Abstract
Background and Aims: A higher frequency of dyslipidemia is reported in children with type 1 diabetes (T1D) and celiac disease (CD). Recently, continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) has been associated with better lipid profiles in patients with T1D. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between treatment modality and lipid profile, metabolic control, and body mass index (BMI)-SDS in children with both T1D and CD. Methods: Cross-sectional study in children registered in the international SWEET database in November 2020. Inclusion criteria were children (2–18 years) with T1D and CD with available data on treatment modality (CSII and injections therapy, IT), triglyceride, total cholesterol, HDL, LDL, dyslipidemia, HbA1c, and BMI-SDS. Overweight/obesity was defined as > +1 BMI-SDS for age. Data were analyzed by linear and logistical regression models with adjustment for age, gender, and diabetes duration. Results: In total 1009 children with T1D and CD (female 54%, CSII 54%, age 13.9 years ±3.6, diabetes duration 7.2 years ±4.1, HbA1c 7.9% ±1.4) were included. Significant differences between children treated with CSII vs. IT were respectively found; HDL 60.0 mg/dL vs. 57.8 mg/dL, LDL 89.4 mg/dL vs. 94.2 mg/dL, HbA1c 7.7 vs. 8.1%, BMI-SDS 0.4 vs. 0.6, overweight and obesity 17% vs. 26% (all p < 0.05). Conclusions: CSII is associated with higher HDL and lower LDL, HbA1c, BMI-SDS, and percentage of overweight and obesity compared with IT in this study. Further prospective studies are required to determine whether CSII improves lipid profile, metabolic control and normalize body weight in children with both T1D and CD.
1. Introduction
Celiac disease (CD) is a systemic immune-mediated disorder caused by the ingestion of gluten-containing grains in genetically susceptible persons [1]. While CD prevalence approaches 1% in the general population, [2] it ranges between 1.6% and 9.7% in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D) worldwide [3], therefore there are a significant number of individuals with both CD and T1D. Despite many prevalence studies, there are few studies about glycemic control, lipid profile, quality of life, microvascular complications, and cardiac risk factors of children with both CD and T1D [4].
Individuals with T1D have a higher risk to develop cardiovascular disease compared with the general population [5]. In children with early atherosclerotic signs, dyslipidemia has been found to be present since childhood [6,7]. In addition, it is well-known, that higher level of triglyceride and LDL predict cardiovascular disease [8]. Recent epidemiological studies described increased mortality and higher microvascular complication in individuals with T1D and concomitant CD, suggesting that these patients represent a distinct risk group [9,10].
Lipid profile is influenced by gluten-free diet (GFD), which is considered the only available treatment for CD, because of a lower intake of carbohydrates and fiber accompanied by a higher intake of saturated fats, compared with an average diet [11]. A recent systematic review published in 2020 highlighted the association between increased prevalence of weight gain, high blood glucose levels, and a worse lipid profile in celiac patients on a GFD [12]. However, there is a paucity of high-quality evidence on the role of GFD in the context of T1D. A recent large population study showed improved lipid profiles in children and adolescents with T1D treated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) therapy as compared with injection therapy (IT) [13].
The aim of the present study was to investigate the association between treatment modality and lipid profile, metabolic control, and body mass index (BMI) in children with both T1D and CD by analyzing data from the International SWEET Registry.
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source and Participants
The SWEET (Better Control in Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes: Working to Create Centers of Reference) registry is promoted by the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes (ISPAD). The aim of SWEET is to include certified centers for childhood diabetes from all over the world in a community useful for comparisons. The SWEET database currently includes 77,254 participants from 112 diabetes centers worldwide.
As a European Union project, SWEET was approved by the ethical committee at the Auf der Bult Diabetes Centre for Children and Adolescents, Hannover, Germany, wherefrom it is still coordinated, since January 2010, with ethical committee number 848.
Every participating center is responsible for obtaining appropriate ethical approval and informed consent from children’s parents and guardians and assent from pediatric participants.
This cross-sectional study included children registered in the SWEET database up to July 2020. Inclusion criteria were (a) diagnosis of type 1 diabetes and celiac disease; (b) age between 2 and 18 years; (c) available data on lipid profile (total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, triglyceride) and treatment modality (CSII and IT). Injection therapy includes conventional therapy (1–3 injections a day) and MDI (more than 3 injection a day).
