Safety and Efficacy of Early High Parenteral Lipid Supplementation in Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
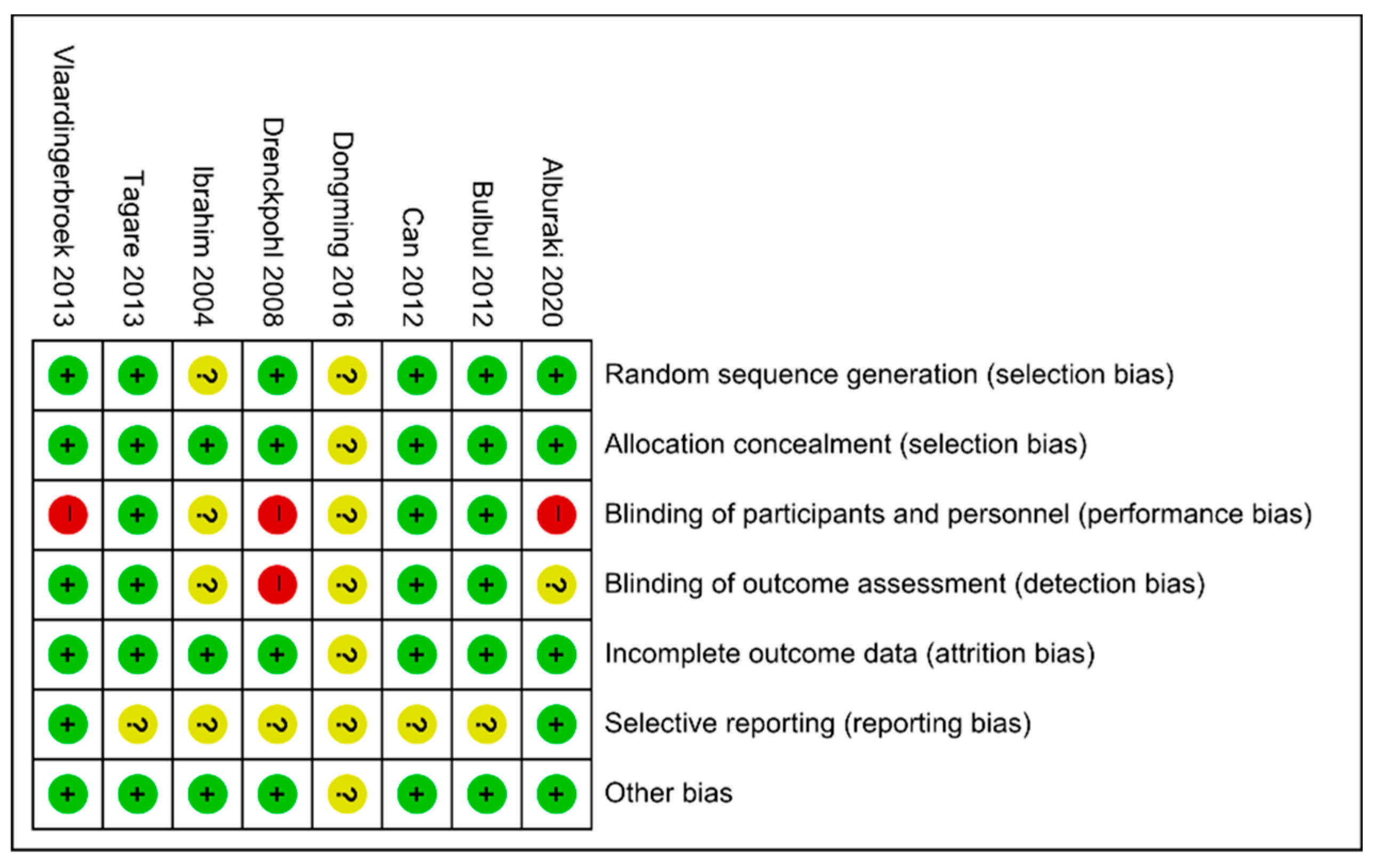
2.3. Data Extraction and Assessment of Risk of Bias
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
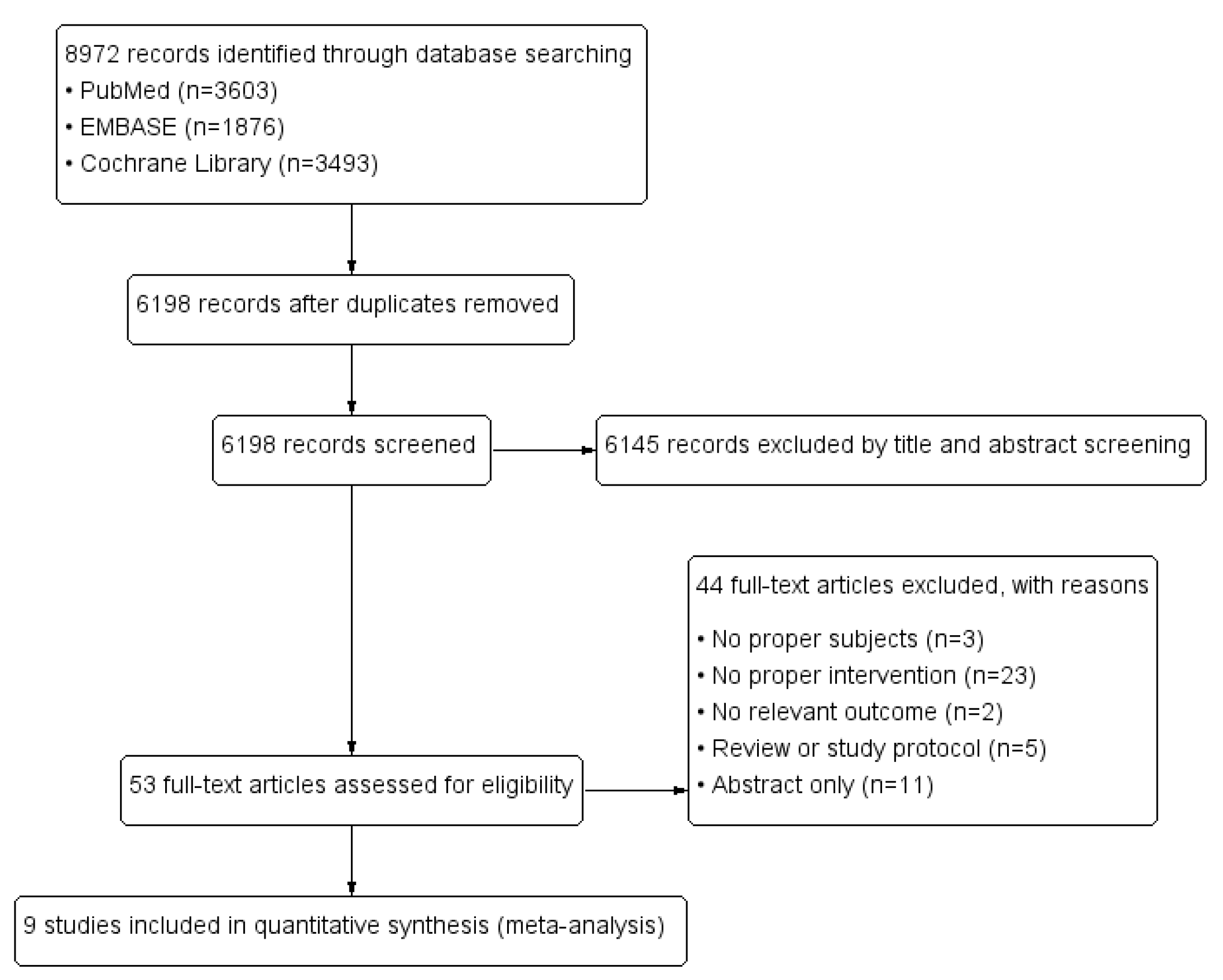
3.1. Systematic Literature Search Results
3.2. Sample Characteristics
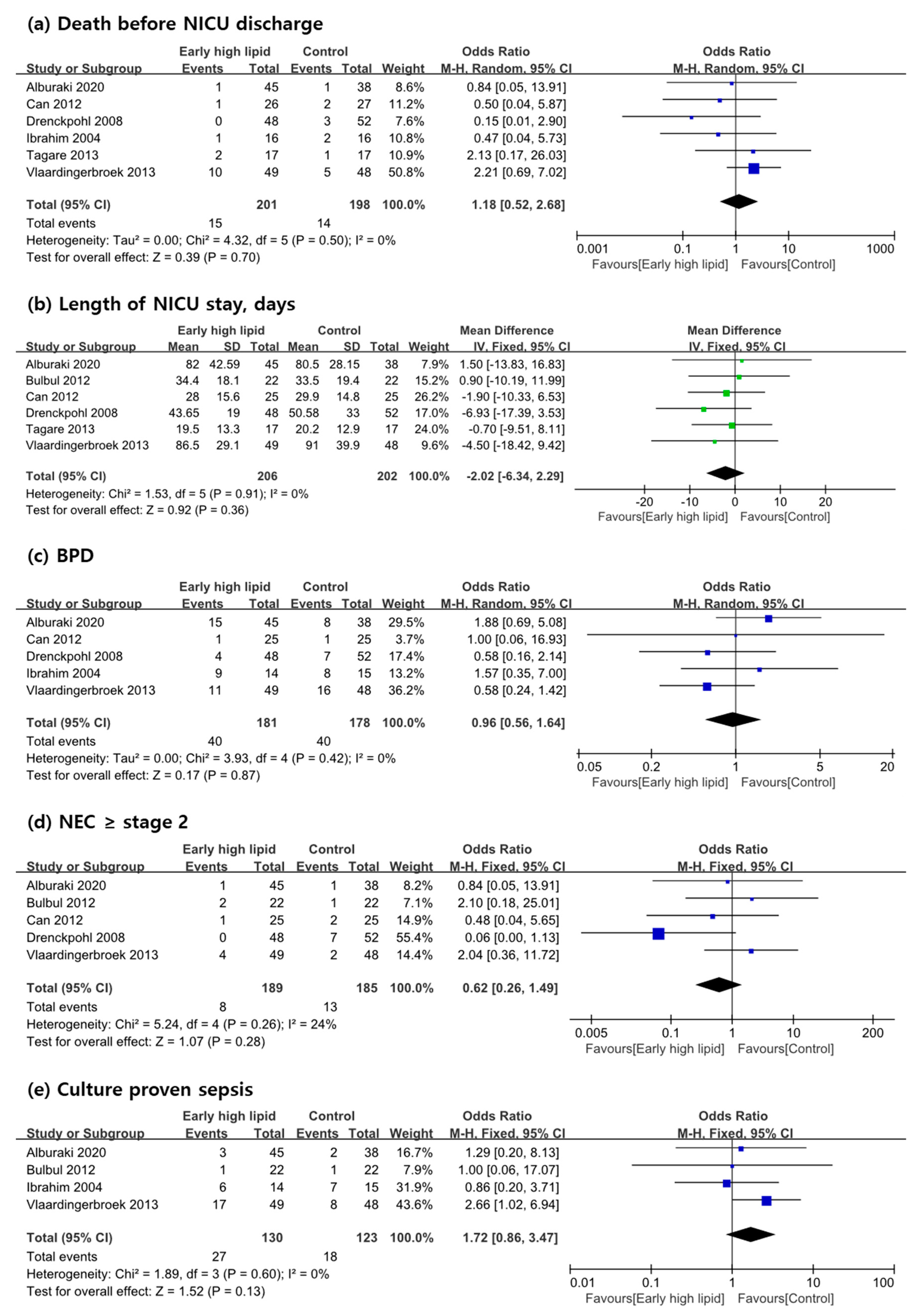
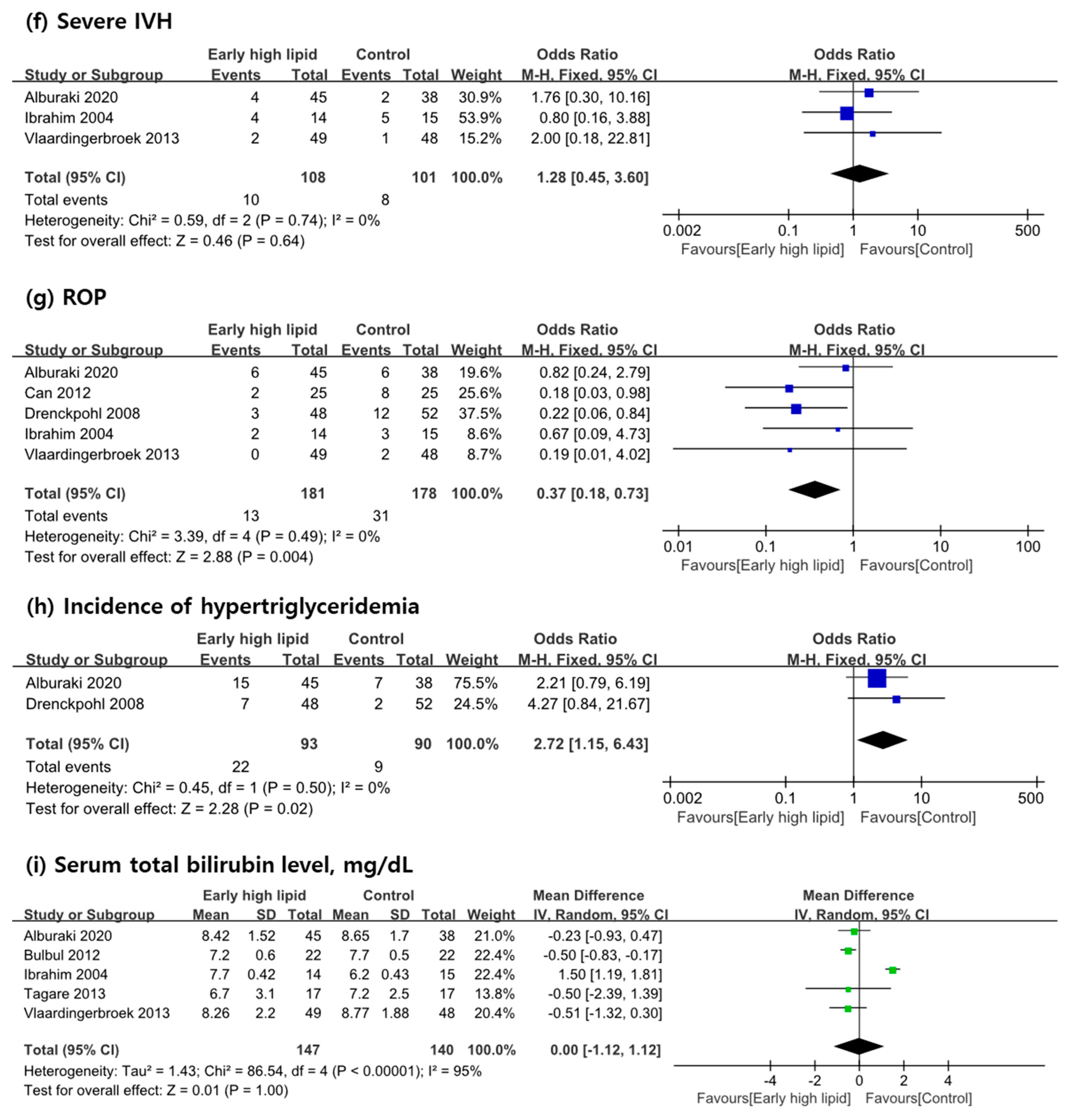
3.3. Primary Outcome Measures
3.4. Secondary Outcome Measures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lapillonne, A.; Griffin, I.J. Feeding preterm infants today for later metabolic and cardiovascular outcomes. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, S7–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embleton, N.E.; Pang, N.; Cooke, R.J. Postnatal malnutrition and growth retardation: An inevitable consequence of current recommendations in preterm infants? Pediatrics 2001, 107, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochow, N.; Raja, P.; Liu, K.; Fenton, T.; Landau-Crangle, E.; Göttler, S.; Jahn, A.; Lee, S.; Seigel, S.; Campbell, D. Physiological adjustment to postnatal growth trajectories in healthy preterm infants. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 79, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmer, K.; Rao, S.C. Early introduction of lipids to parenterally-fed preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2005, 18, CD005256. [Google Scholar]
- Vlaardingerbroek, H.; Veldhorst, M.A.; Spronk, S.; van den Akker, C.H.; van Goudoever, J.B. Parenteral lipid administration to very-low-birth-weight infants—early introduction of lipids and use of new lipid emulsions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, C.J.; Maucort-Boulch, D.; Megnier-Mbo, C.M.E.; Remontet, L.; Claris, O. Early parenteral lipids and growth velocity in extremely-low-birth-weight infants. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dit Trolli, S.E.; Kermorvant-Duchemin, E.; Huon, C.; Bremond-Gignac, D.; Lapillonne, A. Early lipid supply and neurological development at one year in very low birth weight (VLBW) preterm infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2012, 88, S25–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapillonne, A.; Mis, N.F.; Goulet, O.; van den Akker, C.H.; Wu, J.; Koletzko, B.