Platycodon grandiflorus Fermented Extracts Attenuate Endotoxin-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of PG extracts
2.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.3. Animals
2.4. An Acute Liver Injury Model and Sample Collection
2.5. Plasma Biochemical Assays
2.6. Cell Culture and Treatment
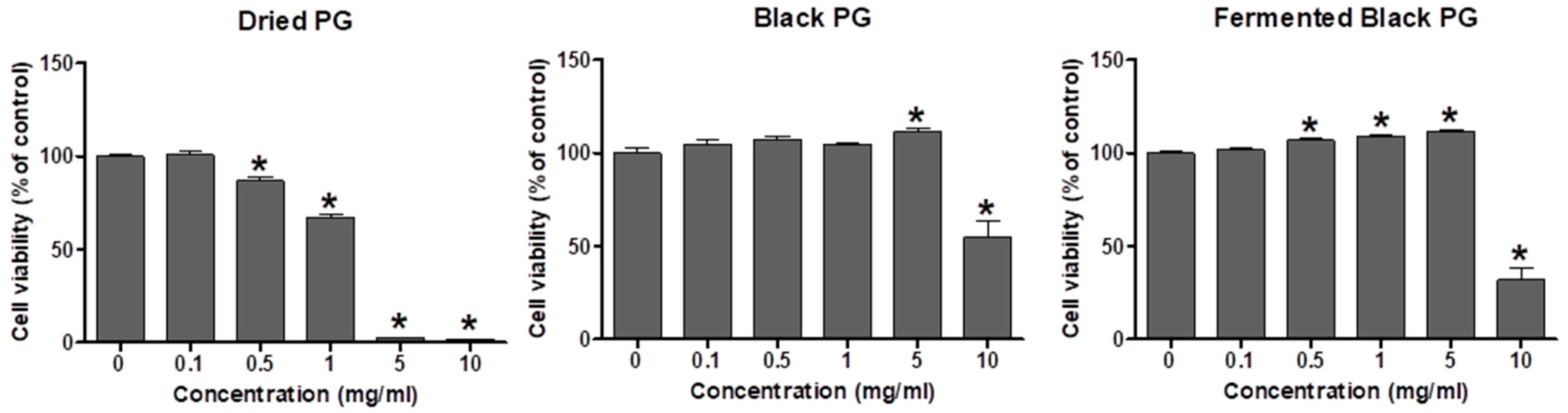
2.7. Cell Viability
2.8. Extracellular NO measurement
2.9. Histology and Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase dUTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. BPG and FBPG Extracts are Rich in Phenolic Acid, Flavonoid, and Triterpenoide Contents
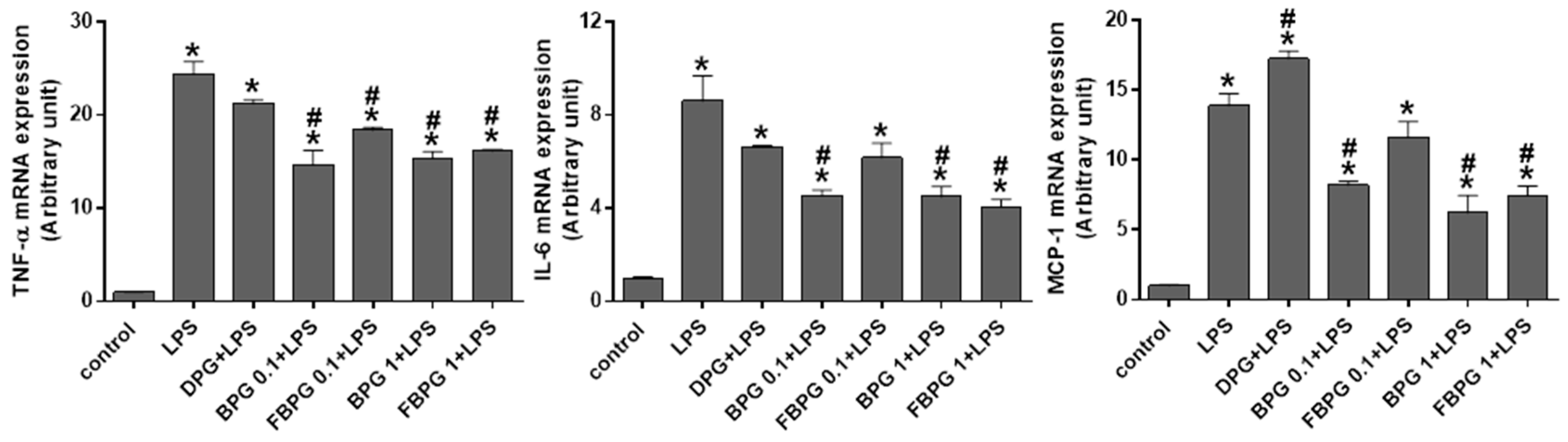
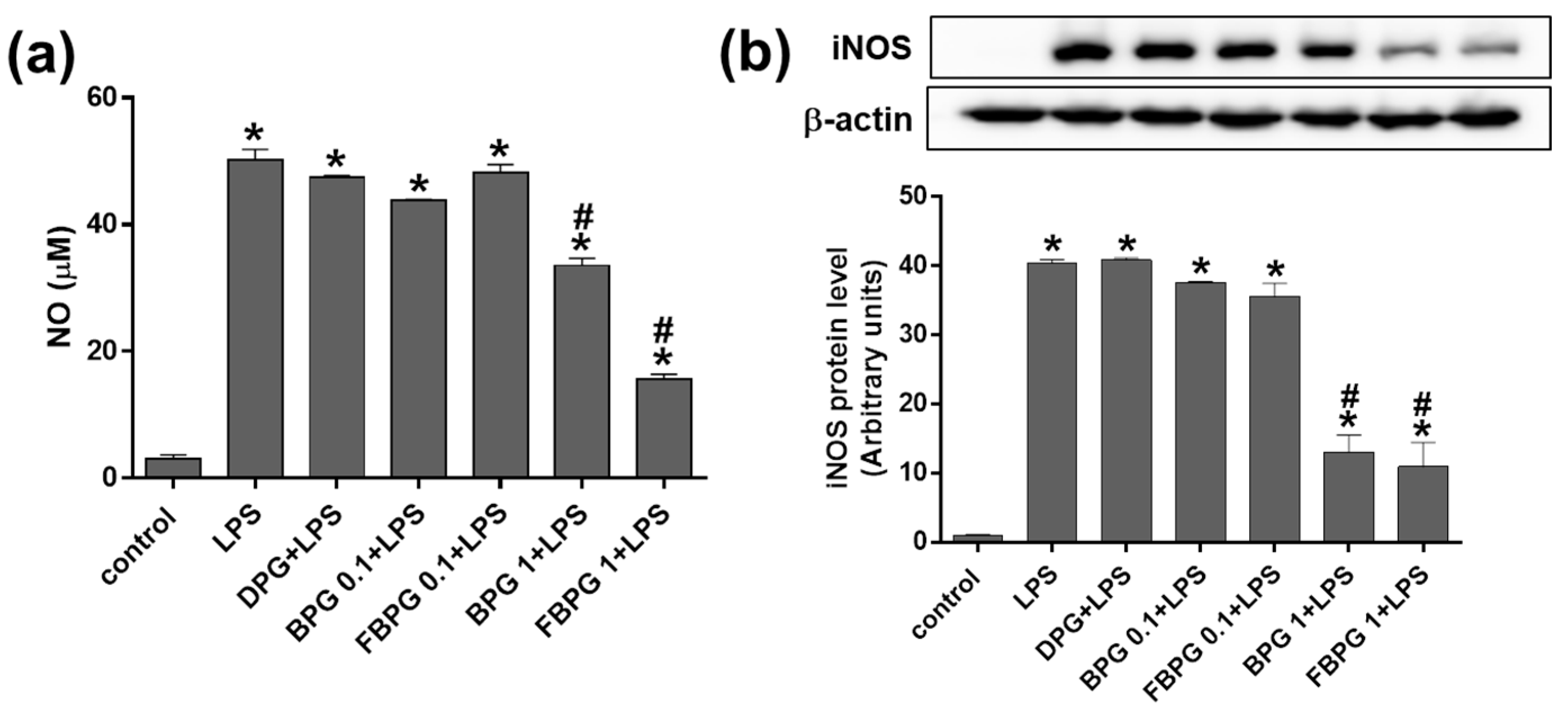
3.2. BPG and FBPG Extracts Reduces Inflammatory Cytokine and Nitric Oxide in Raw264.7 Cells
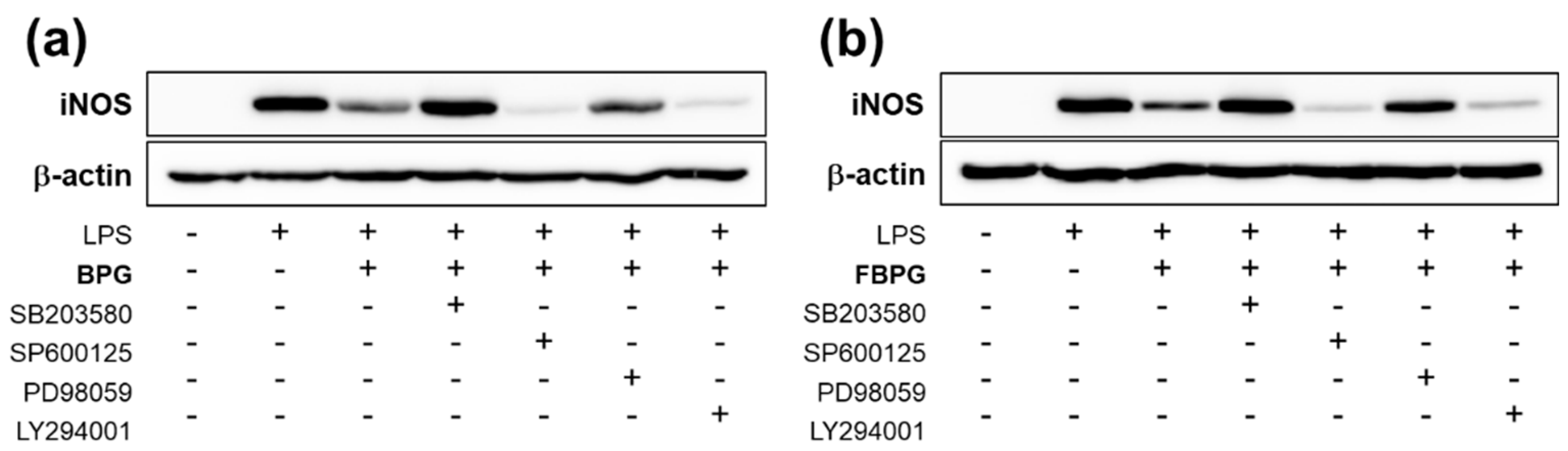
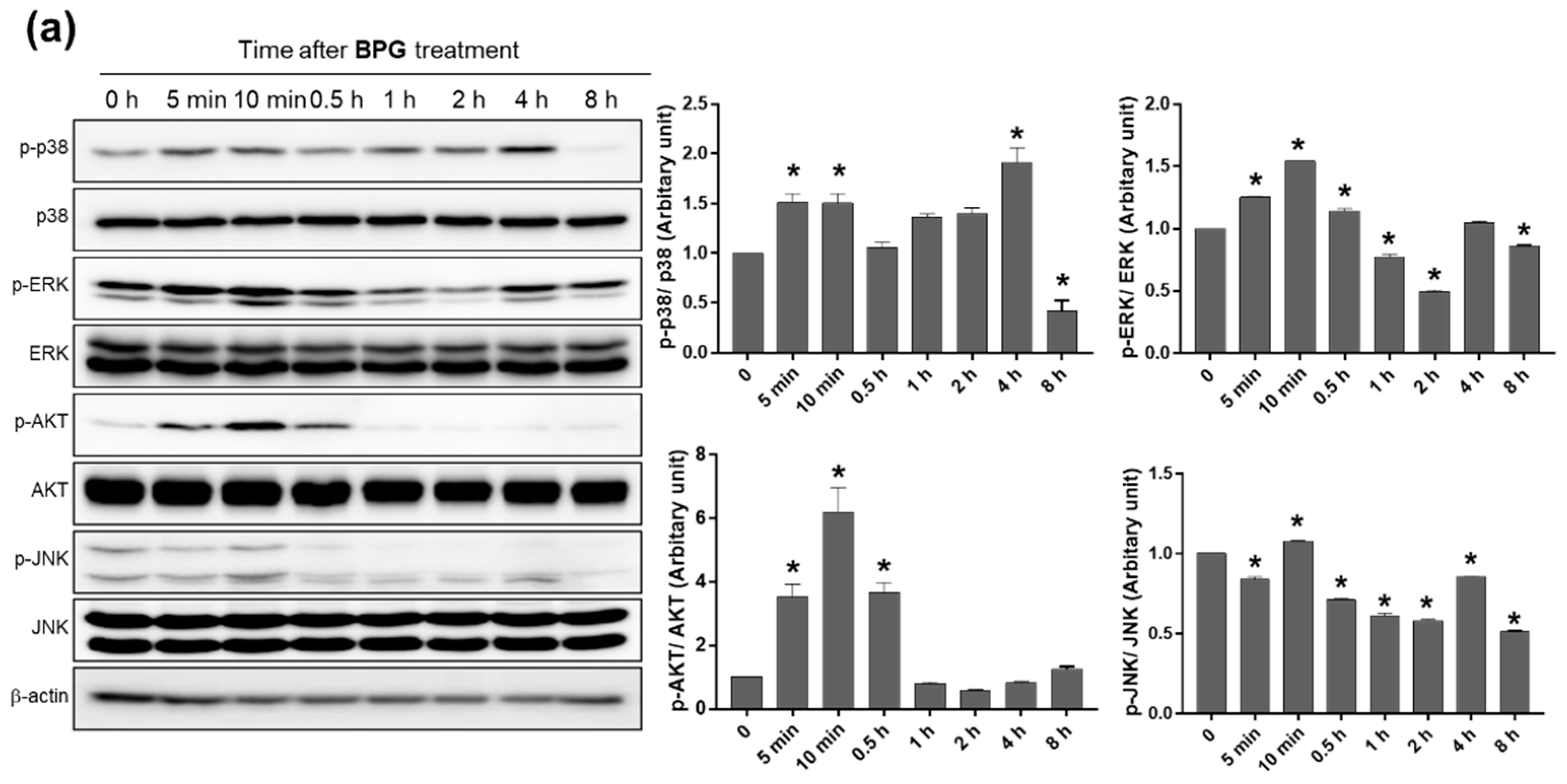
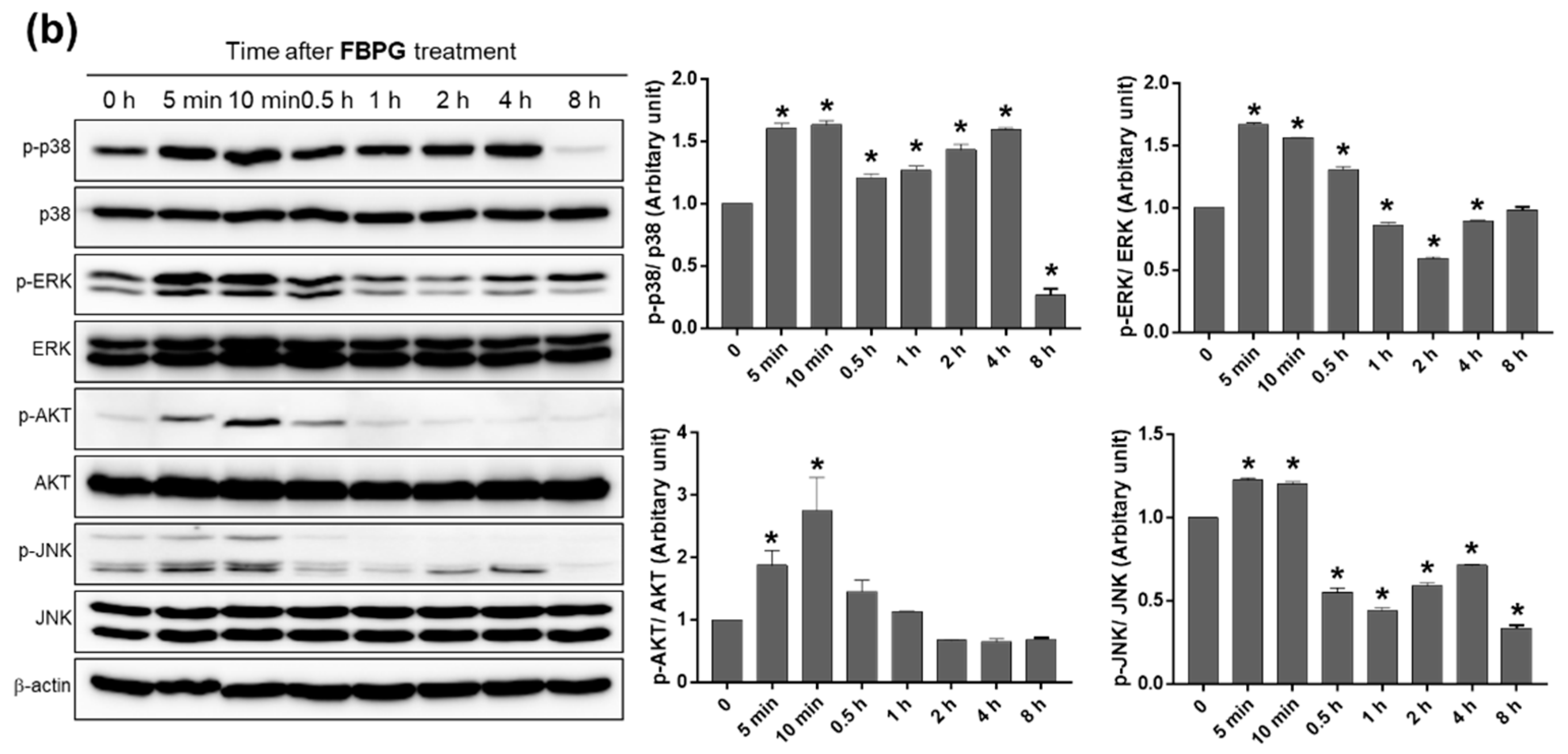
3.3. BPG and FBPG Extracts Reduces iNOS Expression through p38 and ERK Signaling Pathway in Raw264.7 Cells
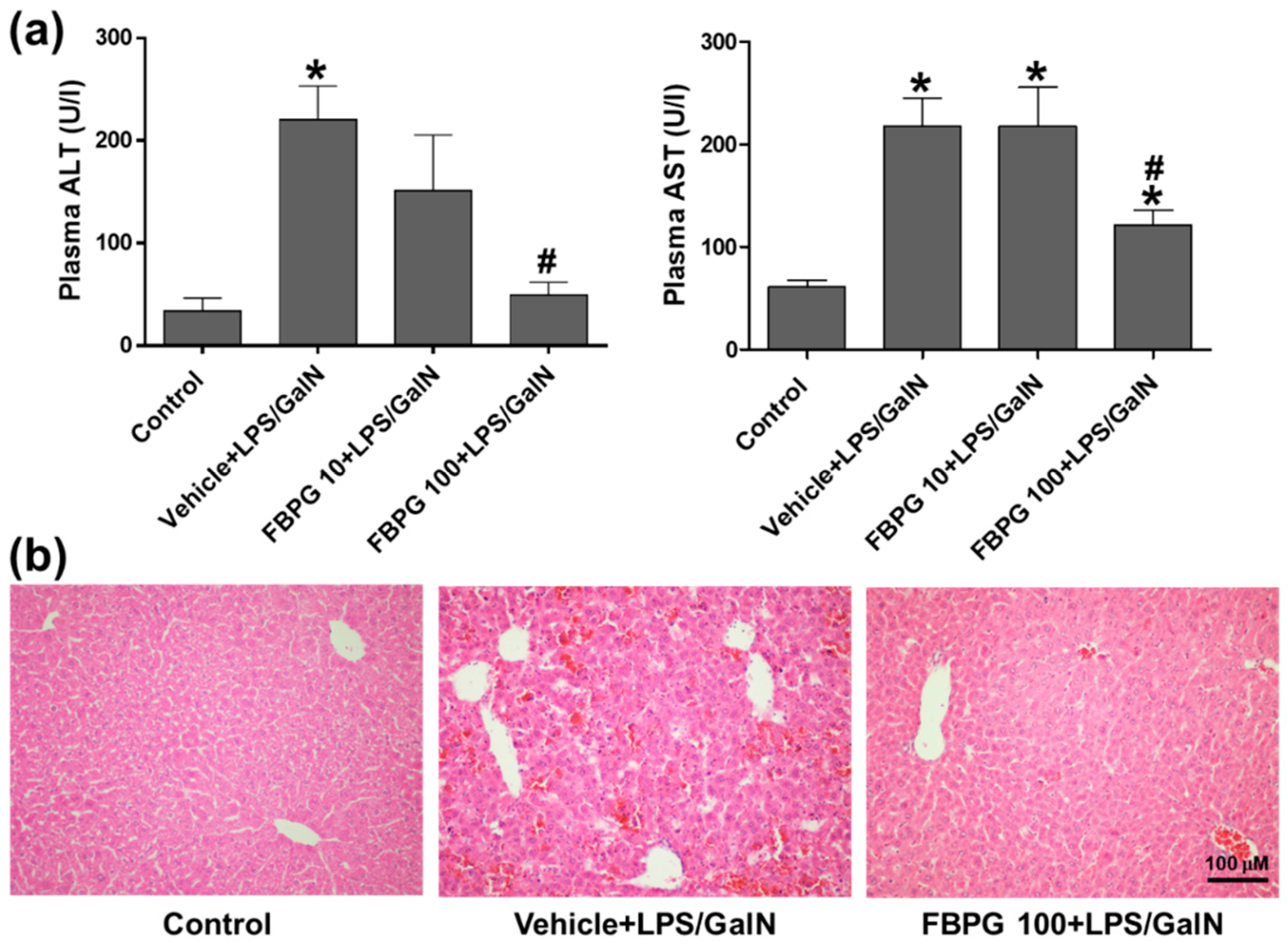
3.4. FBPG Extracts Reduces Hepatic Damage and Necrosis in an LPS/GalN-Induced Liver Injury
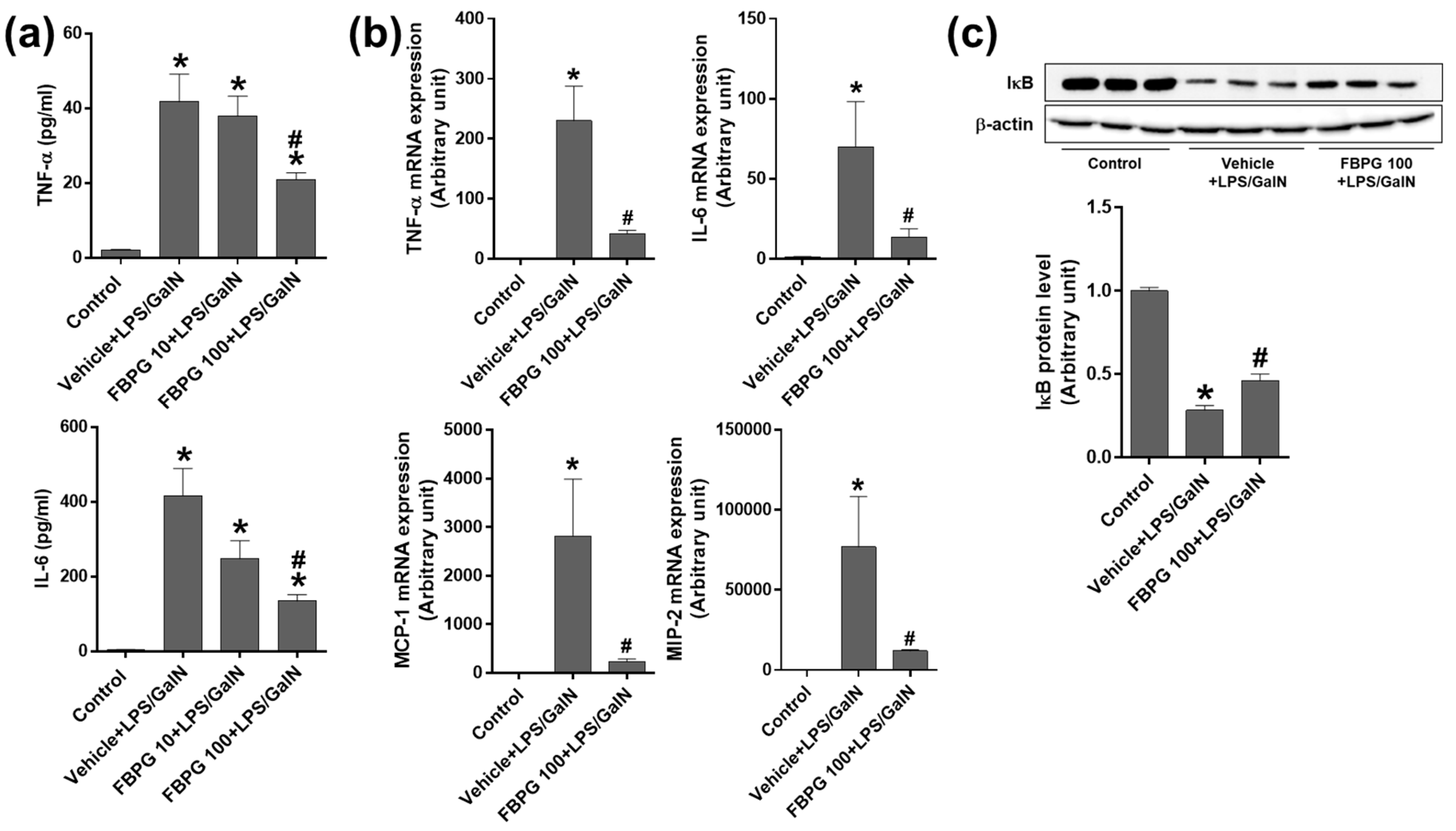
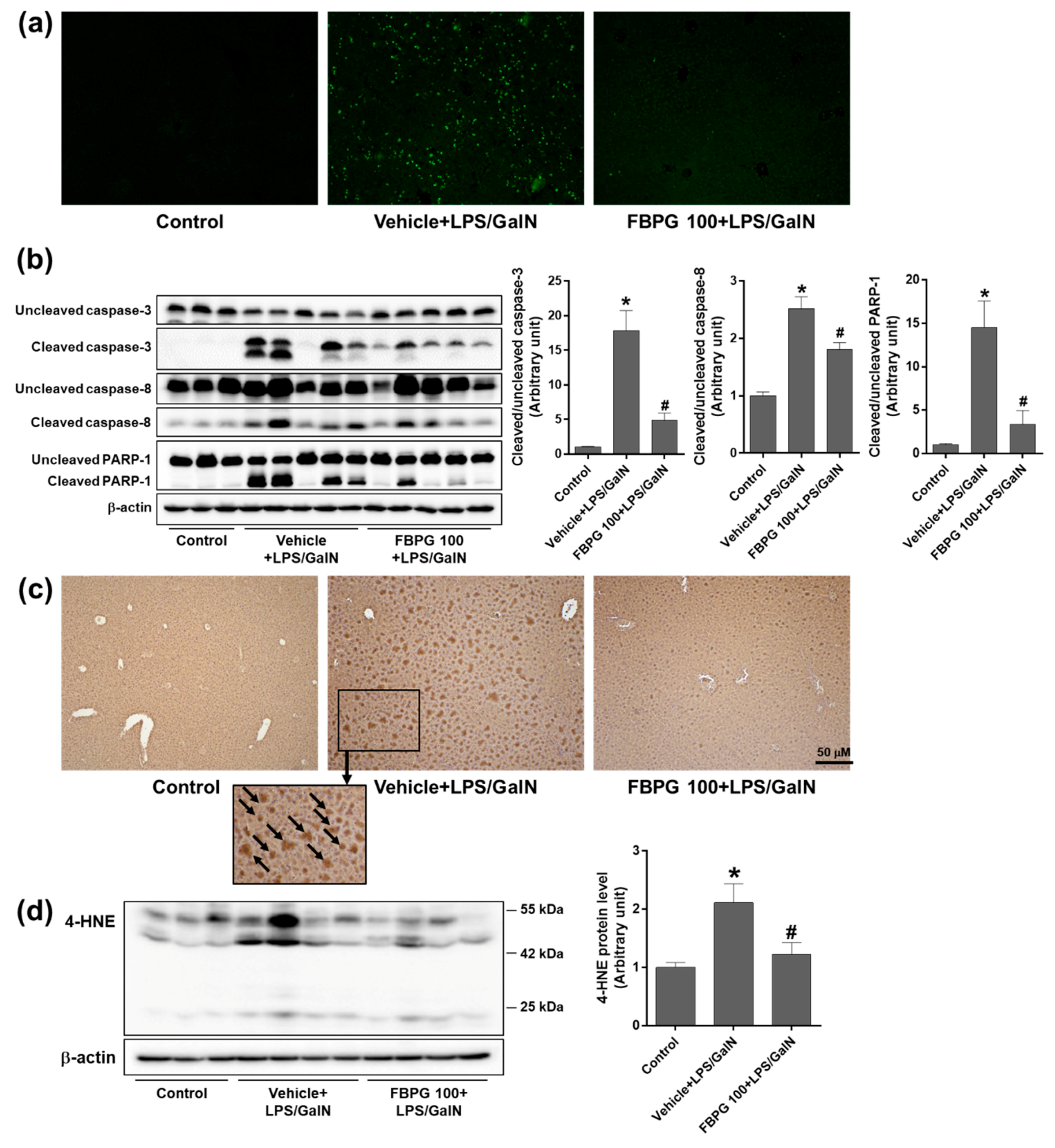
3.5. FBPG Extract Reduces Hepatic Inflammation, Apoptosis, and Lipid Peroxidation in an LPS/GalN-Induced Liver Injury
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jarrar, D.; Wang, P.; Chaudry, I.H. Hepatocellular dysfunction–basic considerations. In Surgical Treatment: Evidence-Based and Problem-Oriented; Holzheimer, R.G., Mannick, J.A., Eds.; Zuckschwerdt: Munich, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Li, S.; Li, S. The role of the liver in sepsis. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 33, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, V.; Nanchal, R.; Karvellas, C.J. Pathophysiology of acute liver failure. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2020, 35, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, W.; Wendon, J. Acute liver failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2525–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Vinken, M.; Jaeschke, H. Experimental models of hepatotoxicity related to acute liver failure. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 290, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagwandeen, S.; Apte, M.V.; Manwarring, L.; Dickeson, J. Endotoxin induced hepatic necrosis in rats on an alcohol diet. J. Pathol. 1987, 152, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broitman, S.A.; Gottlieb, L.S.; Zamcheck, N. Influence of neomycin and ingested endotoxin in the pathogenesis of choline deficiency cirrhosis in the adult rat. J. Exp. Med. 1964, 119, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, M.J.; Xu, J.; Ju, Y.; Alt, E.; Schmiedeberg, P. Lipopolysaccharide-neutralizing antibody reduces hepatocyte injury from acute hepatotoxin administration. Hepatology 1994, 19, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.L. Lipopolysaccharides in liver injury: Molecular mechanisms of Kupffer cell activation. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2002, 283, G256–G265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Shibazaki, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kai, K.; Sugawara, S.; Takada, H.; Kikuchi, H.; Kumagai, K. Enhancement by galactosamine of lipopolysaccharide(LPS)-induced tumour necrosis factor production and lethality: Its suppression by LPS pretreatment. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 128, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantel, H.; Schulze-Osthoff, K. Mechanisms of cell death in acute liver failure. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujral, J.S.; Hinson, J.A.; Farhood, A.; Jaeschke, H. NADPH oxidase-derived oxidant stress is critical for neutrophil cytotoxicity during endotoxemia. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2004, 287, G243–G252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeschke, H.; Ho, Y.