The Impact of Gestational Weight Gain on the Risks of Adverse Maternal and Infant Outcomes among Normal BMI Women with High Triglyceride Levels during Early Pregnancy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection and Independent Variables
2.3. Definition of Outcomes
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Population
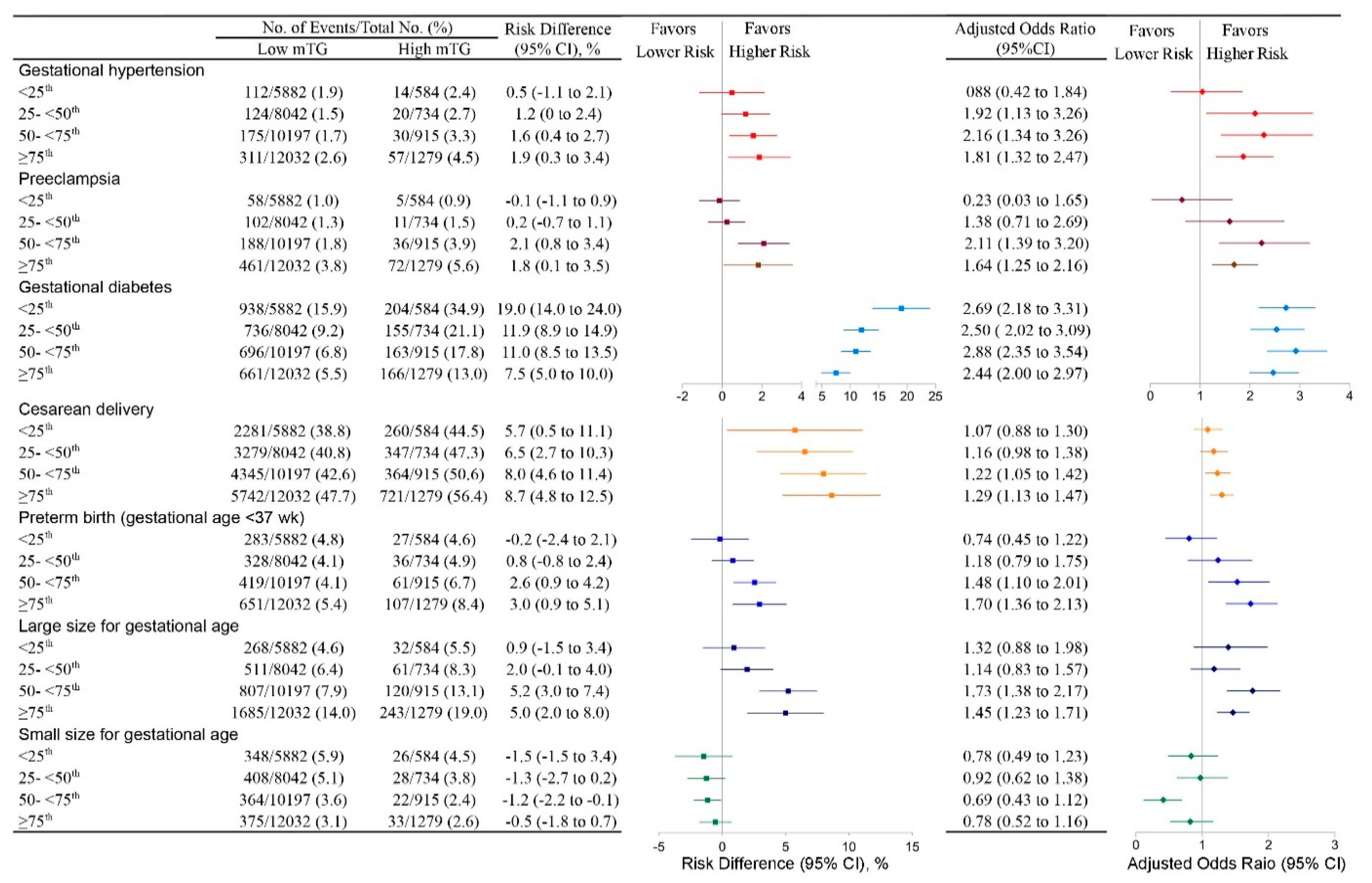
4.2. Maternal TG in Early Pregnancy and Risks of Adverse Maternal and Neonatal Outcomes
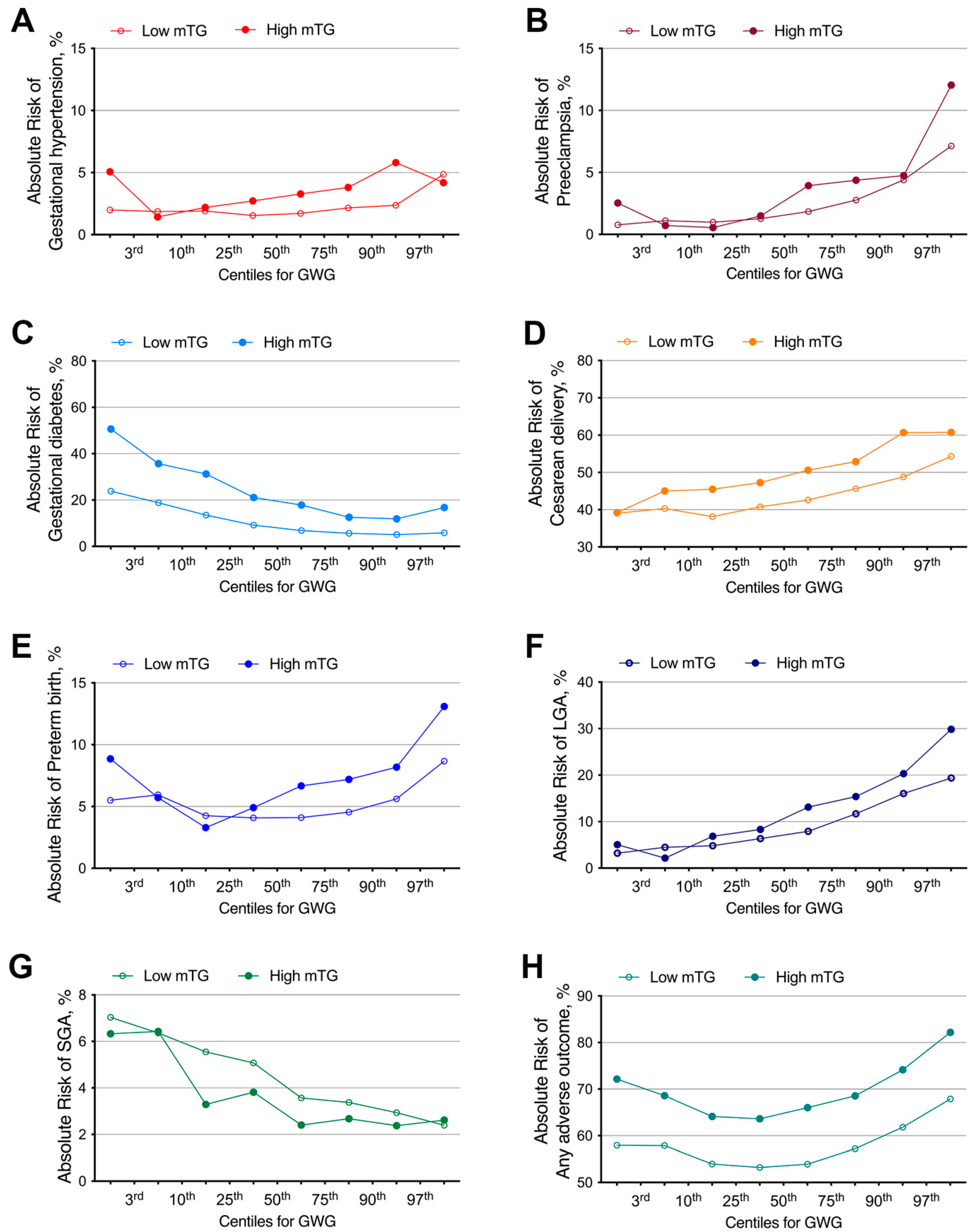
4.3. The Absolute Risk for Any Adverse Outcome Categorized by Maternal Early Pregnancy TG Level in Gestational Weight Gain (GWG) Percentiles
4.4. High mTG and the Risk of Any Adverse Outcome in Different GWG Groups in Women with Normal Early Pregnancy BMI
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brizzi, P.; Tonolo, G.; Esposito, F.; Puddu, L.; Dessole, S.; Maioli, M.; Milia, S. Lipoprotein metabolism during normal pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1999, 181, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warth, M.R.; Arky, R.A.; Knopp, R.H. Lipid Metabolism in Pregnancy. II. Altered Lipid Composition in Intermediate, Very Low, Low, and High-Density Lipoprotein Fractions. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1975, 41, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desoye, G.; Schweditsch, M.O.; Pfeiffer, K.P.; Zechner, R.; Kostner, G.M. Correlation of Hormones with Lipid and Lipoprotein Levels During Normal Pregnancy and Postpartum. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1987, 64, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordovas, J.; Pocovi, M.; Grande, F. Plasma lipids and cholesterol esterification rate during pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 1984, 63, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fåhraeus, L.; Larsson-Cohn, U.; Wallentin, L. Plasma lipoproteins including high density lipoprotein subfractions during normal pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 1985, 66, 468–472. [Google Scholar]