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition: Lipids. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2324–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alburaki, W.; Yusuf, K.; Dobry, J.; Sheinfeld, R.; Alshaikh, B. High Early Parenteral Lipid in Very Preterm Infants: A Randomized-Controlled Trial. J. Pediatr. 2021, 228, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, T.R.; Nasser, R.; Eliasziw, M.; Kim, J.H.; Bilan, D.; Sauve, R. Validating the weight gain of preterm infants between the reference growth curve of the fetus and the term infant. BMC Pediatr. 2013, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.J.; Ternberg, J.L.; Feigin, R.D.; Keating, J.P.; Marshall, R.; Barton, L.; Brotherton, T. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Ann. Surg. 1978, 187, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papile, L.-A.; Burstein, J.; Burstein, R.; Koffler, H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: A study of infants with birth weights less than 1500 gm. J. Pediatr. 1978, 92, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Committee for the Classification of Retinopathy of Prematurity. The international classification of retinopathy of prematurity revisited. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2005, 123, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.; Green, S. 17.8. 2 Study summaries using more than one patient-reported outcome. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, Version 6.2; Cochrane: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongming, L.; Fengran, Z.; Zhaojun, Z. The study of early intravenous nutrition therapy in very low birth weight infants. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 29, 2293–2295. [Google Scholar]
