Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease with Low and Very Low GFR: Can a Low-Protein Diet Supplemented with Ketoanalogues Delay Dialysis?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
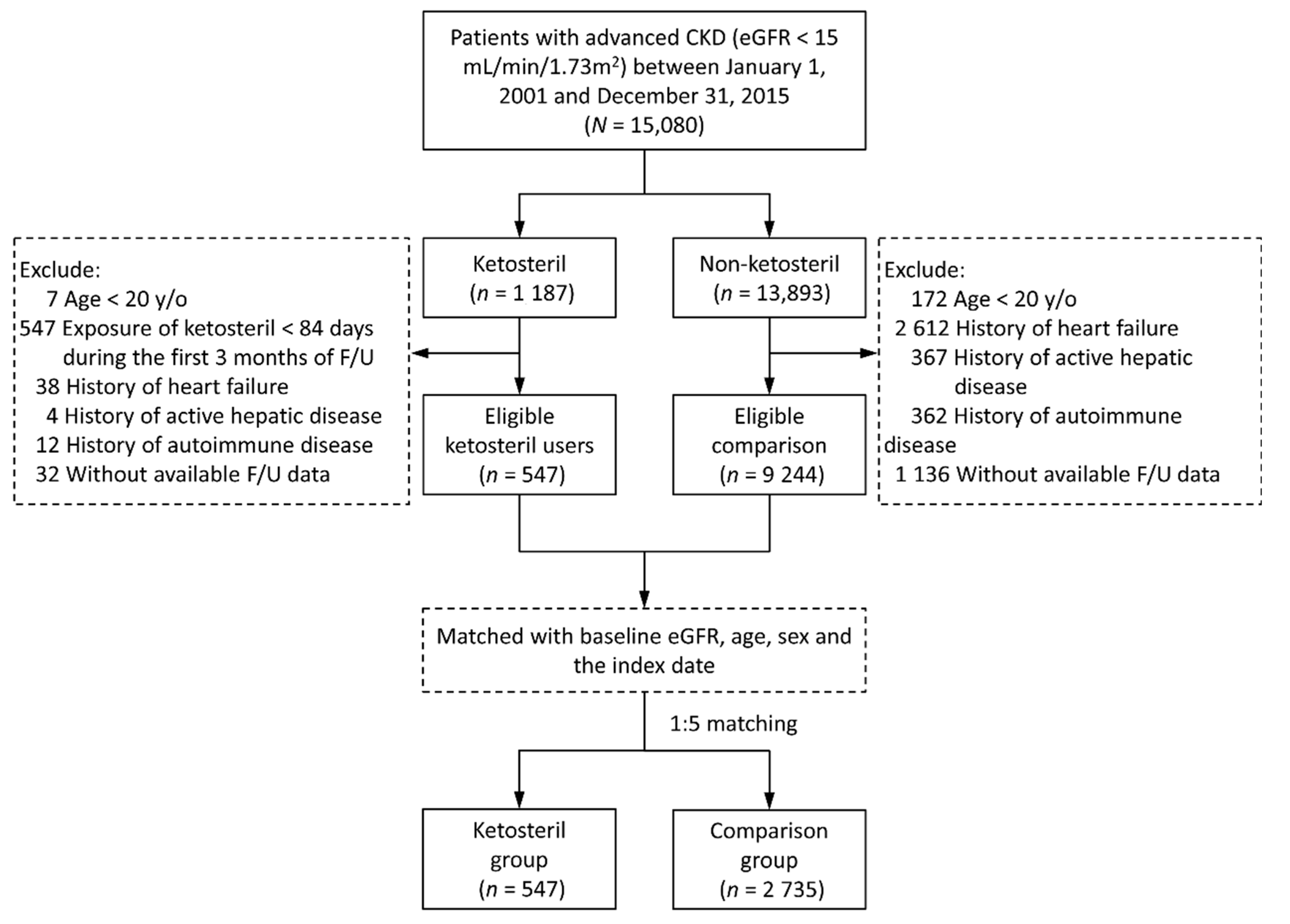
2.2. Patient Selection and Study Design
2.3. Covariates
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
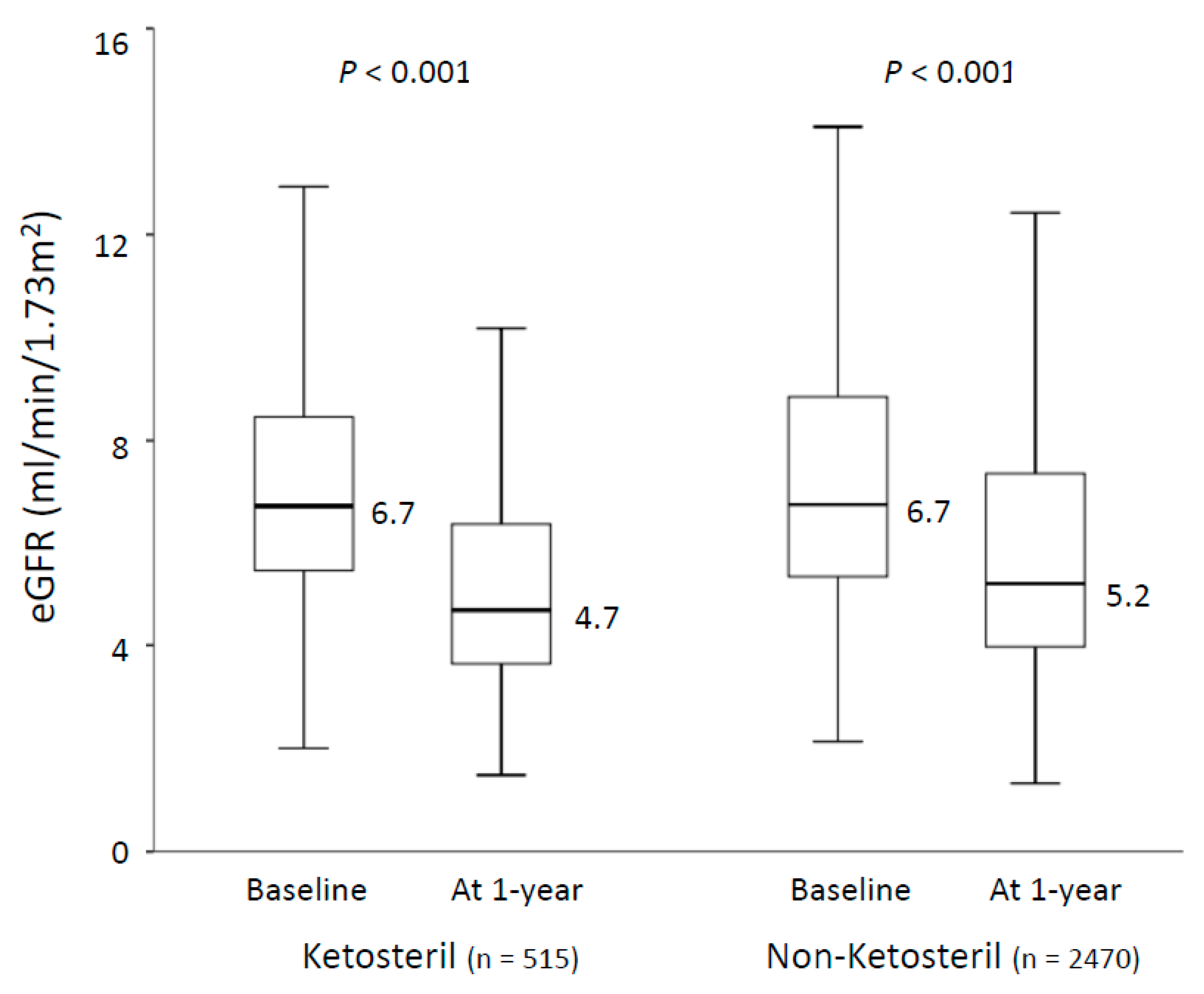
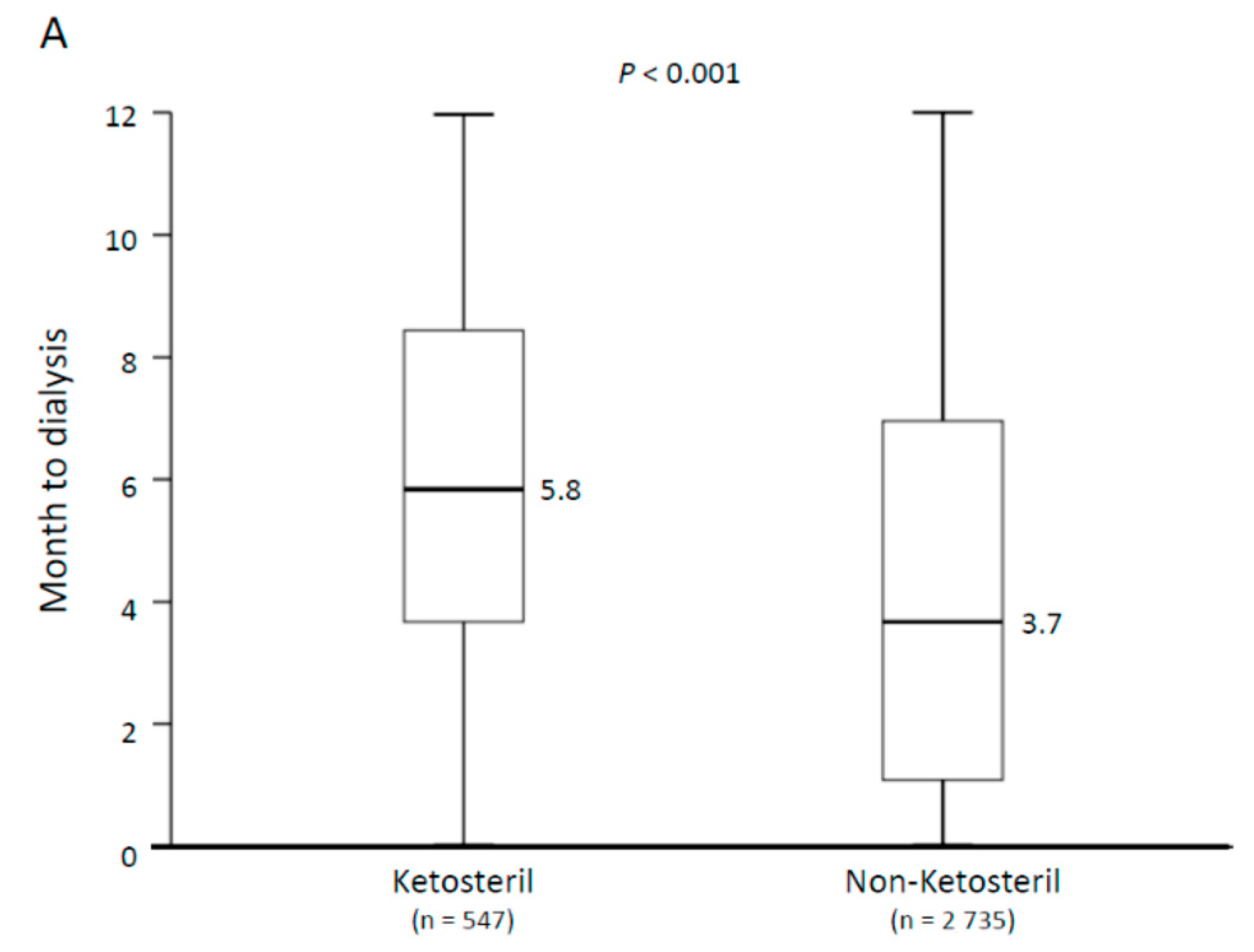
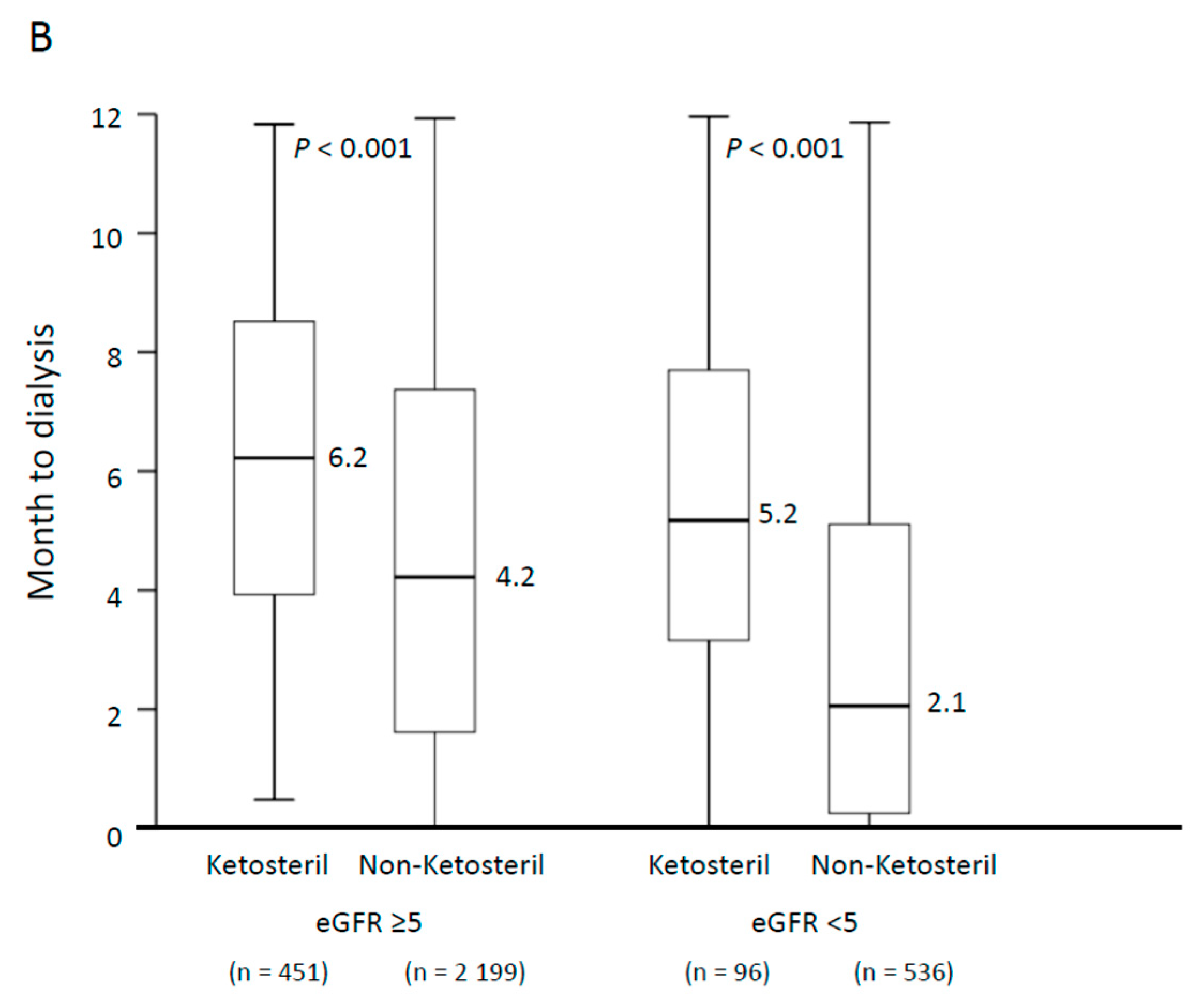
3.2. Outcomes during 1 Year Follow-Up
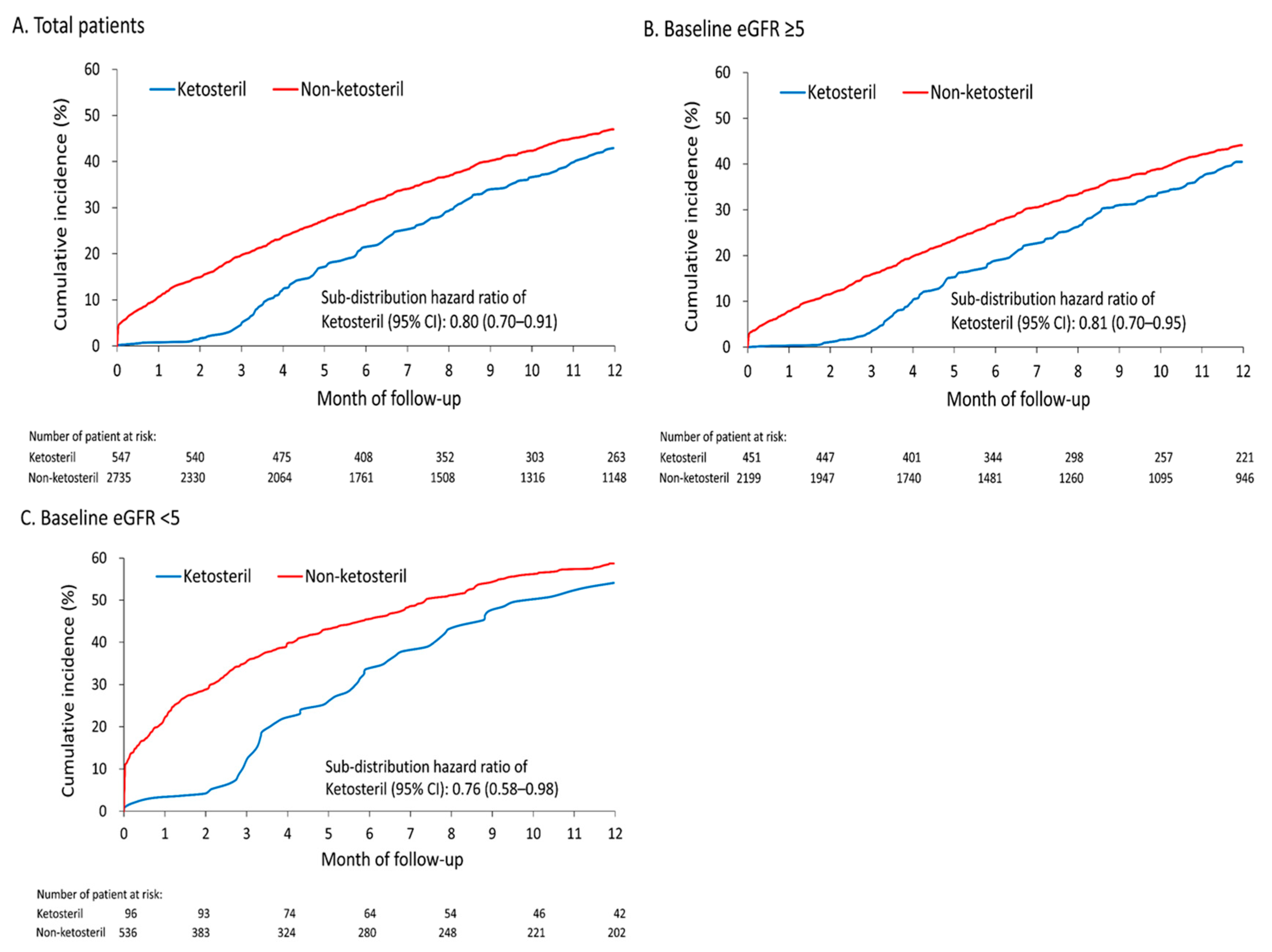
3.3. Risk of Dialysis across Different Baseline eGFRs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Addis, T.; Lew, W. Diet and Death in Acute Uremia. J. Clin. Investig. 1939, 18, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, D.S. On the Influence of a Diet with High Protein Content on the Kidney. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1921, 11, 682–683. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cuppari, L.; Meireles, M.S.; Ramos, C.I.; Kamimura, M.A. Subjective Global Assessment for the Diagnosis of Protein–Energy Wasting in Nondialysis-Dependent Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2014, 24, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walser, M. Ketoacids in the treatment of uremia. Clin. Nephrol. 1975, 3, 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C.W.; Tungsanga, K.; Walser, M. Effect of the level of dietary protein on the utilization of alpha-ketoisocaproate for protein synthesis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1986, 43, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, P.; Pande, D.P.