Comparison of Preoperative Nutritional Indexes for Outcomes after Primary Esophageal Surgery for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
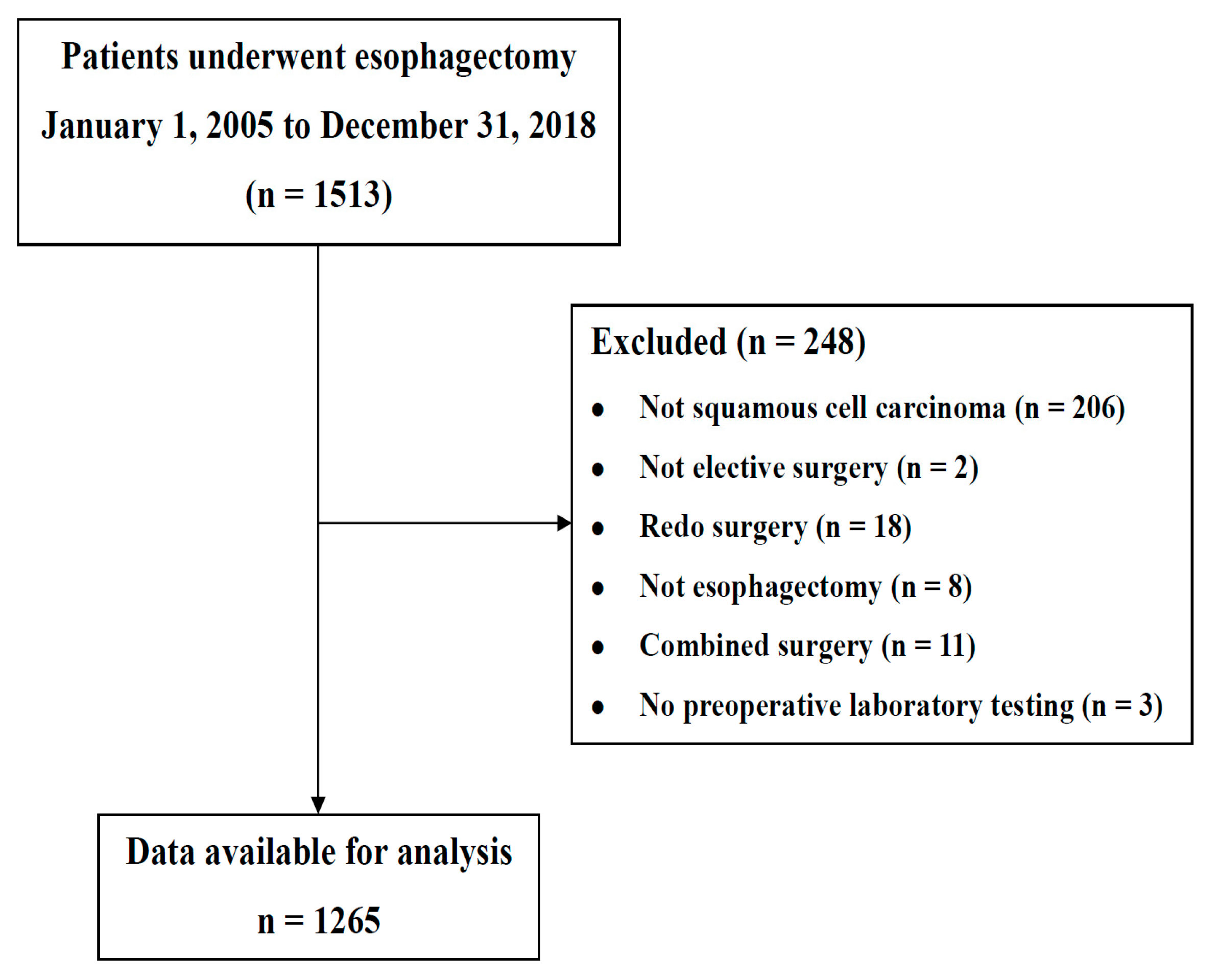
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
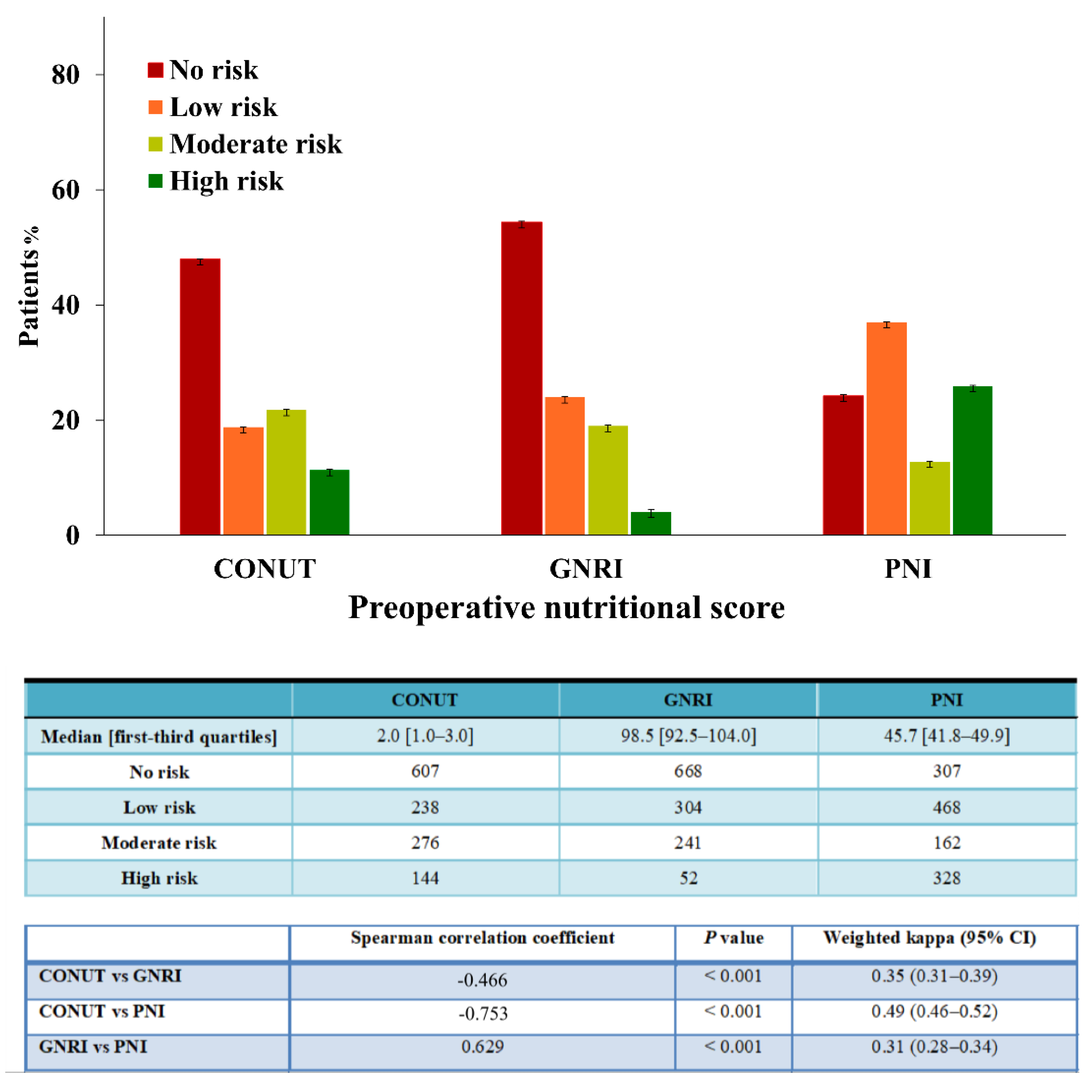
2.2. Calculation of Preoperative Nutritional Status
2.3. End Points
2.4. Statistical Analysis
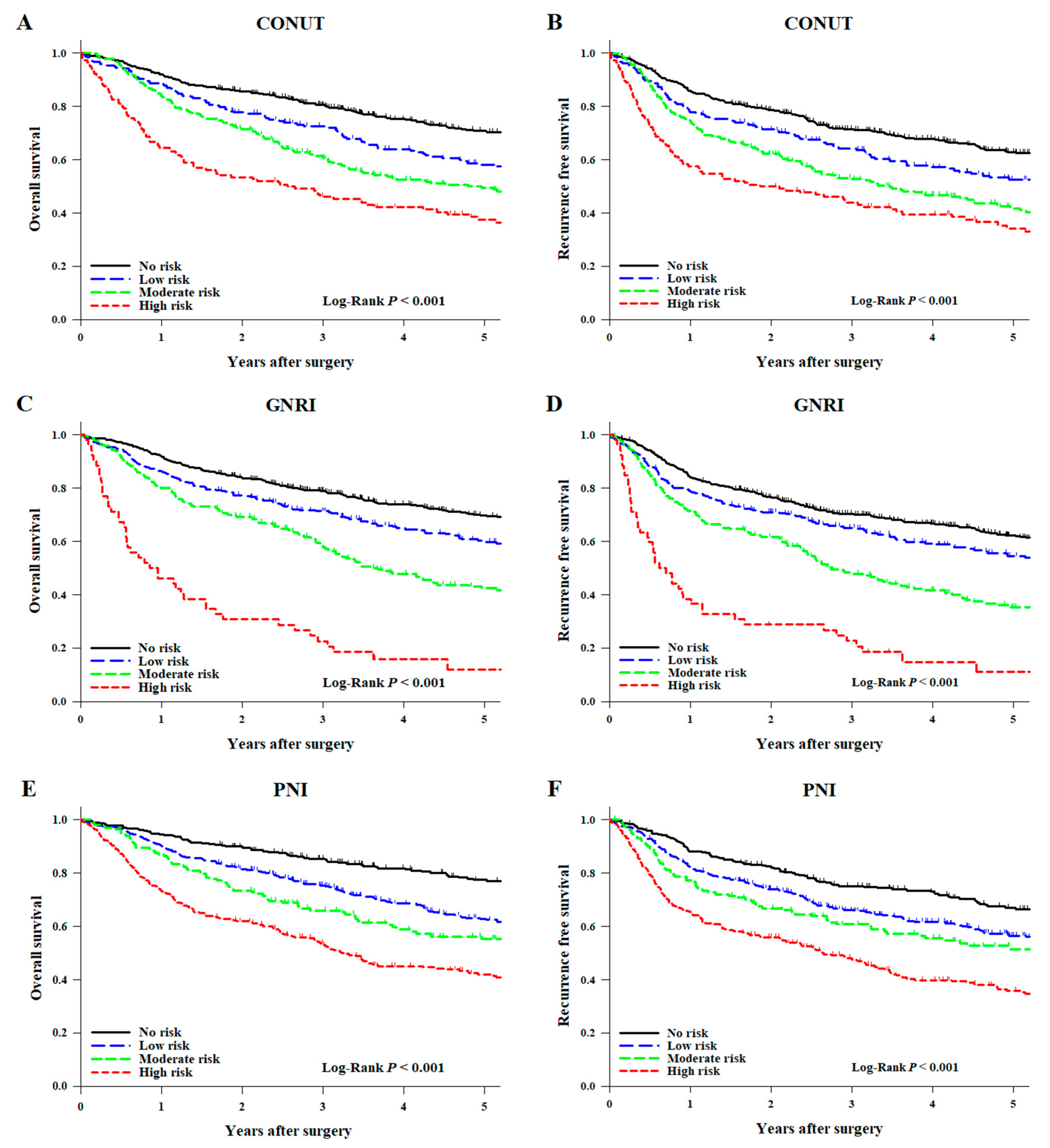
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anandavadivelan, P.; Lagergren, P. Cachexia in patients with oesophageal cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 13, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inciong, J.F.B.; Chaudhary, A.; Hsu, H.-S.; Joshi, R.; Seo, J.-M.; Trung, L.V.; Ungpinitpong, W.; Usman, N. Hospital malnutrition in northeast and southeast Asia: A systematic literature review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 39, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, L.A.; Gout, B.S.; Crowe, T.C. Hospital Malnutrition: Prevalence, Identification and Impact on Patients and the Healthcare System. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 514–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Ulíbarri, J.I.; González-Madroño, A.; de Villar, N.G.; González, P.; González, B.; Mancha, A.; Rodríguez, F.; Fernández, G. CONUT: A tool for controlling nutritional status. First validation in a hos-pital population. Nutr. Hosp. 2005, 20, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bouillanne, O.; Morineau, G.; Dupont, C.; Coulombel, I.; Vincent, J.-P.; Nicolis, I.; Benazeth, S.; Cynober, L.; Aussel, C. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index: A new index for evaluating at-risk elderly medical patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onodera, T.; Goseki, N.; Kosaki, G. prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of malnourished cancer patients. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi 1984, 85, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Buzby, G.P.; Mullen, J.L.; Matthews, D.C.; Hobbs, C.L.; Rosato, E.F. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery. Am. J. Surg. 1980, 139, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; You, J.; Cui, H.; Zhu, Y.; Lü, Q.; Yuan, L. The Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index Predicts Survival in Elderly Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients with Radiotherapy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirahara, N.; Matsubara, T.; Hayashi, H.; Takai, K.; Nakada, S.; Tajima, Y. Prognostic Importance of Controlling Nutritional Status in Patients Undergoing Curative Thoracoscopic Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer. Am. J. Ther. 2018, 25, e524–e532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Sohda, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Yoshida, T.; Kumakura, Y.; Honjo, H.; Hara, K.; Ozawa, D.; Suzuki, S.; Tanaka, N.; et al. Association of Preoperative Nutritional Status with Prognosis in Patients with Esophageal Cancer Undergoing Salvage Esophagectomy. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, N.; Sakurai, K.; Tamura, T.; Toyokawa, T.; Tanaka, H.; Muguruma, K.; Yashiro, M.; Ohira, M. The impact of geriatric nutritional risk index on surgical outcomes after esophagectomy in patients with esophageal cancer. Esophagus 2019, 16, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xue, L.; Zhou, R.; Luo, J. The role of pretreatment prognostic nutritional index in esophageal cancer: A meta-analysis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 19655–19662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, H.; Tang, S.; Wei, L.; Gan, J. Geriatric nutritional risk index as a predictor of complications and long-term outcomes in patients with gastrointestinal malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyokawa, T.; Kubo, N.; Tamura, T.; Sakurai, K.; Amano, R.; Tanaka, H.; Muguruma, K.; Yashiro, M.; Hirakawa, K.; Ohira, M. The pretreatment Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score is an independent prognostic factor in patients with resectable thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Results from a retrospective study. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; Baba, Y.; Shigaki, H.; Harada, K.; Iwatsuki, M.; Kurashige, J.; Sakamoto, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ishimoto, T.; Kosumi, K.; et al. Preoperative Nutritional Assessment by Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) is Useful to estimate Postoperative Morbidity After Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer. World J. Surg. 2016, 40, 1910–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamana, I.; Takeno, S.; Shimaoka, H.; Yamashita, K.; Yamada, T.; Shiwaku, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Hasegawa, S. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index as a prognostic factor in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma–retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 56, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Chen, C.; Wan, F.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, N.; Yang, J.; Pu, Q. Prognostic Value of Pre-Treatment Prognostic Nutritional Index in Esophageal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun-Young, J.; Wook-Jong, K.; Kim, J.-I.; Chin, J.-H.; Kim, W.-J.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, E.-H.; Choi, I.-C. Impact of anesthetic agents on overall and recurrence-free survival in patients undergoing esophageal cancer surgery: A retrospective observational study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Br. Med. J. 2007, 335, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, S.; Shimada, J.; Kato, D.; Tsunezuka, H.; Teramukai, S.; Inoue, M. Clinical Significance of Prognostic Nutritional Index After Surgical Treatment in Lung Cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 104, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, M.; Sowa, T.; Tokumasu, H.; Gomyoda, T.; Okada, H.; Ota, S.; Terada, Y. Comparison of three nutritional scoring systems for outcomes after complete resection of non–small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 162, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.-F.; Lu, J.; Xie, J.-W.; Wang, J.-B.; Lin, J.-X.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Cao, L.-L.; Lin, M.; Tu, R.-H.; Zheng, C.-H.; et al. Preoperative skeletal muscle index vs the controlling nutritional status score: Which is a better objective predictor of long-term survival for gastric cancer patients after radical gastrectomy? Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 3537–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.-H.; Chin, J.-H.; Choi, D.-K.; Hwang, B.-Y.; Choo, S.-J.; Song, J.-G.; Kim, T.-Y.; Choi, I.-C. Postoperative Hypoalbuminemia Is Associated With Outcome in Patients Undergoing Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2011, 25, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jammer, I.; Wickboldt, N.; Sander, M.; Smith, A.; Schultz, M.J.; Pelosi, P.; Leva, B.; Rhodes, A.; Hoeft, A.; Walder, B.; et al. Standards for definitions and use of outcome measures for clinical effectiveness research in perioperative medicine. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2015, 32, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, N.; Harada, K.; Baba, Y.; Kosumi, K.; Iwatsuki, M.; Kinoshita, K.; Nakamura, K.; Sakamoto, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Karashima, R.; et al. Preoperative controlling nutritional status (CONUT) is useful to estimate the prognosis after esophagectomy for esophageal cancer. Langenbeck Arch. Surg. 2017, 402, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, X.; Lai, Y.; Zhou, K.; Tang, Y.; Che, G. The prognostic value of pre-treatment prognostic nutritional index in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Medicine 2019, 98, e15280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpa, M.; Filip, B.; Cavallin, F.; Alfieri, R.; Saadeh, L.; Cagol, M.; Castoro, C. Esophagectomy in elderly patients: Which is the best prognostic score? Dis. Esophagus 2015, 29, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozoe, T.; Kimura, Y.; Ishida, M.; Saeki, H.; Korenaga, D.; Sugimachi, K. Correlation of pre-operative nutritional condition with post-operative complications in surgical treatment for oesophageal carcinoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2002, 28, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han-Geurts, I.; Hop, W.; Tran, T.; Tilanus, H. Nutritional Status as a Risk Factor in Esophageal Surgery. Dig. Surg. 2006, 23, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, D.N.; Gianotti, L.; Adiamah, A.; Barazzoni, R.; Deutz, N.E.; Dhatariya, K.; Greenhaff, P.L.; Hiesmayr, M.; Jakobsen, D.H.; Klek, S.; et al. Perioperative nutrition: Recommendations from the ESPEN expert group. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3211–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, B.-G.; Han, S.-S.; Cho, Y.-A.; Wie, G.-A.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-M.; Lee, S.D.; Kim, S.H.; Park, S.-J. Nutritional Status of Patients with Cancer: A Prospective Cohort Study of 1,588 Hospitalized Patients. Nutr. Cancer 2018, 70, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Ihmaidat, H. Nutritional effects of oesophageal, gastric and pancreatic carcinoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2003, 29, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballmer, P. Causes and mechanisms of hypoalbuminaemia. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 20, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitvogel, L.; Pietrocola, F.; Kroemer, G. Nutrition, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadgil, M.D.