- Tagare, A.; Walawalkar, M.; Vaidya, U. Aggressive parenteral nutrition in sick very low birth weight babies: A randomized controlled trial. Indian Pediatr. 2013, 50, 954–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaardingerbroek, H.; Vermeulen, M.J.; Rook, D.; van den Akker, C.H.; Dorst, K.; Wattimena, J.L.; Vermes, A.; Schierbeek, H.; van Goudoever, J.B. Safety and efficacy of early parenteral lipid and high-dose amino acid administration to very low birth weight infants. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelants, J.A.; Vlaardingerbroek, H.; van den Akker, C.H.; de Jonge, R.C.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Vermeulen, M.J. Two-Year Follow-up of a Randomized Controlled Nutrition Intervention Trial in Very Low-Birth-Weight Infants. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2018, 42, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulbul, A.; Okan, F.; Bulbul, L.; Nuhoglu, A. Effect of low versus high early parenteral nutrition on plasma amino acid profiles in very low birth-weight infants. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012, 25, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, E.; Bülbül, A.; Uslu, S.; Cömert, S.; Bolat, F.; Nuhoğlu, A. Effects of aggressive parenteral nutrition on growth and clinical outcome in preterm infants. Pediatrics Int. 2012, 54, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drenckpohl, D.; McConnell, C.; Gaffney, S.; Niehaus, M.; Macwan, K.S. Randomized trial of very low birth weight infants receiving higher rates of infusion of intravenous fat emulsions during the first week of life. Pediatrics 2008, 122, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Jeroudi, M.A.; Baier, R.; Dhanireddy, R.; Krouskop, R.W. Aggressive early total parental nutrition in low-birth-weight infants. J. Perinatol. 2004, 24, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobe, A.H.; Bancalari, E. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.C.; Yao, Q.; Gettner, P.; Hale, E.; Collins, M.; Hensman, A.; Everette, R.; Peters, N.; Miller, N.; Muran, G.; et al. Impact of a physiologic definition on bronchopulmonary dysplasia rates. Pediatrics 2004, 114, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larqué, E.; Demmelmair, H.; Gil-Sánchez, A.; Prieto-Sánchez, M.T.; Blanco, J.E.; Pagán, A.; Faber, F.L.; Zamora, S.; Parrilla, J.J.; Koletzko, B. Placental transfer of fatty acids and fetal implications. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 1908S–1913S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraghty, A.A.; Alberdi, G.; O’Sullivan, E.J.; O’Brien, E.C.; Crosbie, B.; Twomey, P.J.; McAuliffe, F.M. Maternal and fetal blood lipid concentrations during pregnancy differ by maternal body mass index: Findings from the ROLO study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2017, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, B.E.; Walden, R.V.; Gargus, R.A.; Tucker, R.; McKinley, L.; Mance, M.; Nye, J.; Vohr, B.R. First-week protein and energy intakes are associated with 18-month developmental outcomes in extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, G.F.; Wilson, D.C.; Ohlsson, A. Effect of Early Vs. Late Introduction of Intravenous Lipid To Preterm Infants on Death and Chronic Lung Disease (CLD)-Results of Meta-Analyses† 1250. Pediatr. Res. 1998, 43, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wilson, D.; Fox, G.; Ohlsson, A. Meta-analyses of effects of early or late introduction of intravenous lipid to preterm infants on mortality and chronic lung disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1998, 26, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correani, A.; Giretti, I.; Antognoli, L.; Monachesi, C.; Cogo, P.; D’Ascenzo, R.; Biagetti, C.; Carnielli, V.P. Hypertriglyceridemia and Intravenous Lipid Titration During Routine Parenteral Nutrition in Small Preterm Infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 69, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, A.; Nilsson, A.K.; Wackernagel, D.; Pivodic, A.; Vanpee, M.; Sjöbom, U.; Hellgren, G.; Hallberg, B.; Domellöf, M.; Klevebro, S.; et al. Effect of Enteral Lipid Supplement on Severe Retinopathy of Prematurity: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwaidh, M.; Bowden, L.; Shaw, B.; Ryan, S. Randomised trial of effect of delayed intravenous lipid administration on chronic lung disease in preterm neonates. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1996, 22, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, K.; Kelly, E.; Ng, P.; Kendall-Smith, S.; Dear, P. Early or late parenteral nutrition for the sick preterm infant? Arch. Dis. Child. 