Effect of Korean Red Ginseng on Cholesterol Metabolites in Postmenopausal Women with Hypercholesterolemia: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Randomization and Masking
2.3. Procedures and Endpoints
2.4. Reagents
2.5. Lipid Extraction and LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Welty, F.K. Cardiovascular Disease and Dyslipidemia in Women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreisberg, R.A.; Kasim, S. Cholesterol metabolism and aging. Am. J. Med. 1987, 82, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.L.; Rifkind, B.M.; Sempos, C.T.; Carroll, M.D.; Bachorik, P.S.; Briefel, R.R.; Gordon, D.J.; Burt, V.L.; Brown, C.D.; Lippel, K.; et al. Declining serum total cholesterol levels among US adults. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. JAMA 1993, 269, 3002–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannel, W.B.; Wilson, P.W. Risk factors that attenuate the female coronary disease advantage. Arch. Intern. Med. 1995, 155, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisano, B.T.; Zhu, L.; Stafford, J.M. Role of Estrogens in the Regulation of Liver Lipid Metabolism. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1043, 227–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeg, I.-H.; So, S.-H. The world ginseng market and the ginseng (Korea). J. Ginseng. Res. 2013, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, S.-H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, Y.-S.; Hyun, S.H.; Han, C.-K. Red ginseng monograph. J. Ginseng. Res. 2018, 42, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.-K. Panax ginseng—A non-organ-specific cancer preventive? Lancet Oncol. 2001, 2, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.; Suk, K.T.; Bang, C.S.; Yoon, J.H.; Baik, G.H.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, M.J. Anti-inflammatory and antifatigue effect of Korean Red Ginseng in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Ginseng. Res. 2016, 40, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, J.-H. A review on the medicinal potentials of ginseng and ginsenosides on cardiovascular diseases. J. Ginseng. Res. 2014, 38, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Seo, S.K.; Choi, Y.S.; Jeon, Y.E.; Lim, K.J.; Cho, S.; Lee, B.S. Effects of red ginseng supplementation on menopausal symptoms and cardiovascular risk factors in postmenopausal women: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Menopause 2012, 19, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Ji, G.E. The effect of fermented red ginseng on depression is mediated by lipids. Nutr. Neurosci. 2013, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, O.Y.; Lee, J.H. Beneficial effects of Korean red ginseng on lymphocyte DNA damage, antioxidant enzyme activity, and LDL oxidation in healthy participants: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr. J. 2012, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, H.; Kwak, J.H.; Ahn, H.Y.; Shin, D.Y.; Lee, J.H. Korean Red Ginseng Improves Glucose Control in Subjects with Impaired Fasting Glucose, Impaired Glucose Tolerance, or Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufourc, E.J. Sterols and membrane dynamics. J. Chem. Biol. 2008, 1, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollam, J.; Antebi, A. Sterol Regulation of Metabolism, Homeostasis, and Development. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 885–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.S.; Choi, M.H. Cholesterol homeostasis in cardiovascular disease and recent advances in measuring cholesterol signatures. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 153, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, Y.; Rogers, M.A. Sterol Metabolism and Transport in Atherosclerosis and Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Research on the menopause in the 1990s. Report of a WHO Scientific Group. World Health Organ. Tech. Rep. Ser. 1996, 866, 1–107. [Google Scholar]
