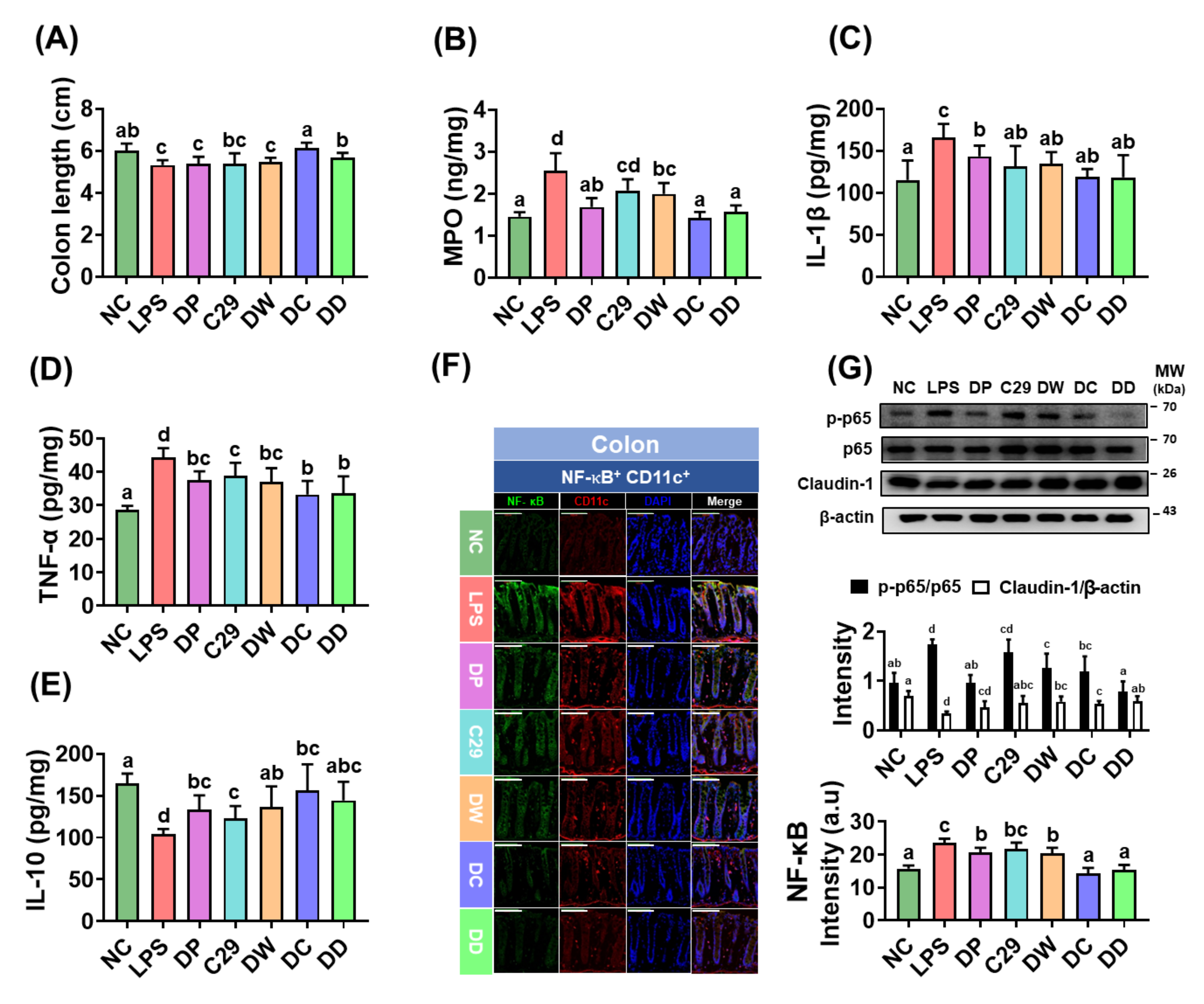
3.3. DC and DD Alleviated Colitis in Mice with LPS-Induced Cognitive Impairment
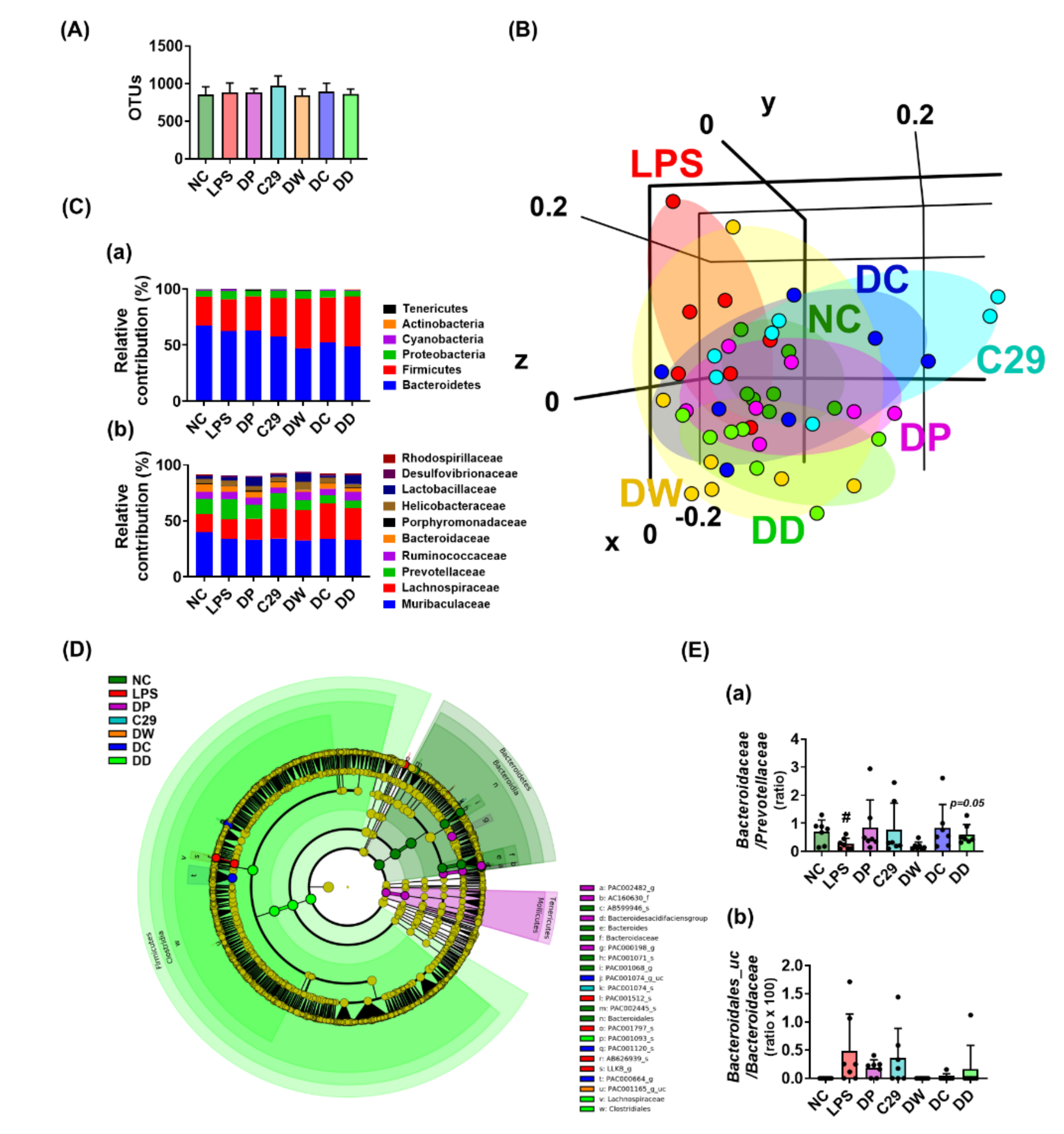
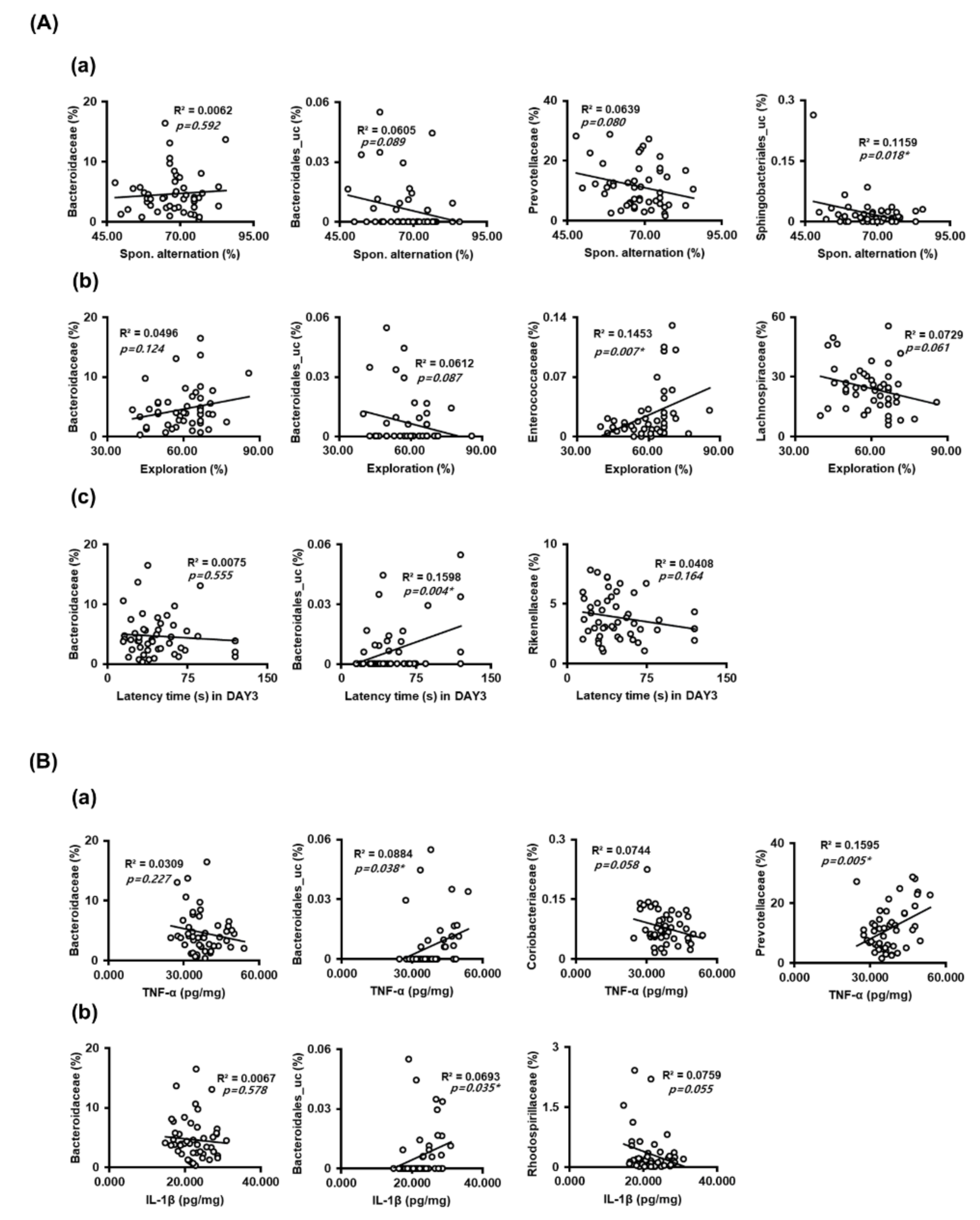
3.4. DC and DD Modulated the Gut Microbiota Composition in Mice with LPS-Induced Cognitive Impairment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, X.; Wang, X.; Geng, M. Alzheimer’s disease hypothesis and related therapies. Transl. Neurodegener. 2018, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, Y.; Tam, K.Y. Pathological mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Regen, F.; Hellmann-Regen, J.; Costantini, E.; Reale, M. Neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s Disease: Implications for Microglial Activation. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2017, 14, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Vieira, T.H.; Guimaraes, I.M.; Silva, F.R.; Ribeiro, F.M. Alzheimer’s disease: Targeting the cholinergic system. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Confaloni, A.; Tosto, G.; Tata, A.M. Promising therapies for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 2050–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Hatayama, Y.; Nakamichi, K.; Yoshida, N. Procognitive effect of AC-3933 in aged mice, and synergistic effect of combination with donepezil in scopolamine-treated mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 745, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, R.T. Memantine and donepezil: A fixed drug combination for the treatment of moderate to severe Alzheimer’s dementia. Drugs Today 2016, 52, 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.S.; Song, E.J.; Nam, Y.D.; Lee, S.Y. Probiotics in human health and disease: From nutribiotics to pharmabiotics. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tojo, R.; Suárez, A.; Clemente, M.G.