Diagnosis of T1D was performed according to the ISPAD guidelines [14]. CD was defined according to the modified criteria of the ESPGHAN [15]. For each participant we analyzed aggregated data from the most recent documented year, including age, gender, diabetes duration, HbA1c, height, weight, BMI, blood pressure, complications, comorbidities, country of origin and lipid profile. HbA1c was measured locally in each center; to adjust for differences between laboratories, the multiple of the mean method was used to standardize local HbA1c mathematically to the DCCT reference of 20–42 mmol/mol (4–6%). The BMI was calculated from registered height and weight as weight/squared height (kg/m [2]) and converted to BMI-SDS (standard deviation score) using WHO growth curves [16,17]. Blood pressure was assessed according to Fourth Report [18] (“Fourth Report on the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents”). Participants were divided into the following three groups based on BMI-SDS: normal weight (BMI-SDS 0 to <1.28), overweight (BMI-SDS 1.28 to <1.88) and obese (BMI-SDS ≥ 1.88). Lipid profile assessment included triglycerides, total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol values. Dyslipidemia was defined in presence of LDL cholesterol ≥100 mg/dL or HDL ≤ 40 mg/dL or total cholesterol ≥ 200 mg/dL. Fasting lipids were measured locally, using standardized, auto-mated instrumentations.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were generated using SAS (Statistical Analysis Software, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) Version 9.4, build TS1M5, on a Windows Server 2016 mainframe.
Descriptive statistics were performed for all included patients. The results are shown as median with quartiles for continuous variables and as proportions for binary variables.
HbA1c (%), BMI-SDS, total cholesterol, LDL, HDL and triglycerides were analyzed using multivariable linear regression models adjusted for age groups (2–12, >12–18 years), gender and diabetes duration groups (≤5, >5 years). The proportions of individuals with dyslipidemia, overweight and obesity were analyzed using multivariable logistic regression models adjusted for the same variables. Sensitivity analyses were conducted with further adjustment for HbA1c groups (<7.5%, ≥7.5%) and/or BMI-SDS groups (<1.28, ≥1.28). Two-sided p < 0.05 indicated a significant difference.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
Overall, 62 different centers (44 from Europe, 9 from Asia, Australia and the Middle East, 8 from North and South America) contributed to this analysis. Figure 1 shows the flow-diagram of the inclusion process of patients.
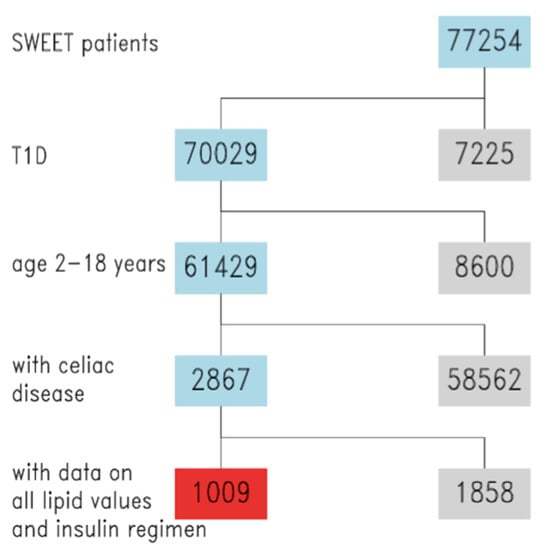
Figure 1.
Study flowchart, inclusion of SWEET patients. Blue = inclusion, grey = exclusion, red = final study cohort.
The final cohort included 1009 children with T1D and CD, 46% male, with mean age 13.9 (range: 11.4–17.2), mean diabetes duration 7.2 years (range: 3.9–10), and mean HbA1c 7.9% (range: 6.9–8.4). CSII therapy was used by 54% of the population, while the others used IT. Demographic features of the study population are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Demographics of study population, stratified by insulin therapy.
Descriptive analysis, stratified by treatment modality, is reported in Table 2.

Table 2.
Descriptive results, stratified by insulin treatment modality.
