Effectiveness of Community-Based Interventions Programs in Childhood Obesity Prevention in a Spanish Population According to Different Socioeconomic School Settings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Protocol
2.2. Statistical Analysis
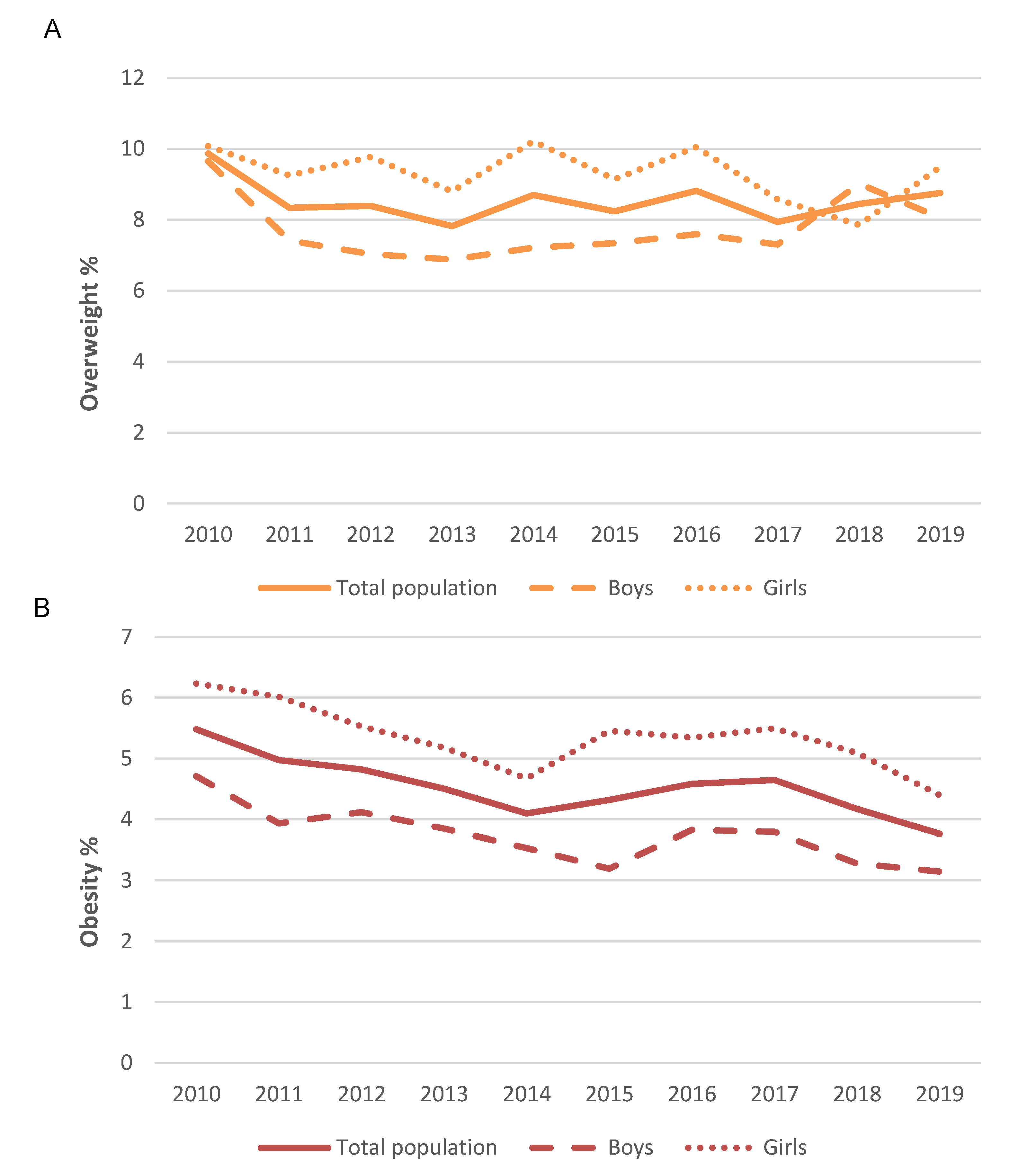
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, J.; Lawlor, D.; Kimm, S. Childhood obesity. Lancet 2010, 375, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Health Risks: Mortality and Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risks; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 21 May 2020).
- Ministerio de Sanidad, Consumo y Bienestar Social. Encuesta Nacional de Salud de España 2017. Available online: https://www.mscbs.gob.es/estadEstudios/estadisticas/encuestaNacional/encuesta2017.htm (accessed on 21 May 2020).
- Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Gil, Á.; González-Gross, M.; Ortega, R.M.; Serra-Majem, L.; Varela-Moreiras, G.; Aranceta-Bartrina, J. Clustering of Dietary Patterns. Lifestyles. and Overweight among Spanish Children and Adolescents in the ANIBES Study. Nutrients 2016, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranceta-Bartrina, J.; Gianzo-Citores, M.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C. Prevalence of overweight, obesity and abdominal obesity in the Spanish population aged 3 to 24 years. The ENPE study. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2020, 73, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, M. Childhood obesity: A life-long health risk. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulgaron, E.R.; Delamater, A.M. Obesity and type 2 diabetes in children: Epidemiology and treatment. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2014, 14, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umer, A.; Kelley, G.A.; Cottrell, L.E.; Giacobbi, P., Jr.; Innes, K.E.; Lilly, C.L. Childhood obesity and adult cardiovascular disease risk factors: A systematic review with meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Yoon, K.H. Epidemic obesity in children and adolescents: Risk factors and prevention. Front. Med. 2018, 12, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttitta, M.; Iliescu, C.; Rousseau, A.; Guerrien, A. Quality of Life in Overweight and Obese Children and Adolescents: A Literature Review. Qual. Life Res. 2014, 23, 1117–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameli, C.; Mazzantini, S.; Zuccotti, G.V. Nutrition in the First 1000 Days: The Origin of Childhood Obesity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laja García, A.I.; Moráis-Moreno, C.; Samaniego-Vaesken, M.L.; Puga, A.M.; Partearroyo, T.; Varela-Moreiras, G. Influence of Water Intake and Balance on Body Composition in Healthy Young Adults from Spain. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laja García, A.I.; Moráis-Moreno, C.; Samaniego-Vaesken, M.L.; Puga, A.M.; Varela-Moreiras, G.; Partearroyo, T. Association between Hydration Status and Body Composition in Healthy Adolescents from Spain. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indiani, C.M.D.S.P.; Rizzardi, K.F.; Castelo, P.M.; Ferraz, L.F.C.; Darrieux, M.; Parisotto, T.M. Childhood Obesity and Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in the Gut Microbiota: A Systematic Review. Child. Obes. 2018, 14, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, A.; Backholer, K.; Wong, E.; Palermo, C.; Keating, C.; Peeters, A. Trends in child and adolescent obesity prevalence in economically