-S.; Fisher, M.A.; Lawson, J.A.; Farhood, A. Glutathione peroxidase-deficient mice are more susceptible to neutrophil-mediated hepatic parenchymal cell injury during endotoxemia: Importance of an intracellular oxidant stress. Hepatology 1999, 29, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, M.Y.; Bo, A.; Yang, M.; Xu, J.F.; Jiang, L.L.; Zhou, B.C.; Li, M.H. The pharmacological effects and health benefits of platycodon grandiflorus—A medicine food homology species. Foods 2020, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyakudya, E.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, N.K.; Jeong, Y.S. Platycosides from the roots of platycodon grandiflorum and their health benefits. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 19, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, N.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Platycodon grandiflorus—An Ethnopharmacological, phytochemical and pharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 164, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.E.; Haque, A.; Lee, J.H.; Song, Y.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, S.C.; Cho, K.M. Bioconversion of γ-aminobutyric acid and isoflavone contents during the fermentation of high-protein soy powder yogurt with Lactobacillus brevis. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2018, 61, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, B.; Hwang, C.E.; Haque, A.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, C.S.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, K.M.; Lee, D.H. Changes in conjugated linoleic acid and isoflavone contents from fermented soymilks using Lactobacillus plantarum P1201 and screening for their digestive enzyme inhibition and antioxidant properties. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 43, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Xie, B.; Shi, H.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ren, F. Kaempferol protects mice from d-GalN/LPS-induced acute liver failure by regulating the ER stress-Grp78-CHOP signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ren, F.; Zhang, X.; Wen, T.; Shi, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Han, Y.; Duan, Z. Oxidative stress promotes D-GalN/LPS-induced acute hepatotoxicity by increasing glycogen synthase kinase 3β activity. Inflamm. Res. 2014, 63, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, J.; Gou, C.; Wen, T.