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Margolles, A.; Gueimonde, M.; Ruas-Madiedo, P. Intestinal microbiota in health and disease: Role of bifidobacteria in gut homeostasis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 15163–15176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libertucci, J.; Young, V.B. The role of the microbiota in infectious diseases. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.E.; Jeong, J.J.; Kim, J.K.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Simultaneous amelioratation of colitis and liver injury in mice by Bifidobacterium longum LC67 and Lactobacillus plantarum LC27. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgibbon, G.; Mills, K.H.G. The microbiota and immune-mediated diseases: Opportunities for therapeutic intervention. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gérard, P. Gut microbiota and obesity. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Lee, K.E.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, D.H. Immobilization stress-induced Escherichia coli causes anxiety by inducing NF-kappaB activation through gut microbiota disturbance. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, K.E.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, D.H. Suppression of gut dysbiosis by Bifidobacterium longum alleviates cognitive decline in 5XFAD transgenic and aged mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, S.; Wang, T.; Hu, X.; Luo, J.; Li, W.; Wu, X.; Duan, Y.; Jin, F. Administration of Lactobacillus helveticus NS8 improves behavioral, cognitive, and biochemical aberrations caused by chronic restraint stress. Neuroscience 2015, 310, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Lee, K.E.; Lee, S.A.; Jang, H.M.; Kim, D.H. Interplay between human gut bacteria Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus mucosae in the occurrence of neuropsychiatric disorders in mice. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Jeong, J.J.