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Kandula, N.R.; Kanaya, A.M. Dietary Patterns Are Associated with Metabolic Risk Factors in South Asians Living in the United States. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, K.; Buettner, S.; Ijzermans, J.N.; Wijnhoven, B.P. Systematic Review on the Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score in Patients Undergoing Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 5343–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fan, J.; Jia, M.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Taylor, P.R. Body mass index and long-term risk of death from esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in a Chinese population. Thorac. Cancer 2016, 7, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, J.; Bodoky, G.; Bozzetti, F.; Fearon, K.; Muscaritoli, M.; Selga, G.; Schueren, M.V.B.-D.V.D.; Von Meyenfeldt, M.; Zürcher, G.; Fietkau, R.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Enteral Nutrition: Non-surgical oncology. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenhagen, E.; Van Vulpen, J.K.; Van Hillegersberg, R.; May, A.M.; Siersema, P.D. Nutrition in peri-operative esophageal cancer management. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 11, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fietkau, R.; Lewitzki, V.; Kuhnt, T.; Hölscher, T.; Hess, C.-F.; Berger, B.; Wiegel, T.; Rödel, C.; Niewald, M.; Hermann, R.M.; et al. A disease-specific enteral nutrition formula improves nutritional status and functional performance in patients with head and neck and esophageal cancer undergoing chemoradiotherapy: Results of a randomized, controlled, multicenter trial. Cancer 2013, 119, 3343–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, K.R.; Bozeman, M.C. Nutrition Therapy Issues in Esophageal Cancer. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2012, 14, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiura, Y.; Takiguchi, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Takahashi, T.; Kurokawa, Y.; Yamasaki, M.; Nakajima, K.; Miyata, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Mori, M.; et al. Effects of ghrelin administration during chemotherapy with advanced esophageal cancer patients. Cancer 2012, 118, 4785–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | Univariate Analysis for Overall Survival | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 1265 (100) | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p Value |