1993, 69, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerman, C.; Aramburo, M.J. Decreased lipid intake reduces morbidity in sick premature neonates. J. Pediatr. 1988, 113, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, T.; Reaman, G.; Outerbridge, E.; Colle, E. Peripheral total parenteral nutrition for premature infants with the respiratory distress syndrome: A controlled study. J. Pediatr. 1978, 92, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.C.; Cairns, P.; Halliday, H.L.; Reid, M.; McClure, G.; Dodge, J.A. Randomised controlled trial of an aggressive nutritional regimen in sick very low birthweight infants. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1997, 77, F4–F11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbertson, N.; Kovar, I.Z.; Cox, D.J.; Crowe, L.; Palmer, N.T. Introduction of intravenous lipid administration on the first day of life in the very low birth weight neonate. J. Pediatr. 1991, 119, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosenko, I.R.; Rodriguez-Pierce, M.; Bancalari, E. Effect of early initiation of intravenous lipid administration on the incidence and severity of chronic lung disease in premature infants. J. Pediatr. 1993, 123, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.J.; Cooke, R.W. Improving head growth in very preterm infants–a randomised controlled trial I: Neonatal outcomes. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2008, 93, F337–F341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Goudoever, J.B.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; de Pipaon, M.S.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Decsi, T.; Domellöf, M.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition: Amino acids. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2315–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study | Characteristics | Intervention (IV Lipid Intake) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Study Period | Design | Population | n | Experimental Group | Control Group | |
| Alburaki, 2020 [9] | Canada | Aug 2018 to Oct 2019 | RCT | PT infants with BW < 1500 g and <32 weeks GA | 83 | Started 2 g/kg/day within 12 h of birth, increased to 3 g/kg/day the next day | Started 0.5 g/kg/day (BW < 1000 g) or 1 g/kg/day (BW ≥ 1000 g) between 12–24 h, and advancing to 3 g/kg/day (increment 0.5 g/kg/day) |
