Exercise and Curcumin in Combination Improves Cognitive Function and Attenuates ER Stress in Diabetic Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal and Experimental Design
2.2. Exercise Protocol
2.3. Morris Water Maze Task
2.4. Blood Biochemistry
2.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.6. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.7. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time qPCR
2.9. Reverse Transcription-PCR
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
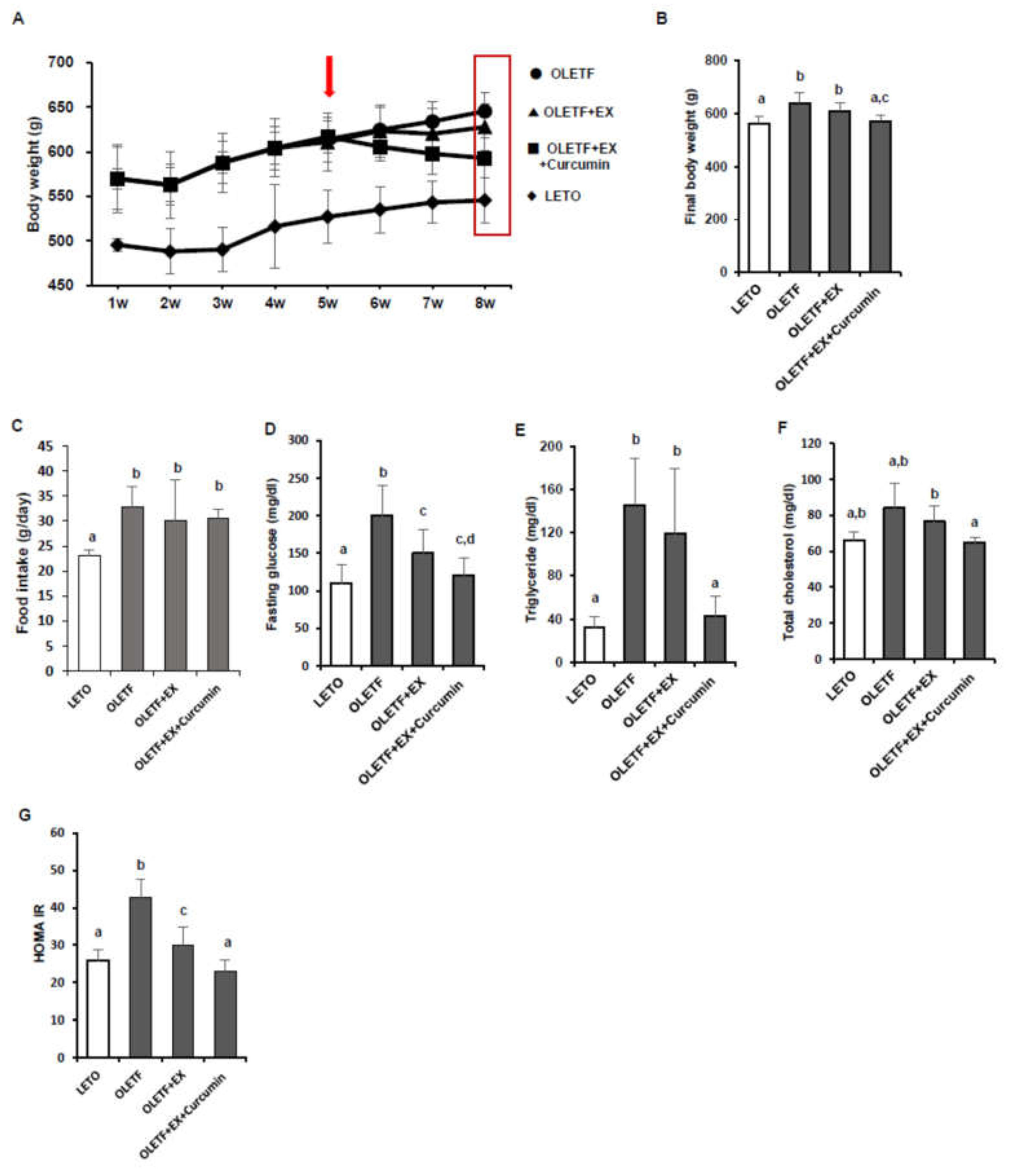
3.1. Effects of Exercise and Curcumin Supplementation on Metabolic Complications in OLETF Rats
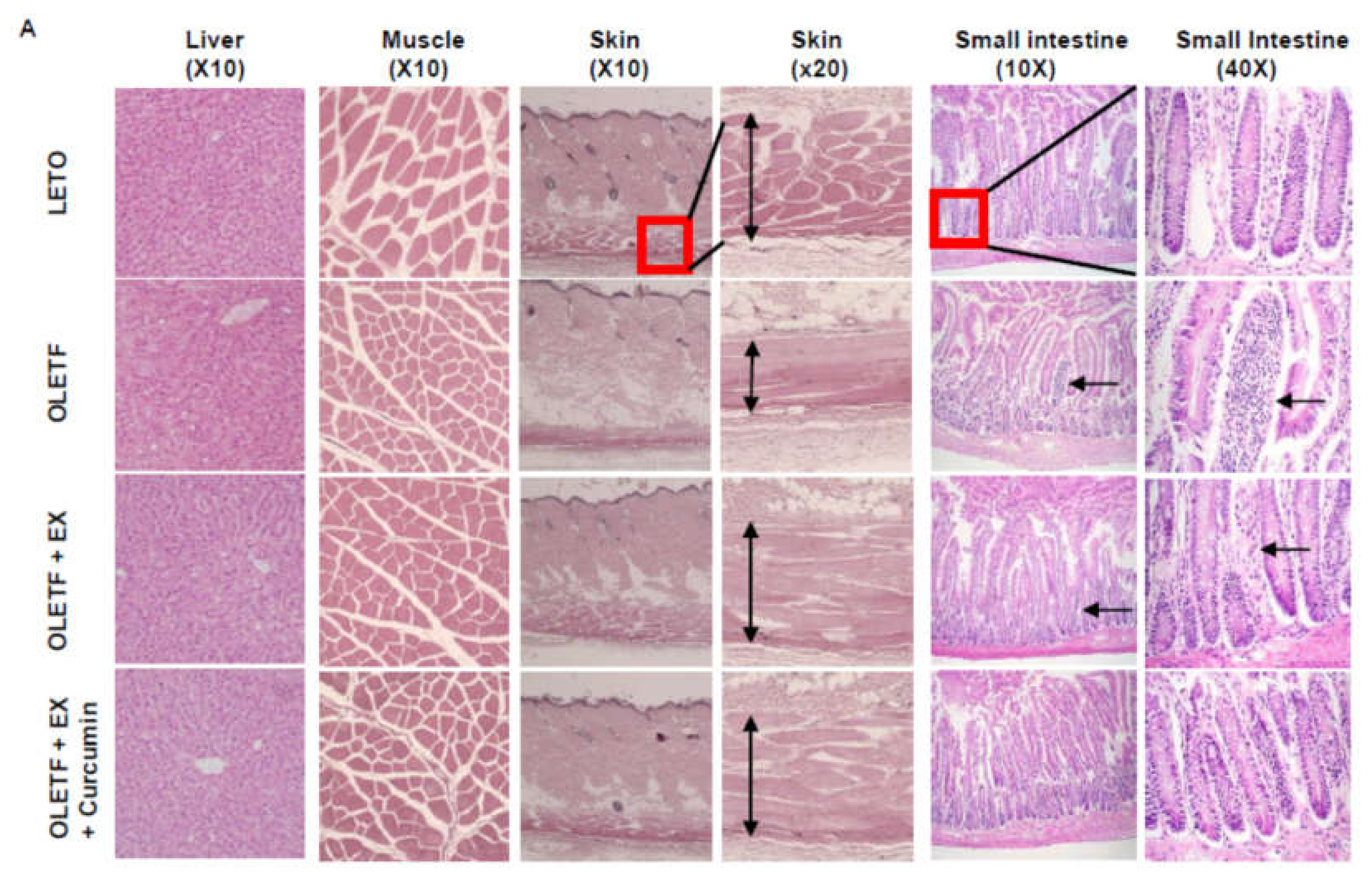
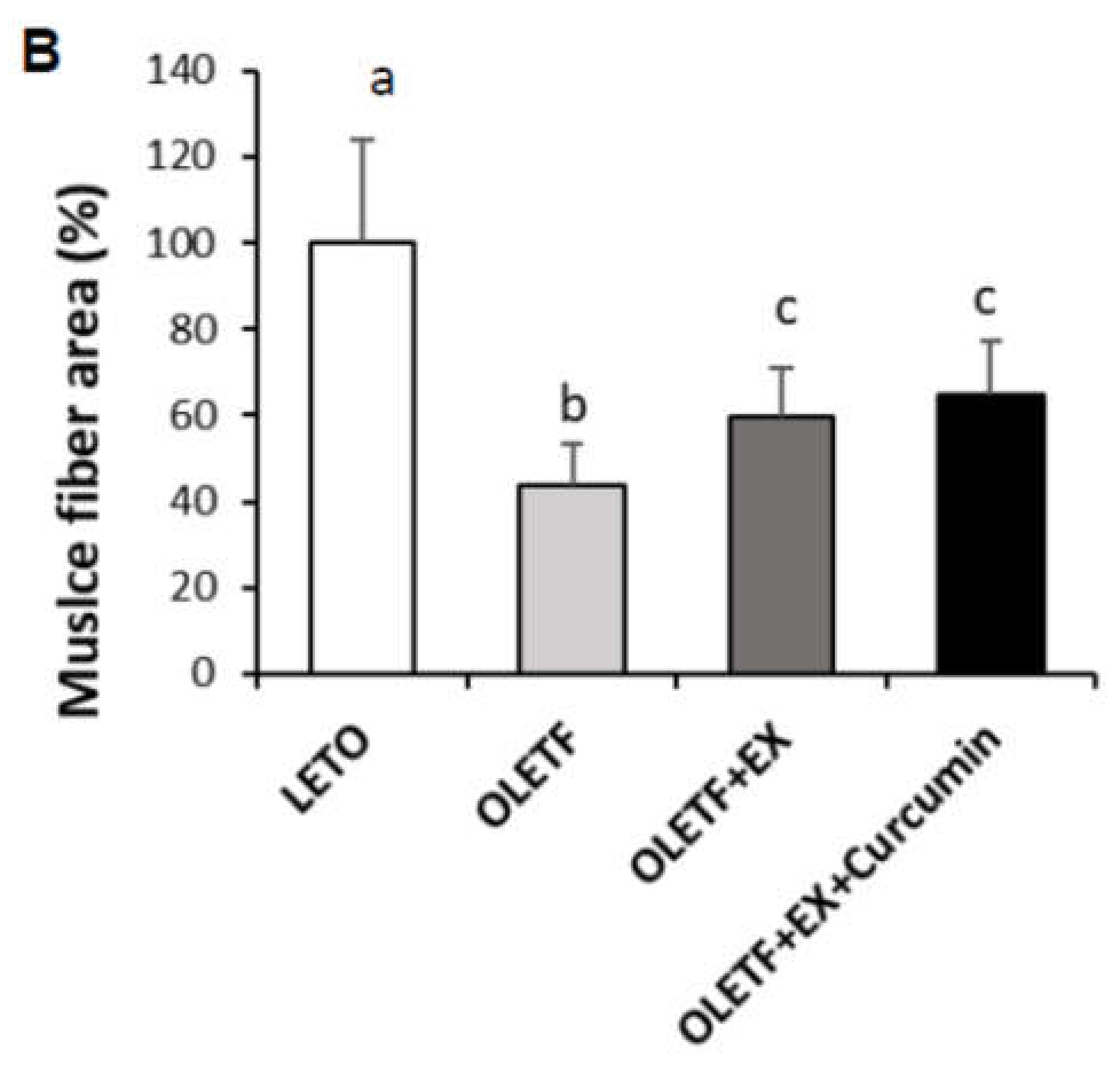
3.2. Effects of Exercise Plus Curcumin Supplementation on Histopathology in OLETF Rats
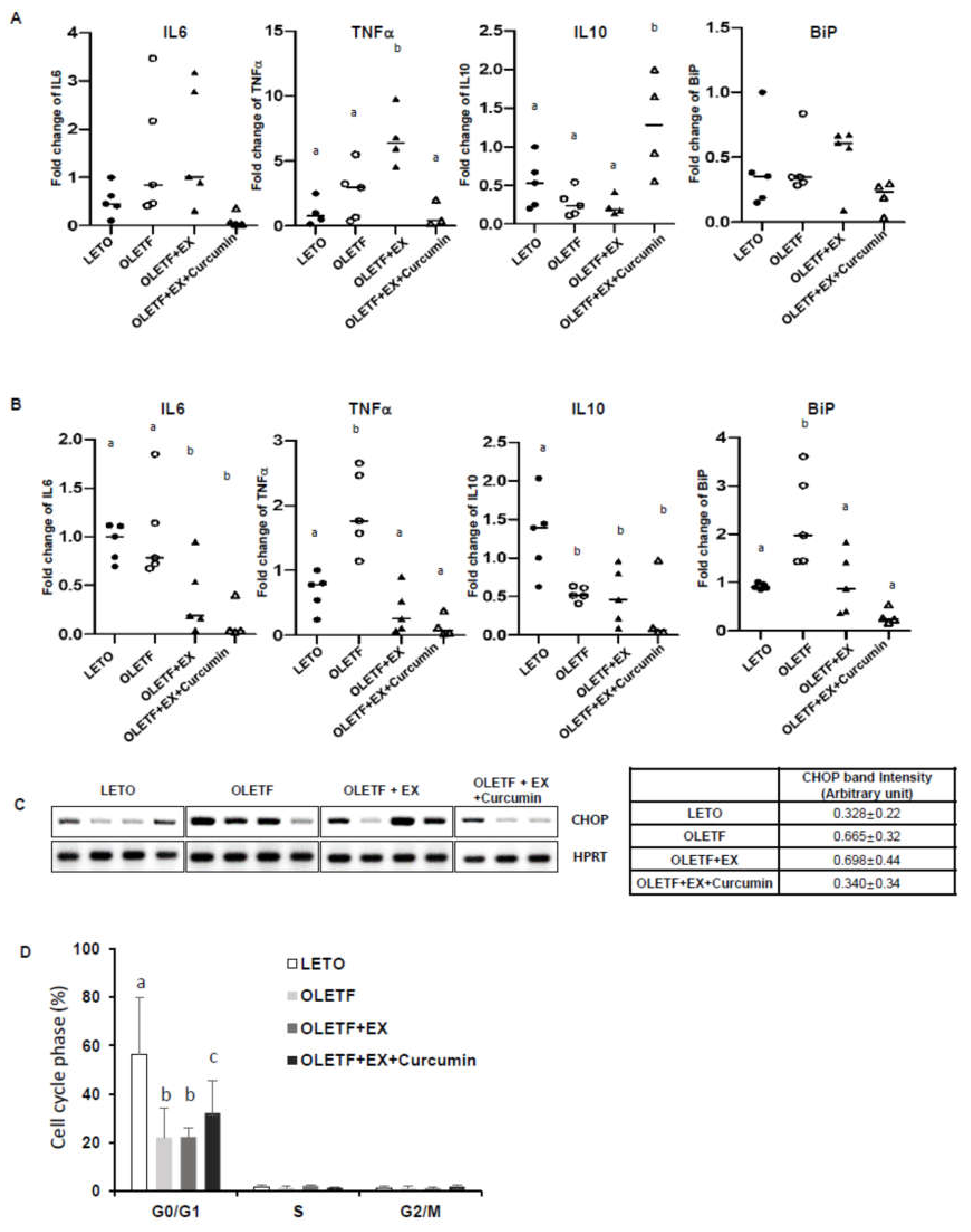
3.3. Effects of Exercise and Curcumin Supplementation on ER Stress in the Small Intestine Tissues of OLETF Rats
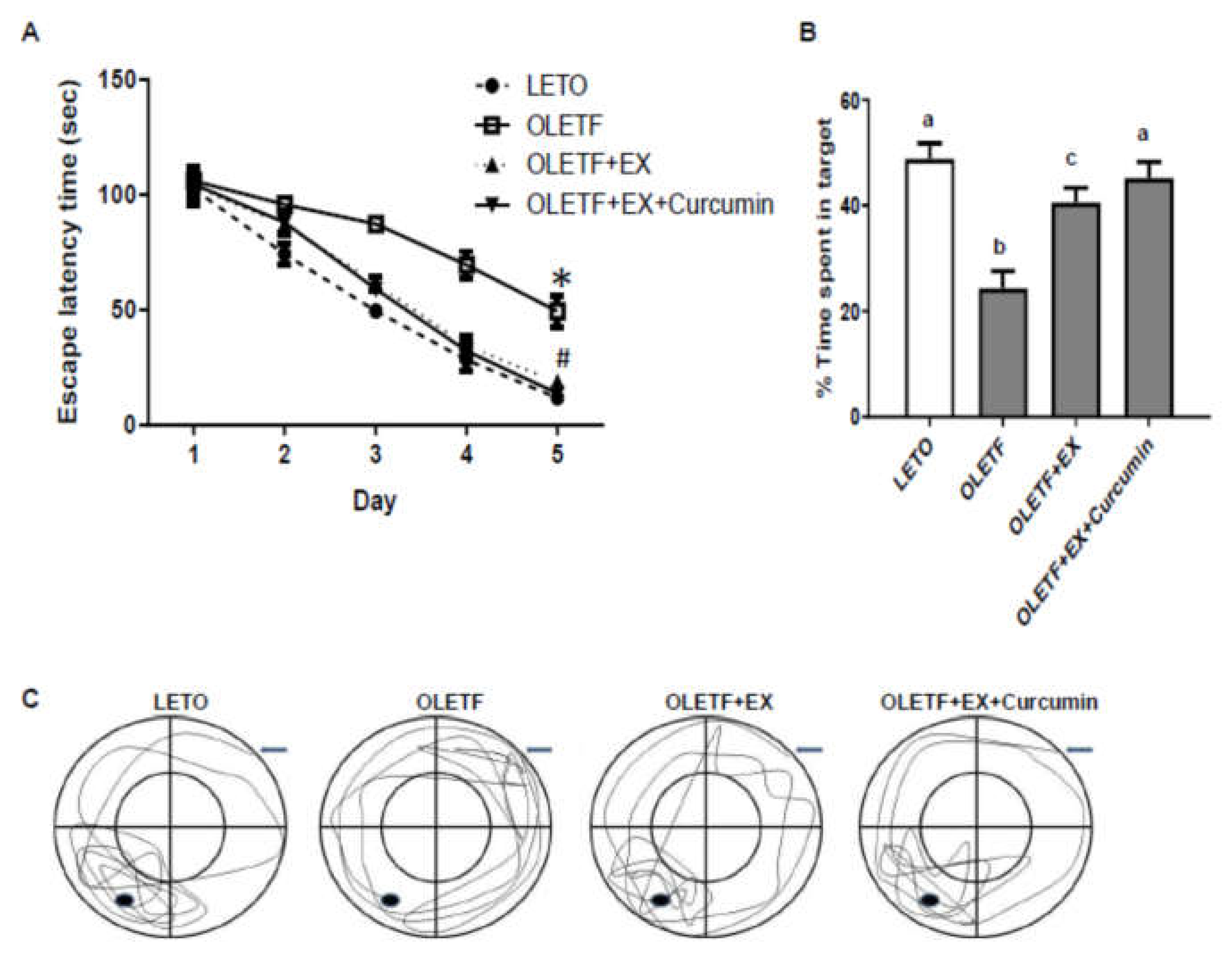
3.4. Effects of Exercise and Curcumin Supplementation on Learning and Memory Deficits in OLETF Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biessels, G.J.; Reijmer, Y.D. Brain Changes Underlying Cognitive Dysfunction in Diabetes: What Can We Learn From MRI? Diabetes 2014, 63, 2244–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biessels, G.J.; Strachan, M.W.J.; Visseren, F.L.; Kappelle, L.J.; A Whitmer, R. Dementia and cognitive decline in type 2 diabetes and prediabetic stages: Towards targeted interventions. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riederer, P.; Korczyn, A.D.; Ali, S.S.; Bajenaru, O.; Choi, M.S.; Chopp, M.; Dermanovic-Dobrota, V.; Grünblatt, E.; Jellinger, K.A.; Kamal, M.A.; et al. The diabetic brain and cognition. J. Neural Transm. 