3.2. Results from Adjusted Regression Models
This difference between CSII and IT group was confirmed by linear regression analysis, adjusted for age, gender, and diabetes duration. HbA1c was significantly lower in children treated with CSII as compared with IT [HbA1c 7.7% vs. 8.1%]. In addition, the group of children treated with CSII compared with IT had a significantly lower BMI-SDS [BMI-SDS 0.41 vs. 0.57]. No significant difference in the level of triglycerides or total cholesterol were found. However, a significantly higher level of HDL and a lower level of LDL were observed in children treated with CSII as compared with IT [HDL 60.1 mg/dL vs. 57.6 mg/dL; LDL 89.9 mg/dL vs. 93.6 mg/dL]. All these results are reported in Table 3.

Table 3.
Results on lipid values from adjusted linear regression models.
In addition, the logistic regression models, adjusted for age, gender, and diabetes duration, showed that the percentage of overweight and obesity was significantly lower in children treated with CSII (17% vs. 26%; p = 0.0002). There was no significant difference in the percentage of dyslipidemia.
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
After linear regression analysis adjusted for BMI-SDS or HbA1c, the differences between the two groups of treatment are significant. There are no anymore significant differences between the two groups in case of HDL adjusted for BMI, or BMI and HbA1c and LDL adjusted for both BMI and HbA1c.
4. Discussion
Life expectancy in young people with diabetes remains lower than in the general population, despite improvements in glycemic control over the years [19]. Individuals with T1D have a high risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality [20]. Subclinical atherosclerotic vascular changes begin in childhood, with several studies showing arterial stiffness and endothelial dysfunction in adolescents with T1D [21,22,23]. LDL-C is a significant predictor of cardiovascular events and mortality in T1D [24]. Each 1 mmol/L (38.7 mg/dL) LDL-C increase is associated with 35–50% more risk of cardiovascular disease, according to a recent study based on the Swedish National Diabetes Registry [24].
It has been established that lowering LDL-C levels, including with lipid-lowering treatment, reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular disease [20]. A reduction of only 1 mmol/dL in LDL-C value is associated with 9% decrease mortality and a 21% decrease in vascular events according to The Cholesterol Treatment Trialists (CCT) study [25].
Recently, Kostaria et al. evaluated the effect of CSII on lipid profile in patients with T1D, showing that CSII was associated with improved lipid profiles compared with IT [13]. In particular, LDL-C and non-HDL levels were lower in the CSII group than in the IT group. This finding has been hypothesized to be linked to the improved glycemic control obtained with CSII [6,8,26,27].
CD is a co-morbidity of T1D [28]. The only available treatment of CD is the GFD, which consists of the dietary exclusion of grains containing gluten (i.e., wheat, rye, barley, triticale, spelt, and kamut) [11]. A body of evidence has so far suggested that a GFD may be nutritionally unbalanced [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39]. Therefore, adhering to a GFD may further impair the nutritional status, as well as metabolic and lipid profile in patients with both CD and T1D.
Our study shows that the use of CSII is associated with improved glycemic control, BMI-SDS and lipid profile as compared with IT in a large cohort of children and adolescents with both CD and T1D. Firstly, HbA1c was significantly lower in children treated with CSII as compared with IT. The effect of CSII on HbA1c levels in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes has been largely demonstrated [26,27].
Moreover, we found an improved lipid profile in children treated with CSII. Specifically, CSII was significantly associated with higher level of HDL and lower level of LDL-C as compared with MDI, even after adjustment for HbA1c.
It has been hypothesized that by improving the glucose variability and reducing the exposure to periods of hyperinsulinemia, CSII may impact oxidative stress markers and lipid profile [40,41,42]. Children with T1D seem to have higher urinary excretion of 8-iso-PGF2α, F2-isoprostanes formation, than healthy subjects [43,44,45]. These oxidative stress markers enhanced lipid peroxidation and they are correlated with lipid profile alterations [45]. Acute glycemic fluctuations have more effect on oxidative stress than chronic sustained hyperglycemia [46]. CSII treatment is associated with reduced glucose variability because it allows more physiological dosing of insulin [47], and lower total doses of insulin [48]. Indeed, CSII is associated with a lower rate of severe acute complications (severe hypoglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis) compared with IT, particularly in school-aged children.
