Role of Glutathionylation in Infection and Inflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
Glutathione, Cellular Thiols, and Glutathionylation
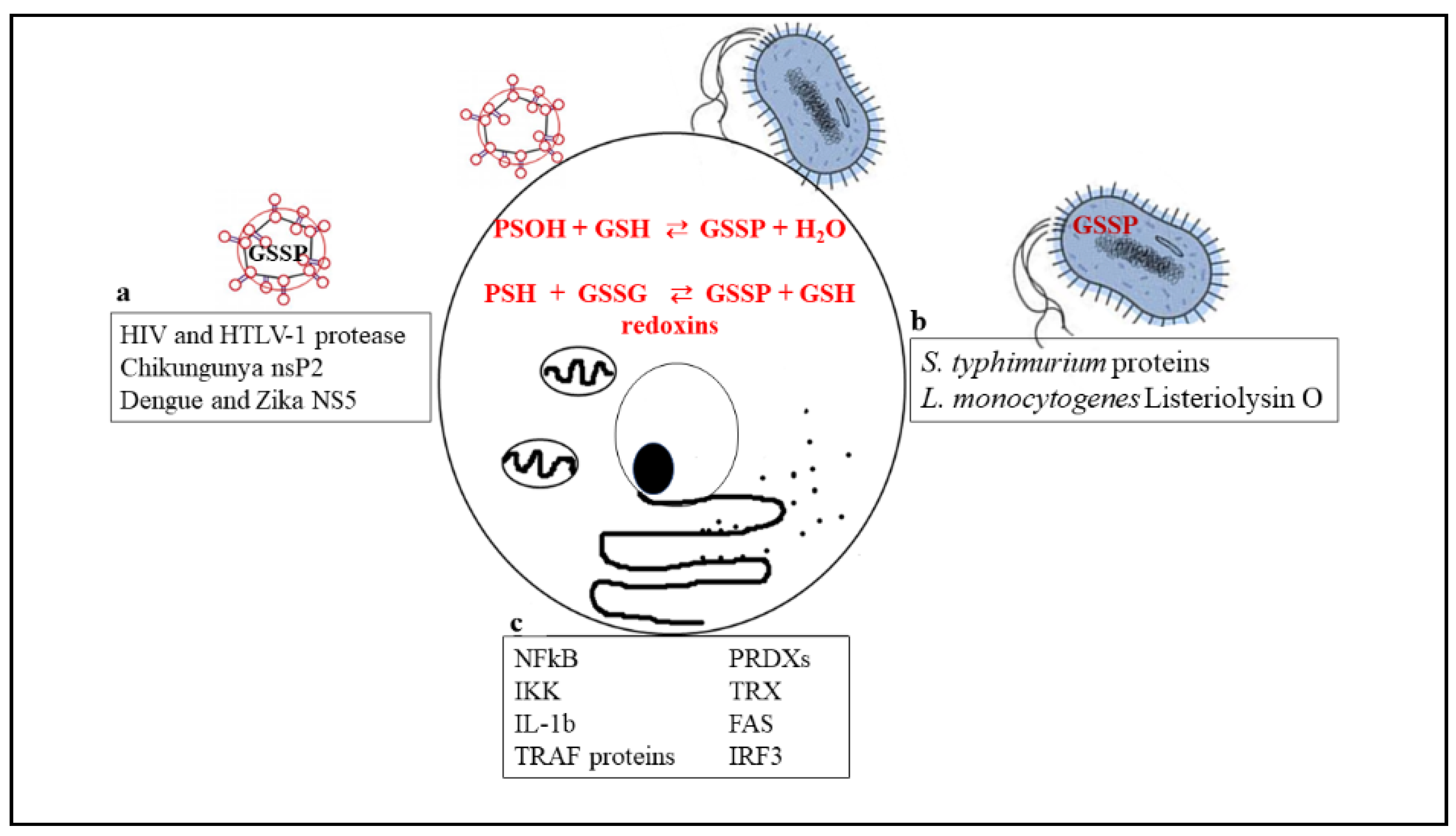
2. Glutathionylation in Infections
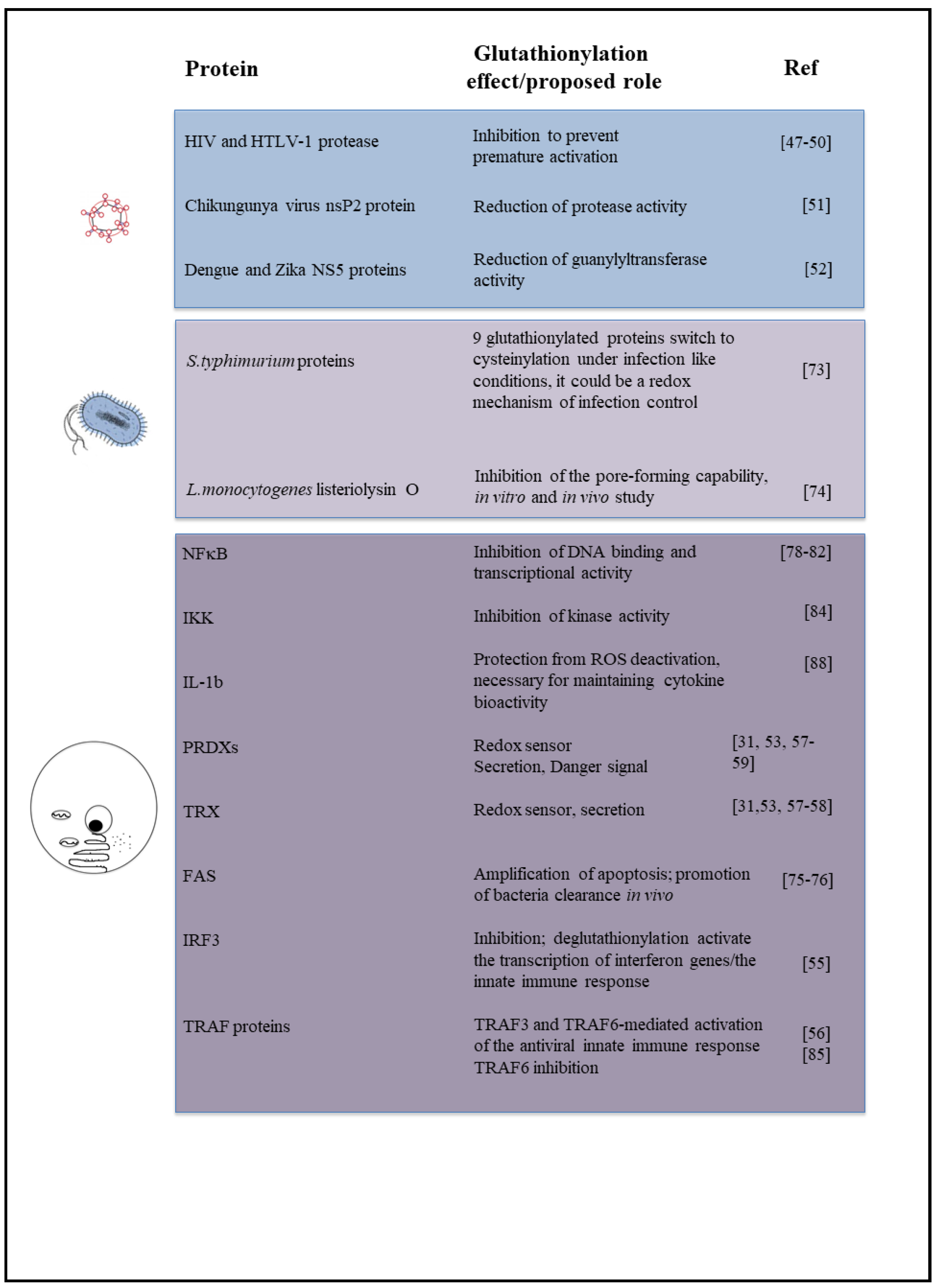
2.1. Viral Infections
2.2. Bacteria
3. Glutathionylation in Inflammation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meister, A. On the discovery of glutathione. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1988, 13, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, D.A.; Forman, H.J. Cellular glutathione and thiols metabolism. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 64, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H.; Rinna, A. Glutathione: Overview of its protective roles, measurement, and biosynthesis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2009, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquilano, K.; Baldelli, S.; Ciriolo, M.R. Glutathione: New roles in redox signaling for an old antioxidant. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratelli, M.; Goodwin, L.O.; Orom, U.A.; Lombardi, S.; Tonelli, R.; Mengozzi, M.; Ghezzi, P. Gene expression profiling reveals a signaling role of glutathione in redox regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13998–14003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diotallevi, M.; Checconi, P.; Palamara, A.T.; Celestino, I.; Coppo, L.; Holmgren, A.; Abbas, K.; Peyrot, F.; Mengozzi, M.; Ghezzi, P. Glutathione fine-tunes the innate immune response toward antiviral pathways in a macrophage cell line independently of its antioxidant properties. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, F.Q.; Buettner, G.R. Redox environment of the cell as viewed through the redox state of the glutathione disulfide/glutathione couple. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 30, 1191–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.G.; Kang, S.W.; Jeong, W.; Chang, T.S.; Yang, K.S.; Woo, H.A. Intracellular messenger function of hydrogen peroxide and its regulation by peroxiredoxins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005, 17, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, H.J.; Maiorino, M.; Ursini, F. Signaling functions of reactive oxygen species. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinho, H.S.; Real, C.; Cyrne, L.; Soares, H.; Antunes, F. Hydrogen peroxide sensing, signaling and regulation of transcription factors. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. Hydrogen peroxide as a central redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress: Oxidative eustress. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marzo, N.; Chisci, E.; Giovannoni, R. The role of hydrogen peroxide in redox-dependent signaling: Homeostatic and pathological responses in mammalian cells. Cells 2018, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, T. Signal transduction by reactive oxygen species. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 194, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratelli, M.; Demol, H.; Puype, M.; Casagrande, S.; Eberini, I.; Salmona, M.; Bonetto, V.; Mengozzi, M.; Duffieux, F.; Miclet, E.; et al. Identification by redox proteomics of glutathionylated proteins in oxidatively stressed human T lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3505–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filomeni, G.; Rotilio, G.; Ciriolo, M.R. Disulfide relays and phosphorylative cascades: Partners in redox-mediated signaling pathways. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigelius, R.; Lenzen, R.; Sies, H. Increase in hepatic mixed disulphide and glutathione disulphide levels elicited by paraquat. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1982, 31, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigelius, R.; Muckel, C.; Akerboom, T.P.; Sies, H. Identification and quantitation of glutathione in hepatic protein mixed disulfides and its relationship to glutathione disulfide. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1983, 32, 2529–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H.; Brigelius, R.; Graf, P. Hormones, glutathione status and protein S-thiolation. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1987, 26, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, D.; Rossi, R.; Milzani, A.; Colombo, R.; Dalle-Donne, I. S-glutathionylation: From redox regulation of protein functions to human diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2004, 8, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, P.; Bonetto, V.; Fratelli, M. Thiol-disulfide balance: From the concept of oxidative stress to that of redox regulation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillig, C.H.; Berndt, C. Glutaredoxins in thiol/disulfide exchange. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1654–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelton, M.D.; Chock, P.B.; Mieyal, J.J. Glutaredoxin: Role in reversible protein s-glutathionylation and regulation of redox signal transduction and protein translocation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 348–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezzi, P. Protein glutathionylation in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3165–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastore, A.; Piemonte, F. S-Glutathionylation signaling in cell biology: Progress and prospects. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 46, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle-Donne, I.; Rossi, R.; Colombo, G.; Giustarini, D.; Milzani, A. Protein S-glutathionylation: A regulatory device from bacteria to humans. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2009, 34, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, M.A.; Handy, J.; Levander, O.A. The role of oxidative stress in viral infections. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 917, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, T. Role of free radicals in viral pathogenesis and mutation. Rev. Med. Virol. 2001, 11, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Valuev-Elliston, V.T.; Ivanova, O.N.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Starodubova, E.S.; Bartosch, B.; Isaguliants, M.G. Oxidative stress during HIV infection: Mechanisms and consequences. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 8910396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limongi, D.; Baldelli, S. Redox imbalance and viral infections in neurodegenerative diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 6547248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anticoli, S.; Amatore, D.; Matarrese, P.; De Angelis, M.; Palamara, A.T.; Nencioni, L.; Ruggieri, A. Counteraction of HCV-induced oxidative stress concurs to establish chronic infection in liver cell cultures. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 6452390. [Google Scholar]