- Vahratian, A.; Misra, V.K.; Trudeau, S.; Misra, D.P. Prepregnancy Body Mass Index and Gestational Age-Dependent Changes in Lipid Levels During Pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 116, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adank, M.C.; Benschop, L.; Kors, A.W.; Peterbroers, K.R.; Gregoor, A.M.S.; Mulder, M.T.; Schalekamp-Timmermans, S.; Van Lennep, J.E.R.; Steegers, E.A.P. Maternal lipid profile in early pregnancy is associated with foetal growth and the risk of a child born large-for-gestational age: A population-based prospective cohort study. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, T.; Burski, T.K.; Øyen, N.; Godang, K.; Bollerslev, J.; Henriksen, T. Maternal anthropometric and metabolic factors in the first half of pregnancy and risk of neonatal macrosomia in term pregnancies. A prospective study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 153, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vrijkotte, T.G.M.; Krukziener, N.; Hutten, B.A.; Vollebregt, K.C.; Van Eijsden, M.; Twickler, M.B. Maternal Lipid Profile During Early Pregnancy and Pregnancy Complications and Outcomes: The ABCD Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3917–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.-H.; Wu, D.-D.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.-J.; Gao, L.; Lass, G.; Zhang, J.; Tian, S.; Ivanova, D.; Tang, L.; et al. Maternal High Triglyceride Levels During Early Pregnancy and Risk of Preterm Delivery: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tieu, J.; Shepherd, E.; Middleton, P.; Crowther, C.A. Dietary advice interventions in pregnancy for preventing gestational diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2017, CD006674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmermans, Y.E.; Van De Kant, K.D.; Oosterman, E.O.; Spaanderman, M.E.; Villamor-Martinez, E.; Kleijnen, J.; Vreugdenhil, A.C. The impact of interpregnancy weight change on perinatal outcomes in women and their children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e12974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oteng-Ntim, E.; Varma, R.; Croker, H.; Poston, L.; Doyle, P. Lifestyle interventions for overweight and obese pregnant women to improve pregnancy outcome: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, K.M.; Yaktine, A.L. Institute of Medicine (US) and National Research Council (US) Committee to Reexamine IOM Pregnancy