Finally, our study shows that in the group of children treated with CSII compared with IT there was a significantly lower BMI-SDS and a significantly lower percentage of overweight and obesity (17% vs. 26%). This finding is of clinical relevance because it is largely known that obesity is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease development in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes [47].
The improved anthropometric status of children treated with CSII may be related to a higher diet quality which is directly correlated to better glycemic control in children with T1D and CD [49,50].
A strength of the present study is the fact that the SWEET database comprises a large and heterogeneous, international population, that allows multiple adjustments for major confounding factors, including HbA1c, BMI, age, gender, and diabetes duration, indicating that CSII treatment by itself may contribute to a better lipid profile even in children and adolescents with both T1D and CD.
Limitations of our study are that the SWEET database does not include the start date of the GFD, thus not allowing us to assess the actual adherence of study population to GFD and observe the effect of the duration of GFD on outcome measures evaluated in the present study.
In addition, the group of IT was significantly higher than the CSII group and had a significantly lower diabetes duration.
Moreover, we are not able to define whether our findings are due to CSII treatment alone, to sensor-augmented pumps (SAP) therapy or to hybrid closed-loop systems (HCL), advanced hybrid closed loop (AHCL). In addition, the glucose-monitoring strategies were not well-defined in this study, either. Therapy and glucose monitoring strategies affect glycemic control in children with T1D [51].
Lastly, there were not available information on socioeconomic status of study participants.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, these findings highlight that the choice of treatment methods may have an impact on risk factors for cardiovascular disease in children, particularly those with T1D and CD.
Further prospective studies are required to investigate the impact of treatment modality and special diet on treatment outcome in children with both T1D and CD and in addition possible underlying pathogenetic mechanisms for this subgroup.
Author Contributions
M.M. and M.E.L. contributed to study design and wrote the first draft for this manuscript. A.J.E. had full access to the data used in this article and performed and was responsible for the integrity of the data and accuracy of the data analysis. V.F.R., A.J.E., C.A.J., S.T. (Shoshana Tell), S.T. (Sladjana Todorovic), N.K., G.D., R.C., E.S., C.M.M. prepared the study tables. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee at the Auf der Bult Diabetes Centre for Children and Adolescents, Hannover, Germany, wherefrom it is still coordinated, since January 2010, with ethical committee number 848.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patients also to publish this paper.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the SWEET corporate members, namely: Abbott, Boehringer Ingelheim, Dexcom, Insulet, Lilly, Medtronic, and Sanofi. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the corporate members. We are thankful for the following individuals for their support of this work: Sandra Linke and Sascha Tittel for the data management as well as Andreas Hungele and Ramona Ranz for the DPV software (all Ulm University, Germany), Michael Witsch (Centre Hospitalier de Luxembourg, Luxembourg) for center integration, Thomas Danne and Olga Kordonouri (Kinder- und Jugendkrankenhaus AUF DER BULT, Hannover, Germany) for initiating the SWEET collaboration, Katharina Klee (Kinder- und Jugendkrankenhaus AUF DER BULT, Hannover, Germany) and Reinhard Holl (Ulm University, Germany) for their invaluable support. Finally, we would like to thank all participating centers of the SWEET network, especially the collaboration centers in this investigation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| AHCL | advanced hybrid closed loop |
| BMI-SDS | body mass index—standard deviation score |
| CCT | cholesterol treatment trialists |
| CD | celiac disease |
| CSII | continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion |
| DCCT/EDIC | diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications |
| ESPGHAN | European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition |
| GFD | gluten-free diet |
| HbA1c | glycated hemoglobin |
| HDL | high-density lipoproteins |
| ISPAD | International Society of Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes |
| IT | injections therapy years |
| LDL | low-density lipoproteins |
| MDI | multiple daily injections |
| SAP | sensor augmented therapy |
| SAS | statistical analysis system |
| T1D | type 1 diabetes |
| WHO | World Health Organisation |
References
