Amino Acids and Lipids Associated with Long-Term and Short-Term Red Meat Consumption in the Chinese Population: An Untargeted Metabolomics Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Serum Metabolomic Profiling
2.3. Dietary Assessment and Covariate Profiling
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
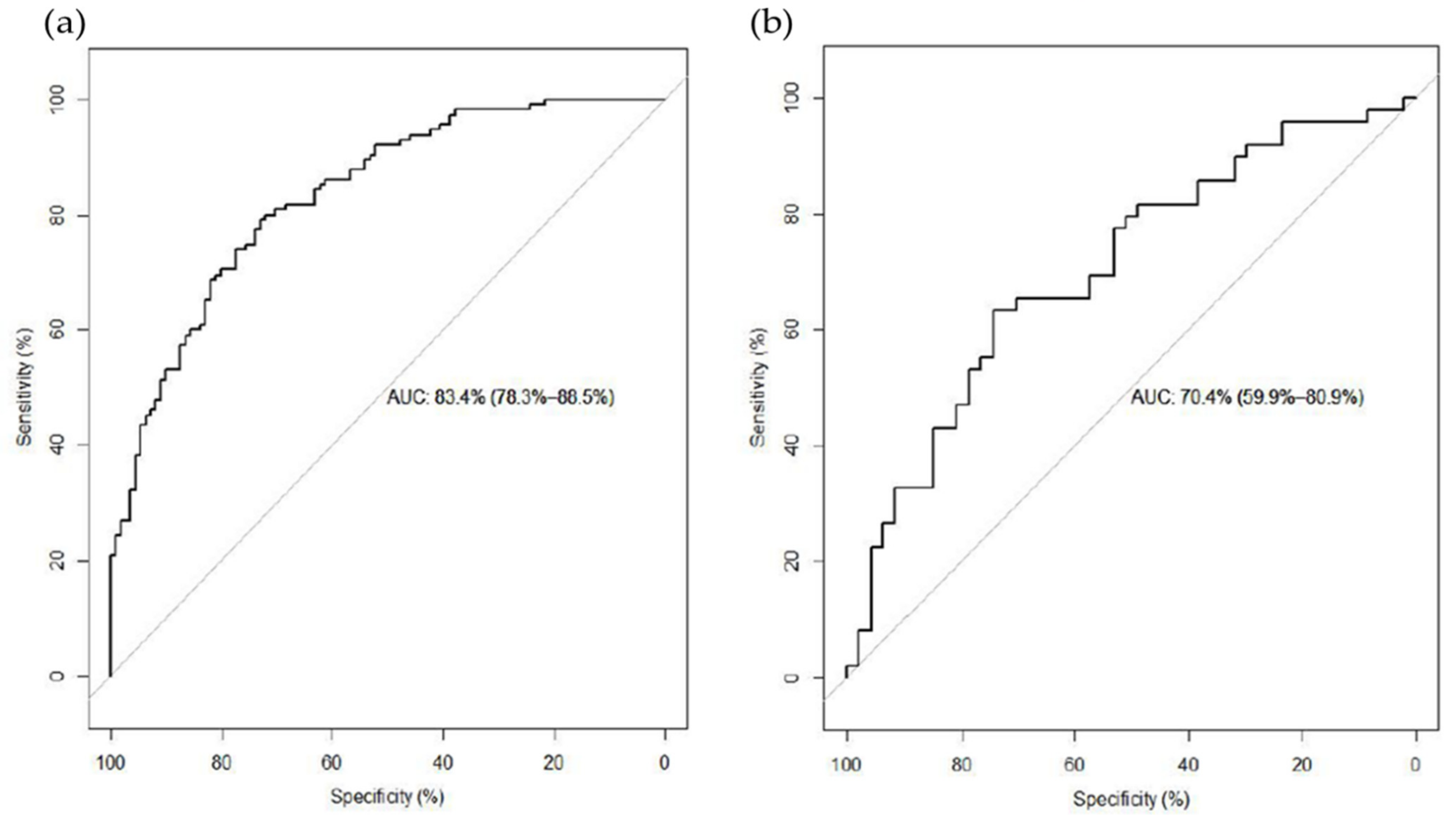
3.1. LT RM Consumption Analysis
3.2. ST RM Consumption Analysis
3.3. Enrichment Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lam, H.-M.; Remais, J.; Fung, M.-C.; Xu, L.; Sun, S.S.-M. Food supply and food safety issues in China. Lancet 2013, 381, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolk, A. Potential health hazards of eating red meat. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 281, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micha, R.; Wallace, S.K.; Mozaffarian, D. Red and processed meat consumption and risk of incident coronary heart disease, stroke, and diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation 2010, 121, 2271–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diallo, A.; Deschasaux, M.; Latino-Martel, P.; Hercberg, S.; Galan, P.; Fassier, P.; Allès, B.; Guéraud, F.; Pierre, F.H.; Touvier, M. Red and processed meat intake and cancer risk: Results from the prospective NutriNet-Santé cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turesky, R.J. Mechanistic Evidence for Red Meat and Processed Meat Intake and Cancer Risk: A Follow-up on the International Agency for Research on Cancer Evaluation of 2015. CHIMIA Int. J. Chem. 2018, 72, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feskens, E.J.; Sluik, D.; van Woudenbergh, G.J. Meat consumption, diabetes, and its complications. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2013, 13, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.; Cross, A.J.; Graubard, B.I.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Schatzkin, A. Meat intake and mortality: A prospective study of over half a million people. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Orsini, N. Red meat and processed meat consumption and all-cause mortality: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 179, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeraatkar, D.; Han, M.A.; Guyatt, G.H.; Vernooij, R.W.M.; El Dib, R.; Cheung, K.; Milio, K.; Zworth, M.; Bartoszko, J.J.; Valli, C.; et al. Red and Processed Meat Consumption and Risk for All-Cause Mortality and Cardiometabolic Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Cohort Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guasch-Ferre, M.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Hu, F.B. Use of Metabolomics in Improving Assessment of Dietary Intake. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scalbert, A.; Brennan, L.; Manach, C.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Dragsted, L.O.; Draper, J.; Rappaport, S.M.; van der Hooft, J.J.; Wishart, D.S. The food metabolome: A window over dietary exposure. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 1286–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Sullivan, A.; Gibney, M.J.; Brennan, L. Dietary intake patterns are reflected in metabolomic profiles: Potential role in dietary assessment studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cross, A.J.; Major, J.M.; Sinha, R. Urinary biomarkers of meat consumption. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2011, 20, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khodorova, N.V.; Rutledge, D.N.; Oberli, M.; Mathiron, D.; Marcelo, P.; Benamouzig, R.; Tome, D.; Gaudichon, C.; Pilard, S. Urinary Metabolomics Profiles Associated to Bovine Meat Ingestion in Humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1700834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuparencu, C.; Pratico, G.; Hemeryck, L.Y.; Sri Harsha, P.S.C.; Noerman, S.; Rombouts, C.; Xi, M.; Vanhaecke, L.; Hanhineva, K.; Brennan, L.; et al. Biomarkers of meat and seafood intake: An extensive literature review. Genes Nutr. 2019, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popkin, B.M.; Du, S.; Zhai, F.; Zhang, B. Cohort Profile: The China Health and Nutrition Survey--monitoring and understanding socio-economic and health change in China, 1989-2011. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, 1435–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhai, F. A Follow-Up Study on the Changes of Dietary Structure and Nutritional Status of Chinese Residents; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sha, W.; Wang, H.; Howard, A.G.; Tsilimigras, M.C.B.; Zhang, J.; Su, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Fodor, A.A.; et al. Urbanization in China is associated with pronounced perturbation of plasma metabolites. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, A.M.; DeHaven, C.D.; Barrett, T.; Mitchell, M.; Milgram, E. Integrated, nontargeted ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry platform for the identification and relative quantification of the small-molecule complement of biological systems. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6656–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Wilson, M.; Wishart, D.S. Translational biomarker discovery in clinical metabolomics: An introductory tutorial. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 280–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, B.; Ding, G. Nutrition transition and related health challenges over decades in China. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Alonso, P.; Papandreou, C.; Bullo, M.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Dennis, C.; Deik, A.; Wang, D.D.; Guasch-Ferre, M.; Yu, E.; Toledo, E.; et al. Plasma Metabolites Associated with Frequent Red Wine Consumption: A Metabolomics Approach within the PREDIMED Study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouin-Chartier, J.P.; Hernandez-Alonso, P.; Guasch-Ferre, M.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Li, J.; Wittenbecher, C.; Razquin, C.; Toledo, E.; Dennis, C.; Corella, D.; et al. Dairy consumption, plasma metabolites, and risk of type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Guasch-Ferre, M.; Chung, W.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Toledo, E.; Corella, D.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Tobias, D.K.; Tabung, F.K.; Hu, J.; et al. The Mediterranean diet, plasma metabolome, and cardiovascular disease risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2645–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynes, M.D.; Leiria, L.O.; Lundh, M.; Bartelt, A.; Shamsi, F.; Huang, T.L.; Takahashi, H.; Hirshman, M.F.; Schlein, C.; Lee, A.; et al. The cold-induced lipokine 12,13-diHOME promotes fatty acid transport into brown adipose tissue. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyness, L. The role of red meat in the diet: Nutrition and health benefits. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edmands, W.M.B.; Gooderham, N.J.; Holmes, E.; Mitchell, S.C. S-Methyl-l-cysteine sulphoxide: The Cinderella phytochemical? Toxicol. Res. 2013, 2, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kellingray, L.; Le Gall, G.; Doleman, J.F.; Narbad, A.; Mithen, R.F. Effects of in vitro metabolism of a broccoli leachate, glucosinolates and S-methylcysteine sulphoxide on the human faecal microbiome. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 2141–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, C.; Xiao, W.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, L. Integrative serum metabolomic analysis for preventive effects of Yaobitong capsule in adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis rat based on RP/HILIC-UHPLC-Q-TOF MS. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 637, 114474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Bazer, F.W.; Burghardt, R.C.; Johnson, G.A.; Kim, S.W.; Knabe, D.A.; Li, P.; Li, X.; McKnight, J.R.; Satterfield, M.C.; et al. Proline and hydroxyproline metabolism: Implications for animal and human nutrition. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsen, M.S.; Jersin, R.Å.; Ulvik, A.; Madsen, A.; McCann, A.; Svensson, P.A.; Svensson, M.K.; Nedrebø, B.G.; Gudbrandsen, O.A.; Tell, G.S.; et al. 3-Hydroxyisobutyrate, A Strong Marker of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity That Modulates White and Brown Adipocyte Metabolism. Diabetes 2020, 69, 1903–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.; Oh, S.F.; Wada, S.; Rowe, G.C.; Liu, L.; Chan, M.C.; Rhee, J.; Hoshino, A.; Kim, B.; Ibrahim, A.; et al. A branched-chain amino acid metabolite drives vascular fatty acid transport and causes insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pekala, J.; Patkowska-Sokoła, B.; Bodkowski, R.; Jamroz, D.; Nowakowski, P.; Lochyński, S.; Librowski, T. L-carnitine--metabolic functions and meaning in humans life. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.B.; Svelander, C.; Undeland, I.; Pinto, R.; Sandberg, A.S. Herring and Beef Meals Lead to Differences in Plasma 2-Aminoadipic Acid, beta-Alanine, 4-Hydroxyproline, Cetoleic Acid, and Docosahexaenoic Acid Concentrations in Overweight Men. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 2456–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Zou, L.; Su, J.; Tai, E.S.; Whitton, C.; Dam, R.M.V.; Ong, C.N. Meat and Seafood Consumption in Relation to Plasma Metabolic Profiles in a Chinese Population: A Combined Untargeted and Targeted Metabolomics Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Characteristics | Long-Term | Short-Term | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Consumers (<50 g/day) | Mid Consumers (50–100 g/day) | High Consumers (>100 g/day) | Low Consumers (<76 g/day) | Mid Consumers (76–136 g/day) | High Consumers (>136 g/day) | |
| N | 158 | 178 | 164 | 167 | 167 | 166 |
| Age (years) | 53 (47–60) | 51 (43–59) | 53 (45–60) | 53 (46–60) | 50 (43–59) | 53 (47–59) |
| Male (%) | 29.7 | 41.6 | 50.6 | 31.7 | 38.9 | 68.7 |
| Rural (%) | 70.9 | 71.3 | 58.5 | 66.5 | 65.9 | 51.8 |
| BMI (kg/m2) a | 23.40 (21.41–26.23) | 24.37 (21.70–26.35) | 23.83 (21.85–26.03) | 23.38 (21.64–26.13) | 24.30 (22.23–26.49) | 23.75 (21.30–25.87) |
| Energy intake b (kilocalories/day) | 1625.50 (1348.99–2009.57) | 1,974.50 c (1469.83–2315.49) | 2052.50 c (1619.00–2496.06) | 1559.72 (1223.70–2013.81) | 1938.71 c (1507.41–2249.08) | 2166.16 c (1768.74–2599.90) |
| Completed high school education (%) | 19.6 | 34.3 | 36.0 | 25.7 | 32.3 | 23.5 |
| Smoker (%) | 15.2 | 24.7 | 37.2 | 21.6 | 23.9 | 33.7 |
| Alcohol consumer (%) | 20.3 | 20.8 | 35.4 | 19.2 | 21.5 | 36.8 |
| Metabolite name | Super Pathway | Sub Pathway | Univariate Analysis | Elastic-Net Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p a | q b | β c | ||||
| 12,13-DiHOME d | lipid | fatty acid, dihydroxy | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.089 | |