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, D.; Bal, C.S.; Kulkarni, H. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate efficacy of ketodiet in predialytic chronic renal failure. J. Ren. Nutr. 2004, 14, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Kidney Foundation Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative. Clinical practice guidelines for nutrition in chronic renal failure. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 35, S1–S140. [Google Scholar]
- Walser, M.; Hill, S.B.; Ward, L.; Magder, L. A crossover comparison of progression of chronic renal failure: Ketoacids versus amino acids. Kidney Int. 1993, 43, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jiang, N.; Qian, J.; Sun, W.; Lin, A.; Cao, L.; Wang, Q.; Ni, Z.; Wan, Y.; Linholm, B.; Axelsson, J.; et al. Better preservation of residual renal function in peritoneal dialysis patients treated with a low-protein diet supplemented with keto acids: A prospective, randomized trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2551–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellizzi, V.; Chiodini, P.; Cupisti, A.; Viola, B.F.; Pezzotta, M.; De Nicola, L.; Minutolo, R.; Barsotti, G.; Piccoli, G.B.; Di Iorio, B. Very low-protein diet plus ketoacids in chronic kidney disease and risk of death during end-stage renal disease: A historical cohort controlled study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Yang, Y.-W.; Hung, S.-C.; Kuo, K.-L.; Wu, K.-D.; Wu, V.-C.; Hsieh, T.