| Dongming 2016 [17] | China | June 2013 to June 2015 | RCT | PT infants with BW < 1500 g | 80 | Started 1.5 g/kg/day within 24 h of birth and advancing to 3 g/kg/day (increment, 0.5 g/kg/day) | Only glucose within 3 days and started same parenteral nutrition after day 3. |
| Tagare, 2013 [18] | India | Oct 2009 to Mar 2010 | RCT | PT infants with BW < 1500 g and <32 weeks GA | 34 | Started with 2 g/kg/day within 24 h of birth, remained same thereafter | Started 1 g/kg/day at day 3, remained same thereafter |
| Vlaardingerbroek, 2013 [19] | Netherland | Dec 2008 to Jan 2012 | RCT | PT infants with BW < 1500 g | 97 1 | Started 2 g/kg/day immediately advancing to 3 g/kg/day, day 2. | Started 1.4 g/kg/day at day 2, next day increased to 2.8 g/kg/day |
| Bulbul, 2012 [21] | Turkey | RCT | PT infants with 750 g < BW < 1500 g and <32 weeks GA | 41 | Started 3 g/kg/day, on day 1, remained same thereafter | Started 1.0 g/kg/day at day 3, advancing up to 3 g/kg/day (increment 1.0 g/kg/day) | |
| Can, 2012 [22] | Turkey | Feb 2009 to May 2010 | RCT | PT infants with <34 weeks GA | 53 | Started 2 g/kg/day on day 1, advancing to 3.0 g/kg/day on day 2. | Started 1.0 g/kg/day on day 1, advancing up to 3 g/kg/day (increment 1.0 g/kg/day) |
| Drenckpohl, 2008 [23] | Illinois, US | June 2005 to Sep 2009 | RCT | PT infants with 750 g < BW < 1500 g | 100 | Started 2 g/kg/day on day 1, advancing to 3 g/kg/day (increment 0.5 g/kg/day) | Started 0.5 g/kg/day on day 1, advancing up to 3 g/kg/day (increment 0.5 g/kg/day) |
| Ibranhim, 2004 [24] | Louisiana, US | July 2001 to Apr 2002 | RCT | PT infants with 500 g < BW < 1250 g and 24 ≤ GA < 32 weeks | 32 | Started 3 g/kg/day within 2 h after birth, remained same thereafter | started 0.5 g/kg/day at 48 h after birth, advancing up to 3 g/kg/day (increment 0.5 g/kg/day) |
| First Author, Year | n | Male | GA | BW | Wt Gain Rate | Max %Age of wt Loss | Time to Regain BW | Wt Near TEA | HC Near TEA | EUGR | Death | NICU Stay | BPD/CLD | NEC ≥ 2 | Proven Sepsis | IVH ≥ 3 | ROP | HyperTG | Hypoglycemia | Hyperglycemia | Serum TB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | wk | g | g/kg/day | % | Day | g | cm | n (%) | n | day | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | mg/dL | ||