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, D.; Lou, J.; Chen, D.; et al. Qingchangligan formula attenuates the inflammatory response to protect the liver from acute failure induced by d -galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 201, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, S.R.; Je, J.; Jeong, K.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.J.; Chang, K.C.; Park, S.W. The proximal tubular α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor attenuates ischemic acute kidney injury through Akt/PKC signaling-mediated HO-1 induction. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M.; Park, E.J.; Kim, H.J.; Chang, K.C. Sirt1 S-nitrosylation induces acetylation of HMGB1 in LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells and endotoxemic mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 501, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, H.J.; Chang, K.C. Luteolin activates ERK1/2- and Ca2+-dependent HO-1 induction that reduces LPS-induced HMGB1, iNOS/NO, and COX-2 expression in RAW264.7 cells and mitigates acute lung injury of endotoxin mice. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Liang, H.; Zen, K. Molecular mechanisms that influence the macrophage m1-m2 polarization balance. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, C.S.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Choung, K.J.; Song, G.Y.; Kim, B.H.; Ryu, S.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, S.K. Evaluation of the total oxidant scavenging capacity of saponins isolated from Platycodon grandiflorum. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakkar, S.; Bais, S. A review on protocatechuic acid and its pharmacological potential. ISRN Pharmacol. 2014, 2014, 952943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Goel, N. Phenolic acids: Natural versatile molecules with promising therapeutic applications. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 24, e00370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangl, V.; Dreger, H.; Lorenz, M. Molecular targets of tea polyphenols in the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 73, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Hwang, Y.P.; Lee, H.S.; Jeong, H.G. Inhibitory effect of Platycodi Radix on ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation in a murine model of asthma. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.Y.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, E.B.; Choi, E.Y.; Ko, K.H. Platycodin D and D3 increase airway mucin release in vivo and in vitro in rats and hamsters. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.S.; Noh, E.J.; Zhao, H.L.; Jung, S.H.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, S.K. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase II by Platycodon grandiflorum saponins via suppression of nuclear factor-κB activation in RAW 264.7 cells. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 2315–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, K.J.; Kim, H.K.; Han, M.H.; Na Oh, Y.; Yoon, H.M.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, B.W.; Choi, Y.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of saponins derived from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorus in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Kang, H.S.; Choi, B.T. An aqueous extract of Platycodi radix inhibits LPS-induced NF-kappaB nuclear translocation in human cultured airway epithelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2004, 13, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roux, P.P.; Blenis, J. ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: A family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 320–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.M.; Kwon, O.K.; Shin, I.S.; Jeon, C.M.; Shin, N.R.; Lee, D.K.; Park, S.H.; Bach, T.T.; Van Hai, D.; Oh, S.R.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of methanol extract of Canarium lyi C.D. Dai & Yakovlev in RAW 264.7 macrophages and a murine model of lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.H.; Cha, H.J.; Choi, E.O.; Leem, S.