advanced countries according to socioeconomic position: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 276–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokholm, B.; Baker, J.L.; Sørensen, T.I.A. The Levelling Off of the Obesity Epidemic Since the Year 1999—A Review of Evidence and Perspectives. Obes. Rev. 2010, 11, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnowski, A. The economics of food choice behavior: Why poverty and obesity are linked. Nestle Nutr. Inst. Workshop Ser. 2012, 73, 95–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, D.L.; O’Connell, M.; Njike, V.Y.; Yeh, M.C.; Nawaz, H. Strategies for the prevention and control of obesity in the school setting: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobstein, T.; Jackson-Leach, R.; Moodie, M.L.; Hall, K.D.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Swinburn, B.A.; James, W.P.T.; Wang, Y.; McPherson, K. Child and adolescent obesity: Part of a bigger picture. Lancet 2015, 285, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Health Promoting Schools: A Healthy Setting for Living, Learning, Working; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Romon, M.; Lommez, A.; Tafflet, M.; Basdevant, A.; Oppert, J.M.; Bresson, J.L.; Ducimetière, P.; Charles, M.A.; Borys, J.M. Downward trends in the prevalence of childhood overweight in the setting of 12-year school- and community-based programmes. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, S.F.; Casas Esteve, R.; Subirana, I.; Serra-Majem, L.; Fletas Torrent, M.; Homs, C.; Ahmed Bawaked, R.; Estrada, L.; Fíto, M.; Schröder, H. Effect of a community-based childhood obesity intervention program on changes in anthropometric variables, incidence of obesity, and lifestyle choices in Spanish children aged 8 to 10 years. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2018, 177, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Santos, S.F.; Estévez Santiago, R.; Palacios Gil-Antuñano, N.; Leis Trabazo, M.R.; Tojo Sierra, R.; Cuadrado Vives, C.; Beltrán de Miguel, B.; Ávila Torres, J.M.; Varela Moreiras, G.; Casas Esteve, R. Thao-Child Health Programme: Community based intervention for healthy lifestyles promotion to children and families: Results of a cohort study. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 32, 2584–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfell-Jones, M.J.; Stewart, A.D.; De Ridder, J.H. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment (ISAK); International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry: Wellington, New Zealand, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, T.; Lowe, C.R. Indices of obesity derived from body weight and height. Br. J. Prev. Soc. Med. 1967, 21, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, T.J.; Lobstein, T. Extended international (IOTF) body mass index cut-offs for thinness, overweight and obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2012, 7, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, C.; Lorenzo, H.; Vrotsou, K.; Aresti, U.; Rica, I.; Sánchez, E. Estudio de Crecimiento de Bilbao, Curvas y Tablas de Crecimiento, Estudio Transversal; Fundación Faustino Orbegozo: Bilbao, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bleich, S.N.; Segal, J.; Wu, Y.; Wilson, R.; Wang, Y. Systematic Review of Community-Based Childhood Obesity Prevention Studies. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e201–e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolland-Cachera, M.F. Childhood obesity: Current definitions and recommendations for their use. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2011, 6, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Casanova, I.; Sarmiento, O.L.; Gazmararian, J.A.; Cunningham, S.A.; Martorell, R.; Pratt, M.; Stein, A.D. Comparing three body mass index classification systems to assess overweight and obesity in children and adolescents. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 2013, 33, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, E.; Carrillo, R.; Roman, E.M.; Bejarano, I.F.; Dipierri, J.E. Prevalence of overweight and obesity in students from different altitudinal zones of Jujuy according to three international references (IOTF, CDC and WHO). Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2013, 111, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.; Eagle, T.F.; Sheetz, A.; Woodward, A.; Leibowitz, R.; Song, M.; Sylvester, R.; Corriveau, N.; Kline-Rogers, E.; Jiang, Q.; et al. The Relationship between Childhood Obesity, Low Socioeconomic Status, and Race/Ethnicity: Lessons from Massachusetts. Child. Obes. 2015, 11, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A. Race, Socioeconomic Status, and Health during Childhood: A Longitudinal Examination of Racial/Ethnic Differences in Parental Socioeconomic Timing and Child Obesity Risk. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piovesan, C.; Pádua, M.C.; Ardenghi, T.M.; Mendes, F.M.; Bonini, G.C. Can type of school be used as an alternative indicator of socioeconomic status in dental caries studies? A cross-sectional study. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2011, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, R.M.; McNaughton, S.A.; Timperio, A. The clustering of diet, physical activity and sedentary behavior in children and adolescents: A review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2014, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone-Heinonen, J.