Allyl Isothiocyanate Protects Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury via NRF2 Activation by Decreasing Spontaneous Degradation in Hepatocyte
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Materials
2.2. APAP-Induced Liver Damage Model and Sample Analysis
2.3. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Immunocytochemistry
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
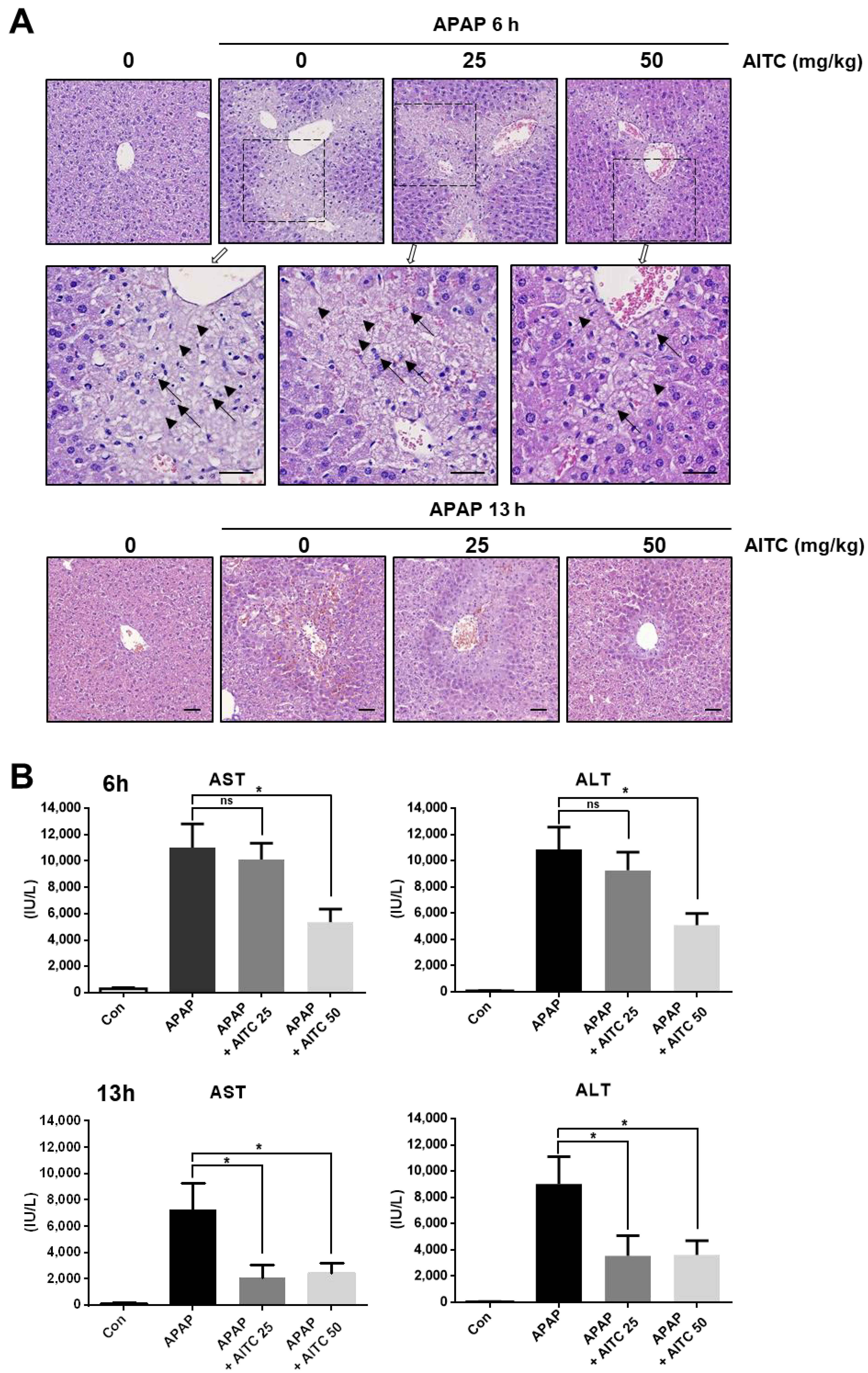
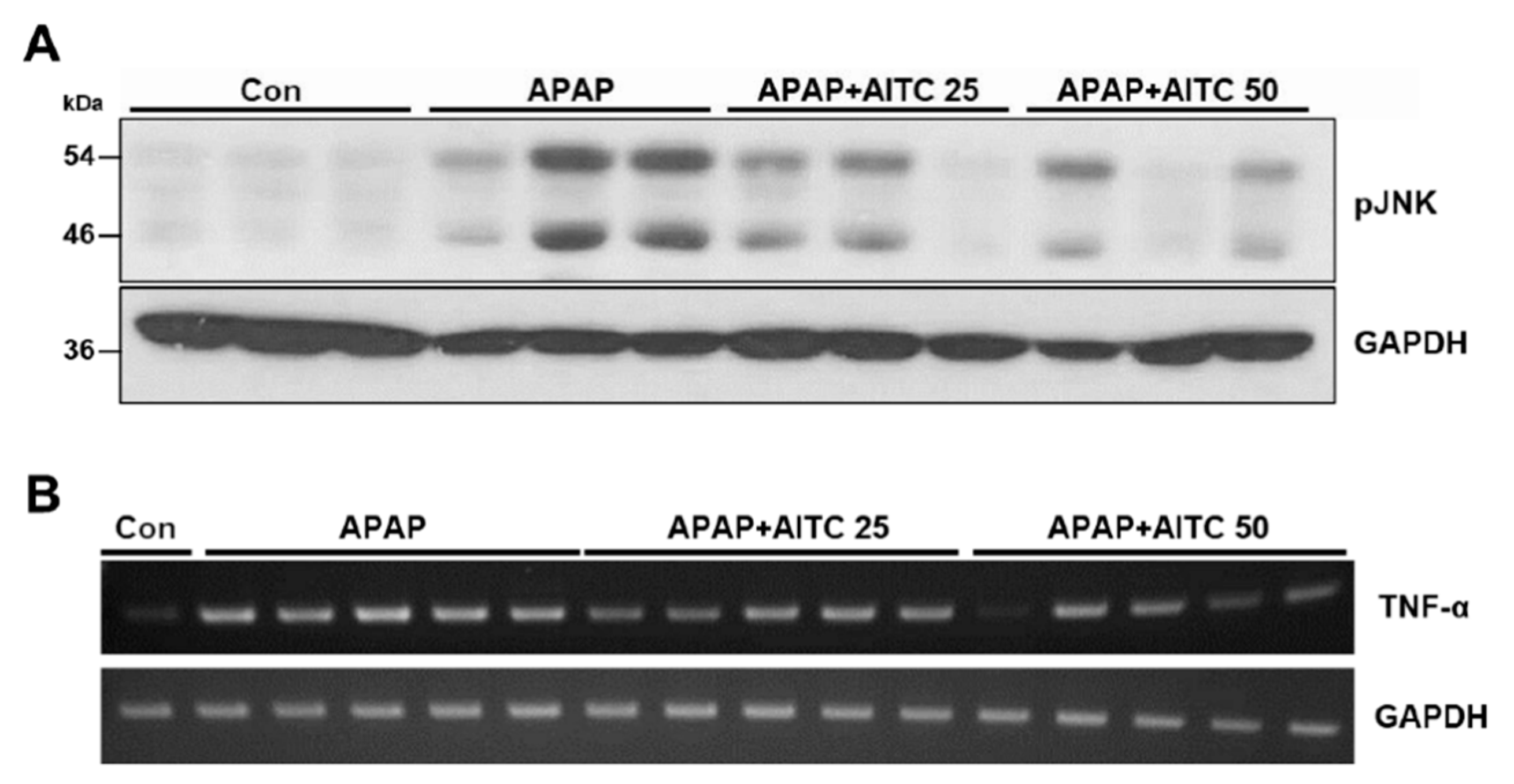
3.1. AITC Pretreatment Attenuates APAP-Induced Hepatotoxicity In Vivo
3.2. AITC Induces NRF2 Activation and Its Target Gene Expression in Hepatocytes
3.3. AITC Protects APAP-Induced Cell Damage via NRF2 Activation
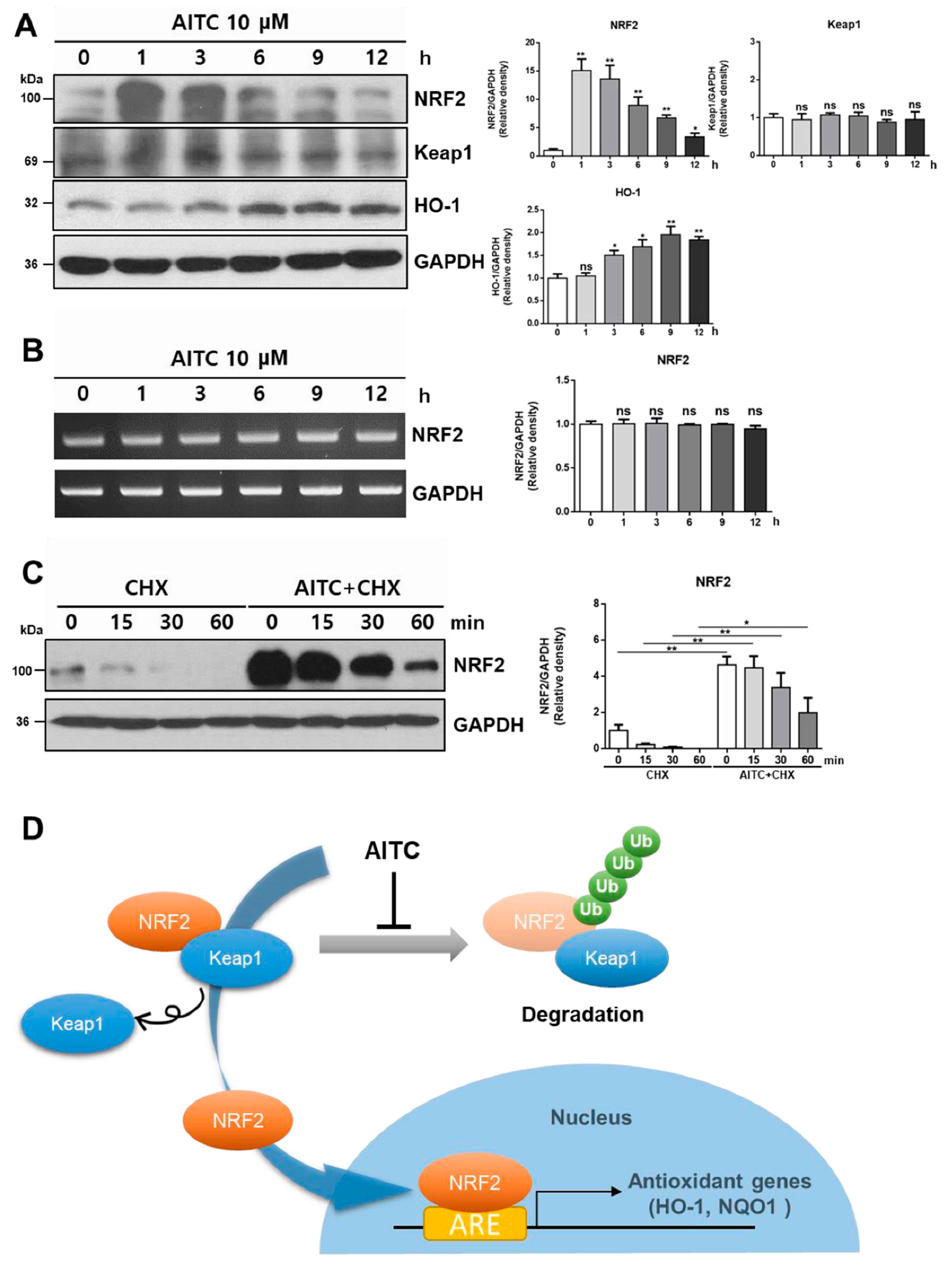
3.4. AITC Rapidly Activates NRF2 by Reducing Spontaneous Degradation
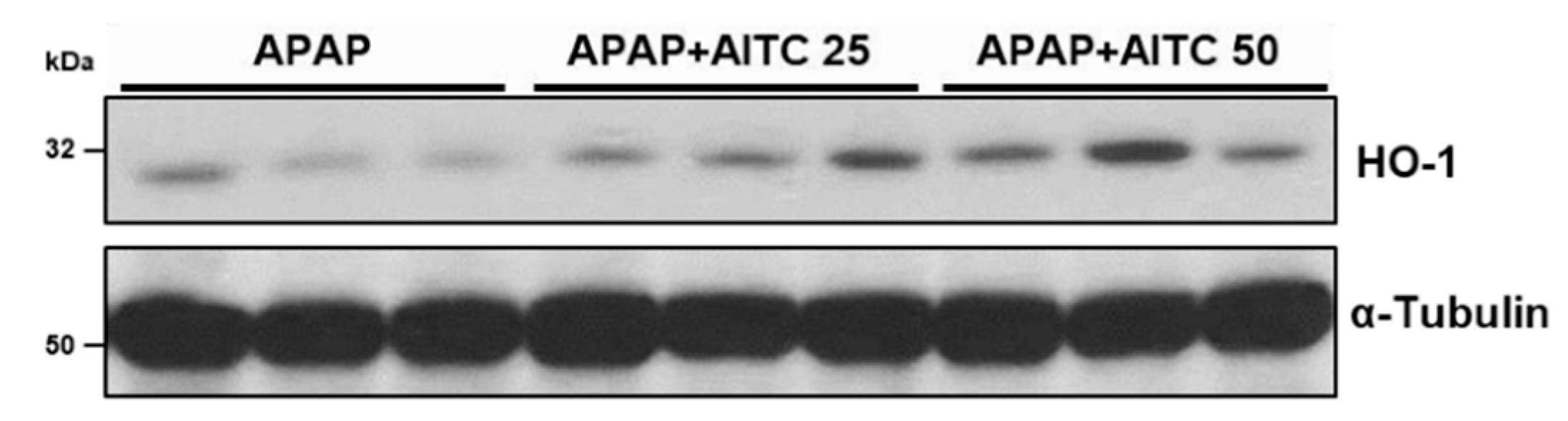
3.5. AITC Elevates HO-1 Expression in Mouse Liver Tissues
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Subedi, L.; Venkatesan, R.; Kim, S.Y. Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory activities of allyl isothiocyanate through attenuation of JNK/NF-κB/TNF-α signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1423. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; Geng, F.; Paonessa, J.D.; Chen, S.C.; Wong, M.K.; Zhang, Y. Inhibition of bladder cancer development by allyl isothiocyanate. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sahin, N.; Orhan, C.; Erten, F.; Tuzcu, M.; Defo Deeh, P.B.; Ozercan, I.H.; Juturu, V.; Kazim, S. Effects of allyl isothiocyanate on insulin resistance, oxidative stress status, and transcription factors in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2019, 33, e22328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olivier, C.; Vaughn, S.F.; Mizubuti, E.S.; Loria, R. Variation in allyl isothiocyanate production within Brassica species and correlation with fungicidal activity. J. Chem. Ecol. 1999, 25, 2687–2701. [Google Scholar]