-H.; Kim, G.Y.; Moon, S.K.; Chang, Y.C.; Yun, S.J.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, B.W.; et al. Schisandrin A suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in RAW 264.7 macrophages by suppressing the NF-κB, MAPKs and PI3K/Akt pathways and activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 41, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.Q.C.; Binh, T.D.; Pham, T.L.A.; Nguyen, Y.D.H.; Đái Trang, T.X.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kanaori, K.; Kamei, K. Anti-inflammatory effects of lasia spinosa leaf extract in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichoz-Lach, H.; Michalak, A. Oxidative stress as a crucial factor in liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8082–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hong, M.; Tan, H.-Y.; Wang, N.; Feng, Y. Insights into the role and interdependence of oxidative stress and inflammation in liver diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4234061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, T.; Choi, J.H.; Hwang, Y.P.; Chung, Y.C.; Jeong, H.G. Saponins isolated from the root of Platycodon grandiflorum protect against acute ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K. Protective effect of saponins derived from roots of Platycodon grandiflorum on tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative hepatotoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 147, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-J.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, H.G.; Han, E.H.; Hwang, Y.P.; Lee, Y.C.; Chung, Y.C.; Jeong, H.G. Protective effect of saponins derived from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorum against carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1778–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, F.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Li, D. Synergistic anti-inflammatory effects of quercetin and catechin via inhibiting activation of TLR4-MyD88-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, T.; Liu, Q.; Ren, Y.F.; Li, H.; Xu, X.; Li, E.; Pan, S.