- Peixoto, A.J. Acute Severe Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.; Nguyen, M.-L.; Patel, R. Hypertension Crisis in the Emergency Department. Cardiol. Clin. 2012, 30, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hoene, M.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Häring, H.-U.; Schleicher, E.D.; Weigert, C.; Xu, G.; Lehmann, R. Simultaneous extraction of metabolome and lipidome with methyl tert-butyl ether from a single small tissue sample for ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1298, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buré, C.; Ayciriex, S.; Testet, E.; Schmitter, J.-M. A single run LC-MS/MS method for phospholipidomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 405, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Mok, H.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Park, S.C.; Kim, G.-S.; Lee, S.-E.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, H.D. UPLC-QqQ/MS-Based Lipidomics Approach To Characterize Lipid Alterations in Inflammatory Macrophages. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, W.J.; Abdel-Khalik, J.; Crick, P.J.; Yutuc, E.; Wang, Y. New methods for analysis of oxysterols and related compounds by LC–MS. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 162, 4–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBose-Boyd, R.A. Feedback regulation of cholesterol synthesis: Sterol-accelerated ubiquitination and degradation of HMG CoA reductase. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Wu, C.; Dou, D.; Chen, Y.; Ogihara, Y. Lipoprotein lipase activation by red Ginseng saponins in hyperlipidemia model animals. Phytomedicine 1999, 6, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, E.; Jeon, B.R.; Jeong, D.-H.; Lee, K.; Goo, Y.-K.; Kim, S.-H.; Sung, C.-K.; Roh, S.-S.; Kim, S.D.; Kim, H.-K.; et al. Black ginseng extract ameliorates hypercholesterolemia in rats. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Lee, N.; Ahn, Y.; Lee, H. Study on improving blood flow with Korean red ginseng substances using digital infrared thermal imaging and Doppler sonography: Randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial with parallel design. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2013, 33, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Jin, Y.; Lim, W.; Ji, S.; Choi, S.; Jang, S.; Lee, S. A ginsenoside-Rh1, a component of ginseng saponin, activates estrogen receptor in human breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 84, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Park, W.; Lee, S.; Ahn, W.; Lee, Y. Ginsenoside-Rb1 from Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer activates estrogen receptor-alpha and -beta, independent of ligand binding. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 3510–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guetta, V.; Cannon, R.O. Cardiovascular Effects of Estrogen and Lipid-Lowering Therapies in Postmenopausal Women. Circulation 1996, 93, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanan, P.; Subramaniyam, S.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Yang, D.-C. Molecular signaling of ginsenosides Rb1, Rg1, and Rg3 and their mode of actions. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, M.-S.; Kim, C.-T.; Kim, I.-H.; Kim, Y. Ginsenoside Rg3 Reduces Lipid Accumulation with AMP-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) Activation in HepG2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 5729–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemot-Legris, O.; Mutemberezi, V.; Muccioli, G.G. Oxysterols in Metabolic Syndrome: From Bystander Molecules to Bioactive Lipids. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 594–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkkonen, V.M.; Béaslas, O.; Nissilä, E. Oxysterols and Their Cellular Effectors. Biomolecules 2012, 2, 76–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, S.; Gamba, P.; Testa, G.; Leonarduzzi, G.M.; Poli, G. The role of oxysterols in vascular ageing. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 2095–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkhem, I.; Diczfalusy, U. Oxysterols: Friends, foes, or just fellow passengers? Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-B.; An, Y.R.; Kim, S.J.; Park, H.-W.; Jung, J.-W.; Kyung, J.-S.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, Y.-S. Lipid metabolic effect of Korean red ginseng extract in mice fed on a high-fat diet. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 92, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Yuan, H.D.; Chung, I.K.; Chung, S.H. Compound K, Intestinal Metabolite of Ginsenoside, Attenuates Hepatic Lipid Accumulation via AMPK Activation in Human Hepatoma Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1532–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Yoon, H.; Park, H.-M.; Song, B.C.; Yeum, K.-J. Implications of red Panax ginseng in oxidative stress associated chronic diseases. J. Ginseng. Res. 2017, 41, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.-H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, C.-B.; Kim, J.-Y.; Shin, S.-H.; Park, J.-K. Effects of ginseng on peripheral blood mitochondrial DNA copy number and hormones in men with metabolic syndrome: A randomized clinical and pilot study. Complement. Ther. Med. 2016, 24, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Ginseng | Placebo | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 36 | 32 | |
| Age, years | 55.9 ± 5.9 | 58.1 ± 4.7 | 0.093 |
| Physical measurement | |||
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 24.3 ± 3.2 | 24.5 ± 3.7 | 0.741 |
| Waist circumference, cm | 82.5 ± 8.7 | 82.6 ± 10.2 | 0.950 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 119.8 ± 13.5 | 116.8 ± 16.5 | 0.409 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 76.7 ± 9.7 | 72.2 ± 9.3 | 0.065 |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 76.8 ± 9.6 | 75.4 ± 11.4 | 0.585 |
| WBC(×103 L) | 5.7 ± 1.4 | 5.8 ± 1.6 | 0.786 |
| AST (IU/L) | 24.5 ± 7.0 | 25.2 ± 6.0 | 0.654 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 21.7 ± 12.6 | 20.5 ± 7.8 | 0.629 |
| Comorbid condition, n (%) | |||
| Hypertension | 5 (13.9) | 5 (15.6) | 0.572 |
| Diabetes | 2 (5.6) | 1 (3.1) | 0.535 |
| Physical activity, n (%) | 15 (41.7) | 10 (31.3) | 0.374 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 2 (5.6) | 1 (3.1) | 0.534 |
| Alcohol consumption, n (%) | 9 (25.0) | 10(13.2) | 0.567 |
| Sterols | |||
| Cholesterol (nmol/mL) | 1634.5 ± 409.3 | 1510.6 ± 339.2 | 0.182 |
| Plant sterols (nmol/mL) | |||
| Sitosterol | 8.2 ± 8.0 | 6.0 ± 3.2 | 0.159 |
| Campesterol | 11.3 ± 12.6 | 8.5 ± 4.8 | 0.245 |
| Cholesterol precursor (nmol/mL) | |||
| Lanosterol | 2.9 ± 1.2 | 3.0 ± 1.2 | 0.626 |
| Desmosterol | 9.6 ± 2.4 | 10.7 ± 13.8 | 0.622 |
| 7-Dehydrocholesterol | 6.2 ± 1.7 | 9.4 ± 22.2 | 0.392 |
| Oxysterols (nmol/mL) | |||
| 7-Hydroxycholesterol | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.2 | 0.123 |
| Cholesterol esters (nmol/mL) | |||
| CE 14:0 | 14.6 ± 15.0 | 16.9 ± 19.0 | 0.572 |
| CE 20:4 | 111.9 ± 124.8 | 99.1 ± 112.3 | 0.659 |
