Effect of Dapagliflozin and Magnesium Supplementation on Renal Magnesium Handling and Magnesium Homeostasis in Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiment
2.2. Biochemical Assay
2.3. Gene Expression Study
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Cell Culture and Intracellular Magnesium Concentration Measurement
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Laboratory Data
3.2. Gene Expression Analysis
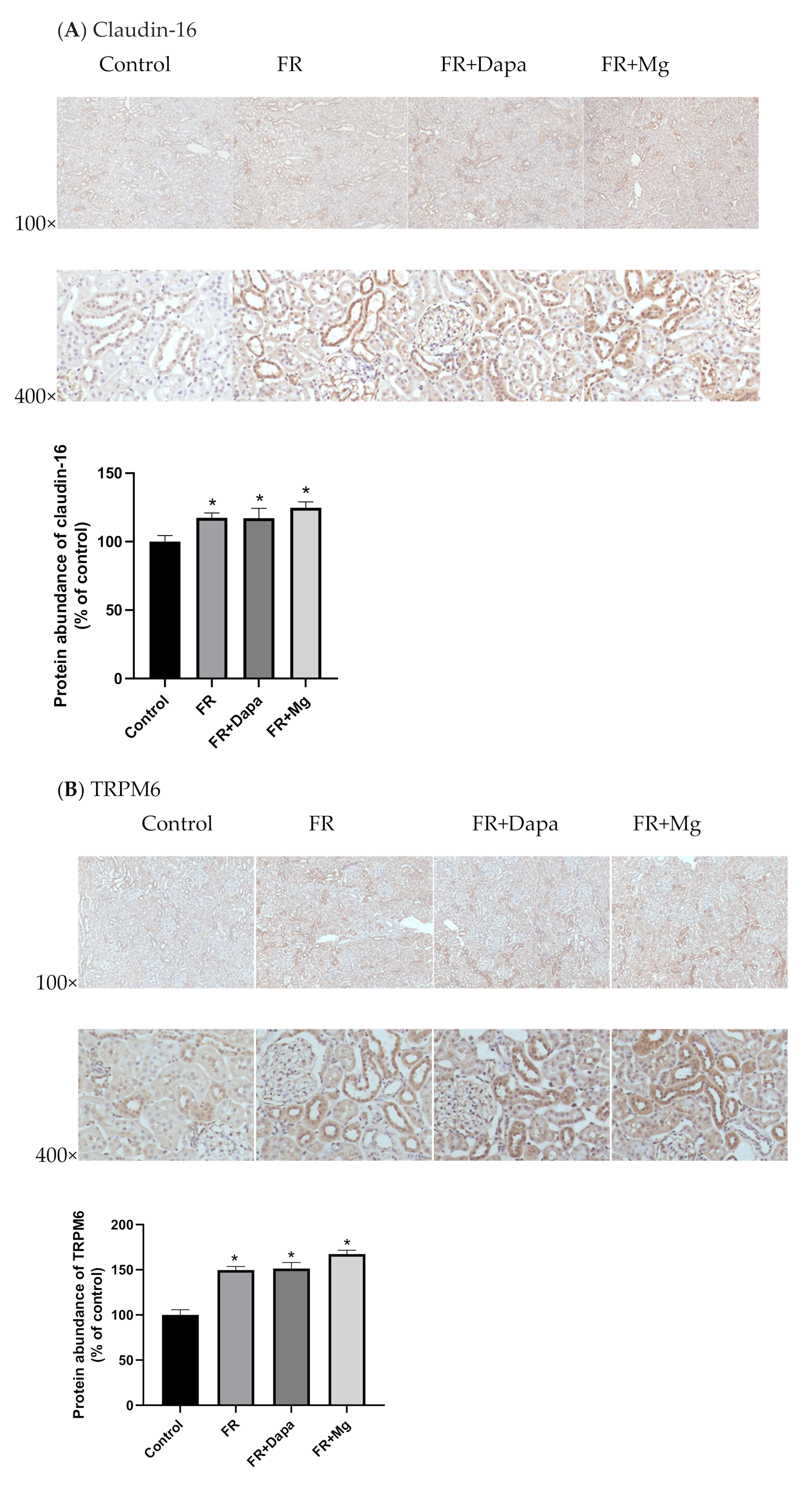
3.3. Immunohistochemistry
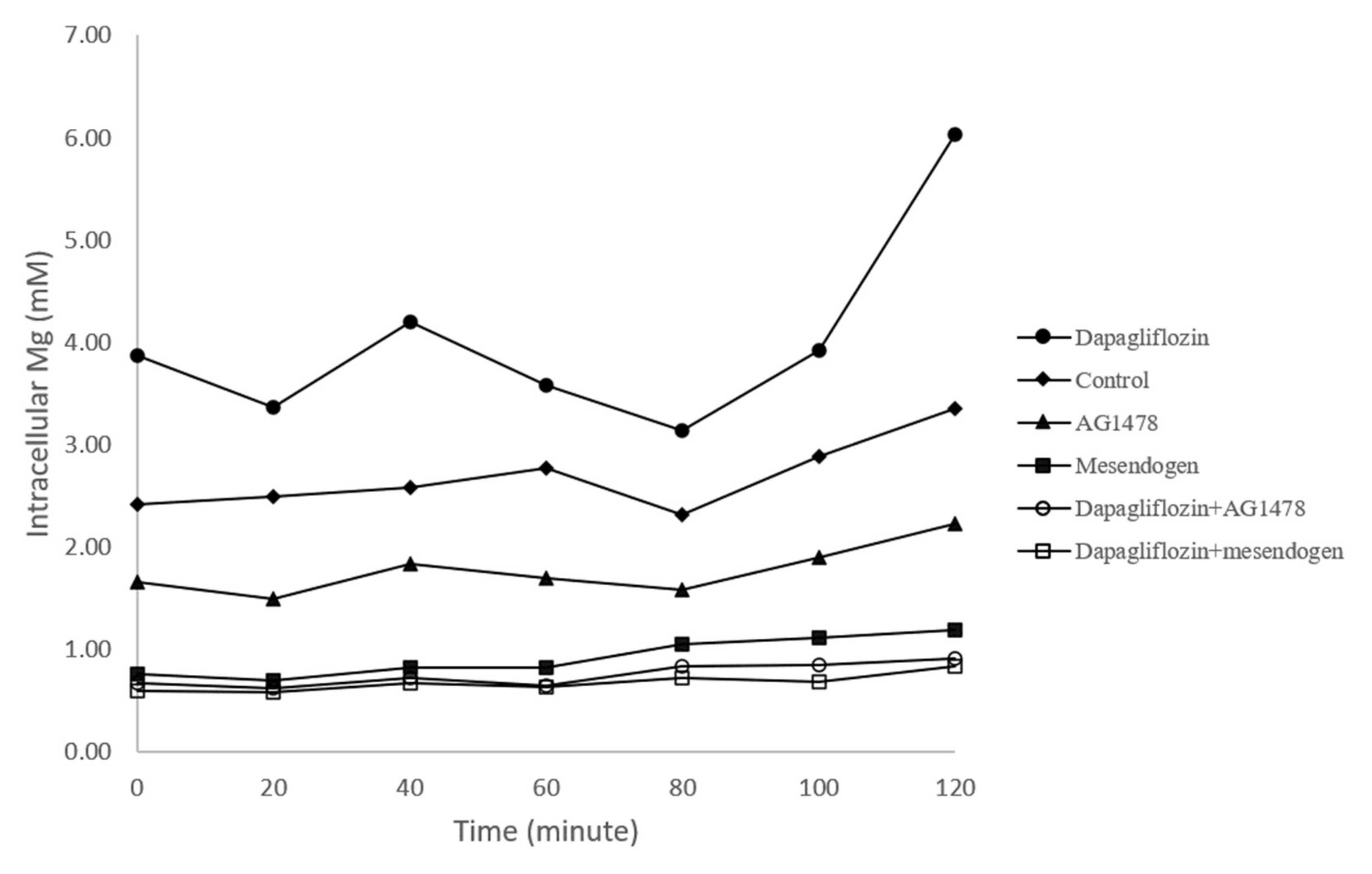
3.4. Intracellular Magnesium Concentration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raimundo, M.; Lopes, J.A. Metabolic syndrome, chronic kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease: A dynamic and life-threatening triad. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2011, 20, 747861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.J.; Nakagawa, T.; Sanchez-Lozada, L.G.; Shafiu, M.; Sundaram, S.; Le, M.; Ishimoto, T.; Sautin, Y.Y.; Lanaspa, M.A. Sugar, uric acid, and the etiology of diabetes and obesity. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3307–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosique-Esteban, N.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Hernández-Alonso, P.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Dietary magnesium and cardiovascular disease: A review with emphasis in epidemiological studies. Nutrients 2018, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieboom, B.C.T.; Ligthart, S.; Dehghan, A.; Kurstjens, S.; de Baaij, J.H.F.; Franco, O.H.; Hofman, A.; Zietse, R.; Stricker, B.H.; Hoorn, E.J. Serum magnesium and the risk of prediabetes: A population-based cohort study. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, N.M.; Jacques, P.F.; Zhang, X.L.; Juan, W.; Sahyoun, N.R. Dietary magnesium intake is related to metabolic syndrome in older Americans. Eur. J. Nutr. 2008, 47, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, D.P.; Sharma, R.; Bansal, D.D. Implications of magnesium deficiency in type 2 diabetes: A review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2010, 134, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, P.C.T.; Pham, P.M.T.; Pham, S.V.; Miller, J.M.; Pham, P.T.T. Hypomagnesemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 2, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viering, D.H.H.M.; de Baaij, J.H.F.; Walsh, S.B.; Kleta, R.; Bockenhauer, D. Genetic cause of hypomagnesemia, a clinical overview. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2017, 32, 1123–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, A.M. Cellular magnesium homeostasis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 512, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral-Rodríguez, M.Á.; Stuiver, M.; Abascal-Palacios, G.; Diercks, T.; Oyenarte, I.; Ereño-Orbea, J.; de Opakua, A.I.; Blanco, F.J.; Encinar, J.A.; Spiwok, V.; et al. Nucleotide binding triggers a conformational change of the CBS module of the magnesium transporter CNNM2 from a twisted towards a flat structure. Biochem. J. 2014, 464, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäffers, O.J.M.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J.M.; de Baaij, J.H.F. The rise and fall of novel renal magnesium transporters. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2018, 314, F1027–F1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlotides, G.; Mertens, P.R. Sodium-glucose contransport inhibitors: Mechanisms, metabolic effects and implications for the treatment of diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Del Gobbo, L.C.; Zhai, S.; Song, Y. Elevated serum magnesium associated with SGLT2 inhibitor use in type 2 diabetes patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2546–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gommers, L.M.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J.; de Baaij, J.H.F. Hypomagnesemia in type 2 diabetes: A vicious circle? Diabetes 2016, 65, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostov, K. Effects of magnesium deficiency on mechanisms of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes: Focusing on the processes of insulin secretion and signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, F.H. Magnesium deficiency and increased inflammation: Current perspectives. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayssiguier, Y.; Gueux, E.; Nowacki, W.; Rock, E.; Mazur, A. High fructose consumption combined with low dietary magnesium intake may increase the incidence of the metabolic syndrome by inducing inflammation. Magnes. Res. 2006, 19, 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- McMurray, J.J.V.; Solomon, S.D.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Martinex, F.A.; Ponikoski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Anand, I.S.; Bělohlávek, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayan, H.; Farfel, Z.; Karlish, S.J.D. Renal Mg handling, FXYD2 and the central role of the Na, K-ATPase. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baaij, J.H.F.; Hoenderop, J.G.J.; Bindels, R.J.M. Magnesium in man: Implications for health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondón, L.J.; Groenestege, W.M.T.; Rayssiguier, Y.; Mazur, A. Relationship between low magnesium status and TRPM6 expression in the kidney and large intestine. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R2001–R2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toto, R.D.; Goldenberg, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Cain, V.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Sjöström, C.D.; Sartipy, P. Correction of hypomagnesemia by dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes: A post hoc analysis of 10 randomized, placebo-controlled trials. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2019, 33, 107402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippatos, T.D.; Tsimihodimos, V.; Liamis, G.; Elisaf, M. SGLT2 inhibitors-induced electrolyte abnormalities: An analysis of the associated mechanisms. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2018, 12, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianciolo, G.; Pascalis, A.D.D.; Gasperoni, L.; Tondolo, F.; Zappulo, F.; Capelli, I.; Cappuccili, M.; Manna, G.L.L. The off-target effects, electrolyte and mineral disorders of SGLT2i. Molecules 2020, 25, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieg, J.A.D.; Xue, J.; Rieg, T. Tubular effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: Intended and unintended consequences. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2020, 29, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bommel, E.J.M.; Geurts, F.; Muskiet, M.H.A.; Post, A.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Danser, A.H.J.; Touw, D.J.; van Berkel, M.; Kramer, M.H.H.; Nieuwdorp, M.; et al. SGLT2 inhibition versus sulfonylurea treatment effects on analysis of a clinical trial reaching glycemic equipoise: Tubular effects of SGLT2 inhibition in type 2 diabetes. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 3107–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douard, V.; Sabbagh, Y.; Lee, J.; Patel, C.; Kemp, F.W.; Bogden, J.D.; Lin, S.; Ferraris, R.P. Excessive fructose intake causes 1,25-(OH)2D3-dependent inhibition of intestinal and renal calcium transport in growing rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 304, E1303–E1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, R. Magnesium metabolism and its disorders. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2003, 24, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uwitonze, A.M.; Razzaque, M.S. Role of magnesium in vitamin D activation and function. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2018, 118, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoback, D.M.; Bilezikian, J.P.; Costa, A.G.; Dempster, D.; Dralle, H.; Khan, A.A.; Peacock, M.; Raffaelli, M.; Silva, B.C.; Thakker, R.V.; et al. Presentation of hypoparathyroidism: Etiologies and clinical features. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 2300–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.J.; González, E.A.; Slatopolsky, E. Clinical consequences and management of hypomagnesemia. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 2291–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaine, J.; Chonchol, M.; Levi, M. Renal control of calcium, phosphate, and magnesium homeostasis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, L.; Martins, S.; Ferreira, D.; Guimarães, J.T.; Santos, A.C. Vitamin D, parathyroid hormone and metabolic syndrome—the PORMETS study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2017, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Claudin-19 | TCATATCCAGTCAGCAAGA | AGCAGTCAAAGTACAGAGA |
| TRPM7 | GTTCAGAGGACCATCAAGA | CAAGAGCATCAAGCATAGC |
| Control (n = 10) | FR (n = 10) | FR+Dapa (n = 10) | FR+Mg (n = 10) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight (g) | 586.6 ± 56.5 | 597.4 ± 57.2 | 521.6 ± 21.6 *,# | 615.1 ±72.0 |
| Blood pressure (mmHg) | 149.4 ± 2.6 | 155.6 ± 7.7 | 145.5 ± 6.9 # | 155.7 ±6.2 |
| Water intake (mL/day) | 52.2 ± 11.0 | 42.5 ± 7.6 | 52.0 ± 3.6 | 40.1 ±12.4 |
| 24h Urine (mL/day) | 29.4 ± 10.9 # | 20.0 ± 8.4 * | 41.7 ± 12.7 *,# | 17.9 ±7.6 * |
| Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | 109.0 ± 14.3 | 134.6 ± 22.4 * | 99.6 ± 12.5 # | 109.1 ± 10.2 # |
| Blood Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 70.7 ± 27.1 | 231.0 ± 137.9 * | 131.0 ± 62.8 # | 192.1 ± 59.8 * |
| Blood Insulin (μU/mL) | 3.0 ± 2.2 | 11.6 ± 9.2 * | 4.2 ± 1.4 # | 7.3 ± 2.7 *,# |
| HOMA-IR | 0.8 ± 0.6 | 3.9 ± 3.1 * | 1.0 ± 0.3# | 1.6 ± 0.6# |
| Blood Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.29 ± 0.05 | 0.26 ± 0.05 | 0.27 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ± 0.06 |
| Blood Calcium (mg/dL) | 9.1 ± 0.7 | 9.2 ± 0.7 | 9.2 ± 0.4 | 9.9 ± 0.5 |