-C.; National Taiwan University Study Group on Acute Renal Failure (NSARF). Ketoanalogues supplementation decreases dialysis and mortality risk in patients with anemic advanced chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianciaruso, B.; Pota, A.; Pisani, A.; Torraca, S.; Annecchini, R.; Lombardi, P.; Capuano, A.; Nazzaro, P.; Bellizzi, V.; Sabbatini, M. Metabolic effects of two low protein diets in chronic kidney disease stage 4-5--a randomized controlled trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, G.B.; Nazha, M.; Capizzi, I.; Vigotti, F.N.; Mongilardi, E.; Bilocati, M.; Avagnina, P.; Versino, E. Patient Survival and Costs on Moderately Restricted Low-Protein Diets in Advanced CKD: Equivalent Survival at Lower Costs? Nutrients 2016, 8, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.-L.; Tu, K.-H.; Lin, M.-S.; Chang, S.-W.; Fan, P.-C.; Hsiao, C.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Hsu, H.-H.; Tian, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-H. Does a Supplemental Low-Protein Diet Decrease Mortality and Adverse Events After Commencing Dialysis? A Nationwide Cohort Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klahr, S.; Levey, A.S.; Beck, G.J.; Caggiula, A.W.; Hunsicker, L.; Kusek, J.W.; Striker, G. The Effects of Dietary Protein Restriction and Blood-Pressure Control on the Progression of Chronic Renal Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianciaruso, B.; Capuano, A.; D’Amaro, E.; Ferrara, N.; Nastasi, A.; Conte, G.; Bellizzi, V.; Andreucci, V.E. Dietary compliance to a low protein and phosphate diet in patients with chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1989, 27, 173–176. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, M.-S.; Lin, M.-H.; Lee, C.-P.; Yang, Y.-H.; Chen, W.-C.; Chang, G.-H.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Chen, P.