- Lionetti, E.; Catassi, C. New Clues in Celiac Disease Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, and Treatment. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 30, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Tapia, A.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Brantner, T.L.; Murray, J.A.; Everhart, J.E. The Prevalence of Celiac Disease in the United States. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, F.H.; De Melo, E.N.; Noordin, K.; Assor, E.; Sahota, K.; Davies-Shaw, J.; Cutz, E.; Somers, G.; Lawson, M.; Mack, D.R.; et al. The Celiac Disease and Diabetes-Dietary Intervention and Evaluation Trial (CD-DIET) protocol: A randomised controlled study to evaluate treatment of asymptomatic coeliac disease in type 1 diabetes. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmud, F.H.; Murray, J.A.; Kudva, Y.C.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Dierkhising, R.A.; Lahr, B.D.; Dyck, P.J.; Kyle, R.A.; El-Youssef, M.; Burgart, L.J.; et al. Celiac Disease in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in a North American Community: Prevalence, Serologic Screening, and Clinical Features. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2005, 80, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lind, M.; Svensson, A.M.; Kosiborod, M.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Pivodic, A.; Wedel, H.; Dahlqvist, S.; Clements, M.; Rosengren, A. Glycemic Control and Excess Mortality in Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1972–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margeirsdottir, H.D.; Stensaeth, K.H.; Larsen, J.R.; Brunborg, C.; Dahl-Jørgensen, K. Early signs of atherosclerosis in diabetic children on intensive insulin treatment: A population-based study. Diabetes Care. 2010, 33, 2043–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berenson, G.S.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Bao, W.; Newman, W.P.; Tracy, R.E.; Wattigney, W.A. Association between Multiple Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Atherosclerosis in Children and Young Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Research Group. Risk factors for Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1722–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Mollazadegan, K.; Kugelberg, M.; Montgomery, S.M.; Sanders, D.S.; Ludvigsson, J.; Ludvigsson, J.F. A Population-Based Study of the Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and Celiac Disease. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollazadegan, K.; Fored, M.; Lundberg, S.; Ludvigsson, J.; Ekbom, A.; Montgomery, S.M.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Risk of renal disease in patients with both type 1 diabetes and coeliac disease. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, E.; Antonucci, N.; Marinelli, M.; Bartolomei, B.; Franceschini, E.; Gatti, S.; Catassi, G.N.; Verma, A.K.; Monachesi, C.; Catassi, C. Nutritional Status, Dietary Intake, and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet of Children with Celiac Disease on a Gluten-Free Diet: A Case-Control Prospective Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valvano, M.; Longo, S.; Stefanelli, G.; Frieri, G.; Viscido, A.; Latella, G. Celiac Disease, Gluten-Free Diet, and Metabolic and Liver Disorders. Nutrients. 2020, 12, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kosteria, I.; Schwandt, A.; Davis, E.; Jali, S.; Prieto, M.; Rottembourg, D. Lipid profile is associated with treatment regimen in a large cohort of children and adolescents with Type 1 diabetes mellitus: A study from the international SWEET database. Diabetic Med. 2019, 36, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Kahkoska, A.R.; Jefferies, C.; Dabelea, D.; Balde, N.; Gong, C.X.; Aschner, P.; Craig, M.E. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: Definition, epidemiology, and classification of diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatric Diabetes 2018, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husby, S.; Koletzko, S.; Korponay-Szabó, I.R.; Mearin, M.L.; Phillips, A.; Shamir, R.; Troncone, R.; Giersiepen, K.; Branski, D.; Catassi, C.; et al. European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Coeliac Disease. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 136–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffeis, C.; Birkebaek, N.H.; Konstantinova, M.; Schwandt, A.; Vazeou, A.; Casteels, K.; Jali, S.; Limbert, C.; Pundziute-Lycka, A.; Toth-Heyn, P.; et al. Prevalence of underweight, overweight, and obesity in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: Data from the international SWEET registry. Pediatric Diabetes 2018, 19, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbauer, J.; Dost, A.; Karges, B.; Hungele, A.; Stahl, A.; Bächle, C.; Gerstl, E.M.; Kastendieck, C.; Hofer, S.E.; Holl, R.W.; et al. Improved Metabolic Control in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes: A trend analysis using prospective multicenter data from Germany and Austria. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- US Department of Health and Human Services. The Fourth Report on the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents; US Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 555–576.
