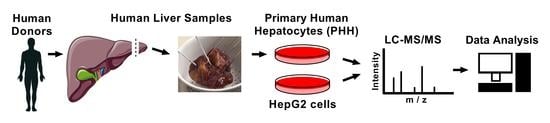
Identification of the Secreted Proteins Originated from Primary Human Hepatocytes and HepG2 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Human Liver Samples
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
2.5. Analysis of LC-MS/MS Data
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trefts, E.; Gannon, M.; Wasserman, D.H. The liver. Curr Biol 2017, 27, R1147–R1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzout-Marniche, D.; Gaudichon, C.; Tome, D. Dietary protein and blood glucose control. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2014, 17, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aden, D.P.; Fogel, A.; Plotkin, S.; Damjanov, I.; Knowles, B.B. Controlled synthesis of HBsAg in a differentiated human liver carcinoma-derived cell line. Nature 1979, 282, 615–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, B.B.; Howe, C.C.; Aden, D.P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science 1980, 209, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sefried, S.; Häring, H.U.; Weigert, C.; Eckstein, S.S. Suitability of hepatocyte cell lines HepG2, AML12 and THLE-2 for investigation of insulin signalling and hepatokine gene expression. Open Biol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillouzo, A.; Corlu, A.; Aninat, C.; Glaise, D.; Morel, F.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. The human hepatoma HepaRG cells: A highly differentiated model for studies of liver metabolism and toxicity of xenobiotics. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2007, 168, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.J.; Johnson, D.; Amin, H.D.; Sivathondan, P.; Silva, M.A.; Wang, L.M.; Stevanato, L.; McNeil, C.A.; Miljan, E.A.; Sinden, J.D.; et al. Characterization of lipid metabolism in a novel immortalized human hepatocyte cell line. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E511–E522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franko, A.; Merkel, D.; Kovarova, M.; Hoene, M.; Jaghutriz, B.A.; Heni, M.; Königsrainer, A.; Papan, C.; Lehr, S.; Häring, H.U.; et al. Dissociation of Fatty Liver and Insulin Resistance in I148M PNPLA3 Carriers: Differences in Diacylglycerol (DAG) FA18:1 Lipid Species as a Possible Explanation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorko, K.; Freeswick, P.D.; Bartoli, F.; Cicalese, L.; Bardsley, B.A.; Tzakis, A.; Nussler, A.K. A new technique for isolating and culturing human hepatocytes from whole or split livers not used for transplantation. Cell Transplant 1994, 3, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, C.; Gerrard, D.T.; Jenkins, R.; Berry, A.; Durkin, K.; Sundstrom, L.; Goldring, C.E.; Park, B.K.; Kitteringham, N.R.; Hanley, K.P.; et al. Proteome-wide analyses of human hepatocytes during differentiation and dedifferentiation. Hepatology 2013, 58, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schyschka, L.; Sanchez, J.J.; Wang, Z.; Burkhardt, B.; Muller-Vieira, U.; Zeilinger, K.; Bachmann, A.; Nadalin, S.; Damm, G.; Nussler, A.K. Hepatic 3D cultures but not 2D cultures preserve specific transporter activity for acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1581–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, P.; Hewitt, N.J.; Albrecht, U.; Andersen, M.E.; Ansari, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bode, J.G.; Bolleyn, J.; Borner, C.; Bottger, J.; et al. Recent advances in 2D and 3D in vitro systems using primary hepatocytes, alternative hepatocyte sources and non-parenchymal liver cells and their use in investigating mechanisms of hepatotoxicity, cell signaling and ADME. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1315–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heslop, J.A.; Rowe, C.; Walsh, J.; Sison-Young, R.; Jenkins, R.; Kamalian, L.; Kia, R.; Hay, D.; Jones, R.P.; Malik, H.Z.; et al. Mechanistic evaluation of primary human hepatocyte culture using global proteomic analysis reveals a selective dedifferentiation profile. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Häring, H.U. The role of hepatokines in metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigert, C.; Hoene, M.; Plomgaard, P. Hepatokines-a novel group of exercise factors. Pflugers Arch. 2018, 471, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, S.; De Filippo, E.; Goddeke, S.; Knebel, B.; Kotzka, J.; Al-Hasani, H.; Roden, M.; Lehr, S.; Sell, H. Exosomal proteins constitute an essential part of the human adipose tissue secretome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, S.; Raschke, S.; Knebel, B.; Scheler, M.; Irmler, M.; Passlack, W.; Muller, S.; Hanisch, F.G.; Franz, T.; Li, X.; et al. Secretome profiling of primary human skeletal muscle cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1844, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iroz, A.; Couty, J.P.; Postic, C. Hepatokines: Unlocking the multi-organ network in metabolic diseases. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, J.R.; Vildhede, A.; Noren, A.; Artursson, P. In-depth quantitative analysis and comparison of the human hepatocyte and hepatoma cell line HepG2 proteomes. J. Proteom. 2016, 136, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, S.; Hartwig, S.; Lamers, D.; Famulla, S.; Muller, S.; Hanisch, F.G.; Cuvelier, C.; Ruige, J.; Eckardt, K.; Ouwens, D.M.; et al. Identification and validation of novel adipokines released from primary human adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, M111.010504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobeloch, D.; Ehnert, S.; Schyschka, L.; Buchler, P.; Schoenberg, M.; Kleeff, J.; Thasler, W.E.; Nussler, N.C.; Godoy, P.; Hengstler, J.; et al. Human hepatocytes: Isolation, culture, and quality procedures. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 806, 99–120. [Google Scholar]