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Adair, L.S. Obesogenic clusters: Multidimensional adolescent obesity-related behaviors in the U. S. Ann. Behav. Med. 2008, 36, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kim, J.; Colabianchi, N.; Ortaglia, A.; Pate, R.R. Co-varying patterns of physical activity and sedentary behaviors and their long-term maintenance among adolescents. J. Phys. Act. Health 2010, 7, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puolakka, E.; Pahkala, K.; Laitinen, T.T.; Magnussen, C.G.; Hutri-Kähönen, N.; Männistö, S.; Pälve, K.S.; Tammelin, T.; Tossavainen, P.; Jokinen, E.; et al. Childhood socioeconomic status and lifetime health behaviors: The Young Finns Study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 258, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.S.; Ge, B.; Petroski, G.; Kruse, R.L.; McElroy, J.A.; Koopman, R.J. Socioeconomic Status and Other Factors Associated with Childhood Obesity. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2018, 31, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Year 2010 | Total Population (n) | 2717 |
|---|---|---|
| Boys (n) | 1337 | |
| Girls (n) | 1380 | |
| Year 2011 | Total Population (n) | 2593 |
| Boys (n) | 1296 | |
| Girls (n) | 1297 | |
| Year 2012 | Total Population (n) | 2801 |
| Boys (n) | 1408 | |
| Girls (n) | 1393 | |
| Year 2013 | Total Population (n) | 2864 |
| Boys (n) | 1455 | |
| Girls (n) | 1409 | |
| Year 2014 | Total Population (n) | 2806 |
| Boys (n) | 1415 | |
| Girls (n) | 1391 | |
| Year 2015 | Total Population (n) | 2733 |
| Boys (n) | 1377 | |
| Girls (n) | 1356 | |
| Year 2016 | Total Population (n) | 2813 |
| Boys (n) | 1410 | |
| Girls (n) | 1403 | |
| Year 2017 | Total Population (n) | 2797 |
| Boys (n) | 1397 | |
| Girls (n) | 1400 | |
| Year 2018 | Total Population (n) | 2878 |
| Boys (n) | 1464 | |
| Girls (n) | 1414 | |
| Year 2019 | Total Population (n) | 2684 |
| Boys (n) | 1366 | |
| Girls (n) | 1318 |
| Baseline | After 9 Years | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | n | Waist Circumference (cm) | Weight (kg) | Height (cm) | BMI (kg/m2) | BMI Z-Score (kg/m2) | Age (year) | n | Waist Circumference (cm) | Weight (kg) | Height (cm) | BMI (kg/m2) | BMI Z-Score (kg/m2) |
| 3 | 52 | 51.7 | 15.8 | 97.4 | 16.4 | 0.1 | 3 | 42 | 50.6 | 15.6 | 97.8 | 16.2 | 0.0 |
| (49.0–54.0) | (14.5–17.5) | (95.7–100.7) | (15.7–17.4) | (−0.4–0.7) | (48.4–53.1) | (13.9–17.7) | (94.3–101.0) | (15.7–17.4) | (−0.3–0.8) | ||||
| 4 | 144 | 51.8 | 17.3 | 102.4 | 16.4 | 0.2 | 4 | 104 | 51.2 | 17.1 | 103.1 | 16.3 | 0.1 |