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Lactobacillus plantarum C29 alleviates TNBS-induced memory impairment in mice. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lim, S.M.; Ko, D.B.; Jeong, J.J.; Hwang, Y.H.; Kim, D.H. Soyasapogenol B and genistein attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced memory impairment in mice by the modulation of NF-κB-mediated BDNF expression. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6877–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.H.; Park, S.; Paik, J.W.; Chae, S.W.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, D.G.; Ha, E.; Kim, M.; Hong, G.; Park, S.H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of Lactobacillus plantarum C29-fermented soybean (DW2009) in individuals with mild cognitive impairment: A 12-week, multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.E.; Kim, J.K.; Han, S.K.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Yim, S.V.; Kim, D.H. The extracellular vesicle of gut microbial Paenalcaligenes hominis is a risk factor for vagus nerve-mediated cognitive impairment. Microbiome 2020, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarter, M.; Bodewitz, G.; Stephens, D.N. Attenuation of scopolamine-induced impairment of spontaneous alteration behaviour by antagonist but not inverse agonist and agonist beta-carbolines. Psychopharmacology 1988, 94, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Obata, Y.; Pachnis, V. The effect of microbiota and the immune system on the development and organization of the enteric nervous system. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fullingv, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.E.; Lim, S.M.; Jeong, J.J.; Jang, H.M.; Lee, H.J.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Gastrointestinal inflammation by gut microbiota disturbance induces memory impairment in mice. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, H.M.