| Baseline characteristics | |||
| Age (years) | 63.0 [57.5–69.0] | 1.02 (1.01–1.04) | <0.001 |
| Female | 85 (6.7) | 0.94 (0.67–1.31) | 0.712 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.1 ± 3.0 | 0.88 (0.86–0.91) | <0.001 |
| ASA class | 0.112 † | ||
| I | 88 (7.0) | reference | |
| II | 1122 (88.7) | 1.12 (0.81–1.53) | 0.501 |
| III | 55 (4.3) | 1.63 (1.01–2.63) | 0.048 |
| Hct (%) | 38.5 [34.8–41.4] | 0.92 (0.90–0.93) | <0.001 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.82 [0.71–0.94] | 0.84 (0.58–1.24) | 0.383 |
| Bilirubin, total (mg/dL) | 0.5 [0.4–0.7] | 0.75 (0.55–1.02) | 0.067 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.7 [3.5–4.0] | 0.36 (0.29–0.45) | <0.001 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 5.2 [4.4–6.2] | 0.87 (0.82–0.92) | <0.001 |
| Lymphocyte count (cells/μL) | 1698 [1172–2215] | 1.00 (0.99–1.00) | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 174 [149–197] | 0.99 (0.98–0.99) | <0.001 |
| LVEF (%) | 62 [59–65] | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) | 0.290 |
| FVC (% predicted) | 92.0 [84.0–100.0] | 0.99 (0.98–0.99) | 0.006 |
| FEV1 (% predicted) | 92.0 [82.0–100.3] | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) | 0.018 |
| FEV1/FVC | 74.0 [68.0–78.0] | 0.99 (0.99–1.01) | 0.310 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 193 (15.3) | 1.37 (1.12–1.69) | 0.003 |
| Hypertension | 459 (36.3) | 0.99 (0.84–1.17) | 0.906 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 40 (3.2) | 1.04 (0.67–1.63) | 0.857 |
| COPD | 27 (2.1) | 1.82 (1.14–2.92) | 0.012 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 49 (3.9) | 1.54 (1.08–2.19) | 0.016 |
| Liver disease | 97 (7.7) | 1.01 (0.75–1.37) | 0.932 |
| Smoking status | 0.155 † | ||
| Non-smoking | 388 (30.7) | reference | |
| Ex-smoking | 609 (48.1) | 1.21 (0.99–1.47) | 0.056 |
| Current smoking | 268 (21.2) | 1.11 (0.88–1.41) | 0.371 |
| Alcohol | 940 (74.3) | 1.09 (0.89–1.34) | 0.405 |
| Chemo-radiation therapy | 474 (37.5) | 1.88 (1.60–2.20) | <0.001 |
| ACEI or ARB | 240 (19.0) | 0.73 (0.59–0.92) | 0.006 |
| β-blocker | 245 (19.4) | 0.92 (0.72–1.17) | 0.491 |
| Calcium channel blocker | 249 (19.7) | 0.83 (0.67–1.03) | 0.084 |
| Diuretics | 108 (8.5) | 1.05 (0.80–1.39) | 0.719 |
| Insulin | 190 (15.0) | 1.37 (1.11–1.69) | 0.004 |