-C.; Tsai, Y.-H. Chang Gung Research Database: A multi-institutional database consisting of original medical records. Biomed. J. 2017, 40, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Chan, Y.; Yang, Y.K.; Lin, S.; Hung, M.; Chien, R.; Lai, C.; Lai, E.C. The Chang Gung Research Database—A multi-institutional electronic medical records database for real-world epidemiological studies in Taiwan. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2019, 28, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiske, B.L.; Lakatua, J.D.; Ma, J.Z.; Louis, T.A. A meta-analysis of the effects of dietary protein restriction on the rate of decline in renal function. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1998, 31, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laville, M.; Boissel, J.-P. Low protein diets for chronic kidney disease in non diabetic adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, CD001892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrini, M.T.; Levey, A.S.; Lau, J.; Chalmers, T.C.; Wang, P.H. The Effect of Dietary Protein Restriction on the Progression of Diabetic and Nondiabetic Renal Diseases. Ann. Intern. Med. 1996, 124, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvy, D.; Maingourd, C.; Pengloan, J.; Bagros, P.; Nivet, H. Effects of severe protein restriction with ketoanalogues in advanced renal failure. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1999, 18, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iorio, B.; Di Micco, L.; Torraca, S.; Sirico, M.L.; Russo, L.; Pota, A.; Mirenghi, F.; Russo, D. Acute Effects of Very-Low-Protein Diet on FGF23 Levels: A Randomized Study. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garneata, L.; Stancu, A.; Dragomir, D.; Stefan, G.; Mircescu, G. Ketoanalogue-Supplemented Vegetarian Very Low–Protein Diet and CKD Progression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2164–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunori, G.; Viola, B.F.; Parrinello, G.; De Biase, V.; Como, G.; Franco, V.; Garibotto, G.; Zubani, R.; Cancarini, G.C. Efficacy and Safety of a Very-Low-Protein Diet When Postponing Dialysis in the Elderly: A Prospective Randomized Multicenter Controlled Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2007, 49, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, V.; Gul, A.; Sarnak, M.J. Cardiovascular risk factors in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.I.C.; Tang, M.; Djurdjev, O.; Langsford, D.; Sood, M.M.; Levin, A. Infection in advanced chronic kidney disease leads to increased risk of cardiovascular events, end-stage kidney disease and mortality. Kidney Int. 2016, 90, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mircescu, G.; Gârneaţă, L.; Stancu, S.; Capuşă, C. Effects of a Supplemented Hypoproteic Diet in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2007, 17, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, S.; Fouque, D.; Laville, M.; Zech, P. Effects of low-protein diet supplemented with ketoacids on plasma lipids in adult chronic renal failure. Miner. Electrolyte Metab. 1996, 22, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bellizzi, V.; Di Iorio, B.; De Nicola, L.; Minutolo, R.; Zamboli, P.; Trucillo, P.; Catapano, F.; Di Cristofano, C.; Scalfi, L.; Conte, G.; et al. Very low protein diet supplemented with ketoanalogs