- Rawshani, A.; Rawshani, A.; Franzén, S.; Eliasson, B.; Svensson, A.M.; Miftaraj, M.; McGuire, D.K.; Sattar, N.; Rosengren, A.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S. Range of Risk Factor Levels: Control, Mortality, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 2017, 135, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tell, S.; Nadeau, K.J.; Eckel, R.H. Lipid management for cardiovascular risk reduction in type 1 diabetes. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2020, 27, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvisalo, M.J.; Raitakari, M.; Toikka, J.O.; Putto-Laurila, A.; Rontu, R.; Laine, S.; Lehtimaki, T.; Ronnemaa, T.; Viikari, J.; Raitakari, O.T. Endothelial Dysfunction and Increased Arterial Intima-Media Thickness in Children With Type 1 Diabetes. Circulation 2004, 109, 1750–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haller, M.J.; Stein, J.; Shuster, J.; Theriaque, D.; Silverstein, J.; Schatz, D.A.; Earing, M.G.; Lerman, A.; Mahmud, F.H. Peripheral artery tonometry demonstrates altered endothelial function in children with type 1 diabetes. Pediatric Diabetes 2007, 8, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.S.; Wadwa, R.P.; Dabelea, D.; Hamman, R.F.; D’Agostino, R., Jr.; Marcovina, S.; Daniels, S.R.; Dolan, L.M.; Fino, N.F.; Urbina, E.M. Arterial stiffness in adolescents and young adults with and without type 1 diabetes: The SEARCH CVD study. Pediatric Diabetes 2015, 16, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rawshani, A.; Rawshani, A.; Sattar, N.; Franzén, S.; McGuire, D.K.; Eliasson, B.; Svensson, A.M.; Zethelius, B.; Miftaraj, M.; Rosengren, A.; et al. Relative Prognostic Importance and Optimal Levels of Risk Factors for Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 2019, 139, 1900–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists. Efficacy of cholesterol-lowering therapy in 18,686 people with diabetes in 14 randomised trials of statins: A meta-analysis. Lancet 2008, 371, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, N.C.; Beck, R.W.; Miller, K.M.; Clements, M.A.; Rickels, M.R.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Maahs, D.M.; Tamborlane, W.V.; Bergenstal, R.; Smith, E.; et al. State of Type 1 Diabetes Management and Outcomes from the T1D Exchange in 2016–2018. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2019, 21, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karges, B.; Schwandt, A.; Heidtmann, B.; Kordonouri, O.; Binder, E.; Schierloh, U.; Boettcher, C.; Kapellen, T.; Rosenbauer, J.; Holl, R.W. Association of Insulin Pump Therapy vs. Insulin Injection Therapy with Severe Hypoglycemia, Ketoacidosis, and Glycemic Control Among Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes. JAMA 2017, 318, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A.; Catassi, C. Clinical practice. Celiac disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penagini, F.; Dilillo, D.; Meneghin, F.; Mameli, C.; Fabiano, V.; Zuccotti, G. Gluten-Free Diet in Children: An Approach to a Nutritionally Adequate and Balanced Diet. Nutrients 2013, 5, 4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fry, L.; Madden, A.M.; Fallaize, R. An investigation into the nutritional composition and cost of gluten-free versus regular food products in the UK. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 31, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornicelli, M.; Saba, M.; Machello, N.; Silano, M.; Neuhold, S. Nutritional composition of gluten-free food versus regular food sold in the Italian market. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 1305–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larretxi, I.; Simon, E.; Benjumea, L.; Miranda, J.; Bustamante, M.A.; Lasa, A.; Eizaguirre, F.J.; Churruca, I. Gluten-free-rendered products contribute to imbalanced diets in children and adolescents with celiac disease. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babio, N.; Alcázar, M.; Castillejo, G.; Recasens, M.; Martínez-Cerezo, F.; Gutiérrez-Pensado, V.; Masip, G.; Vaqué, C.; Vila-Martí, A.; Torres-Moreno, M.; et al. Patients with Celiac Disease Reported Higher Consumption of Added Sugar and Total Fat Than Healthy Individuals. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautto, E.; Ivarsson, A.; Norström, F.; Högberg, L.; Carlsson, A.; Hörnell, A. Nutrient intake in adolescent girls and boys diagnosed with coeliac disease at an early age is mostly comparable to their non-coeliac contemporaries. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 27, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccotti, G.; Fabiano, V.; Dilillo, D.; Picca, M.; Cravidi, C.; Brambilla, P. Intakes of nutrients in Italian children with celiac disease and the role of commercially available gluten-free products. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 26, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, S.J.; Gibson, P.R. Nutritional inadequacies of the gluten-free diet in both recently-diagnosed and long-term patients with coeliac disease. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 26, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhlund, K.; Olsson, C.; Hernell, O.; Öhlund, I. Dietary shortcomings in children on a gluten-free diet. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2010, 23, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopman, E.G.D.; le Cessie, S.; von Blomberg, B.M.E.; Mearin, M.L. Nutritional Management of the Gluten-free Diet in Young People with Celiac Disease in The Netherlands. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 43, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bardella, M.T.; Fredella, C.; Prampolini, L.; Molteni, N.; Giunta, A.M.; Bianchi, P.A. Body composition and dietary intakes in adult celiac disease patients consuming a strict gluten-free diet. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 937–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erciyas, F.; Taneli, F.; Arslan, B.; Uslu, Y. Glycemic control, oxidative stress, and lipid profile in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Med. Res. 2004, 35, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiver, C.; Jacoby, U.; Watzer, B.; Thomas, A.; Haffner, D.; Fischer, D.-C. Glycaemic variability in paediatric patients with type 1 diabetes on continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) or multiple daily injections (MDI): A cross-sectional cohort study. Clin. Endocrinol. 2013, 79, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Gong, C.; Cao, B.; Peng, X.; Wu, D.; Gu, Y.; Wei, L.; Liang, X.; Liu, M.; Li, W.; et al. Glucose Fluctuations in Association with Oxidative Stress Among Children With T1DM: Comparison of Different Phases. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 1828–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altıncık, A.; Tuğlu, B.; Demir, K.; Çatli, G.; Abacı, A.; Böber, E. Relationship between oxidative stress and blood glucose fluctuations evaluated with daily glucose monitoring in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Pediatric Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 29, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzetti, A. Oxidative stress and cardiovascular complications in diabetes: Isoprostanes as new markers on an old paradigm. Cardiovasc. Res. 2000, 47, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davi, G.; Ciabattoni, G.; Consoli, A.; Mezzetti, A.; Falco, A.; Santarone, S.; Pennese, E.; Vitacolonna, E.; Bucciarelli, T.; Costantini, F.; et al. In Vivo Formation of 8-Iso-Prostaglandin F 2α and Platelet Activation in Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation 1999, 99, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quagliaro, L.; Piconi, L.; Assaloni, R.; Martinelli, L.; Motz, E.; Ceriello, A. Intermittent High Glucose Enhances Apoptosis Related to Oxidative Stress in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells: The Role of Protein Kinase C and NAD(P)H-Oxidase Activation. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2795–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shanik, M.H.; Xu, Y.; Skrha, J.; Dankner, R.; Zick, Y.; Roth, J. Insulin Resistance and Hyperinsulinemia: Is hyperinsulinemia the cart or the horse? Diabetes Care 2008, 31 (Suppl. S2), S262–S268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braffett, B.H.; Dagogo-Jack, S.; Bebu, I.; Sivitz, W.I.; Larkin, M.; Kolterman, O.; Lachin, J.M. Association of Insulin Dose, Cardiometabolic Risk Factors, and Cardiovascular Disease in Type 1 Diabetes During 30 Years of Follow-up in the DCCT/EDIC Study. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pham-Short, A.; Donaghue, K.C.; Ambler, G.; Garnett, S.; Craig, M.E. Quality of Life in Type 1 Diabetes and Celiac Disease: Role of the Gluten-Free Diet. J. Pediatrics 2016, 179, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nansel, T.R.; Lipsky, L.M.; Liu, A. Greater diet quality is associated with more optimal glycemic control in a longitudinal study of youth with type 1 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherubini, V.; Bonfanti, R.; Casertano, A.; De Nitto, E.; Iannilli, A.; Lombardo, F.; Maltoni, G.; Marigliano, M.; Bassi, M.; Minuto, N.; et al. Time in Range in Children with Type 1 Diabetes Using Treatment Strategies Based on Nonautomated Insulin Delivery Systems in the Real World. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2020, 22, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).