A Cross-Sectional Study of Evening Hyperphagia and Nocturnal Ingestion: Core Constituents of Night Eating Syndrome with Different Background Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Outcomes
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Descriptive and Clinical Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lundgren, J.D.; Allison, K.C.; O’Reardon, J.P.; Stunkard, A.J. A descriptive study of non-obese persons with night eating syndrome and a weight-matched comparison group. Eat. Behav. 2008, 9, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluck, M.E.; Geliebter, A.; Satov, T. Night eating syndrome is associated with depression, low self-esteem, reduced daytime hunger, and less weight loss in obese outpatients. Obes. Res. 2001, 9, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stunkard, A.J.; Grace, W.J.; Wolff, H.G. The night-eating syndrome; a pattern of food intake among certain obese patients. Am. J. Med. 1955, 19, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaggiari, M.C.; Granella, F.; Parrino, L.; Marchesi, C.; Melli, I.; Terzano, M.G. Nocturnal eating syndrome in adults. Sleep 1994, 17, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birketvedt, G.S.; Florholmen, J.; Sundsfjord, J.; Osterud, B.; Dinges, D.; Bilker, W.; Stunkard, A. Behavioral and neuroendocrine characteristics of the night-eating syndrome. JAMA 1999, 282, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®); American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, K.C.; Lundgren, J.D.; O’Reardon, J.P.; Geliebter, A.; Gluck, M.E.; Vinai, P.; Mitchell, J.E.; Schenck, C.H.; Howell, M.J.; Crow, S.J.; et al. Proposed diagnostic criteria for night eating syndrome. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2010, 43, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y. Sleep-related eating disorder and its associated conditions. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 69, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinai, P.; Ferri, R.; Ferini-Strambi, L.; Cardetti, S.; Anelli, M.; Vallauri, P.; Ferrato, N.; Zucconi, M.; Carpegna, G.; Manconi, M. Defining the borders between sleep-related eating disorder and night eating syndrome. Sleep Med. 2012, 13, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenck, C.H.; Mahowald, M.W. Review of nocturnal sleep-related eating disorders. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1994, 15, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkelman, J.W. Clinical and polysomnographic features of sleep-related eating disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1998, 59, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenck, C.H.; Hurwitz, T.D.; O’Connor, K.A.; Mahowald, M.W. Additional categories of sleep-related eating disorders and the current status of treatment. Sleep 1993, 16, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine. International Classification of Sleep Disorders—Third Edition (ICSD-3); American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fulda, S.; Hornyak, M.; Müller, K.; Cerny, L.; Beitinger, P.A.; Wetter, T.C. Development and validation of the Munich Parasomnia Screening (MUPS). Somnol.-Schlafforschung Schlafmed. 2008, 12, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komada, Y.; Breugelmans, R.; Fulda, S.; Nakano, S.; Watanabe, A.; Noda, C.; Nishida, S.; Inoue, Y. Japanese version of the Munich Parasomnia Screening: Translation and linguistic validation of a screening instrument for parasomnias and nocturnal behaviors. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, K.; Komada, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Kuriyama, K.; Inoue, Y. Prevalence and associated factors of nocturnal eating behavior and sleep-related eating disorder-like behavior in Japanese young adults: Results of an internet survey using Munich Parasomnia Screening. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loddo, G.; Zanardi, M.; Caletti, M.T.; Mignani, F.; Petroni, M.L.; Chiaro, G.; Marchesini, G.; Provini, F. Searching food during the night: The role of video-polysomnography in the characterization of the night eating syndrome. Sleep Med. 2019, 64, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komada, Y.; Okajima, I.; Kitamura, S.; Inoue, Y. A survey on social jetlag in Japan: A nationwide, cross-sectional internet survey. Sleep Biol. Rhythm. 2019, 17, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, A.; Arima, H.; Ohkubo, T.; Nishi, N.; Okuda, N.; Ae, R.; Inoue, M.; Kurita, S.; Murakami, K.; Kadota, A.; et al. Associations of socioeconomic status with prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in a general Japanese population: NIPPON DATA2010. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastien, C.H.; Vallières, A.; Morin, C.M. Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index as an outcome measure for insomnia research. Sleep Med. 2001, 2, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munezawa, T.; Morin, C.M.; Inoue, Y.; Nedate, K. Development of the Japanese version of the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI-J). Jpn. J. Psychiatr. Treat. 2009, 24, 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjelland, I.; Dahl, A.A.; Haug, T.T.; Neckelmann, D. The validity of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. An updated literature review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2002, 52, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, H.; Higashi, A.; Yashiro, H.; Ozasa, K.; Hayashi, K.; Kiyota, K.; Inokuchi, H.; Ikeda, J.; Fujita, K.; Watanabe, Y.; et al. A Validation of the Hospital Anxiety and Dipression Scale. Jpn. J. Psychosom. Med. 1998, 38, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juda, M.; Vetter, C.; Roenneberg, T. Chronotype modulates sleep duration, sleep quality, and social jet lag in shift-workers. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2013, 28, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Expert Panel on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight in Adults. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: Executive summary. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 899–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rand, C.S.; Macgregor, A.M.; Stunkard, A.J. The night eating syndrome in the general population and among postoperative obesity surgery patients. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1997, 22, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zwaan, M.; Marschollek, M.; Allison, K.C. The Night Eating Syndrome (NES) in bariatric surgery patients. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. J. Eat. Disord. Assoc. 2015, 23, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceru-Bjork, C.; Andersson, I.; Rossner, S. Night eating and nocturnal eating-two different or similar syndromes among obese patients? Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2001, 25, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, T.E.; Van Wijk, M.; Singleton, C.; Carter, J.C. An examination of the relationship between binge eating disorder and insomnia symptoms. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. J. Eat. Disord. Assoc. 2018, 26, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trace, S.E.; Thornton, L.M.; Runfola, C.D.; Lichtenstein, P.; Pedersen, N.L.; Bulik, C.M. Sleep problems are associated with binge eating in women. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2012, 45, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, K.; Tasali, E.; Penev, P.; Van Cauter, E. Brief communication: Sleep curtailment in healthy young men is associated with decreased leptin levels, elevated ghrelin levels, and increased hunger and appetite. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 141, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Furihata, R.; Konno, C.; Konno, M.; Kaneita, Y.; Ohida, T.; Gon, Y.; Uchiyama, M. Sleep disturbance is associated with not only shorter sleep duration, but also longer time in bed: A Japanese general population survey. Sleep Biol. Rhythm. 2019, 17, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boston, R.C.; Moate, P.J.; Allison, K.C.; Lundgren, J.D.; Stunkard, A.J. Modeling circadian rhythms of food intake by means of parametric deconvolution: Results from studies of the night eating syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1672–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, N.; Stunkard, A.J.; Rogers, N.L.; Van Dongen, H.P.; Allison, K.C.; O’Reardon, J.P.; Ahima, R.S.; Cummings, D.E.; Heo, M.; Dinges, D.F. Circadian rhythm profiles in women with night eating syndrome. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2009, 24, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.F.; Thorsteinsson, E.B.; Smithson, M.; Birmingham, C.L.; Aljarallah, H.; Nolan, C. Can body temperature dysregulation explain the co-occurrence between overweight/obesity, sleep impairment, late-night eating, and a sedentary lifestyle? Eat. Weight Disord. 2017, 22, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guentcheva, I.; Dugas, E.N.; Hanusaik, N.; Drapeau, V.; Sylvestre, M.P.; O’Loughlin, J. Depression symptoms and night eating in young adulthood. Eat. Weight Disord. 2020, 25, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.Y.; Meg Tseng, M.C.; Chang, C.H. Night eating syndrome in patients with eating disorders: Is night eating syndrome distinct from bulimia nervosa? J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019, 118, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geliebter, A.; McOuatt, H.; Tetreault, C.B.; Kordunova, D.; Rice, K.; Zammit, G.; Gluck, M. Is night eating syndrome associated with obstructive sleep apnea, BMI, and depressed mood in patients from a sleep laboratory study? Eat. Behav. 2016, 23, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle Grave, R.; Calugi, S.; Ruocco, A.; Marchesini, G. Night eating syndrome and weight loss outcome in obese patients. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2011, 44, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Meyer, A.H.; Hermann, E.; Tuch, A.; Munsch, S. Night eating syndrome in young adults: Delineation from other eating disorders and clinical significance. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 200, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striegel-Moore, R.H.; Rosselli, F.; Wilson, G.T.; Perrin, N.; Harvey, K.; DeBar, L. Nocturnal eating: Association with binge eating, obesity, and psychological distress. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2010, 43, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calugi, S.; Dalle Grave, R.; Marchesini, G. Night eating syndrome in class II-III obesity: Metabolic and psychopathological features. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Saraçlı, Ö.; Atasoy, N.; Akdemir, A.; Güriz, O.; Konuk, N.; Sevinçer, G.M.; Ankaralı, H.; Atik, L. The prevalence and clinical features of the night eating syndrome in psychiatric out-patient population. Compr. Psychiatry 2015, 57, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, K.C.; Wadden, T.A.; Sarwer, D.B.; Fabricatore, A.N.; Crerand, C.E.; Gibbons, L.M.; Stack, R.M.; Stunkard, A.J.; Williams, N.N. Night eating syndrome and binge eating disorder among persons seeking bariatric surgery: Prevalence and related features. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bariatr. Surg. 2006, 2, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, O.S.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.E.; Jung, H. Night-eating syndrome and the severity of self-reported depressive symptoms from the Korea Nurses’ Health Study: Analysis of propensity score matching and ordinal regression. Public Health 2016, 141, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Striegel-Moore, R.H.; Franko, D.L.; Thompson, D.; Affenito, S.; May, A.; Kraemer, H.C. Exploring the typology of night eating syndrome. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2008, 41, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, N.L.; Dinges, D.F.; Allison, K.C.; Maislin, G.; Martino, N.; O’Reardon, J.P.; Stunkard, A.J. Assessment of sleep in women with night eating syndrome. Sleep 2006, 29, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, S.A.; Ciechanowski, P.S.; Katon, W.J.; Hirsch, I.B. Isn’t this just bedtime snacking? The potential adverse effects of night-eating symptoms on treatment adherence and outcomes in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1800–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, K.C.; Grilo, C.M.; Masheb, R.M.; Stunkard, A.J. Binge eating disorder and night eating syndrome: A comparative study of disordered eating. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2005, 73, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukgoncu, S.; Tek, C.; Bestepe, E.; Musket, C.; Guloksuz, S. Clinical features of night eating syndrome among depressed patients. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. J. Eat. Disord. Assoc. 2014, 22, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, M.C.A.; de Oliveira Ribeiro, M.; de Araújo, C.F.C.; de Mesquita, L.M.F.; de Bruin, P.F.C.; de Bruin, V.M.S. Night eating in bipolar disorder. Sleep Med. 2018, 48, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eley, T.C.; Stevenson, J. Exploring the covariation between anxiety and depression symptoms: A genetic analysis of the effects of age and sex. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry Allied Discip. 1999, 40, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reardon, J.P.; Stunkard, A.J.; Allison, K.C. Clinical trial of sertraline in the treatment of night eating syndrome. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2004, 35, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reardon, J.P.; Allison, K.C.; Martino, N.S.; Lundgren, J.D.; Heo, M.; Stunkard, A.J. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of sertraline in the treatment of night eating syndrome. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Wal, J.S.; Gang, C.H.; Griffing, G.T.; Gadde, K.M. Escitalopram for treatment of night eating syndrome: A 12-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 32, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, K.C.; Studt, S.K.; Berkowitz, R.I.; Hesson, L.A.; Moore, R.H.; Dubroff, J.G.; Newberg, A.; Stunkard, A.J. An open-label efficacy trial of escitalopram for night eating syndrome. Eat. Behav. 2013, 14, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Kuriyama, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Inada, K.; Nishimura, K.; Inoue, Y. The efficacy of add-on ramelteon and subsequent dose reduction of benzodiazepine derivatives/Z-drugs for the treatment of sleep-related eating disorder and night eating syndrome: A retrospective analysis of consecutive cases. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2021, 17, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Petrecca, A.M.; Khuhro, A.L. Sleep-Related Eating Disorder (SRED): Paradoxical effect of clonazepam. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 1261–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, S.M.; Joshi, K.G. A case of zaleplon-induced amnestic sleep-related eating disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2010, 71, 210–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaesu, Y.; Ishikawa, J.; Komada, Y.; Murakoshi, A.; Futenma, K.; Nishida, S.; Inoue, Y. Prevalence of and factors associated with sleep-related eating disorder in psychiatric outpatients taking hypnotics. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2016, 77, e892–e898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.P.; Fong, S.Y.; Ho, C.K.; Yu, M.W.; Wing, Y.K. Parasomnia among psychiatric outpatients: A clinical, epidemiologic, cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2008, 69, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.; Jimenez, A.; Sanchez, I.; Seeger, C.; Joseph, M. Sleep-related eating disorder associated with zolpidem: Cases compiled from a literature review. Sleep Med. X 2020, 2, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruzas, M.B.; Allison, K.C. A Review of the relationship between night eating syndrome and body mass index. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, A.R.; Lundgren, J.; Drapeau, V. The night-eating syndrome and obesity. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2012, 13, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tholin, S.; Lindroos, A.; Tynelius, P.; Akerstedt, T.; Stunkard, A.J.; Bulik, C.M.; Rasmussen, F. Prevalence of night eating in obese and nonobese twins. Obesity 2009, 17, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiseman, C.V.; Turco, R.M.; Sunday, S.R.; Halmi, K.A. Smoking and body image concerns in adolescent girls. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1998, 24, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulik, C.M.; Epstein, L.H.; McKee, M.; Kaye, W. Drug use in women with bulimia and anorexia nervosa. NIDA Res. Monogr. 1990, 105, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, N.A.; Heinberg, L.J.; Guarda, A.S. Cigarette smoking and its relationship to other substance use among eating disordered inpatients. Eat. Weight Disord. 2001, 6, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzengruber, D.; Klump, K.L.; Thornton, L.; Brandt, H.; Crawford, S.; Fichter, M.M.; Halmi, K.A.; Johnson, C.; Kaplan, A.S.; LaVia, M.; et al. Smoking in eating disorders. Eat. Behav. 2006, 7, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumeister, R.F. Addiction, cigarette smoking, and voluntary control of action: Do cigarette smokers lose their free will? Addict. Behav. Rep. 2017, 5, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, K.L.; Collins, P.F. Relationship between living alone and food and nutrient intake. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 594–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinenberg, E. Social isolation, loneliness, and living alone: Identifying the risks for public health. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, 786–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvers, D.J.; Scheer, F.; Schrauwen, P.; la Fleur, S.E.; Kalsbeek, A. Circadian clocks and insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, N.; Gradisar, M. Electronic media use and sleep in school-aged children and adolescents: A review. Sleep Med. 2010, 11, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, Y.K.; Shin, E.; Bautista, M.A.; Foo, K. The associations between self-reported sleep duration and adolescent health outcomes: What is the role of time spent on Internet use? Sleep Med. 2013, 14, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, M.P. Endocrine manifestations of eating disorders. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanina, Y.; Podolskaya, A.; Sedky, K.; Shahab, H.; Siddiqui, A.; Munshi, F.; Lippmann, S. Body weight changes associated with psychopharmacology. Psychiatr. Serv. 2002, 53, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Non-NES Group (n = 8021) | Evening Hyperphagia Group (n = 119) | Nocturnal Ingestion Group (n = 208) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (range), years | 50 (16–79) | 47 (21–72) 3 | 41.5 (19–79) 1 | <0.001 |
| Female, n (%) | 4024 (50.2) | 66 (55.5) | 92 (44.2) | n.s. |
| BMI, median (range), kg/m2 | 21.8 (12.0–49.1) | 21.5 (15.1–32) | 21.4 (13.3–34.6) | n.s. |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 1506 (18.8) | 31 (26.1) 5 | 55 (26.4) 5 | <0.01 |
| Habitual alcohol intake, n (%) | 3515 (43.8) | 56 (47.1) | 101 (48.6) | n.s. |
| Regular employment or school attendance, n (%) | 4720 (58.8) | 70 (58.8) | 128 (61.5) | n.s. |
| Living alone, n (%) | 1244 (15.5) | 29 (24.4) 4 | 48 (23.1) 4 | <0.001 |
| Regular physical activity, n (%) | 2748 (34.3) | 32 (26.9) | 81 (38.9) | n.s. |
| Hypnotic medication use, n (%) | 579 (7.2) | 13 (10.9) 6 | 25 (12.0) 6 | <0.05 |
| Average sleep duration, median (range), min | 400 (206–599) | 375 (225–595) 3 | 418.3 (220–595) 1 | <0.001 |
| Sleep midpoint, median (range), h: min | 3:17 (0:00–7:15) | 3:59 (0:18–7:15) 1 | 3:03 (0:15–6:49) 2 | <0.001 |
| Absolute social jet lag, median (range), h | 0 (0–398) | 0 (0–390) | 15 (0–360) 3 | <0.05 |
| ISI score, median (range), points | 4 (0–28) | 6 (0–28) 1 | 7 (0–27) 1 | <0.001 |
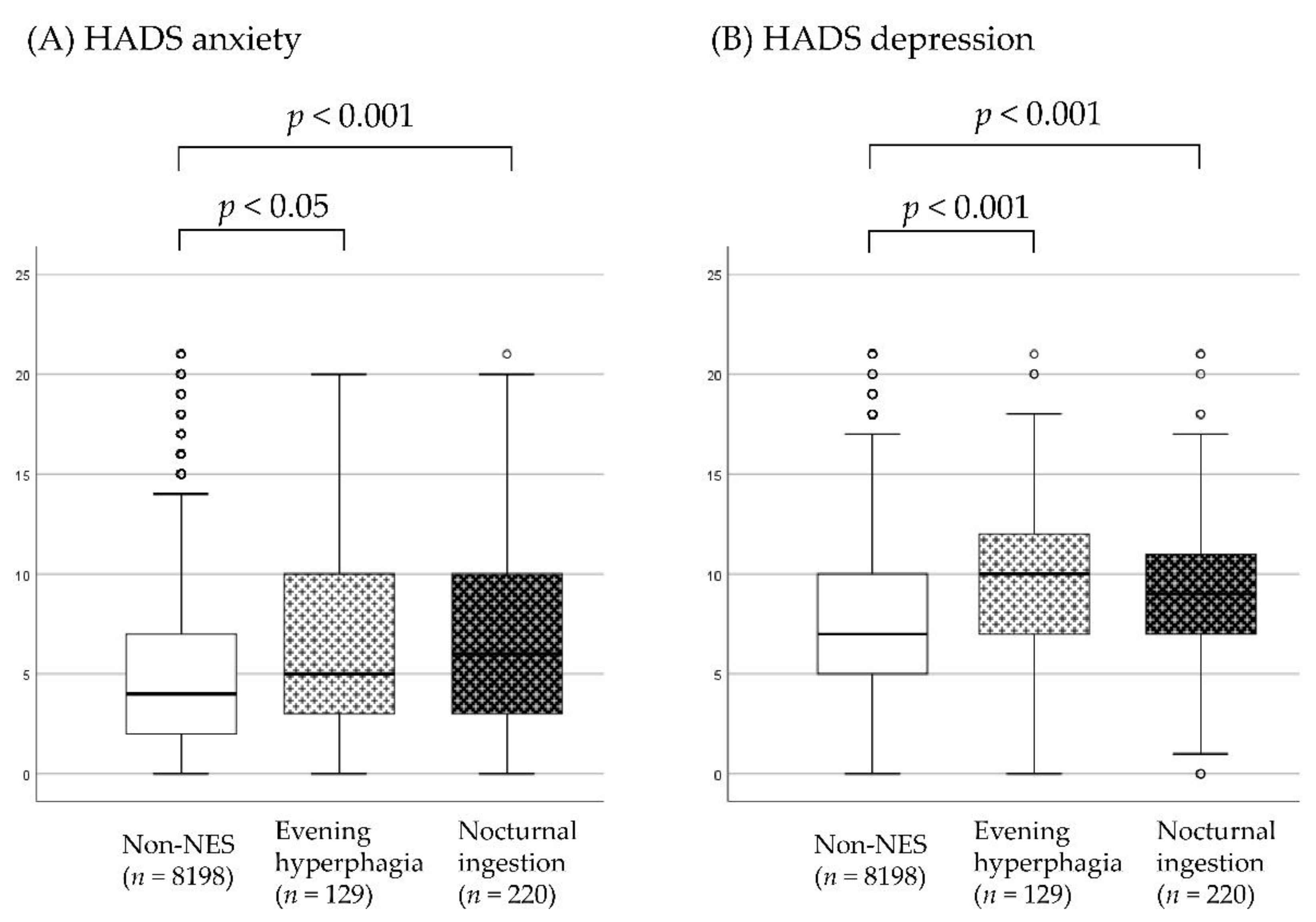
| HADS anxiety score, median (range), points | 4 (0–21) | 5 (0–20) 1 | 6 (0–21) 1 | <0.001 |
| HADS depression score, median (range), points | 7 (0–21) | 10 (0–21) 1 | 9 (0–21) 1 | <0.001 |
| Age, median (range), years | 50 (16–79) | 47 (21–72) 3 | 41.5 (19–79) 1 | <0.001 |
| Predictor | n | Univariate Relative Risk (95% CI) 1 | p | Multivariate Relative Risk (95% CI) 1 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||||
| 16–39 | 2544 | ||||
| 40–59 | 2843 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| 60–79 | 2961 | 0.541 (0.330–0.887) | <0.05 | n.s. | |
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 4166 | ||||
| Female | 4182 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||||
| <25 | 6808 | ||||
| ≥25 | 1540 | 1.639 (1.089–2.468) | <0.05 | 1.525 (1.005–2.313) | <0.05 |
| Current smoker | |||||
| No | 6756 | ||||
| Yes | 1592 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Habitual alcohol intake | |||||
| No | 4676 | ||||
| Yes | 3672 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Regular employment or school attendance | |||||
| No | 3430 | ||||
| Yes | 4918 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Living alone | |||||
| No | 7027 | ||||
| Yes | 1321 | 1.730 (1.134–2.640) | <0.05 | n.s. | |
| Regular physical activity | |||||
| No | 5487 | ||||
| Yes | 2861 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Hypnotic medication use | |||||
| No | 7731 | ||||
| Yes | 617 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Average sleep duration (h) | |||||
| ≥6 | 6196 | ||||
| <6 | 2152 | 2.345 (1.628–3.378) | <0.001 | 1.687 (1.152–2.472) | < 0.01 |
| Sleep-wake schedule | |||||
| Normal | 4217 | ||||