- Franko, A.; Kovarova, M.; Feil, S.; Feil, R.; Wagner, R.; Heni, M.; Königsrainer, A.; Ruoss, M.; Nüssler, A.K.; Weigert, C.; et al. cGMP-dependent protein kinase I (cGKI) modulates human hepatic stellate cell activation. Metabolism 2018, 88, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzka, J.; Knebel, B.; Haas, J.; Kremer, L.; Jacob, S.; Hartwig, S.; Nitzgen, U.; Muller-Wieland, D. Preventing phosphorylation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1a by MAP-kinases protects mice from fatty liver and visceral obesity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Hesse, D.; Raabe, M.; Urlaub, H.; Jahn, O. An automated in-gel digestion/iTRAQ-labeling workflow for robust quantification of gel-separated proteins. Proteomics 2013, 13, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Cox, J. The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2301–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, C.; Dihazi, H. Introduction to Proteomics Technologies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1362, 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Bendtsen, J.D.; Jensen, L.J.; Blom, N.; Von Heijne, G.; Brunak, S. Feature-based prediction of non-classical and leaderless protein secretion. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2004, 17, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franko, A.; Huypens, P.; Neschen, S.; Irmler, M.; Rozman, J.; Rathkolb, B.; Neff, F.; Prehn, C.; Dubois, G.; Baumann, M.; et al. Bezafibrate Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Flexibility in STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2540–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meex, R.C.R.; Watt, M.J. Hepatokines: Linking nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichelbaum, K.; Winter, M.; Berriel Diaz, M.; Herzig, S.; Krijgsveld, J. Selective enrichment of newly synthesized proteins for quantitative secretome analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigert, C.; Lehmann, R.; Hartwig, S.; Lehr, S. The secretome of the working human skeletal muscle-a promising opportunity to combat the metabolic disaster? Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2014, 8, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bihan, M.C.; Bigot, A.; Jensen, S.S.; Dennis, J.L.; Rogowska-Wrzesinska, A.; Laine, J.; Gache, V.; Furling, D.; Jensen, O.N.; Voit, T.; et al. In-depth analysis of the secretome identifies three major independent secretory pathways in differentiating human myoblasts. J. Proteom. 2012, 77, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang-Doran, I.; Zhang, C.Y.; Vidal-Puig, A. Extracellular Vesicles: Novel Mediators of Cell Communication in Metabolic Disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slany, A.; Haudek, V.J.; Zwickl, H.; Gundacker, N.C.; Grusch, M.; Weiss, T.S.; Seir, K.; Rodgarkia-Dara, C.; Hellerbrand, C.; Gerner, C. Cell characterization by proteome profiling applied to primary hepatocytes and hepatocyte cell lines Hep-G2 and Hep-3B. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tascher, G.; Burban, A.; Camus, S.; Plumel, M.; Chanon, S.; Le Guevel, R.; Shevchenko, V.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Lefai, E.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C.; et al. In-Depth Proteome Analysis Highlights HepaRG Cells as a Versatile Cell System Surrogate for Primary Human Hepatocytes. Cells 2019, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanebratt, K.P.; Andersson, T.B. HepaRG cells as an in vitro model for evaluation of cytochrome P450 induction in humans. Drug. Metab. Dispos. 