| 2-naphthol sulfate e | xenobiotic | Chemical | <0.001 | <0.001 | −0.158 | |
| androstenediol (3α, 17α) monosulfate 2 d | lipid | androgenic steroid | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.217 | |
| S-methylcysteine sulfoxide e | amino acid | methionine, cysteine, S-adenosylmethionine and taurine metabolism | <0.001 | <0.001 | −0.130 | |
| 7alpha-Hydroxy-3-oxo-4-cholestenoate | lipid | Sterol | 0.001 | 0.041 | 0.008 | |
| Perfluorooctane sulfonate | xenobiotic | Chemical | 0.001 | 0.041 | 0.042 | |
| S-methylcysteine | amino acid | methionine, cysteine, S-adenosylmethionine and taurine metabolism | 0.001 | 0.041 | −0.014 | |
| 2-oxoarginine | amino acid | urea cycle, arginine and proline metabolism | 0.002 | 0.065 | 0.054 | |
| gamma-Glutamyl-2-aminobutyrate d | peptide | gamma-glutamyl amino acid | 0.003 | 0.082 | 0.153 | |
| epsilon-(gamma-Glutamyl)-lysine | peptide | gamma-glutamyl amino acid | 0.003 | 0.082 | 0.126 | |
| Metabolite name | Superpathway | Sub Pathway | Univariate Analysis | Elastic-Net Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p a | q b | β c | ||||
| 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)lactate | amino acid | tyrosine metabolism | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.590 | |
| asparagine d | amino acid | alanine and aspartate metabolism | <0.001 | <0.001 | 3.235 | |
| 4-hydroxyproline d | amino acid | urea cycle, arginine and proline metabolism | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.187 | |
| cinnamoylglycine | xenobiotic | food component/plant | 0.001 | 0.053 | −0.096 | |
| leucine | amino acid | leucine, isoleucine, and valine metabolism | 0.001 | 0.053 | 0.658 | |
| lysine | amino acid | lysine metabolism | 0.001 | 0.053 | 0.226 | |
| tricosanoyl sphingomyelin (d18:1/23:0) | lipid | sphingomyelin | 0.001 | 0.053 | −0.329 | |
| androstenediol (3α, 17α) monosulfate (3) | lipid | androgenic steroid | 0.002 | 0.073 | 0.268 | |
| S-allylcysteine | xenobiotic | food component/plant | 0.002 | 0.073 | 0.267 | |
| 3-hydroxyisobutyrate d | amino acid | leucine, isoleucine, and valine metabolism | 0.003 | 0.094 | 0.384 | |
| behenoyl sphingomyelin (d18:1/22:0) e | lipid | sphingomyelin | 0.003 | 0.094 | −0.437 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, F.; Du, W.; Zhang, J.; Su, C.; Zhang, B.; Deng, K.; Du, S.; Wang, H. Amino Acids and Lipids Associated with Long-Term and Short-Term Red Meat Consumption in the Chinese Population: An Untargeted Metabolomics Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4567. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124567
Guan F, Du W, Zhang J, Su C, Zhang B, Deng K, Du S, Wang H. Amino Acids and Lipids Associated with Long-Term and Short-Term Red Meat Consumption in the Chinese Population: An Untargeted Metabolomics Study. Nutrients. 2021; 13(12):4567. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124567
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Fangxu, Wenwen Du, Jiguo Zhang, Chang Su, Bing Zhang, Kui Deng, Shufa Du, and Huijun Wang. 2021. "Amino Acids and Lipids Associated with Long-Term and Short-Term Red Meat Consumption in the Chinese Population: An Untargeted Metabolomics Study" Nutrients 13, no. 12: 4567. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124567
APA StyleGuan, F., Du, W., Zhang, J., Su, C., Zhang, B., Deng, K., Du, S., & Wang, H. (2021). Amino Acids and Lipids Associated with Long-Term and Short-Term Red Meat Consumption in the Chinese Population: An Untargeted Metabolomics Study. Nutrients, 13(12), 4567. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124567