- Depree, J.; Howard, T.; Savage, G. Flavour and pharmaceutical properties of the volatile sulphur compounds of Wasabi (Wasabia japonica). Food Res. Int. 1998, 31, 329–337. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.; Liu, X.; Lei, P.; Zhang, X.; Shan, Y. Microbiota: A mediator to transform glucosinolate precursors in cruciferous vegetables to the active isothiocyanates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Narbad, A.; Rossiter, J.T. Gut glucosinolate metabolism and isothiocyanate production. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700991. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.W.; Choi, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Yoon, Y.S.; Kang, J.-H.; Oh, S.H. Allyl isothiocyanate ameliorates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mouse by enhancing tight junction and mucin expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, D.-H.; Ahn, J.; Chung, W.-J.; Jang, Y.J.; Seong, K.-S.; Moon, J.-H.; Ha, T.Y.; Jung, C.H. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, and anti-lipogenic/adipogenic effects of allyl-isothiocyanate metabolites. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132151. [Google Scholar]
- Mazaleuskaya, L.L.; Sangkuhl, K.; Thorn, C.F.; FitzGerald, G.A.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. PharmGKB summary: Pathways of acetaminophen metabolism at the therapeutic versus toxic doses. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2015, 25, 416. [Google Scholar]
- Du, K.; Ramachandran, A.; Jaeschke, H. Oxidative stress during acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: Sources, pathophysiological role and therapeutic potential. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, D.W.; Goedken, M.J.; Rommelaere, S.; Chasson, L.; Galland, F.; Naquet, P.; Manautou, J.E. Enhanced hepatotoxicity by acetaminophen in Vanin-1 knockout mice is associated with deficient proliferative and immune responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2016, 1862, 662–669. [Google Scholar]