Weight Guidelines (Eds.). In Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Nutritional Status During Pregnancy and Lactation. Nutrition During Pregnancy: Part I Weight Gain. Part II Nutrient Supplements; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, L.C.; Bishop, D.C.; Pang, R.; Ohuma, E.O.; Kac, G.; Abrams, B.; Rasmussen, K.; Barros, F.C.; Hirst, J.E.; Lambert, A.; et al. Gestational weight gain standards based on women enrolled in the Fetal Growth Longitudinal Study of the INTERGROWTH-21st Project: A prospective longitudinal cohort study. BMJ 2016, 352, i555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LifeCycle Project-Maternal Obesity and Childhood Outcomes Study Group; Voerman, E.; Santos, S.; Inskip, H.; Amiano, P.; Barros, H.; Charles, M.-A.; Chatzi, L.; Chrousos, G.P.; Corpeleijn, E.; et al. Association of Gestational Weight Gain with Adverse Maternal and Infant Outcomes. JAMA 2019, 321, 1702–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cinelli, G.; Fabrizi, M.; Ravà, L.; Degli Atti, M.C.; Vernocchi, P.; Vallone, C.; Pietrantoni, E.; Lanciotti, R.; Signore, F.; Manco, M. Influence of Maternal Obesity and Gestational Weight Gain on Maternal and Foetal Lipid Profile. Nutrients 2016, 8, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osterman, M.J.K.; Martin, J.A. Recent declines in induction of labor by gestational age. NCHS Data Brief 2014, 155, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- American Diabetes Association 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, S11–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups Consensus Panel; Metzger, B.E.; Gabbe, S.G.; Persson, B.; Buchanan, T.A.; Catalano, P.A.; Damm, P.; Dyer, A.R.; Leiva, A.; Hod, M.; et al. International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups Recommendations on the Diagnosis and Classification of Hyperglycemia in Pregnancy. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shindo, R.; Aoki, S.; Kasai, J.; Saigusa, Y.; Nakanishi, S.; Miyagi, E. Impact of introducing the International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups (IADPSG) criteria on pregnancy outcomes in Japan. Endocr. J. 2020, 67, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schechtman, E. Odds