A Single-Carbon Stable Isotope Ratio Model Prediction Equation Can Estimate Self-Reported Added Sugars Intake in an Adult Population Living in Southwest Virginia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Design
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Measures
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
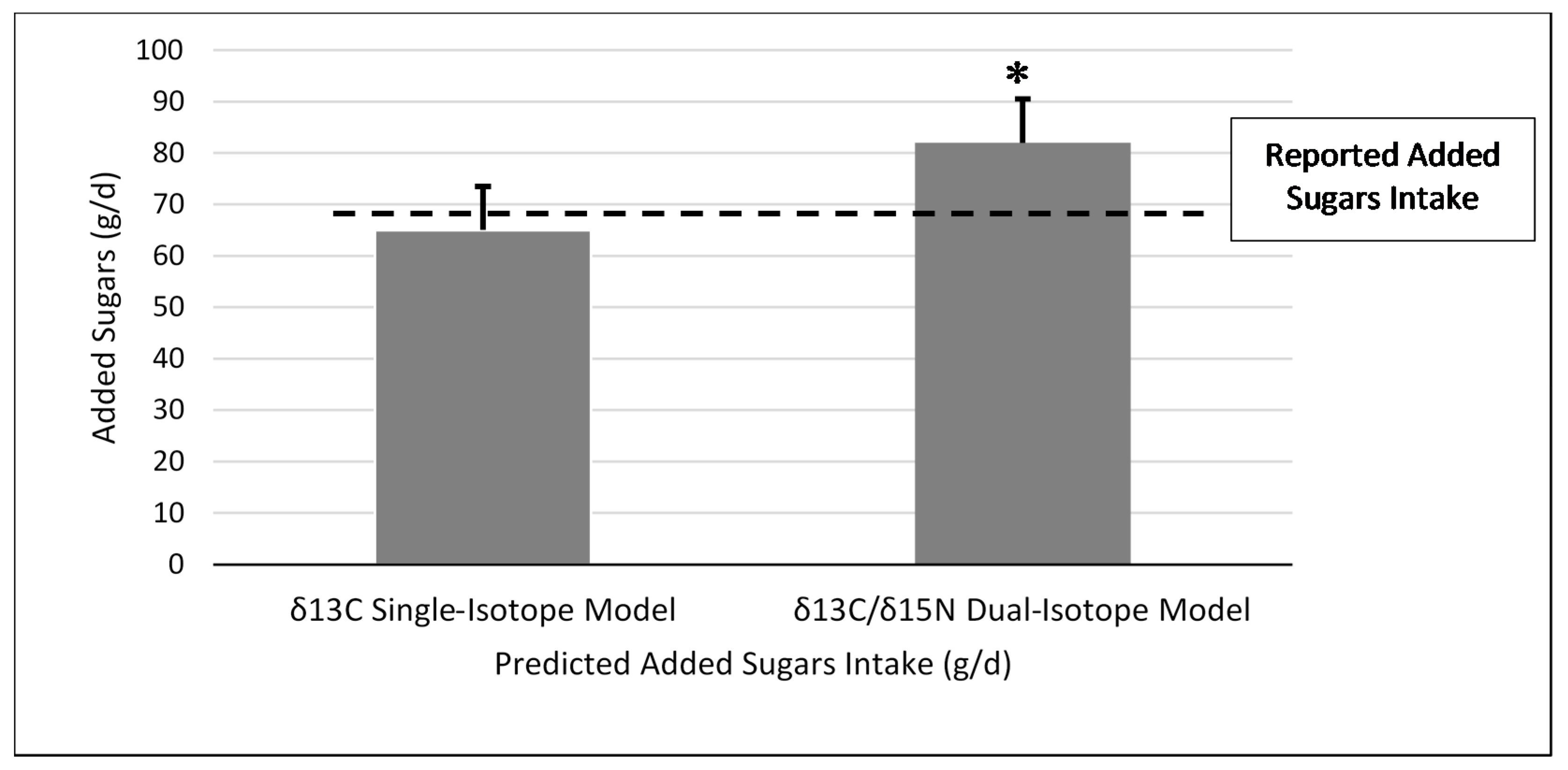
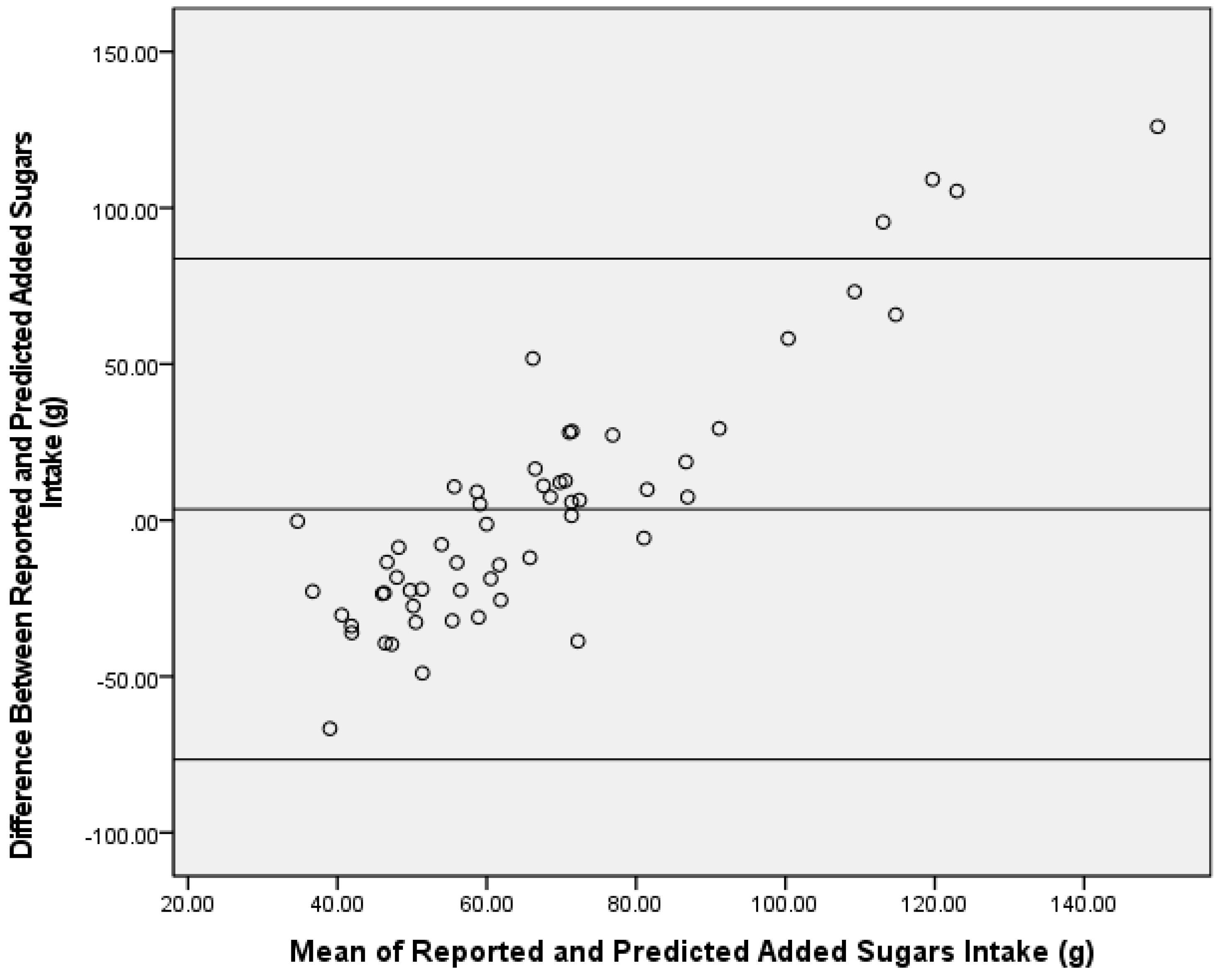
3.2. Single-Isotope Equation
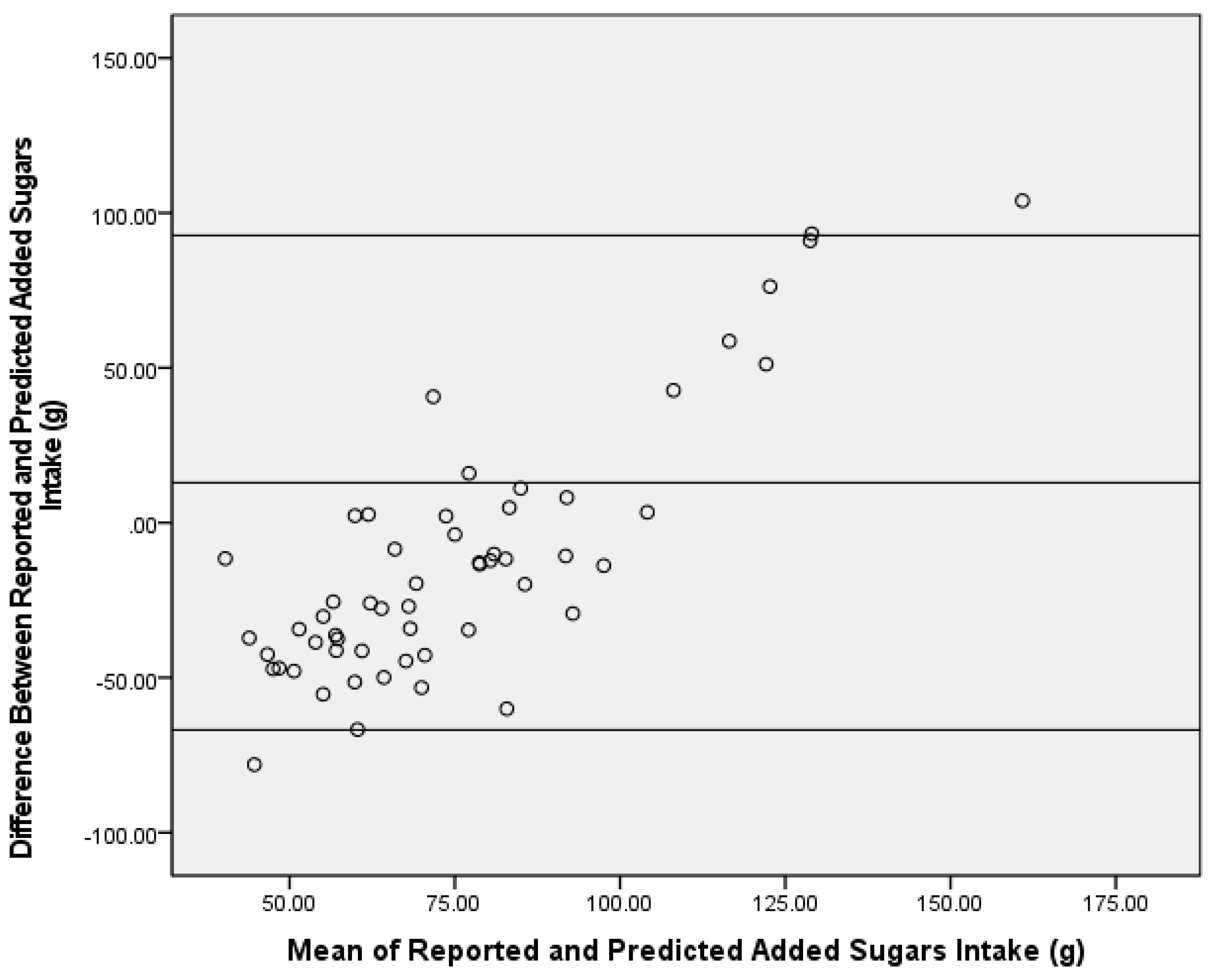
3.3. Dual-Isotope Equation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, F.E.; Subar, A.F. Dietary Assessment Methodology. In Nutrition in the Prevention and Treatment of Disease, 4th ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 5–48. [Google Scholar]
- Willett, W.C. Nutritional Epidemiology, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Brownell, K.D.; Farley, T.; Willett, W.C.; Popkin, B.; Chaloupka, F.J.; Thompson, J.W.; Ludwig, D. The Public Health and Economic Benefits of Taxing Sugar-Sweetened Beverages. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, V.E.; Dietrich, A.M.; Estabrooks, P.A.; Savla, J.; Serrano, E.; Davy, B.M. Dietary biomarkers: Advances, limitations and future directions. Nutr. J. 2012, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, B.; Jahren, H. New markers of dietary added sugar intake. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2016, 19, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahren, A.H.; Saudek, C.; Yeung, E.; Kao, W.H.L.; Kraft, R.A.; Caballero, B. An isotopic method for quantifying sweeteners derived from corn and sugar cane. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 1380–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, B.M.; Jahren, A.H.; Hedrick, V.E.; Comber, D.L. Association of δ13C in Fingerstick Blood with Added-Sugar and Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2011, 111, 874–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, B.M.; Jahren, A.H.; Hedrick, V.E.; You, W.; Zoellner, J.M. Influence of an intervention targeting a reduction in sugary beverage intake on the δ13C sugar intake biomarker in a predominantly obese, health-disparate sample. Public Health Nutr. 2016, 20, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hedrick, V.E.; Zoellner, J.M.; Jahren, A.H.; Woodford, N.A.; Bostic, J.N.; Davy, B.M. A dual-carbon-and-nitrogen stable isotope ratio model is not superior to a single-carbon stable isotope ratio model for predicting added sugar intake in southwest Virginian adults. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, S.H.; Kristal, A.; Bersamin, A.; Hopkins, S.E.; Boyer, B.B.; O’Brien, D. Carbon and Nitrogen Stable Isotope Ratios Predict Intake of Sweeteners in a Yup’ik Study Population. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, E.H.; Saudek, C.D.; Jahren, A.H.; Kao, W.H.L.; Islas, M.; Kraft, R.; Coresh, J.; Anderson, C.A.M. Evaluation of a Novel Isotope Biomarker for Dietary Consumption of Sweets. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 172, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDougall, C.R.; Hill, C.E.; Jahren, A.H.; Savla, J.; Riebl, S.K.; Hedrick, V.E.; Raynor, H.; Dunsmore, J.C.; Frisard, M.I.; Davy, B.M. The δ13C Value of Fingerstick Blood Is a Valid, Reliable, and Sensitive Biomarker of Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake in Children and Adolescents. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subar, A.F.; Freedman, L.S.; Tooze, J.A.; Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Boushey, C.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Thompson, F.E.; Potischman, N.; Guenther, P.M.; Tarasuk, V.; et al. Addressing Current Criticism Regarding the Value of Self-Report Dietary Data. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 2639–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.; Yon, B.; Hankin, J. Research: Successful Approaches, Dietary Assessment and Validation, 3rd ed.; Monsen, E., Van Horn, L., Eds.; American Dietetic Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, C.M.; Alvig, A.L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Schoeller, D.A. The Natural 13C Abundance of Plasma Glucose Is a Useful Biomarker of Recent Dietary Caloric Sweetener Intake. J. Nutr. 2009, 140, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahren, A.H.; Bostic, J.N.; Davy, B.M. The potential for a carbon stable isotope biomarker of dietary sugar intake. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2014, 29, 795–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsemann, F.; Koehler, K.; Braun, H.; Schaenzer, W.; Flenker, U. Human dietary δ15N intake: Representative data for principle food items. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2013, 152, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, S.H.; Kristal, A.R.; Bersamin, A.; Choy, K.; E Hopkins, S.; Stanhope, K.L.; Havel, P.J.; Boyer, B.B.; O’Brien, D.M. Isotopic estimates of sugar intake are related to chronic disease risk factors but not obesity in an Alaska native (Yup’ik) study population. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 68, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dengo, A.L.; Dennis, E.A.; Orr, J.S.; Marinik, E.L.; Ehrlich, E.; Davy, B.M.; Davy, K.P. Arterial Destiffening With Weight Loss in Overweight and Obese Middle-Aged and Older Adults. Hypertension 2010, 55, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, J.S.; Dengo, A.L.; Rivero, J.M.; Davy, K.P. Arterial Destiffening With Atorvastatin in Overweight and Obese Middle-Aged and Older Adults. Hypertension 2009, 54, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, J.S.; Gentile, C.L.; Davy, B.M.; Davy, K.P. Large artery stiffening with weight gain in humans: Role of visceral fat accumulation. Hypertension 2008, 51, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoellner, J.M.; Hedrick, V.E.; You, W.; Chen, Y.; Davy, B.M.; Porter, K.J.; Bailey, A.; Lane, H.; Alexander, R.; Estabrooks, P.A. Effects of a behavioral and health literacy intervention to reduce sugar-sweetened beverages: A randomized-controlled trial. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutrition Data System for Research (NDSR) Software, 2011 version; Nutrition Coordinating Center, University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2017.