- Checconi, P.; Salzano, S.; Bowler, L.; Mullen, L.; Mengozzi, M.; Hanschmann, E.M.; Lillig, C.H.; Sgarbanti, R.; Panella, S.; Nencioni, L.; et al. Redox proteomics of the inflammatory secretome identifies a common set of redoxins and other glutathionylated proteins released in inflammation, influenza virus infection and oxidative stress. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgarbanti, R.; Nencioni, L.; Amatore, D.; Coluccio, P.; Fraternale, A.; Sale, P.; Mammola, C.L.; Carpino, G.; Gaudio, E.; Magnani, M.; et al. Redox regulation of the influenza hemagglutinin maturation process: A new cell-mediated strategy for anti-influenza therapy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nencioni, L.; Sgarbanti, R.; Amatore, D.; Checconi, P.; Celestino, I.; Limongi, D.; Anticoli, S.; Palamara, A.T.; Garaci, E. Intracellular redox signaling as therapeutic target for novel antiviral strategy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 3898–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlahos, R.; Stambas, J.; Bozinovski, S.; Broughton, B.R.; Drummond, G.R.; Selemidis, S. Inhibition of Nox2 oxidase activity ameliorates influenza A virus-induced lung inflammation. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, E.E.; Vlahos, R.; Luong, R.; Halls, M.L.; Reading, P.C.; King, P.T.; Chan, C.; Drummond, G.R.; Sobey, C.G.; Broughton, B.R.S.; et al. Endosomal NOX2 oxidase exacerbates virus pathogenicity and is a target for antiviral therapy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomich, O.A.; Kochetkov, S.N.; Bartosch, B.; Ivanov, A.V. Redox biology of respiratory viral infections. Viruses 2018, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzarri, B.M.; Botta, L.; Capecchi, E.; Celestino, I.; Checconi, P.; Palamara, A.T.; Nencioni, L.; Saladino, R. Regioselective IBX-mediated synthesis of coumarin derivatives with antioxidant and anti-influenza activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 3248–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, T.; Maeda, H. Nitric oxide and virus infection. Immunology 2000, 101, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Akaike, T.; Hamamoto, T.; Suzuki, F.; Hirano, T.; Maeda, H. Oxygen radicals in influenza-induced pathogenesis and treatment with pyran polymer-conjugated SOD. Science 1989, 244, 974–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamara, A.T.; Perno, C.F.; Ciriolo, M.R.; Dini, L.; Balestra, E.; D’Agostini, C.; Di Francesco, P.; Favalli, C.; Rotilio, G.; Garaci, E. Evidence for antiviral activity of glutathione: In vitro inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 replication. Antivir. Res. 1995, 27, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamara, A.T.; Perno, C.F.; Aquaro, S.; Bue, M.C.; Dini, L.; Garaci, E. Glutathione inhibits HIV replication by acting at late stages of the virus life cycle. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 1996, 12, 1537–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciriolo, M.R.; Palamara, A.T.; Incerpi, S.; Lafavia, E.; Bue, M.C.; De Vito, P.; Garaci, E.; Rotilio, G. Loss of GSH, oxidative stress, and decrease of intracellular pH as sequential steps in viral infection. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 2700–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garaci, E.; Palamara, A.T.; Ciriolo, M.R.; D’Agostini, C.; Abdel-Latif, M.S.; Aquaro, S.; Lafavia, E.; Rotilio, G. Intracellular GSH content and HIV replication in human macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1997, 62, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzenberg, L.A.; De Rosa, S.C.; Dubs, J.G.; Roederer, M.; Anderson, M.T.; Ela, S.W.; Deresinski, S.C.; Herzenberg, L.A. Glutathione deficiency is associated with impaired survival in HIV disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 1967–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checconi, P.; Sgarbanti, R.; Celestino, I.; Limongi, D.; Amatore, D.; Iuvara, A.; Alimonti, A.; Garaci, E.; Palamara, A.T.; Nencioni, L. The environmental pollutant cadmium promotes influenza virus replication in MDCK cells by altering their redox state. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 4148–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amatore, D.; Sgarbanti, R.; Aquilano, K.; Baldelli, S.; Limongi, D.; Civitelli, L.; Nencioni, L.; Garaci, E.; Ciriolo, M.R.; Palamara, A.T. Influenza virus replication in lung epithelial cells depends on redox-sensitive pathways activated by NOX4-derived ROS. Cell. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, D.A.; Dorsey, K.; Wingfield, P.T.; Stahl, S.J.; Kaufman, J.; Fales, H.M.; Levine, R.L. Regulation of HIV-1 protease activity through cysteine modification. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 2482–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, D.A.; Newcomb, F.M.; Starke, D.W.; Ott, D.E.; Mieyal, J.J.; Yarchoan, R. Thioltransferase (glutaredoxin) is detected within HIV-1 and can regulate the activity of glutathionylated HIV-1 protease in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 25935–25940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.A.; Yusa, K.; Gillim, L.A.; Newcomb, F.M.; Mitsuya, H.; Yarchoan, R. Conserved cysteines of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease are involved in regulation of polyprotein processing and viral maturation of immature virions. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, D.A.; Brown, C.A.; Newcomb, F.M.; Boja, E.S.; Fales, H.M.; Kaufman, J.; Stahl, S.J.; Wingfield, P.; Yarchoan, R. Reversible oxidative modification as a mechanism for regulating retroviral protease dimerization and activation. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 3319–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisawang, C.; Kuadkitkan, A.; Smith, D.R.; Ubol, S.; Ketterman, A.J. Glutathionylation of chikungunya nsP2 protein affects protease activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1861, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saisawang, C.; Kuadkitkan, A.; Auewarakul, P.; Smith, D.R.; Ketterman, A.J. Glutathionylation of dengue and Zika NS5 proteins affects guanylyltransferase and RNA dependent RNA polymerase activities. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, Y.M.; Jones, D.P. The redox proteome. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 26512–26520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghezzi, P.; Romines, B.; Fratelli, M.; Eberini, I.; Gianazza, E.; Casagrande, S.; Laragione, T.; Mengozzi, M.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Herzenberg, L.A. Protein glutathionylation: Coupling and uncoupling of glutathione to protein thiol groups in lymphocytes under oxidative stress and HIV infection. Mol. Immunol. 2002, 38, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinarakis, E.; Chantzoura, E.; Thanos, D.; Spyrou, G. S-glutathionylation of IRF3 regulates IRF3-CBP interaction and activation of the IFN beta pathway. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Dosal, R.; Horan, K.A.; Rahbek, S.H.; Ichijo, H.; Chen, Z.J.; Mieyal, J.J.; Hartmann, R.; Paludan, S.R. HSV infection induces production of ROS, which potentiate signaling from pattern recognition receptors: Role for S-glutathionylation of TRAF3 and 6. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, Y.M.; Chandler, J.D.; Jones, D.P. The cysteine proteome. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 84, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzano, S.; Checconi, P.; Hanschmann, E.M.; Lillig, C.H.; Bowler, L.D.; Chan, P.; Vaudry, D.; Mengozzi, M.; Coppo, L.; Sacre, S.; et al. Linkage of inflammation and oxidative stress via release of glutathionylated peroxiredoxin-2, which acts as a danger signal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12157–12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Limmon, G.V.; Zheng, D.; Li, N.; Li, L.; Yin, L.; Chow, V.T.; Chen, J.; Engelward, B.P. Major shifts in the spatio-temporal distribution of lung antioxidant enzymes during influenza pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; De Rosa, S.; Roederer, M.; Anderson, M.T.; Dubs, J.G.; Yodoi, J.; Holmgren, A.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Herzenberg, L.A. Elevation of plasma thioredoxin levels in HIV-infected individuals. Int. Immunol. 1996, 8, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertini, R.; Howard, O.M.; Dong, H.F.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Bizzarri, C.; Sergi, R.; Caselli, G.; Pagliei, S.; Romines, B.; Wilshire, J.A.; et al. Thioredoxin, a redox enzyme released in infection and inflammation, is a unique chemoattractant for neutrophils, monocytes, and T cells. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, Y.M.; Kang, S.M.; Roede, J.R.; Orr, M.; Jones, D.P. Increased inflammatory signaling and lethality of influenza H1N1 by nuclear thioredoxin-1. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Tamura, S.; Watanabe, I.; Iwasaki, T.; Yodoi, J. Enhanced resistancy of thioredoxin-transgenic mice against influenza virus-induced pneumonia. Immunol. Lett. 2002, 82, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashiro, M.; Tsukahara, H.; Matsukawa, A.; Yamada, M.; Fujii, Y.; Nagaoka, Y.; Tsuge, M.; Yamashita, N.; Ito, T.; Yamada, M.; et al. Redox-active protein thioredoxin-1 administration ameliorates influenza A virus (H1N1)-induced acute lung injury in mice. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, R.; Ishima, Y.; Enoki, Y.; Kimachi, K.; Shirai, T.; Watanabe, H.; Chuang, V.T.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M. Therapeutic impact of human serum albumin-thioredoxin fusion protein on influenza virus-induced lung injury mice. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, Y.M.; Jones, D.P. Redox compartmentalization in eukaryotic cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1780, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, J.A.; Croft, N.P.; Dudek, N.L.; Channappanavar, R.; Theodossis, A.; Webb, A.I.; Dunstone, M.A.; Illing, P.T.; Butler, N.S.; Fett, C.; et al. The cellular redox environment alters antigen presentation. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27979–27991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, V.V.; Rossius, M.; Antelmann, H. Redox regulation by reversible protein S-thiolation in bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reniere, M.L.; Whiteley, A.T.; Hamilton, K.L.; John, S.M.; Lauer, P.; Brennan, R.G.; Portnoy, D.A. Glutathione activates virulence gene expression of an intracellular pathogen. Nature 2015, 517, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pother, D.C.; Gierok, P.; Harms, M.; Mostertz, J.; Hochgrafe, F.; Antelmann, H.; Hamilton, C.J.; Borovok, I.; Lalk, M.; Aharonowitz, Y.; et al. Distribution and infection-related functions of bacillithiol in Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada, A.C.; Kolar, S.L.; Dusi, R.G.; Francois, P.; Roberts, A.A.; Hamilton, C.J.; Liu, G.Y.; Cheung, A. Importance of bacillithiol in the oxidative stress response of staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassetti, C.M.; Rubin, E.J. Genetic requirements for mycobacterial survival during infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12989–12994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansong, C.; Wu, S.; Meng, D.; Liu, X.; Brewer, H.M.; Deatherage Kaiser, B.L.; Nakayasu, E.S.; Cort, J.R.; Pevzner, P.; Smith, R.D.; et al. Top-down proteomics reveals a unique protein S-thiolation switch in Salmonella Typhimurium in response to infection-like conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10153–10158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portman, J.L.; Huang, Q.Y.; Reniere, M.L.; Iavarone, A.T.; Portnoy, D.A. Activity of the pore-forming virulence factor listeriolysin O is reversibly inhibited by naturally occurring S-glutathionylation. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00959-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anathy, V.; Aesif, S.W.; Guala, A.S.; Havermans, M.; Reynaert, N.L.; Ho, Y.S.; Budd, R.C.; Janssen-Heininger, Y.M. Redox amplification of apoptosis by caspase-dependent cleavage of glutaredoxin 1 and S-glutathionylation of Fas. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 184, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anathy, V.; Aesif, S.W.; Hoffman, S.M.; Bement, J.L.; Guala, A.S.; Lahue, K.G.; Leclair, L.W.; Suratt, B.T.; Cool, C.D.; Wargo, M.J.; et al. Glutaredoxin-1 attenuates S-glutathionylation of the death receptor fas and decreases resolution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerstholt, M.; Vrijmoeth, H.; Lachmandas, E.; Oosting, M.; Lupse, M.; Flonta, M.; Dinarello, C.A.; Netea, M.G.; Joosten, L.A.B. Role of glutathione metabolism in host defense against Borrelia burgdorferi infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2320–E2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klatt, P.; Molina, E.P.; De Lacoba, M.G.; Padilla, C.A.; Martinez-Galesteo, E.; Barcena, J.A.; Lamas, S. Redox regulation of c-Jun DNA binding by reversible S-glutathiolation. FASEB J. 1999, 13, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qanungo, S.; Starke, D.W.; Pai, H.V.; Mieyal, J.J.; Nieminen, A.L. Glutathione supplementation potentiates hypoxic apoptosis by S-glutathionylation of p65-NFkappaB. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 18427–18436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.C.; Hsieh, C.W.; Lin, Y.C.; Wung, B.S. The glutaredoxin/glutathione system modulates NF-kappaB activity by glutathionylation of p65 in cinnamaldehyde-treated endothelial cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 116, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Huang, G.D.; Hsieh, C.W.; Wung, B.S. The glutathionylation of p65 modulates NF-kappa B activity in 15-deoxy-Delta,(12,14)-prostaglandin J(2)-treated endothelial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 1844–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alisi, A.; Pastore, A.; Passarelli, C.; Tozzi, G.; Bottazzo, G.F.; Nobili, V.; Piemonte, F. Glutathionylation of p65NF-KB correlates with proliferating/apoptotic hepatoma cells exposed to pro- and anti-oxidants. Free Radic. Res. 2009, 43, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Pineda-Molina, E.; Klatt, P.; Vazquez, J.; Marina, A.; de Lacoba, M.G.; Perez-Sala, D.; Lamas, S. Glutathionylation of the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B: A mechanism for redox-induced inhibition of DNA binding. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 14134–14142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynaert, N.L.; van der Vliet, A.; Guala, A.S.; McGovern, T.; Hristova, M.; Pantano, C.; Heintz, N.H.; Heim, J.; Ho, Y.S.; Matthews, D.E.; et al. Dynamic redox control of NF-kappa B through glutaredoxin-regulated S-glutathionylation of inhibitory kappa B kinase beta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13086–13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantzoura, E.; Prinarakis, E.; Panagopoulos, D.; Mosialos, G.; Spyrou, G. Glutaredoxin-1 regulates TRAF6 activation and the IL-1 receptor/TLR4 signalling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 403, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolin, J.D.; Tully, J.E.; Hoffman, S.M.; Guala, A.S.; van der Velden, J.L.; Poynter, M.E.; van der Vliet, A.; Anathy, V.; Janssen-Heininger, Y.M. The glutaredoxin/S-glutathionylation axis regulates interleukin-17A-induced proinflammatory responses in lung epithelial cells in association with S-glutathionylation of nuclear factor kappaB family proteins. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 73, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.T.; Qian, X.; van der Velden, J.L.J.; Chia, S.B.; McMillan, D.H.; Flemer, S.; Hoffman, S.M.; Lahue, K.G.; Schneider, R.W.; Nolin, J.D.; et al. Glutathione S-transferase pi modulates NF-kappa B activation and pro-inflammatory responses in lung epithelial cells. Redox Biol. 2016, 8, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C.; Chiewchengchol, D.; Zhao, F.; Yu, H.; Li, J.; Kambara, H.; Luo, K.Y.; Venkataraman, A.; et al. Positive regulation of interleukin-1beta bioactivity by physiological ROS-mediated cysteine S-glutathionylation. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Checconi, P.; Limongi, D.; Baldelli, S.; Ciriolo, M.R.; Nencioni, L.; Palamara, A.T. Role of Glutathionylation in Infection and Inflammation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081952
Checconi P, Limongi D, Baldelli S, Ciriolo MR, Nencioni L, Palamara AT. Role of Glutathionylation in Infection and Inflammation. Nutrients. 2019; 11(8):1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081952
Chicago/Turabian StyleChecconi, Paola, Dolores Limongi, Sara Baldelli, Maria Rosa Ciriolo, Lucia Nencioni, and Anna Teresa Palamara. 2019. "Role of Glutathionylation in Infection and Inflammation" Nutrients 11, no. 8: 1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081952
APA StyleChecconi, P., Limongi, D., Baldelli, S., Ciriolo, M. R., Nencioni, L., & Palamara, A. T. (2019). Role of Glutathionylation in Infection and Inflammation. Nutrients, 11(8), 1952. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081952