| Ginseng | Placebo | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic Parameters | Baseline | After 4 Weeks | p † | Change | Baseline | After 4 Weeks | p † | Change | p ‡ |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.3 ± 3.2 | 24.4 ± 3.0 | 0.315 | 0.1 ± 0.8 | 24.5 ± 3.7 | 24.5 ± 4.0 | 0.986 | −0.00 ± 0.8 | 0.473 |
| WC (cm) | 82.5 ± 8.7 | 83.3 ± 8.8 | 0.145 | 0.9 ± 3.4 | 82.6 ± 10.2 | 83.1 ± 10.2 | 0.494 | 0.5 ± 3.7 | 0.648 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 119.8 ± 13.5 | 116.6 ± 15.1 | 0.056 | −3.2 ± 9.7 | 116.8 ± 16.5 | 116.8 ± 17.5 | 0.989 | 0.03 ± 12.6 | 0.239 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 76.7 ± 9.7 | 73.1 ± 8.8 | 0.017 | −3.6 ± 8.7 | 72.4 ± 9.3 | 71.6 ± 11.4 | 0.661 | −0.8 ± 10.0 | 0.212 |
| HR (bpm) | 76.8 ± 9.6 | 76.1 ± 11.2 | 0.555 | −0.3 ± 1.2 | 75.4 ± 11.4 | 74.7 ± 12.5 | 0.771 | −0.7 ± 7.0 | 0.988 |
| WBC L) | 5.7 ± 1.4 | 5.5 ± 1.4 | 0.828 | −0.05 ± 1.3 | 5.8 ± 1.6 | 5.5 ± 1.2 | 0.239 | −0.3 ± 1.2 | 0.487 |
| AST (IU/L) | 24.5 ± 7.0 | 25.9 ± 18.2 | 0.659 | 1.4 ± 19.5 | 25.2 ± 6.0 | 25.9 ± 7.9 | 0.602 | 0.7 ± 7.7 | 0.844 |
| ALT(IU/L) | 21.7 ± 12.6 | 21.8 ± 21.8 | 0.989 | 0.1 ± 23.9 | 20.5 ± 7.8 | 19.8 ± 10.5 | 0.720 | −0.7 ± 10.7 | 0.872 |
| Ginseng | Placebo | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sterols (nmol/mL) | Baseline | After 4 Weeks | p † | Change | Baseline | After 4 Weeks | p † | Change | p ‡ | p |
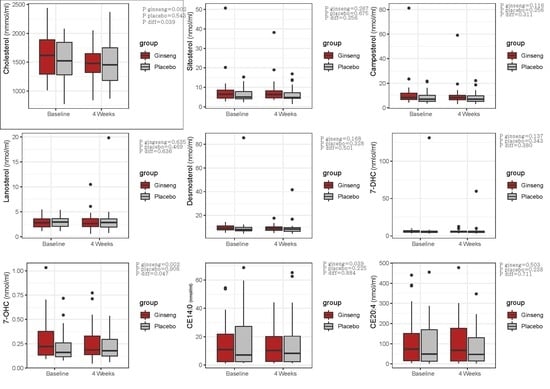
| Cholesterol | 1634.4 ± 409.4 | 1486.1 ± 312.8 | 0.002 | −148.3 ± 261.1 | 1510.6 ± 339.2 | 1486.6 ± 338.0 | 0.543 | −23.0 ± 220.5 | 0.039 | 0.047 |
| Sitosterol | 8.2 ± 8.0 | 7.7 ± 6.1 | 0.267 | −0.5 ± 0.09 | 6.0 ± 3.2 | 6.1 ± 3.6 | 0.675 | 0.1 ± 1.5 | 0.256 | 0.804 |
| Campesterol | 11.3 ± 12.6 | 10.1 ± 9.0 | 0.116 | −1.1 ± 4.2 | 8.5 ± 4.8 | 8.2 ± 4.6 | 0.256 | −0.3 ± 1.6 | 0.311 | 0.937 |
| Lanosterol | 2.9 ± 1.2 | 3.0 ± 1.7 | 0.635 | 0.1 ± 1.6 | 3.0 ± 1.2 | 3.4 ± 3.2 | 0.469 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 0.636 | 0.568 |
| Desmosterol | 9.6 ± 2.4 | 9.1 ± 2.5 | 0.168 | −0.5 ± 2.0 | 10.7 ± 13.8 | 9.3 ± 6.3 | 0.328 | −1.4 ± 8.0 | 0.501 | 0.551 |
| 7-DHC | 6.2 ± 1.7 | 5.9 ± 1.8 | 0.137 | −0.3 ± 1.1 | 9.4 ± 22.2 | 7.2 ± 9.7 | 0.343 | −2.1 ± 12.7 | 0.380 | 0.829 |
| 7-OHC | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.2 ± 0.2 | 0.002 | −0.05 ± 0.09 | 0.2 ± 0.6 | 0.2 ± 1.4 | 0.908 | −0.002 ± 0.1 | 0.047 | 0.063 |
| CE14:0 | 14.6 ± 14.9 | 13.1 ± 12.8 | 0.393 | −1.4 ± 9.9 | 16.9 ± 19.0 | 15.2 ± 17.4 | 0.225 | −1.8 ± 8.0 | 0.884 | 0.896 |
| CE20:4 | 111.9 ± 124.8 | 102.8 ± 107.6 | 0.503 | −9.1 ± 80.9 | 99.1 ± 112.3 | 82.9 ± 88.1 | 0.238 | −16.2 ± 76.2 | 0.711 | 0.459 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, Y.-J.; Jang, S.-N.; Liu, K.-H.; Jung, D.-H. Effect of Korean Red Ginseng on Cholesterol Metabolites in Postmenopausal Women with Hypercholesterolemia: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113423
Kwon Y-J, Jang S-N, Liu K-H, Jung D-H. Effect of Korean Red Ginseng on Cholesterol Metabolites in Postmenopausal Women with Hypercholesterolemia: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2020; 12(11):3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113423
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Yu-Jin, Su-Nyeong Jang, Kwang-Hyeon Liu, and Dong-Hyuk Jung. 2020. "Effect of Korean Red Ginseng on Cholesterol Metabolites in Postmenopausal Women with Hypercholesterolemia: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial" Nutrients 12, no. 11: 3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113423
APA StyleKwon, Y.-J., Jang, S.-N., Liu, K.-H., & Jung, D.-H. (2020). Effect of Korean Red Ginseng on Cholesterol Metabolites in Postmenopausal Women with Hypercholesterolemia: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 12(11), 3423. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113423