2017, 124, 1431–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.R.; O’Sullivan, A.J.; Singh, M.A.F. Exercise or physical activity and cognitive function in adults with type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance or impaired glucose tolerance: A systematic review. Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act. 2018, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harding, H.P.; Zhang, Y.; Ron, D. Protein translation and folding are coupled by an endoplasmic-reticulum-resident kinase. Nature 1999, 397, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Qi, L. Quality Control in the Endoplasmic Reticulum: Crosstalk between ERAD and UPR pathways. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2018, 43, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, U.; Yilmaz, E.; Ozcan, L.; Furuhashi, M.; Vaillancourt, E.; Smith, R.O.; Görgün, C.Z.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Chemical Chaperones Reduce ER Stress and Restore Glucose Homeostasis in a Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes. Science 2006, 313, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and the Inflammatory Basis of Metabolic Disease. Cell 2010, 140, 900–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Shi, J.; Yin, Q.; Li, X.; Sheng, Y.; Han, J.; Zhuang, P.; Zhang, Y. Morphological and Pathological Characteristics of Brain in Diabetic Encephalopathy. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 65, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; He, D.; Ling, S. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Hippocampal Neuron Apoptosis Involved in Diabetic Cognitive Impairment. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.A.; Park, E. Curcumin utilizes the anti-inflammatory response pathway to protect the intestine against bacterial invasion. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2015, 9, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.E.; Park, E. Curcumin enhances poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor sensitivity to chemotherapy in breast cancer cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1442–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugliani, M.; Mossuto, S.; Grano, F.; Suleiman, M.; Marselli, L.; Boggi, U.; De Simone, P.; Eizirik, D.L.; Cnop, M.; Marchetti, P.; et al. Modulation of Autophagy Influences the Function and Survival of Human Pancreatic Beta Cells Under Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Conditions and in Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawano, K.; Hirashima, T.; Mori, S.; Saitoh, Y.; Kurosumi, M.; Natori, T. Spontaneous Long-Term Hyperglycemic Rat With Diabetic Complications: Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) Strain. Diabetes 1992, 41, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-J.; Song, W. Resistance training increases fibroblast growth factor-21 and irisin levels in the skeletal muscle of Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J. Exerc. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 21, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorhees, C.V.; Williams, M.T. Morris water maze: Procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawano, K.; Hirashima, T.; Mori, S.; Natori, T. OLETF (Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty) rat: A new NIDDM rat strain. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1994, 24, S317–S320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims-Robinson, C.; Zhao, S.; Hur, J.; Feldman, E.L. Central nervous system endoplasmic reticulum stress in a murine model of type 2 diabetes. Diabetol. 2012, 55, 2276–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Karin, M.; Bai, H.; Cai, D. Hypothalamic IKKβ/NF-κB and ER Stress Link Overnutrition to Energy Imbalance and Obesity. Cell 2008, 135, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Li, C.; Che, L.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y. Downregulation of long noncoding RNA H19 rescues hippocampal neurons from apoptosis and oxidative stress by inhibiting IGF2 methylation in mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 10655–10670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, C.; Beare, R.; Phan, T.G.; Bruce, D.G.; Callisaya, M.; Srikanth, V.K. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and biomarkers of neurodegeneration. Neurology 2015, 85, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belotto, M.F.; Magdalon, J.; Rodrigues, H.G.; Vinolo, M.A.R.; Curi, R.; Pithon-Curi, T.C.; Hatanaka, E. Moderate exercise improves leucocyte function and decreases inflammation in diabetes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 162, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karstoft, K.; Pedersen, B.K. Exercise and type 2 diabetes: Focus on metabolism and inflammation. Immunol. Cell Boil. 2015, 94, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lemos, E.T.; Pinto, R.M.; Oliveira, J.; Garrido, P.; Sereno, J.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Pinheiro, J.P.; Teixeira, F.; Reis, F. Differential Effects of Acute (Extenuating) and Chronic (Training) Exercise on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Status in an Animal Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Mediat. Inflamm. 2011, 2011, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waddington, G. Exercise intensity and inflammation in type 2 diabetes. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2017, 20, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoppini, G.; Targher, G.; Zamboni, C.; Venturi, C.; Cacciatori, V.; Moghetti, P.; Muggeo, M. Effects of moderate-intensity exercise training on plasma biomarkers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in older patients with type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2006, 16, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Chen, S.; Liang, G.; Feng, B.; Cai, L.; Khan, Z.A.; Chakrabarti, S. Curcumin Analogs Reduce Stress and Inflammation Indices in Experimental Models of Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Banerjee, S.; Sil, P.C. The beneficial role of curcumin on inflammation, diabetes and neurodegenerative disease: A recent update. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 83, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, K.; Chowdhury, S.; Ghosh, S.; Sil, P.C. Curcumin attenuates oxidative stress induced NFκB mediated inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum dependent apoptosis of splenocytes in diabetes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 143, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, S.; Leibel, R.; Tortoriello, D.V. Dietary curcumin significantly improves obesity-associated inflammation and diabetes in mouse models of diabesity. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 3549–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Z.; Dai, Y.; Fu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Bao, D.; Yin, Y.; Chen, Q.; Nie, X.; Hao, Q.; Hou, D.-R.; et al. Curcumin exerts a protective effect against premature ovarian failure in mice. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 60, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Wang, P.; Wei, P.; Feng, H.; Ren, Y.; Yang, J.; Rao, Y.; Shi, J.; Tian, J. Effects of curcumin on synapses in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Q.-L.; Zuo, X.; Yang, F.; Ubeda, O.J.; Gant, D.J.; Alaverdyan, M.; Teng, E.; Hu, S.; Chen, P.-P.; Maiti, P.; et al. Curcumin suppresses soluble tau dimers and corrects molecular chaperone, synaptic, and behavioral deficits in aged human tau transgenic mice. J. Boil. Chem. 2012, 288, 4056–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, H.-L.; Dang, H.-Z.; Fan, H.; Chen, X.-P.; Rao, Y.-X.; Ren, Y.; Yang, J.-D.; Shi, J.; Wang, P.; Tian, J.-Z. Curcumin ameliorates insulin signalling pathway in brain of Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Kong, X.-J.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Xu, F.-S.; Zhu, Y.-T. A study on neuroprotective effects of curcumin on the diabetic rat brain. J. Nutr. Heal. Aging 2016, 20, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Su, C.; Feng, H.; Chen, X.; Dong, Y.; Rao, Y.; Ren, Y.; Yang, J.; Shi, J.; Tian, J.; et al. Curcumin regulates insulin pathways and glucose metabolism in the brains of APPswe/PS1dE9 mice. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2017, 30, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozcan, L.; Ergin, A.S.; Lu, A.; Chung, J.; Sarkar, S.; Nie, D.; Myers, M.G.; Ozcan, U. Endoplasmic reticulum stress plays a central role in development of leptin resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Busquets, O.; Eritja, À.; López, B.M.; Ettcheto, M.; Manzine, P.; Castro-Torres, R.D.; Verdaguer, E.; Olloquequi, J.; Vázquez-Carrera, M.; Auladell, C.; et al. Role of brain c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2 in the control of the insulin receptor and its relationship with cognitive performance in a high-fat diet pre-clinical model. J. Neurochem. 