Ratio, Relative Risk, Absolute Risk Reduction, and the Number Needed to Treat—Which of These Should We Use? Value Health 2002, 5, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, C.; Li, J.; Leng, J.; Ma, R.; Yang, X. Lifestyle intervention can reduce the risk of gestational diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, A.L.M.; Cliver, S.P.; Tita, A.T.; Biggio, J.R.; Durst, J.K. Impact of Gestational Weight Gain on Perinatal Outcomes in Obese Women. Am. J. Perinatol. 2016, 33, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.-H.; Hsieh, T.-T. Pregestational body mass index, gestational weight gain, and risks for adverse pregnancy outcomes among Taiwanese women: A retrospective cohort study. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 55, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enomoto, K.; Aoki, S.; Toma, R.; Fujiwara, K.; Sakamaki, K.; Hirahara, F. Pregnancy Outcomes Based on Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index in Japanese Women. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominiarek, M.A.; Saade, G.; Mele, L.; Bailit, J.; Reddy, U.M.; Wapner, R.; Varner, M.W.; Thorp, J.M.; Caritis, S.N.; Prasad, M.; et al. Association Between Gestational Weight Gain and Perinatal Outcomes. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 132, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamor, E.; Cnattingius, S. Interpregnancy weight change and risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes: A population-based study. Lancet 2006, 368, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, E.; Kleinman, K.P.; Belfort, M.B.; Hammitt, J.K.; Gillman, M.W. Associations of Gestational Weight Gain With Short- and Longer-term Maternal and Child Health Outcomes. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 170, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crane, J.M.; White, J.; Murphy, P.; Burrage, L.; Hutchens, D. The effect of gestational weight gain by body mass index on maternal and neonatal outcomes. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Can. 2009, 31, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamor, E.; Cnattingius, S. Interpregnancy weight change and risk of preterm delivery. Obesity 2016, 24, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horton, T.J.; Drougas, H.; Brachey, A.; Reed, G.W.; Peters, J.C.; Hill, J.O. Fat and carbohydrate overfeeding in humans: Different effects on energy storage. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 62, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Catov, J.M.; Bodnar, L.M.; Kip, K.E.; Hubel, C.; Ness, R.B.; Harger, G.; Roberts, J.M. Early pregnancy lipid concentrations and spontaneous preterm birth. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 197, 610.e1–610.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackman, F.; Capewell, V.; Richardson, B.; daSilva, O.; Gagnon, R. The risks of spontaneous preterm delivery and perinatal mortality in relation to size at birth according to fetal versus neonatal growth standards. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2001, 184, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, S.; Tataranno, M.L.; Negro, S.; Longini, M.; Toti, M.S.; Alagna, M.G.; Proietti, F.; Bazzini, F.; Toti, P.; Buonocore, G. Placental histological examination and the relationship with oxidative stress in preterm infants. Placenta 2016, 46, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
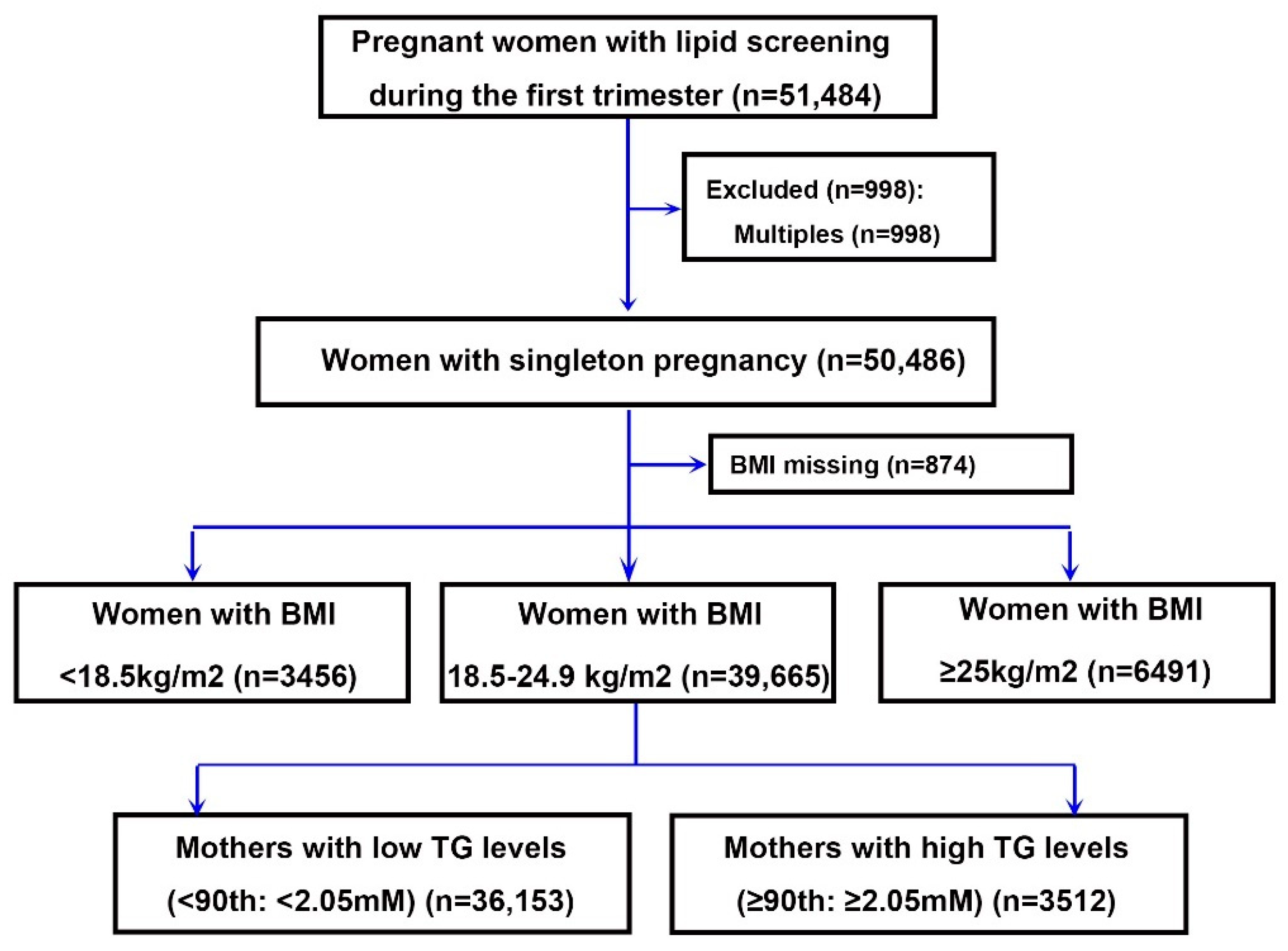
| Entire Population | Low mTG | High mTG | p Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 39,665 | n = 36,153 | n = 3512 | |||||
| Total gestational weight gain, median (q1 and q3), kg | 14.10 (11.10 and 17.10) | 14.10 (11.50 and 17.10) | 14.20 (11.3 and 17.5) | ||||
| Maternal TG level, median (q1 and q3), mM | 1.20 (0.95 and 1.55) | 1.15 (0.92 and 1.44) | 2.40 (2.20 and 2.76) | ||||
| Early pregnancy BMI a, median (q1 and q3), kg/m2 | 21.42 (20.16 and 22.80) | 21.34 (20.13 and 22.74) | 22.40 (20.79 and 23.40) | ||||
| Maternal age (yr), No. (%) | <0.001 | ||||||
| ≤24 | 1552 | (3.91) | 1480 | (4.09) | 72 | (2.05) | |
| 25–29 | 17,590 | (44.35) | 16,381 | (45.31) | 1209 | (34.42) | |
| 30–34 | 15,709 | (39.60) | 14,143 | (39.12) | 1566 | (44.59) | |
| ≥35 | 4814 | (12.14) | 4149 | (11.48) | 665 | (18.94) | |
| Height, No. (%) | <0.001 | ||||||
| ≤154 | 2048 | (5.16) | 1851 | (5.12) | 197 | (5.61) | |
| 155–164 | 24,695 | (62.26) | 22,395 | (61.95) | 2298 | (65.43) | |