| Oral hypoglycemic agent | 135 (10.7) | 1.41 (1.11–1.79) | 0.005 |
| Statins | 161 (12.7) | 1.13 (0.88–1.44) | 0.337 |
| Perioperative data | |||
| Anesthesia time (hours) | 6.8 [5.6–8.0] | 1.11 (1.06–1.16) | <0.001 |
| Crystalloid (L) | 1.7 [1.2–2.2] | 1.19 (1.10–1.28) | < 0.001 |
| Colloid (L) | 0.6 [0.1–1.0] | 1.05 (0.89–1.23) | 0.598 |
| Use of pRBC * | 206 (16.3) | 2.17 (1.80–2.61) | < 0.001 |
| Ivor Lewis | 581 (45.9) | 0.81 (0.69–0.96) | 0.012 |
| Minimally invasive surgery | 385 (30.4) | 0.72 (0.59–0.88) | 0.001 |
| Weight gain (%) | 0.9 [−0.2–2.3] | 1.04 (1.01–1.07) | 0.035 |
| Immediate postoperative Hct (%) | 36.0 [32.0–39.5] | 0.92 (0.90–0.93) | <0.001 |
| Maximal SOFAc score | 0 [0–2] | 1.32 (1.24–1.40) | <0.001 |
| Pathologic stage of cancer | <0.001 † | ||
| 0 | 238 (18.8) | reference | |
| I | 562 (44.4) | 0.76 (0.60–0.96) | 0.021 |
| II | 248 (19.6) | 1.81 (1.42–2.32) | <0.001 |
| III | 204 (16.1) | 3.79 (2.95–4.89) | <0.001 |
| IV | 13 (1.0) | 3.70 (1.99–6.89) | <0.001 |
| CONUT | p Value | GNRI | p Value | PNI | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Malnutrition | Normal | Malnutrition | Normal | Malnutrition | ||||
| ≤2 | ≥3 | ≥92 | <92 | ≥44.16 | <44.16 | ||||
| N | 845 (66.8) | 420 (33.2) | 972 (76.8) | 293 (23.2) | 775 (61.3) | 490 (38.7) | |||
| ICU stay (d) | 1.0 [0.8–1.8] | 1.0 [0.9–1.9] | 0.005 | 1.0 [0.8–1.8] | 1.0 [0.9–1.9] | 0.003 | 1.0 [0.8–1.8] | 1.0 [0.9–1.9] | 0.007 |
| Hospital stay (d) | 13 [11–16] | 15 [12–18] | <0.001 | 13 [11–16] | 15 [12–21] | <0.001 | 13 [11–16] | 14 [12–18] | <0.001 |
| MACCE | 22 (2.6) | 21 (5.0) | 0.040 | 27 (2.8) | 16 (5.5) | 0.042 | 20 (2.6) | 23 (4.7) | 0.063 |
| Respiratory complications | 117 (13.8) | 89 (21.2) | 0.001 | 133 (13.7) | 73 (24.9) | <0.001 | 106 (13.7) | 100 (20.4) | 0.002 |
| KDIGO ≥ 2 | 30 (3.6) | 21 (5.0) | 0.279 | 35 (3.6) | 16 (5.5) | 0.212 | 24 (3.1) | 27 (5.5) | 0.048 |
| Wound complications | 55 (6.5) | 24 (5.7) | 0.670 | 56 (5.8) | 23 (7.9) | 0.247 | 50 (6.5) | 29 (5.9) | 0.793 |
| Composite complications | 134 (15.9) | 99 (23.6) | 0.001 | 149 (15.3) | 84 (28.7) | <0.001 | 112 (14.5) | 121 (24.7) | <0.001 |
| 90-day death | 20 (2.4) | 20 (4.8) | 0.034 | 22 (2.3) | 18 (6.1) | 0.002 | 15 (1.9) | 25 (5.1) | 0.003 |
| 1-year death | 78 (9.2) | 96 (22.9) | <0.001 | 98 (10.1) | 76 (25.9) | <0.001 | 65 (8.4) | 109 (22.2) | <0.001 |