2008, 36, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, N.; Zacharias, E.; Muller, W.; Resch, B. An update on the use of C-reactive protein in early-onset neonatal sepsis: Current insights and new tasks. Neonatology 2012, 102, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, H.R.; Yu, X.N.; Shi, X.; Bilegsaikhan, E.; Guo, H.Y.; Huang, R.Z.; Liu, T.T.; Shen, X.Z.; Zhu, J.M. Overexpressed pepsinogen C is associated with poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma: A tissue microarray study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 2927–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, J.M.; Elortza, F.; Lu, S.C.; Brun, V.; Paradela, A.; Corrales, F.J. Liver cancer-associated changes to the proteome: What deserves clinical focus? Expert. Rev. Proteom. 2018, 15, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennemann, R.; Federico, G.; Mathow, D.; Rabionet, M.; Rampoldi, F.; Popovic, Z.V.; Volz, M.; Hielscher, T.; Sandhoff, R.; Grone, H.J. Inhibition of hepatocellular carcinoma growth by blockade of glycosphingolipid synthesis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 109201–109216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Term ID | Term Name | adj. p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| GO:0006956 | complement activation | <0.0001 |
| GO:0006958 | complement activation, classical pathway | <0.0001 |
| GO:0006957 | complement activation, alternative pathway | <0.0001 |
| GO:0007596 | blood coagulation | <0.0001 |
| GO:0007597 | blood coagulation, intrinsic pathway | <0.0001 |
| GO:0072378 | blood coagulation, fibrin clot formation | <0.0001 |
| GO:0042730 | fibrinolysis | <0.0001 |
| GO:0006953 | acute-phase response | <0.0001 |
| GO:0002526 | acute inflammatory response | <0.0001 |
| GO:0019538 | protein metabolic process | <0.0001 |
| GO:0051246 | regulation of protein metabolic process | <0.0001 |
| GO:1901605 | alpha-amino acid metabolic process | <0.0001 |
| GO:1901135 | carbohydrate derivative metabolic process | <0.0001 |
| GO:0006629 | lipid metabolic process | <0.0001 |
| GO:0097006 | regulation of plasma lipoprotein particle levels | <0.0001 |
| GO:0034369 | plasma lipoprotein particle remodeling | <0.0001 |
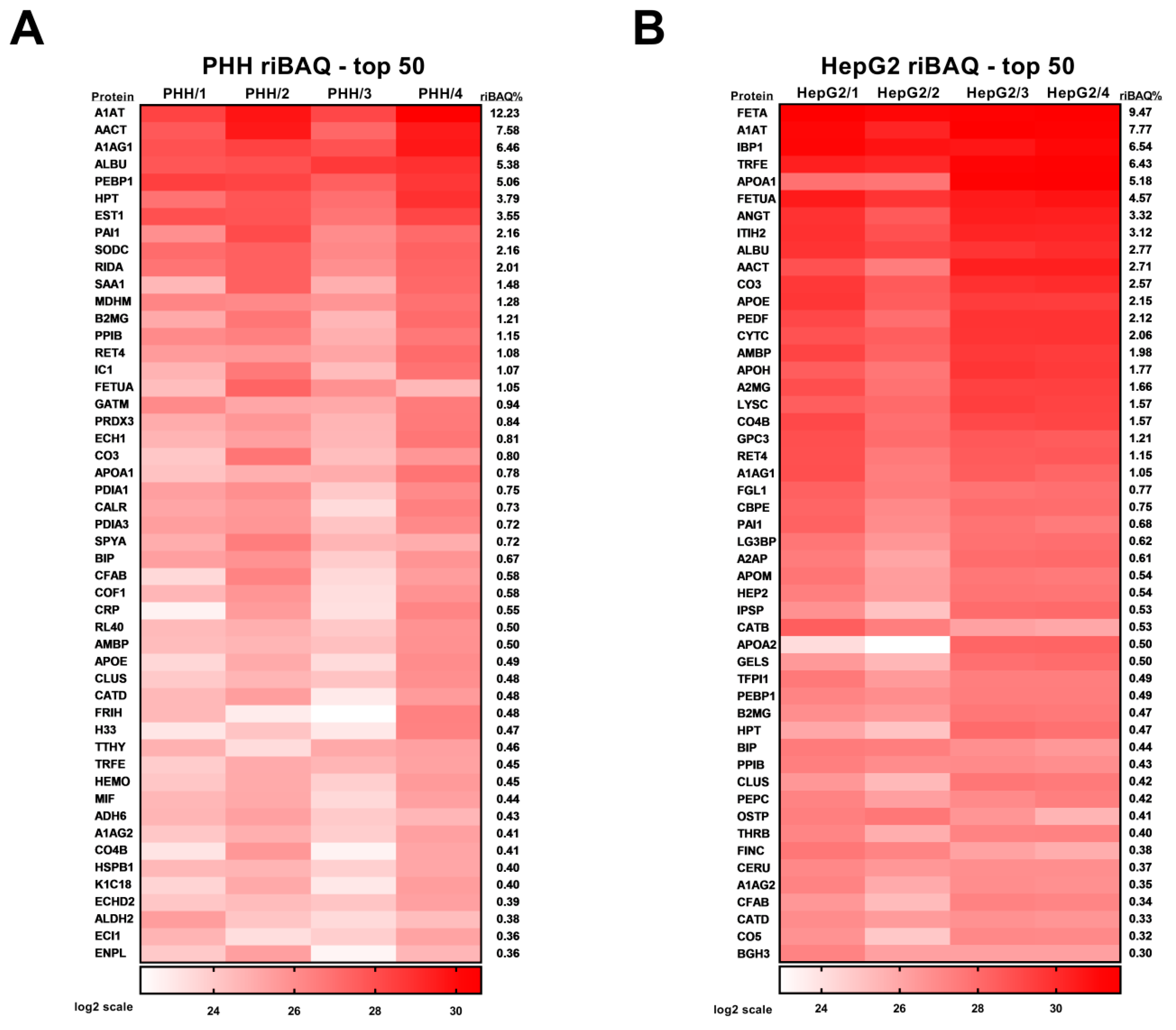
| Prot. ID | Prot. Name | Prot. Symb. | Possib. Contam. 1 | av iBAQ 2 | riBAQ (%) 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P01009 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin | A1AT | 789277500 | 12.23 | |
| P01011 | Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin | AACT | 489095000 | 7.58 | |
| P02763 | Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1 | A1AG1 | 417130000 | 6.46 | |
| P02768 | Serum albumin | ALBU | 346990000 | 5.38 | |
| P30086 | Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1 | PEBP1 | 326665000 | 5.06 | |
| P00738 | Haptoglobin | HPT | 244395000 | 3.79 | |
| P23141 | Liver carboxylesterase 1 | EST1 | 229112500 | 3.55 | |
| P05121 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 | PAI1 | 139604500 | 2.16 | |
| P00441 | Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] | SODC | 139590750 | 2.16 | |