| 165–174 | 12,462 | (31.42) | 11,483 | (31.76) | 981 | (27.93) | |
| ≥175 | 460 | (1.16) | 424 | (1.17) | 36 | (1.03) | |
| Education (years), No. (%) | <0.001 | ||||||
| ≤9 | 790 | (1.99) | 677 | (1.87) | 113 | (3.22) | |
| 10–12 | 2364 | (5.96) | 2117 | (5.86) | 247 | (7.03) | |
| 13–15 | 8439 | (21.28) | 7646 | (21.15) | 793 | (22.58) | |
| ≥16 | 27,538 | (69.43) | 25,229 | (69.78) | 2309 | (65.75) | |
| Missing | 534 | (1.35) | 484 | (1.34) | 50 | (1.42) | |
| Birth place, No. (%) | <0.001 | ||||||
| Residents | 29,690 | (74.85) | 27,243 | (75.35) | 2447 | (69.68) | |
| Immigrants | 9975 | (25.15) | 8910 | (24.65) | 1065 | (30.32) | |
| Parity, No. (%) | <0.001 | ||||||
| 1 | 32,614 | (82.22) | 29,998 | (82.98) | 2616 | (74.49) | |
| 2 | 6848 | (17.26) | 5988 | (16.56) | 860 | (24.49) | |
| ≥3 | 203 | (0.51) | 167 | (0.46) | 36 | (1.03) | |
| Ethnicity, No. (%) | <0.001 | ||||||
| Han Chinese | 39,080 | (98.53) | 35,635 | (98.57) | 3446 | (98.12) | |
| Other | 585 | (1.47) | 518 | (1.43) | 66 | (1.88) | |
| Entire Population | mTG 10–90th | mTG > 90th | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 39,665 | n = 36,153 | n = 3512 | ||||||
| Types of adverse outcomes, No. (%), AOR (95% CI) | ||||||||
| Gestational hypertension | 843 | (2.13) | 722 | (2.00) | 1.00 (ref) | 121 | (3.45) | 1.80 (.46, 2.24) |
| Preeclampsia | 933 | (2.35) | 809 | (2.24) | 1.00 (ref) | 124 | (3.53) | 1.70 (1.38, 2.11) |
| Gestational diabetes | 3719 | (9.38) | 3031 | (8.38) | 1.00 (ref) | 688 | (19.59) | 2.50 (2.26, 2.76) |
| Cesarean delivery | 17,438 | (43.96) | 15,647 | (43.28) | 1.00 (ref) | 1791 | (51.00) | 1.22 (1.13, 1.32) |
| Placental abruption | 25 | (0.06) | 22 | (0.06) | 1.00 (ref) | 3 | (0.09) | 1.64 (0.48, 5.58) |
| Placenta previa | 477 | (1.20) | 437 | (1.21) | 1.00 (ref) | 40 | (1.14) | 0.84 (0.59, 1.19) |
| Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy (ICP) | 443 | (1.12) | 412 | (1.14) | 1.00 (ref) | 31 | (0.88) | 0.67 (0.44, 1.03) |
| Postpartum hemorrhage | 540 | (1.36) | 473 | (1.31) | 1.00 (ref) | 67 | (1.91) | 1.50(1.14, 1.99) |
| Preterm birth | 1912 | (4.82) | 1681 | (4.65) | 1.00 (ref) | 231 | (6.58) | 1.42 (1.21, 1.66) |
| Small size for gestational age | 1604 | (4.04) | 1495 | (4.14) | 1.00 (ref) | 109 | (3.10) | 0.78 (0.63, 0.97) |