| (50.0−54.0) | (16.0−18.7) | (100.3–106.6) | (15.6–16.9) | (−0.3–0.5) | (49.9–53.0) | (15.8–18.2) | (99.7–105.9) | (15.4–16.9) | (−0.4–0.5) | ||||
| 5 | 163 | 53.3 | 19.1 | 109.5 | 16.2 | 0.1 | 5 | 100 | 52.7 | 19.1 | 109.7 | 15.9 | 0.0 |
| (51.0–56.0) | (17.9–21.2) | (107.0–113.0) | (15.7–17.0) | (−0.5–0.6) | (50.6–54.5) | (17.8–20.8) | (107.0–113.0) | (15.0–16.7) | (−0.5–0.4) | ||||
| 6 | 162 | 55.0 | 22.2 | 116.3 | 16.4 | 0.2 | 6 | 107 | 53.8 ** | 21.3 | 115.8 | 15.8 ** | −0.1 ** |
| (53.0–59.0) | (20.2–24.6) | (112.5–119.5) | (15.4–17.4) | (−0.3–0.7) | (51.55–57.0) | (19.4–23.9) | (112.9–119.8) | (15.1–16.7) | (−0.4–0.4) | ||||
| 7 | 150 | 57.0 | 24.8 | 123.0 | 16.5 | 0.0 | 7 | 185 | 55.5 * | 23.8 * | 121.5 | 16.0 * | −0.2 * |
| (54.2–60.2) | (22.8–26.8) | (119.7–125.6) | (15.3–17.7) | (−0.4–0.6) | (53.5–58.1) | (22.1–26.3) | (118.7–125.8) | (15.1–17.2) | (−0.6–0.4) | ||||
| 8 | 162 | 58.4 | 27.4 | 129.2 | 16.4 | −0.1 | 8 | 181 | 57.7 | 27.1 | 128.6 | 16.4 | −0.2 |
| (55.7–63.0) | (24.8–31.1) | (125.8–132.2) | (15.4–18.0) | (−0.6–0.6) | (55.0–61.7) | (24.7–30.5) | (125.6–132.2) | (15.4–17.7) | (−0.6–0.4) | ||||
| 9 | 156 | 61.0 | 30.1 | 133.1 | 17.0 | −0.1 | 9 | 176 | 60.5 | 30.6 | 133.9 | 16.8 | −0.2 |
| (58.0–65.7) | (27.4–34.2) | (129.6–137.4) | (15.9–18.8) | (−0.6–0.5) | (57.0–64.1) | (27.2–34.0) | (130.1–137.7) | (15.5–18.9) | (−0.6–0.6) | ||||
| 10 | 149 | 63.0 | 33.6 | 139.0 | 17.6 | −0.2 | 10 | 173 | 62.0 | 33.1 | 139.2 | 17.1 | −0.3 |
| (59.7–69.9) | (30.4–39.4) | (134.3–142.5) | (16.1–20.0) | (−0.7–0.5) | (58.5–70.0) | (30.0–37.8) | (135.7–143.4) | (16.1–18.7) | (−0.7–0.1) | ||||
| 11 | 116 | 66.3 | 37.9 | 145.3 | 18.5 | −0.2 | 11 | 183 | 64.9 | 37.0 | 144.7 | 17.7 | −0.4 |
| (62.3–72.0) | (33.6–44.5) | (141.4–148.8) | (16.5–20.5) | (−0.7–0.5) | (60.5–71.5) | (33.6–42.4) | (140.2–148.4) | (16.1–19.9) | (−0.8–0.3) | ||||
| 12 | 83 | 70.2 | 43.9 | 148.2 | 19.5 | −0.2 | 12 | 115 | 66.0 * | 42.4 | 149.2 | 18.2 * | −0.3 * |
| (65.0–77.5) | (37.4–50.8) | (144.0–153.5) | (17.6–21.8) | (−0.6–0.5) | (62.1–72.5) | (36.1–47.8) | (147.0–155.1) | (16.7–20.6) | (−0.8–0.3) | ||||
| Baseline | After 9 Years | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | n | Waist Circumference (cm) | Weight (kg) | Height (cm) | BMI (kg/m2) | BMI Z−Score (kg/m2) | Age (year) | n | Waist Circumference (cm) | Weight (kg) | Height (cm) | BMI (kg/m2) | BMI Z−Score (kg/m2) |
| 3 | 55 | 51.0 | 15.4 | 96.4 | 16.6 | 0.6 (−0.1–1.2) | 3 | 33 | 49.0 | 14.9 | 95.7 | 15.9 | 0.1 |
| (48.5–54.0) | (13.8–17.1) | (93.4–99.2) | (15.7–17.4) | (47.2–53.2) | (13.2–16.4) | (93.8–99.1) | (15.1–17.0) | (−0.6–0.9) | |||||
| 4 | 147 | 52.5 | 16.8 | 102.1 | 16.2 | 0.4 (−0.3–0.9) | 4 | 105 | 50.5 ** | 16.4 | 101.6 | 15.6 ** | 0.0 ** |