- Banshoya, K.; Nakamura, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneo, Y. Coenzyme Q10-Polyethylene Glycol Monostearate Nanoparticles: An Injectable Water-Soluble Formulation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 86. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.; Nioi, P.; Pickett, C.B. The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 13291–13295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Katoh, Y.; Iida, K.; Kang, M.-I.; Kobayashi, A.; Mizukami, M.; Tong, K.I.; McMahon, M.; Hayes, J.D.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M. Evolutionary conserved N-terminal domain of Nrf2 is essential for the Keap1-mediated degradation of the protein by proteasome. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 433, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.M.U.; Luo, L.; Namani, A.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Nrf2 signaling pathway: Pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 585–597. [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto, A.; Itoh, K.; Nagayoshi, E.; Haruta, J.; Kimura, T.; O’Connor, T.; Harada, T.; Yamamoto, M. High sensitivity of Nrf2 knockout mice to acetaminophen hepatotoxicity associated with decreased expression of ARE-regulated drug metabolizing enzymes and antioxidant genes. Toxicol. Sci. 2001, 59, 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, K.; Han, X.-D.; Kan, Y.W. An important function of Nrf2 in combating oxidative stress: Detoxification of acetaminophen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4611–4616. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Jiang, Y.-F.; Ponnusamy, M.; Diallo, M. Role of Nrf2 in chronic liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 13079. [Google Scholar]