| Large size for gestational age | 3727 | (9.40) | 3271 | (9.05) | 1.00 (ref) | 456 | (12.98) | 1.49 (1.33, 1.68) |
| Birth weight | ||||||||
| Low birthweight (<2500 g) | 1050 | (2.65) | 762 | (2.11) | 1.00 (ref) | 101 | (2.88) | 1.10 (088, 1.39) |
| Macrosomia (>=4000 g) | 2123 | (5.35) | 1863 | (5.15) | 1.00 (ref) | 260 | (7.40) | 1.50 (1.29, 1.74) |
| NICU admission | 3675 | (9.27) | 3297 | (9.12) | 1.00 (ref) | 378 | (10.76) | 1.27 (1.13, 1.44) |
| Any adverse outcome | 22,637 | (57.07) | 20,255 | (56.03) | 1.00 (ref) | 2382 | (67.82) | 1.54 (1.42, 1.67) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, X.-F.; Wang, H.; Wu, D.-D.; Zhang, J.-L.; Gao, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.-X.; Huang, H.-F.; Wu, Y.-T.; et al. The Impact of Gestational Weight Gain on the Risks of Adverse Maternal and Infant Outcomes among Normal BMI Women with High Triglyceride Levels during Early Pregnancy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3454. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103454
Jiang X-F, Wang H, Wu D-D, Zhang J-L, Gao L, Chen L, Zhang J, Fan J-X, Huang H-F, Wu Y-T, et al. The Impact of Gestational Weight Gain on the Risks of Adverse Maternal and Infant Outcomes among Normal BMI Women with High Triglyceride Levels during Early Pregnancy. Nutrients. 2021; 13(10):3454. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103454
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Xia-Fei, Hui Wang, Dan-Dan Wu, Jian-Lin Zhang, Ling Gao, Lei Chen, Jian Zhang, Jian-Xia Fan, He-Feng Huang, Yan-Ting Wu, and et al. 2021. "The Impact of Gestational Weight Gain on the Risks of Adverse Maternal and Infant Outcomes among Normal BMI Women with High Triglyceride Levels during Early Pregnancy" Nutrients 13, no. 10: 3454. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103454
APA StyleJiang, X.-F., Wang, H., Wu, D.-D., Zhang, J.-L., Gao, L., Chen, L., Zhang, J., Fan, J.-X., Huang, H.-F., Wu, Y.-T., & Lin, X.-H. (2021). The Impact of Gestational Weight Gain on the Risks of Adverse Maternal and Infant Outcomes among Normal BMI Women with High Triglyceride Levels during Early Pregnancy. Nutrients, 13(10), 3454. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103454