| Intervention | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Alburaki, 2020 [9] | 45 | 28 (62) | 27.1 ± 2.3 | 1019 ± 271 | 15.2 ± 2.0 1 | 10.4 ± 3.6 2 | 10.5 (8,13) | 2278 ± 303 3 | 31.3 ± 1.5 3 | 17 (38.6) 3 | 1 | 82 (49.5,107) | 15 (33.3) 4 | 1 (2.2) | 3 (6.7) | 4 (8.9) | 6 (25) 5 | 15 (33.3) 6 | 14 (31.1) 7 | 0 8 | 8.42 ± 1.52 9 |
| Dongming, 2016 [17] | 40 | 24 (60) | 30.2 (28,34) | 1140 ± 220 | - | 7.7 ± 1.5 | 8.2 ± 2.4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - |
| Tagare, 2013 [18] | 17 | 30.5 ± 2.6 | 1162 ± 224 | - | - | 9.5 ± 6.7 | - | - | - | 2 | 19.5 ± 13.3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 6.7 ± 3.1 10 | |
| Vlaardingerbroek, 2013 [19] | 49 | 19 (39) | 27.2 ± 2.2 | 876 ± 209 | 25.0 ± 5.2 11 | - | 8 (5,12), ns | - | - | - | 10 | 86.5 ± 29.1 | 11 (22) 12 | 4 (8) | 17 (35) | 2 (4) | 0 (0) | 27% 13 | - | 24% 8 | 8.26 ± 2.2 9 |
| Bulbul, 2012 [21] | 22 | 70% | 29.1 ± 1.1 | 1316 ± 247 | - | - | 12.5 ± 5.4 | 2210 ± 91 14 | 32.1 ± 2.3 14 | - | - | 34.4 ± 18.1 | - | 2 (9) | 1 (4.5) | 0 | - | - | - | - | 7.2 ± 0.6 10 |
| Can, 2012 [22] | 25 | 16 (64) | 31.3 (27,33) | 1622 ± 276 | - | - | 12.7 ± 2.8 | 3180 ± 474 15 | 34.7 ± 1.5 15 | 13 (52) 15 | 1 | 28 ± 15.6 | 1 (4) 16 | 1 (4) | - | - | 2 (8) 17 | - | - | - | - |
| Drenckpohl, 2008 [23] | 48 | 58.3% | 28.8 ± 1.7 | 1182 ± 198 | - | - | 12.5 ± 3.7 | 1894 ± 392 14 | 30.9 ± 2.2 14 | 28 (58) 14 | 0 | 43.65 ± 19 | 4 (8) 16 | 0 (0) | - | 11 (23) 18 | 3 (6) 19 | 7 (15) 20 | - | 0 % 8 | - |
| Ibranhim, 2004 [24] | 16 | 10 (63) | 27 ± 1.6 | 846 ± 261 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 9 (56.25) 16 | - | 6 | 4 | 2 | - | - | - | 7.7 ± 0.42 21 |
| Control | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Alburaki, 2020 [9] | 38 | 25 (66) | 27.3 ± 2.4 | 1011 ± 250 | 15.3 ± 3.5 1 | 12.7 ± 4.6 2 | 11.5 (8,16) | 2165 ± 301 3 | 30.5 ± 1.4 3 | 25 (67.6) 3 | 1 | 80.5 (58,96) | 8 (21.1) 4 | 1 (2.6) | 2 (5.3) | 2 (5.3) | 6 (26.1) 5 | 7 (18.4) 6 | 11 (28.9) 7 | 08 | 8.65 ± 1.7 9 |
| Dongming, 2016 [17] | 40 | 25 (63) | 30.4 (28,34) | 1148 ± 216 | - | 10.6 ± 3.3 | 11.6 ± 3.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 | - |