2019, 149, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.-J.; Ma, L.-L.; Guo, J.-J.; Xu, L.-H.; Li, Y.; Qu, S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress/autophagy pathway is involved in diabetes-induced neuronal apoptosis and cognitive decline in mice. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriach, M.; Flores-Bellver, M.; Romero, F.J.; Barcia, J.M. Diabetes and the Brain: Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Autophagy. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, S.; Yin, J. The dynamic changes of endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway markers GRP78 and CHOP in the hippocampus of diabetic mice. Brain Res. Bull. 2015, 111, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-altering microorganisms: The impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Clercq, N.C.; Frissen, M.N.; Groen, A.K.; Nieuwdorp, M. Gut Microbiota and the Gut-Brain Axis. Psychosom. Med. 2017, 79, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, T.; Bäckhed, F. The gut microbiota and metabolic disease: Current understanding and future perspectives. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 280, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianiro, G.; Bibbò, S.; Antonio, G.; Cammarota, G. Therapeutic modulation of gut microbiota: Current clinical applications and future perspectives. Curr. Drug Targets 2014, 15, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Lloyd, J.; Walter, P.; Rane, S.G. Beneficial metabolic effects of a probiotic via butyrate-induced GLP-1 Hormone Secretion. J. Boil. Chem. 2013, 288, 25088–25097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caricilli, A.M.; Picardi, P.K.; De Abreu, L.L.; Ueno, M.; Prada, P.O.; Ropelle, E.R.; Hirabara, S.M.; Castoldi, A.; De