| Earlier 2 | 2053 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Later 3 | 2078 | 2.723 (1.834–4.044) | <0.001 | 2.196 (1.450–3.326) | <0.001 |
| Absolute social jet lag (h) | |||||
| <1 | 6500 | ||||
| 1–2 | 1335 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| ≥2 | 513 | 1.852 (1.028–3.336) | < 0.05 | n.s. | |
| ISI score (points) 4 | |||||
| 0–7 | 5875 | ||||
| 8–14 | 1974 | 1.613 (1.066–2.441) | < 0.05 | n.s. | |
| 15–28 | 499 | 3.538 (2.104–5.949) | < 0.001 | 2.653 (1.558–4.515) | <0.001 |
| Predictor | n | Univariate Relative Risk (95% CI) 1 | p | Multivariate Relative Risk (95% CI) 1 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||||
| 16–39 | 2544 | ||||
| 40–59 | 2843 | 0.622 (0.453–0.855) | <0.01 | 0.532 (0.382–0.741) | <0.001 |
| 60–79 | 2961 | 0.407 (0.285–0.581) | <0.001 | 0.355 (0.241–0.523) | <0.001 |
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 4166 | ||||
| Female | 4182 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||||
| <25 | 6808 | ||||
| ≥25 | 1540 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Current smoker | |||||
| No | 6756 | ||||
| Yes | 1592 | 1.544 (1.129–2.112) | < 0.01 | 1.558 (1.129–2.152) | <0.01 |
| Habitual alcohol intake | |||||
| No | 4676 | ||||
| Yes | 3672 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Regular employment or school attendance | |||||
| No | 3430 | ||||
| Yes | 4918 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Living alone | |||||
| No | 7027 | ||||
| Yes | 1321 | 1.618 (1.166–2.247) | <0.01 | 1.569 (1.121–2.196) | <0.01 |
| Regular physical activity | |||||
| No | 5487 | ||||
| Yes | 2861 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Hypnotic medication use | |||||
| No | 7731 | ||||
| Yes | 617 | 1.742 (1.137–2.667) | < 0.05 | n.s. | |
| Average sleep duration (h) | |||||
| ≥6 | 6196 | ||||
| <6 | 2152 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Sleep-wake schedule | |||||
| Normal | 4217 | ||||
| Earlier 2 | 2053 | 1.804 (1.321–2.463) | <0.001 | 2.153 (1.562–2.967) | <0.001 |
| Later 3 | 2078 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| Absolute social jet lag (h) | |||||
| <1 | 6500 | ||||
| 1–2 | 1335 | n.s. | n.s. | ||
| ≥2 | 513 | 1.694 (1.053–2.725) | <0.05 | n.s. | |
| ISI score (points) 4 | |||||
| 0–7 | 5875 | ||||
| 8–14 | 1974 | 1.705 (1.253–2.322) | <0.001 | 1.577 (1.149–2.165) | <0.01 |
| 15–28 | 499 | 2.978 (1.949–4.548) | <0.001 | 2.507 (1.571–4.001) | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsui, K.; Komada, Y.; Okajima, I.; Takaesu, Y.; Kuriyama, K.; Inoue, Y. A Cross-Sectional Study of Evening Hyperphagia and Nocturnal Ingestion: Core Constituents of Night Eating Syndrome with Different Background Factors. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114179
Matsui K, Komada Y, Okajima I, Takaesu Y, Kuriyama K, Inoue Y. A Cross-Sectional Study of Evening Hyperphagia and Nocturnal Ingestion: Core Constituents of Night Eating Syndrome with Different Background Factors. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114179
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsui, Kentaro, Yoko Komada, Isa Okajima, Yoshikazu Takaesu, Kenichi Kuriyama, and Yuichi Inoue. 2021. "A Cross-Sectional Study of Evening Hyperphagia and Nocturnal Ingestion: Core Constituents of Night Eating Syndrome with Different Background Factors" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114179
APA StyleMatsui, K., Komada, Y., Okajima, I., Takaesu, Y., Kuriyama, K., & Inoue, Y. (2021). A Cross-Sectional Study of Evening Hyperphagia and Nocturnal Ingestion: Core Constituents of Night Eating Syndrome with Different Background Factors. Nutrients, 13(11), 4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114179