| Tagare, 2013 [18] | 17 | 32.1 ± 2.8 | 1264 ± 194 | - | - | 11.5 ± 6.7 | - | - | - | 1 | 20.2 ± 12.9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 7.2 ± 2.5 10 | |
| Vlaardingerbroek, 2013 [19] | 48 | 25 (52) | 27.8 ± 2.3 | 843 ± 224 | 25.8 ± 8.1 11 | - | 8 (5,12), ns | - | - | - | 5 | 91.0 ± 39.9 | 16 (33) 12 | 2 (4) | 8 (17) | 1 (2) | 2 (4) | 44% 13 | - | 6% 8 | 8.77 ± 1.88 9 |
| Bulbul, 2012 [21] | 22 | 52% | 29.4 ± 1.8 | 1355 ± 237 | - | - | 10.2 ± 3.9 | 2155 ± 180 14 | 31.2 ± 2.1 14 | - | - | 33.5 ± 19.4 | - | 1 (4.5) | 1 (4.5) | 0 | - | - | - | - | 7.7 ± 0.5 10 |
| Can, 2012 [22] | 25 | 15 (60) | 31.4 (27,33) | 1598 ± 346 | - | - | 14.2 ± 3.0 | 2992 ± 445 15 | 33.6 ± 1.5 15 | 22 (88) 15 | 2 | 29.9 ± 4.8 | 1 (4) | 2 (8) | - | - | 8 (32) 17 | - | - | - | - |
| Drenckpohl, 2008 [23] | 52 | 55.8% | 28.6 ± 1.8 | 1134 ± 223 | - | - | 12.9 ± 3.8 | 1946 ± 771 14 | 31 ± 2 14 | 43 (83) 14 | 3 | 50.58 ± 33 | 7 (14) 16 | 7 (14) | - | 11 (21) 18 | 12 (23) 19 | 2 (4) 20 | - | 10 % 8 | - |
| Ibranhim, 2004 [24] | 16 | 9 (56) | 26.8 ± 1.5 | 968 ± 244 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | 8 (50) 16 | - | 7 | 5 | 3 | - | - | - | 6.2 ± 0.43 21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.; Kim, N.J.; Kim, S.Y. Safety and Efficacy of Early High Parenteral Lipid Supplementation in Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051535
Kim K, Kim NJ, Kim SY. Safety and Efficacy of Early High Parenteral Lipid Supplementation in Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2021; 13(5):1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051535
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kyunghoon, Na Jin Kim, and Sae Yun Kim. 2021. "Safety and Efficacy of Early High Parenteral Lipid Supplementation in Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 13, no. 5: 1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051535
APA StyleKim, K., Kim, N. J., & Kim, S. Y. (2021). Safety and Efficacy of Early High Parenteral Lipid Supplementation in Preterm Infants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 13(5), 1535. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051535