| (50.0–54.5) | (15.6–18.4) | (98.8–105.1) | (15.4–17.0) | (48.2–53.2) | (15.1–18.1) | (99.4–104.1) | (14.9–16.8) | (−0.5–0.7) | |||||
| 5 | 149 | 53.0 | 18.5 | 108.1 | 15.9 | 0.1 (−0.3–0.7) | 5 | 117 | 52.5 | 18.6 | 107.9 | 15.8 | 0.1 |
| (51.0–55.3) | (17.2–20.4) | (104.9–111.2) | (15.2–16.9) | (50.0–55.5) | (16.8–20.6) | (104.7–112.5) | (15.0–16.8) | (−0.4–0.7) | |||||
| 6 | 167 | 55.0 | 21.4 | 115.4 | 16.0 | 0.1 (−0.3–0.6) | 6 | 122 | 53.7 * | 20.8 | 114.1 | 15.8 | −0.1 |
| (52.2–57.9) | (19.3–23.3) | (111.7–118.3) | (15.3–16.9) | (51.5–56.6) | (18.8–22.8) | (111.6–118.1) | (15.1–16.7) | (−0.4–0.5) | |||||
| 7 | 160 | 57.2 | 24.9 | 122.2 | 16.7 | 0.2 (−0.4–0.9) | 7 | 136 | 55.8 | 24.2 | 122.0 | 16.1 * | −0.1 |
| (53.9–62.0) | (22.3–27.6) | (118.9–125.0) | (15.2–18.2) | (53.4–59.1) | (21.8–26.9) | (118.2–126.4) | (15.2–17.4) | (−0.4–0.6) | |||||
| 8 | 165 | 59.0 | 27.4 | 128.0 | 16.7 | 0.1 (−0.4–0.6) | 8 | 168 | 57.2 | 26.5 | 128.8 | 16.5 | −0.2 |
| (56.0–64.0) | (24.8–30.9) | (124.3–131.5) | (15.8–18.2 | (54.4–63.4) | (24.5–30.8) | (124.6–131.7) | (15.3–18.4 | (−0.6–0.5) | |||||
| 9 | 169 | 61.0 | 30.0 | 132.8 | 17.0 | −0.2 (−0.5–0.5) | 9 | 193 | 59.0 * | 29.5 | 133.5 | 16.8 | −0.2 |
| (57.7–65.4) | (26.9–37.0) | (129.6–136.7) | (15.8 –18.7) | (56.1–64.2) | (26.9–34.6) | (129.4–137.3) | (15.6 –18.5) | (−0.7–0.3) | |||||
| 10 | 149 | 64.8 | 33.3 | 137.2 | 17.8 | −0.1 (−0.7–0.8) | 10 | 149 | 60.6 * | 32.5 | 138.4 | 17.1 | −0.3 |
| (58.1–71.0) | (29.5–39.3) | (133.1–141.6) | (15.8–20.4) | (57.1–67.0) | (29.8–38.5) | (134.5–143.1) | (15.9–19.2) | (−0.6–0.4) | |||||
| 11 | 135 | 64.0 | 37.0 | 145.0 | 17.9 | −0.2 (−0.8–0.4) | 11 | 156 | 61.6 * | 36.4 | 143.8 | 17.4 | −0.4 |
| (61.0–70.9) | (33.9–43.7) | (140.5–149.2) | (16.2–19.9) | (58.2–67.8) | (32.4–43.1) | (139.3–150.0) | (15.9–19.5) | (−0.9–0.2) | |||||
| 12 | 84 | 68.9 | 43.8 | 151.5 | 17.5 | −0.2 (−0.6–0.5) | 12 | 139 | 65.5 * | 43.1 | 151.2 | 18.6 | −0.2 |
| (64.0–74.2) | (38.4–49.2) | (146.9–156.4) | (18.8–21.1) | (60.5–70.8) | (37.2–43.1) | (146.3–156.2) | (17.2–20.6 | (−0.6–0.3) | |||||
| Total Population | State Schools | Charter Schools | Private Schools | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
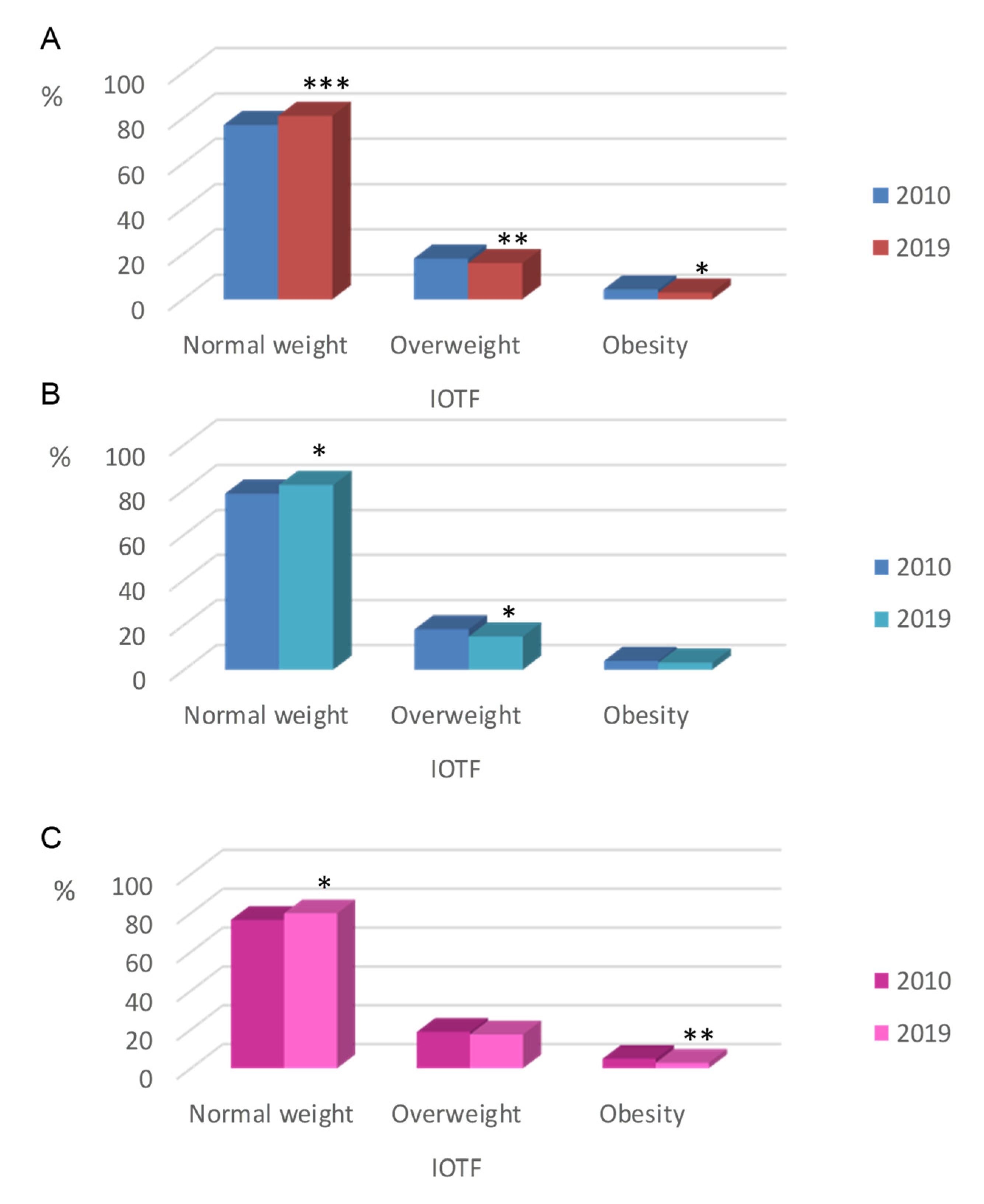
| International Obesity Task Force (IOTF) | Normal weight | 75.6% (5889) a | 80.1% (6128) b | 82.4% (10,088) c |
| Overweight | 19.2% (1493) a | 16.4% (1253) b | 15.2% (1856) c | |
| Obesity | 5.3% (411) a | 3.6% (273) b | 2.4% (295) c | |
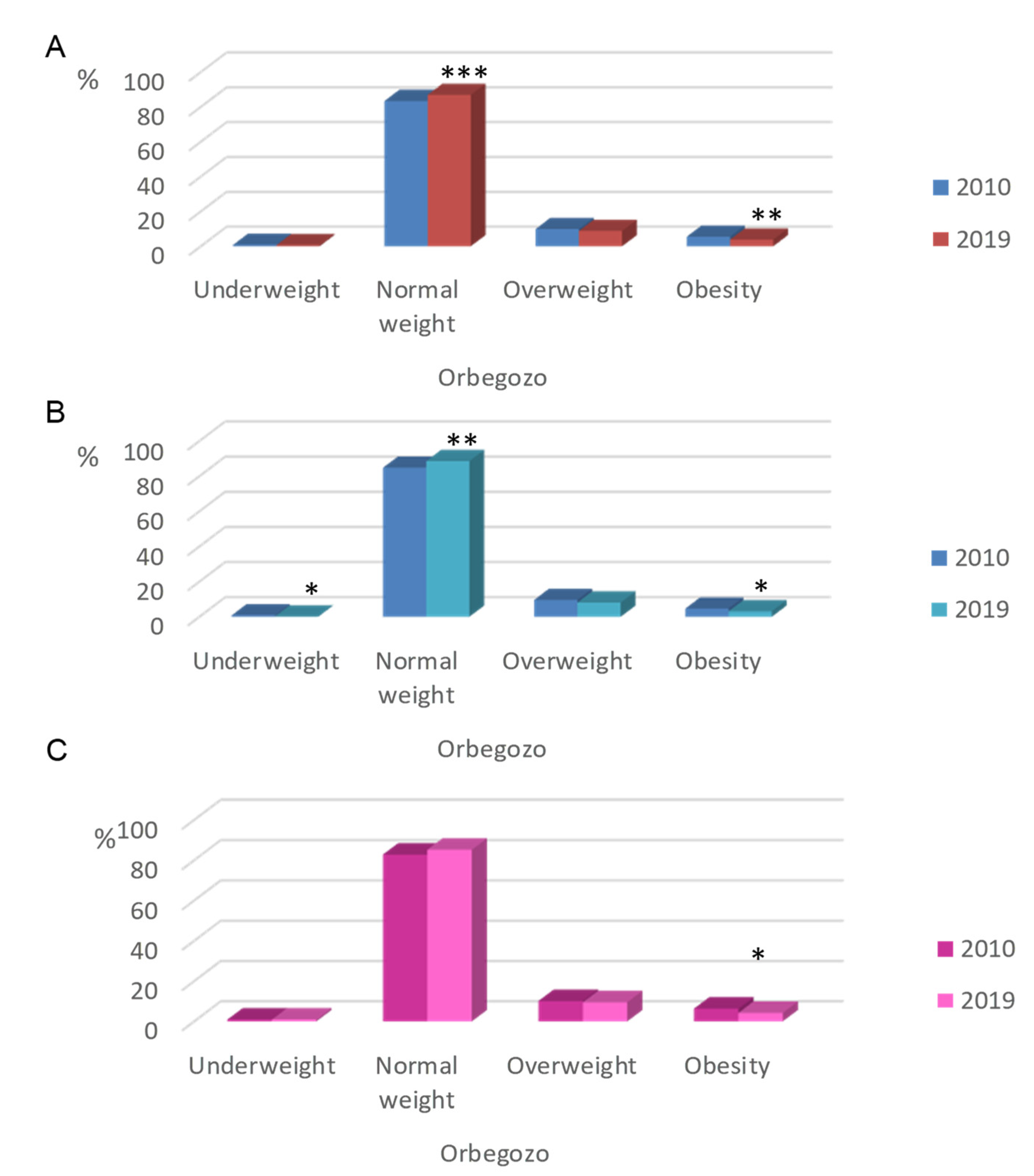
| Faustino Orbegozo Foundation (OF) | Underweight | 0.5% (38) | 0.4% (34) | 0.6% (71) |
| Normal weight | 82.4% (6422) a | 86.7% (6636) b | 88.8% (10,870) c | |