Moraes-Vieira, P.M.M.; Câmara, N.O.S.; et al. Gut microbiota is a key modulator of insulin resistance in TLR 2 knockout mice. PLoS Boil. 2011, 9, e1001212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Seo, D.Y.; Kim, T.N.; Ko, J.; Han, J. Resistance Exercise Training Attenuates the Loss of Endogenous GLP-1 Receptor in the Hypothalamus of Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravindranath, V.; Chandrasekhara, N. Absorption and tissue distribution of curcumin in rats. Toxicol. 1980, 16, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L. Study of the Intestinal Absorption Characteristics of Curcumin In Vivo and In Vitro. J. Appl. Pharm. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, J.A.; Park, S.H.; Cho, J.; Kim, J.-O.; Yoon, J.H.; Park, E. Exercise and Curcumin in Combination Improves Cognitive Function and Attenuates ER Stress in Diabetic Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051309
Cho JA, Park SH, Cho J, Kim J-O, Yoon JH, Park E. Exercise and Curcumin in Combination Improves Cognitive Function and Attenuates ER Stress in Diabetic Rats. Nutrients. 2020; 12(5):1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051309
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Jin Ah, Se Hwan Park, Jinkyung Cho, Jong-Oh Kim, Jin Hwan Yoon, and Eunmi Park. 2020. "Exercise and Curcumin in Combination Improves Cognitive Function and Attenuates ER Stress in Diabetic Rats" Nutrients 12, no. 5: 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051309
APA StyleCho, J. A., Park, S. H., Cho, J., Kim, J.-O., Yoon, J. H., & Park, E. (2020). Exercise and Curcumin in Combination Improves Cognitive Function and Attenuates ER Stress in Diabetic Rats. Nutrients, 12(5), 1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12051309