improves blood pressure control in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauveau, P.; Combe, C.; Rigalleau, V.; Vendrely, B.; Aparicio, M. Restricted Protein Diet Is Associated With Decrease in Proteinuria: Consequences on the Progression of Renal Failure. J. Ren. Nutr. 2007, 17, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Valid N | Ketosteril Group (n = 547) | Non- Ketosteril Group (n = 2735) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex | 3282 | 278 (50.8) | 1383 (50.6) | 0.913 |
| Age (years) | 3282 | 62.2 (53.3, 72.0) | 62.7 (53.7, 71.7) | 0.777 |
| Baseline comorbidity | ||||
| Diabetes | 3282 | 224 (41.0) | 1122 (41.0) | 0.975 |
| Hepatitis B virus infection | 3282 | 5 (0.9) | 10 (0.4) | 0.083 |
| Hepatitis C virus infection | 3282 | 6 (1.1) | 3 (0.1) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 3282 | 366 (66.9) | 1758 (64.3) | 0.240 |
| Renal function | ||||
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 3282 | 6.7 (5.4, 8.5) | 6.7 (5.3, 8.8) | 0.830 |
| Baseline eGFR < 10 (%) | 3282 | 477 (87.2) | 2322 (84.9) | 0.165 |
| Baseline eGFR < 5 (%) | 3282 | 96 (17.6) | 536 (19.6) | 0.268 |
| Albumin/creatinine ratio (mg/d) | 152 | 2072 (1106, 3448) | 1857 (575, 4029) | 0.842 |
| Urine protein (U)/creatinine ratio (mg/d) | 556 | 2053 (1104, 4987) | 2688 (1046, 5640) | 0.440 |
| Laboratory data | ||||
| HbA1c (%) | 1420 | 6.2 (5.6, 7.0) | 6.3 (5.7, 7.2) | 0.174 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 1674 | 172 (146, 196) | 170 (144, 199) | 0.556 |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 1652 | 118 (83, 185) | 123 (86, 181) | 0.692 |
| Antihypertensive therapy | ||||