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, K.X. Enhanced anti-inflammatory effects of DHA and quercetin in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 macrophages by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.N.; Shin, S.A.; Choo, G.S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, S.K.; Cho, S.D.; Nam, J.S.; Choi, C.S.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of quercetin and galangin in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages and DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis animal models. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, T.M.; Rayburn, K.S.; Holloway, S.W.; Sanchez-Yamamoto, D.S.; Allen, B.L.; Lam, T.; So, B.K.; Tran, D.H.; Greyber, E.R.; Kantor, S.; et al. Adverse interactions between herbal and dietary substances and prescription medications: A clinical survey. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2007, 13, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Gurib-Fakim, A. Medicinal plants: Traditions of yesterday and drugs of tomorrow. Mol. Asp. Med. 2006, 27, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kårlund, A.; Gómez-Gallego, C.; Korhonen, J.; Palo-Oja, O.M.; El-Nezami, H.; Kolehmainen, M. Harnessing microbes for sustainable development: Food fermentation as a tool for improving the nutritional quality of alternative protein sources. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H.; Gam, C.O.; Ku, S.K.; Choi, S.H. Single oral dose toxicity test of platycodin D, a saponin from platycodin radix in mice. Toxicol. Res. 2011, 27, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Contents 1 (mg/g d.w.) | DPG | BPG | FBPG |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gallic acid | 6.10 | ND | ND |
| Protocatechuic acid | 11.57 | 133.57 | 126.71 |
| Chlorgenic acid | 38.26 | 235.66 | 244.51 |
| p-Hydrobenzoic acid | 14.80 | 61.25 | 57.72 |
| Vanillic acid | ND | 11.10 | 12.44 |
| p-Coumaric acid | 1.09 | ND | ND |
| Ferulic acid | 5.88 | ND | ND |
| Vertaric acid | 9.26 | ND | 17.10 |
| t-Cinnamic acid | 0.73 | 0.79 | 0.86 |
| Total | 87.69 | 442.37 | 459.34 |