- Giavarina, D. Understanding Bland Altman analysis. Biochem. Medica 2015, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, D.G.; Bland, J.M. Measurement in Medicine: The Analysis of Method Comparison Studies. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. D 1983, 32, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myles, P.; Cui, J.I. Using the Bland–Altman method to measure agreement with repeated measures. Br. J. Anaesth. 2007, 99, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, D.L.; Hopkins, S.; O’Brien, D.; Mancl, L.; Orr, E.; Lenaker, D. Association between added sugar intake and dental caries in Yup’ik children using a novel hair biomarker. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, S.H.; Kristal, A.; Hopkins, S.E.; Boyer, B.B.; O’Brien, D. Stable Isotope Models of Sugar Intake Using Hair, Red Blood Cells, and Plasma, but Not Fasting Plasma Glucose, Predict Sugar Intake in a Yup’ik Study Population. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, R.A.; Jahren, A.H.; Saudek, C.D. Clinical-scale investigation of stable isotopes in human blood: δ13C and δ15N from 406 patients at the Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 3683–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissner, L.; Troiano, R.; Midthune, D.; Heitmann, B.L.; Kipnis, V.; Subar, A.F.; Potischman, N. OPEN about obesity: Recovery biomarkers, dietary reporting errors and BMI. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Dodd, K.W.; Kipnis, V.; E Thompson, F.; Potischman, N.; Schoeller, D.A.; Baer, D.J.; Midthune, D.; Troiano, R.; Bowles, H.; et al. Comparison of self-reported dietary intakes from the Automated Self-Administered 24-h recall, 4-d food records, and food-frequency questionnaires against recovery biomarkers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, A.S.; Kelly, S.D.; Woolfe, M. Nitrogen Isotope Composition of Organically and Conventionally Grown Crops. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 2664–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoellner, J.; Krzeski, E.; Harden, S.; Cook, E.; Allen, K.; Estabrooks, P.A. Qualitative Application of the Theory of Planned Behavior to Understand Beverage Consumption Behaviors among Adults. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantha, O.L.; Polakof, S.; Huneau, J.-F.; Mariotti, F.; Poupin, N.; Zalko, D.; Fouillet, H. Early changes in tissue amino acid metabolism and nutrient routing in rats fed a high-fat diet: Evidence from natural isotope abundances of nitrogen and carbon in tissue proteins. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantha, O.L.; Patel, M.L.; Hankard, R.; De Luca, A. Effect of Organic Food Intake on Nitrogen Stable Isotopes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemin, D.; Rittenberg, D. The Life Span of the Human Red Blood Cell. J. Biol. Chem. 1946, 166, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Reference Group (n = 256) n (%) Unless Otherwise Noted | Test Group (n = 56) n (%) Unless Otherwise Noted | Test Statistic and p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 60 (23) | 34 (61) | χ2 = 30.6 |
| Female | 197 (77) | 22 (39) | p ≤ 0.001 |
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 42.4 ± 14.7 | 53.1 ± 16.0 | F = 23.7 |
| p ≤ 0.001 | |||
| Age category, n (%) | χ2 = 28.5 p ≤ 0.001 | ||
| 18–24 years | 33 (13) | 7 (12.5) | |
| 25–44 years | 117 (46) | 7 (12.5) | |
| 45–64 years | 91 (35) | 30 (53.5) | |
| ≥65 years | 16 (6) | 12 (21.5) | |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean ± SD | 31.8 ± 9.2 | 29.5 ± 4.1 | F = 3.4 p = 0.07 |
| BMI category, n (%) | χ2 = 10.0 p = 0.02 | ||
| Underweight, ≤18.4 | 3 (1) | 0 (0) | |
| Normal weight, 18.5–24.9 | 65 (25.5) | 6 (11) | |
| Overweight, 25–29.9 | 65 (25.5) | 24 (43) | |
| Obese, ≥30 | 124 (48) | 26 (46) | |
| Added sugars intake (g), mean ± SD | 88.8 ± 58.8 | 68.8 ± 43.4 | F = 5.8 p = 0.02 |
| δ13C (‰), mean ± SD | −19.1 ± 0.8 | −19.5 ± 0.8 | F = 10.3 p = 0.001 |
| δ15N (‰), mean ± SD a | 7.4 ± 0.5 | 9.1 ± 0.3 | F = 526.9 p ≤ 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hedrick, V.E.; Halliday, T.M.; Davy, B.M.; Zoellner, J.M.; Jahren, A.H. A Single-Carbon Stable Isotope Ratio Model Prediction Equation Can Estimate Self-Reported Added Sugars Intake in an Adult Population Living in Southwest Virginia. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3842. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113842
Hedrick VE, Halliday TM, Davy BM, Zoellner JM, Jahren AH. A Single-Carbon Stable Isotope Ratio Model Prediction Equation Can Estimate Self-Reported Added Sugars Intake in an Adult Population Living in Southwest Virginia. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):3842. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113842
Chicago/Turabian StyleHedrick, Valisa E., Tanya M. Halliday, Brenda M. Davy, Jamie M. Zoellner, and A. Hope Jahren. 2021. "A Single-Carbon Stable Isotope Ratio Model Prediction Equation Can Estimate Self-Reported Added Sugars Intake in an Adult Population Living in Southwest Virginia" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 3842. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113842
APA StyleHedrick, V. E., Halliday, T. M., Davy, B. M., Zoellner, J. M., & Jahren, A. H. (2021). A Single-Carbon Stable Isotope Ratio Model Prediction Equation Can Estimate Self-Reported Added Sugars Intake in an Adult Population Living in Southwest Virginia. Nutrients, 13(11), 3842. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113842