| Blood Mg (mg/dL) | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 1.8 ± 0.2 * | 2.1 ± 0.4 *,# | 2.2 ± 0.2# |
| Blood i-PTH (pg/mL) | 326.6 ± 104.1 | 149.9 ± 32.6 * | 175.2 ± 50.0 * | 181.9 ± 63.8 * |
| Blood 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin-D3 (pg/mL) | 71.0 ± 19.8 | 53.6 ± 11.6 * | 54.2 ± 20.5 * | 56.8 ± 8.9 * |
| FEMg(%) Urine Mg (mg/24 h) | 4.1 ± 2.9 19.6 ± 7.3 | 2.7 ± 1.4 * 10.1 ± 4.9 * | 1.9 ± 1.3 *,# 5.3 ± 3.6 *,# | 6.7 ± 1.8 *,# 19.6 ± 4.4 # |
| 0 min | 20 min | 40 min | 60 min | 80 min | 100 min | 120 min | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 2.41 ± 0.68 | 2.5 ± 0.83 | 2.58 ± 1.05 | 2.77 ± 1.57 | 2.31 ± 0.77 | 2.88 ± 0.98 | 3.36 ± 0.69 |
| Mesendogen | 0.77 ± 0.41 * | 0.71 ± 0.35 * | 0.83 ± 0.43 * | 0.83 ± 0.38 | 1.05 ± 0.52 | 1.12 ± 0.47 * | 1.2 ± 0.62 * |
| AG1478 | 1.66 ± 0.71 * | 1.49 ± 0.72 * | 1.83 ± 1.04 | 1.69 ± 0.64 | 1.59 ± 0.55 | 1.90 ± 0.69 * | 2.23 ± 0.86 * |
| Dapagliflozin | 3.87 ± 1.85 * | 3.36 ± 2.53 | 4.20 ± 2.74 * | 3.58 ± 1.52 * | 3.31 ± 0.62 | 3.92 ± 0.76 * | 6.03 ± 1.84 * |
| Dapagliflozin+Mesendogen | 0.60 ± 0.39 * | 0.58 ± 0.38 * | 0.67 ± 0.42 * | 0.64 ± 0.34 | 0.73 ± 0.45 | 0.68 ± 0.36 * | 0.84 ± 0.57 * |
| Dapagliflozin+AG1478 | 0.67 ±0.70 * | 0.62 ± 0.65 | 0.73 ± 0.76 * | 0.65 ± 0.77 | 0.84 ± 0.95 * | 0.86 ± 1.01 | 0.91 ± 0.95 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ng, H.-Y.; Kuo, W.-H.; Tain, Y.-L.; Leung, F.-F.; Lee, W.-C.; Lee, C.-T. Effect of Dapagliflozin and Magnesium Supplementation on Renal Magnesium Handling and Magnesium Homeostasis in Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114088
Ng H-Y, Kuo W-H, Tain Y-L, Leung F-F, Lee W-C, Lee C-T. Effect of Dapagliflozin and Magnesium Supplementation on Renal Magnesium Handling and Magnesium Homeostasis in Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114088
Chicago/Turabian StyleNg, Hwee-Yeong, Wei-Hung Kuo, You-Lin Tain, Foong-Fah Leung, Wen-Chin Lee, and Chien-Te Lee. 2021. "Effect of Dapagliflozin and Magnesium Supplementation on Renal Magnesium Handling and Magnesium Homeostasis in Metabolic Syndrome" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114088
APA StyleNg, H.-Y., Kuo, W.-H., Tain, Y.-L., Leung, F.-F., Lee, W.-C., & Lee, C.-T. (2021). Effect of Dapagliflozin and Magnesium Supplementation on Renal Magnesium Handling and Magnesium Homeostasis in Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients, 13(11), 4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13114088