| Contents 1 (mg/g d.w.) | DPG | BPG | FBPG |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epigallocatechin | 160.67 | 323.83 | 397.05 |
| Catechin | 15.22 | 57.84 | 43.23 |
| Epicatechin | 20.90 | 130.39 | 146.25 |
| Epigallocatechin gallate | 5.39 | 58.24 | ND |
| Vanillin | ND | 1.23 | ND |
| Rutin | 9.86 | ND | ND |
| Catechin gallate | 8.23 | ND | ND |
| Quercetin | 130.32 | 320.11 | 345.23 |
| Naringin | ND | 25.14 | 29.24 |
| Naringenin | 8.92 | 14.86 | 6.61 |
| Formonoetin | 3.82 | 3.45 | 3.61 |
| Total | 363.33 | 935.09 | 971.22 |
| Contents 1 (mg/g d.w.) | DPG | BPG | FBPG |
|---|---|---|---|
| Platycodin D3 | ND | 1.67 | 0.87 |
| Deapioplatycodin D | 0.18 | 0.77 | 0.50 |
| Polygalcin D | ND | 0.27 | 0.19 |
| Total | 0.18 | 2.71 | 1.56 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.R.; Park, E.J.; Dusabimana, T.; Je, J.; Jeong, K.; Yun, S.P.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, K.M.; Kim, H.; Park, S.W. Platycodon grandiflorus Fermented Extracts Attenuate Endotoxin-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092802
Kim SR, Park EJ, Dusabimana T, Je J, Jeong K, Yun SP, Kim HJ, Cho KM, Kim H, Park SW. Platycodon grandiflorus Fermented Extracts Attenuate Endotoxin-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice. Nutrients. 2020; 12(9):2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092802
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, So Ra, Eun Jung Park, Theodomir Dusabimana, Jihyun Je, Kyuho Jeong, Seung Pil Yun, Hye Jung Kim, Kye Man Cho, Hwajin Kim, and Sang Won Park. 2020. "Platycodon grandiflorus Fermented Extracts Attenuate Endotoxin-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice" Nutrients 12, no. 9: 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092802
APA StyleKim, S. R., Park, E. J., Dusabimana, T., Je, J., Jeong, K., Yun, S. P., Kim, H. J., Cho, K. M., Kim, H., & Park, S. W. (2020). Platycodon grandiflorus Fermented Extracts Attenuate Endotoxin-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice. Nutrients, 12(9), 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092802