- Carvajal-Yepes, M.; Himmelsbach, K.; Schaedler, S.; Ploen, D.; Krause, J.; Ludwig, L.; Weiss, T.; Klingel, K.; Hildt, E. Hepatitis C virus impairs the induction of cytoprotective Nrf2 target genes by delocalization of small Maf proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 8941–8951. [Google Scholar]
- Shimozono, R.; Asaoka, Y.; Yoshizawa, Y.; Aoki, T.; Noda, H.; Yamada, M.; Kaino, M.; Mochizuki, H. Nrf2 Activators Attenuate the Progression of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis–Related Fibrosis in a Dietary Rat Model. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 84, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Lamlé, J.; Marhenke, S.; Borlak, J.; Von Wasielewski, R.; Eriksson, C.P.; Geffers, R.; Manns, M.P.; Yamamoto, M.; Vogel, A. Nuclear factor-eythroid 2–related factor 2 prevents alcohol-induced fulminant liver injury. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1159–1168.e2. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bataille, A.; Manautou, J. Nrf2: A potential target for new therapeutics in liver disease. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 92, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Bang, H.; Ahn, M.; Choi, Y.; Kim, G.O.; Shin, T. Allyl isothiocyanate reduces liver fibrosis by regulating Kupffer cell activation in rats. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-X.; Gao, J.-G.; Wan, X.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, C.-F.; Feng, Z.-M.; Zeng, H.; Lin, Y.-M.; Ma, H.; Xu, P. Allyl isothiocyanate ameliorates lipid accumulation and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via the Sirt1/AMPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 5120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeong, T.B.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.; Son, S.W.; Lim, Y.; Cho, J.