| Antihypertensive drugs | 3282 | 366 (66.9) | 1758 (64.3) | 0.240 |
| ACEIs/ARBs | 3282 | 324 (59.2) | 1318 (48.2) | <0.001 |
| Nitrogen waste products | ||||
| Serum urea (mg/dL) | 3055 | 77.6 (62.0, 93.5) | 74.0 (58.0, 93.0) | 0.022 |
| Serum uric acid (mg/dL) | 2036 | 7.6 (6.6, 8.8) | 7.5 (6.4, 8.9) | 0.434 |
| Acid-base balance | ||||
| Serum bicarbonate (mEq/L) | 1542 | 19.5 (17.0, 22.0) | 20.4 (17.6, 22.8) | 0.008 |
| Calcium-phosphorus metabolism | ||||
| Serum calcium (mg/dL) | 2839 | 8.6 (8.2, 8.9) | 8.6 (8.1, 9.1) | 0.106 |
| Serum phosphates (mg/dL) | 2725 | 5.1 (4.3, 5.8) | 5.1 (4.3, 5.9) | 0.951 |
| Calcium supplementation | 3282 | 145 (26.5) | 566 (20.7) | 0.003 |
| Vitamin D therapy | 3282 | 62 (11.3) | 174 (6.4) | <0.001 |
| Unadjusted Analysis | Adjusted Analysis # | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome | Ketosteril Group (n = 547) | Non-Ketosteril Group (n = 2735) | HR or SHR of Ketosteril (95% CI) | p Value | HR or SHR of Ketosteril (95% CI) | p Value |
| Primary outcome: dialysis | 220 (40.2) | 1215 (44.4) | 0.80 (0.70–0.91) | 0.001 | 0.73 (0.64–0.84) | <0.001 |
| Secondary outcome: | ||||||
| All-cause mortality | 10 (1.8) | 67 (2.4) | 0.73 (0.38–1.43) | 0.362 | 0.74 (0.38–1.43) | 0.367 |
| Acute myocardial infarction | 7 (1.3) | 63 (2.3) | 0.55 (0.25–1.19) | 0.129 | 0.50 (0.23–1.11) | 0.088 |
| Ischemic stroke | 6 (1.1) | 46 (1.7) | 0.64 (0.28–1.50) | 0.309 | 0.61 (0.26–1.42) | 0.253 |
| MACCE * | 20 (3.7) | 160 (5.9) | 0.61 (0.38–0.97) | 0.035 | 0.58 (0.36–0.92) | 0.021 |
| Infection-related hospitalization | 85 (15.5) | 479 (17.5) | 0.86 (0.68–1.08) | 0.193 | 0.83 (0.66–1.05) | 0.126 |