| Overweight | 10.0% (778) a | 8.6% (660) b | 7.5% (922) c | |
| Obesity | 7.1% (555) a | 4.2% (324) b | 3.1% (376) c | |
| State Schools | Charter Schools | Private Schools | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boys | IOTF | Normal weight | 77.3% (3134) a | 82.4% (3228) b | 83.0% (4942) b |
| Overweight | 18.2% (739) a | 14.3% (560) b | 14.5% (865) b | ||
| Obesity | 4.5% (411) a | 3.3% (128) b | 2.5% (148) c | ||
| Girls | IOTF | Normal weight | 73.7% (2755) a | 77.6% (2900) b | 81.9% (5146) c |
| Overweight | 20.2% (754) a | 18.5% (693) a | 15.8% (991) b | ||
| Obesity | 6.2% (230) a | 3.9% (145) b | 2.3% (147) c | ||
| Boys | OF | Underweight | 0.3% (14) | 0.4% (14) | 0.4% (24) |
| Normal weight | 84.8% (6422) a | 89.1% (3490) b | 89.8% (5350) b | ||
| Overweight | 9.5% (385) a | 7.2% (281) b | 6.9% (412) b | ||
| Obesity | 5.4% (555) a | 3.3% (131) b | 2.9% (219) b | ||
| Girls | OF | Underweight | 0.6% (24) | 0.5% (20) | 0.8% (48) |
| Normal weight | 79.9% (2986) a | 84.2% (3146) b | 87.8% (5520) c | ||
| Overweight | 10.5% (393) a | 10.1% (379) a | 8.1% (510) b | ||
| Obesity | 9.0% (336) a | 5.2% (193) b | 3.3% (206) c | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puga, A.M.; Carretero-Krug, A.; Montero-Bravo, A.M.; Varela-Moreiras, G.; Partearroyo, T. Effectiveness of Community-Based Interventions Programs in Childhood Obesity Prevention in a Spanish Population According to Different Socioeconomic School Settings. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2680. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092680
Puga AM, Carretero-Krug A, Montero-Bravo AM, Varela-Moreiras G, Partearroyo T. Effectiveness of Community-Based Interventions Programs in Childhood Obesity Prevention in a Spanish Population According to Different Socioeconomic School Settings. Nutrients. 2020; 12(9):2680. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092680
Chicago/Turabian StylePuga, Ana M., Alejandra Carretero-Krug, Ana M. Montero-Bravo, Gregorio Varela-Moreiras, and Teresa Partearroyo. 2020. "Effectiveness of Community-Based Interventions Programs in Childhood Obesity Prevention in a Spanish Population According to Different Socioeconomic School Settings" Nutrients 12, no. 9: 2680. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092680
APA StylePuga, A. M., Carretero-Krug, A., Montero-Bravo, A. M., Varela-Moreiras, G., & Partearroyo, T. (2020). Effectiveness of Community-Based Interventions Programs in Childhood Obesity Prevention in a Spanish Population According to Different Socioeconomic School Settings. Nutrients, 12(9), 2680. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092680