-Y.; Hwang, D.Y.; Kim, K.S.; Kwak, J.-H. Comparison of toxic responses to acetaminophen challenge in ICR mice originating from different sources. Lab. Anim. Res. 2019, 35, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.W.; Kang, J.-H.; Shin, E.; Shim, K.-S.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, C.-K.; Yoon, Y.S.; Oh, S.H. Processed Aloe vera gel attenuates non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)-induced small intestinal injury by enhancing mucin expression. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6088–6097. [Google Scholar]
- Gunawan, B.K.; Liu, Z.X.; Han, D.; Hanawa, N.; Gaarde, W.A.; Kaplowitz, N. c-Jun N-terminal kinase plays a major role in murine acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 165–178. [Google Scholar]
- Mossanen, J.; Tacke, F. Acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice. Lab. Anim. 2015, 49, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, I.M.; Wagner, A.E.; Schuemann, C.; Storm, N.; Höppner, W.; Döring, F.; Stocker, A.; Rimbach, G. Allyl-, butyl-and phenylethyl-isothiocyanate activate Nrf2 in cultured fibroblasts. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 63, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Fontana, R.J. Acute liver failure including acetaminophen overdose. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 92, 761–794. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caglayan, B.; Kilic, E.; Dalay, A.; Altunay, S.; Tuzcu, M.; Erten, F.; Orhan, C.; Gunal, M.Y.; Yulug, B.; Juturu, V. Allyl isothiocyanate attenuates oxidative stress and inflammation by modulating Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB pathways in traumatic brain injury in mice. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rushworth, S.A.; Zaitseva, L.; Murray, M.Y.; Shah, N.M.; Bowles, K.M.; MacEwan, D.J. The high Nrf2 expression in human acute myeloid leukemia is driven by NF-κB and underlies its chemo-resistance. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2012, 120, 5188–5198. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, S.H.; Sung, S.H.; Oh, S.Y.; Lim, J.M.; Lee, S.K.; Park, Y.N.; Lee, H.E.; Kang, D.; Rhee, S.G. Sestrins activate Nrf2 by promoting p62-dependent autophagic degradation of Keap1 and prevent oxidative liver damage. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.W.; Kang, J.-H.; Jung, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Phan, T.H.L.; Namgung, H.; Seo, S.-Y.; Yoon, Y.S.; Oh, S.H. Allyl Isothiocyanate Protects Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury via NRF2 Activation by Decreasing Spontaneous Degradation in Hepatocyte. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113585
Kim MW, Kang J-H, Jung HJ, Park SY, Phan THL, Namgung H, Seo S-Y, Yoon YS, Oh SH. Allyl Isothiocyanate Protects Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury via NRF2 Activation by Decreasing Spontaneous Degradation in Hepatocyte. Nutrients. 2020; 12(11):3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113585
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min Woo, Ju-Hee Kang, Hyun Jin Jung, Se Yong Park, Thu Han Le Phan, Hee Namgung, Seung-Yong Seo, Yeo Sung Yoon, and Seung Hyun Oh. 2020. "Allyl Isothiocyanate Protects Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury via NRF2 Activation by Decreasing Spontaneous Degradation in Hepatocyte" Nutrients 12, no. 11: 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113585
APA StyleKim, M. W., Kang, J.-H., Jung, H. J., Park, S. Y., Phan, T. H. L., Namgung, H., Seo, S.-Y., Yoon, Y. S., & Oh, S. H. (2020). Allyl Isothiocyanate Protects Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury via NRF2 Activation by Decreasing Spontaneous Degradation in Hepatocyte. Nutrients, 12(11), 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113585