| Heart failure hospitalization | 15 (2.7) | 95 (3.5) | 0.78 (0.45–1.34) | 0.362 | 0.73 (0.42–1.25) | 0.247 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yen, C.-L.; Fan, P.-C.; Lee, C.-C.; Kuo, G.; Tu, K.-H.; Chen, J.-J.; Lee, T.-H.; Hsu, H.-H.; Tian, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-H. Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease with Low and Very Low GFR: Can a Low-Protein Diet Supplemented with Ketoanalogues Delay Dialysis? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3358. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113358
Yen C-L, Fan P-C, Lee C-C, Kuo G, Tu K-H, Chen J-J, Lee T-H, Hsu H-H, Tian Y-C, Chang C-H. Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease with Low and Very Low GFR: Can a Low-Protein Diet Supplemented with Ketoanalogues Delay Dialysis? Nutrients. 2020; 12(11):3358. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113358
Chicago/Turabian StyleYen, Chieh-Li, Pei-Chun Fan, Cheng-Chia Lee, George Kuo, Kun-Hua Tu, Jia-Jin Chen, Tao-Han Lee, Hsiang-Hao Hsu, Ya-Chun Tian, and Chih-Hsiang Chang. 2020. "Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease with Low and Very Low GFR: Can a Low-Protein Diet Supplemented with Ketoanalogues Delay Dialysis?" Nutrients 12, no. 11: 3358. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113358
APA StyleYen, C.-L., Fan, P.-C., Lee, C.-C., Kuo, G., Tu, K.-H., Chen, J.-J., Lee, T.-H., Hsu, H.-H., Tian, Y.-C., & Chang, C.-H. (2020). Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease with Low and Very Low GFR: Can a Low-Protein Diet Supplemented with Ketoanalogues Delay Dialysis? Nutrients, 12(11), 3358. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113358