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, S.E.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.H. Evidence for interplay among antibacterial-induced gut microbiota disturbance, neuro-inflammation, and anxiety in mice. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catorce, M.N.; Gevorkian, G. LPS-induced murine neuroinflammation model: Main features and suitability for pre-clinical assessment of nutraceuticals. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lima Giacobbo, B.; Doorduin, J.; Klein, H.C.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Bromberg, E.; de Vries, E.F.J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in brain disorders: Focus on neuroinflammation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 3295–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lukiw, W.J. Bacteroides fragilis lipopolysaccharide and inflammatory signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.-Y.; Kim, J.-K.; Yun, S.-W.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.-H. DW2009 Elevates the Efficacy of Donepezil against Cognitive Impairment in Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093273
Lee D-Y, Kim J-K, Yun S-W, Han MJ, Kim D-H. DW2009 Elevates the Efficacy of Donepezil against Cognitive Impairment in Mice. Nutrients. 2021; 13(9):3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093273
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dong-Yun, Jeon-Kyung Kim, Soo-Won Yun, Myung Joo Han, and Dong-Hyun Kim. 2021. "DW2009 Elevates the Efficacy of Donepezil against Cognitive Impairment in Mice" Nutrients 13, no. 9: 3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093273
APA StyleLee, D.-Y., Kim, J.-K., Yun, S.-W., Han, M. J., & Kim, D.-H. (2021). DW2009 Elevates the Efficacy of Donepezil against Cognitive Impairment in Mice. Nutrients, 13(9), 3273. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093273