| Overall Survival | Recurrence-Free Survival | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutritional Index | HR (95% CI) * | p for Trend | HR (95% CI) † | p for Trend |
| CONUT | 1.23 (1.140–1.34) | <0.001 | 1.18 (1.10–1.28) | <0.001 |
| No risk (0–1) | reference | reference | ||
| Low risk (2) | 1.17 (0.92–1.48) | 1.15 (0.92–1.44) | ||
| Moderate risk (3–4) | 1.55 (1.24–1.92) **** | 1.40 (1.45–1.72) *** | ||
| High risk (≥5) | 1.91 (1.47–2.48) **** | 1.65 (1.29–2.11) **** | ||
| GNRI | 1.28 (1.13–1.45) | <0.001 | 1.21 (1.08–1.37) | 0.001 |
| No risk (>98) | reference | reference | ||
| Low risk (92 to ≤98) | 1.23 (0.97–1.56) | 1.06 (0.85–1.32) | ||
| Moderate risk (82 to <92) | 1.61 (1.22–2.12) *** | 1.38 (1.07–1.79) ** | ||
| High risk (<82) | 2.54 (1.64–3.93) **** | 2.03 (1.33–3.09) *** | ||
| PNI | 1.27 (1.17–1.38) | <0.001 | 1.21 (1.12–1.30) | <0.001 |
| No risk (>50) | reference | reference | ||
| Low risk (44.16 to ≤50) | 1.58 (1.23–2.03) **** | 1.44 (1.15–1.81) *** | ||
| Moderate risk (42 to <44.16) | 1.65 (1.20–2.26) *** | 1.40 (1.05–1.88) ** | ||
| High risk (<42) | 2.32 (1.77–3.06) **** | 1.90 (1.48–2.44) **** | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, J.-P.; Nam, J.-S.; Abidin, M.F.B.Z.; Kim, S.-O.; Lee, E.-H.; Choi, I.-C.; Chin, J.-H. Comparison of Preoperative Nutritional Indexes for Outcomes after Primary Esophageal Surgery for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4086. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114086
Yoon J-P, Nam J-S, Abidin MFBZ, Kim S-O, Lee E-H, Choi I-C, Chin J-H. Comparison of Preoperative Nutritional Indexes for Outcomes after Primary Esophageal Surgery for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):4086. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114086
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Jung-Pil, Jae-Sik Nam, Mohd Fitry Bin Zainal Abidin, Seon-Ok Kim, Eun-Ho Lee, In-Cheol Choi, and Ji-Hyun Chin. 2021. "Comparison of Preoperative Nutritional Indexes for Outcomes after Primary Esophageal Surgery for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 4086. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114086
APA StyleYoon, J.-P., Nam, J.-S., Abidin, M. F. B. Z., Kim, S.-O., Lee, E.-H., Choi, I.-C., & Chin, J.-H. (2021). Comparison of Preoperative Nutritional Indexes for Outcomes after Primary Esophageal Surgery for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Nutrients, 13(11), 4086. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114086