| P52758 | 2-iminobutanoate/2-iminopropanoate deaminase | RIDA | 129657750 | 2.01 | |
| P0DJI8 | Serum amyloid A-1 protein | SAA1 | 95757500 | 1.48 | |
| P40926 | Malate dehydrogenase, mito. | MDHM | x | 82348750 | 1.28 |
| P61769 | Beta-2-microglobulin | B2MG | 78243000 | 1.21 | |
| P23284 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase B | PPIB | 73998500 | 1.15 | |
| P02753 | Retinol-binding protein 4 | RET4 | 69459500 | 1.08 | |
| P05155 | Plasma protease C1 inhibitor | IC1 | 68893500 | 1.07 | |
| P02765 | Fetuin-A | FETUA | 67909500 | 1.05 | |
| P50440 | Glycine amidinotransferase, mito. | GATM | 60424000 | 0.94 | |
| P30048 | Thioredoxin-dependent peroxide reductase, mito. | PRDX3 | 53912250 | 0.84 | |
| Q13011 | Delta(3,5)-Delta(2,4)-dienoyl-CoA isomerase, mito. | ECH1 | 52252250 | 0.81 | |
| P01024 | Complement C3 | CO3 | 51702000 | 0.80 | |
| P02647 | Apolipoprotein A-I | APOA1 | 50100750 | 0.78 | |
| P07237 | Protein disulfide-isomerase | PDIA1 | x | 48349000 | 0.75 |
| P27797 | Calreticulin | CALR | 47263000 | 0.73 | |
| P30101 | Protein disulfide-isomerase A3 | PDIA3 | 46786500 | 0.72 | |
| P21549 | Serine-pyruvate aminotransferase | SPYA | 46203500 | 0.72 | |
| P11021 | Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP | BIP | x | 43119250 | 0.67 |
| P00751 | Complement factor B | CFAB | 37699500 | 0.58 | |
| P23528 | Cofilin-1 | COF1 | x | 37466000 | 0.58 |
| P02741 | C-reactive protein | CRP | 35494325 | 0.55 | |
| P62987 | Ubiquitin-60S ribosomal protein L40 | RL40 | x | 32257250 | 0.50 |
| P02760 | Protein AMBP | AMBP | 32188750 | 0.50 | |
| P02649 | Apolipoprotein E | APOE | 31445250 | 0.49 | |
| P10909 | Clusterin | CLUS | 31080000 | 0.48 | |
| P07339 | Cathepsin D | CATD | 30845450 | 0.48 | |
| P02794 | Ferritin heavy chain | FRIH | 30716925 | 0.48 | |
| P84243 | Histone H3.3 | H33 | x | 30172300 | 0.47 |
| P02766 | Transthyretin | TTHY | 29464250 | 0.46 | |
| P02787 | Serotransferrin | TRFE | 28945750 | 0.45 | |
| P02790 | Hemopexin | HEMO | 28893000 | 0.45 | |
| P14174 | Macrophage migration inhibitory factor | MIF | 28618500 | 0.44 | |
| P28332 | Alcohol dehydrogenase 6 | ADH6 | 27676000 | 0.43 | |
| P19652 | Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 2 | A1AG2 | 26294000 | 0.41 | |
| P0C0L5 | Complement C4-B | CO4B | 26207125 | 0.41 | |
| P04792 | Heat shock protein beta-1 | HSPB1 | 25729750 | 0.40 | |
| P05783 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 18 | K1C18 | 25491850 | 0.40 | |
| Q86YB7 | Enoyl-CoA hydratase domain-containing protein 2, mito. | ECHD2 | x | 25239750 | 0.39 |
| P05091 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase, mito. | ALDH2 | 24239250 | 0.38 | |
| P42126 | Enoyl-CoA delta isomerase 1, mito. | ECI1 | 23068000 | 0.36 | |
| P14625 | Endoplasmin | ENPL | x | 23033875 | 0.36 |
| Prot. ID | Prot. Name | Prot. Symb. | Possib. Contam. 1 | av iBAQ 2 | riBAQ (%) 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P02771 | Alpha-fetoprotein | FETA | 2998500000 | 9.47 | |
| P01009 | Alpha-1-antitrypsin | A1AT | 2460775000 | 7.77 | |
| P08833 | Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 | IBP1 | 2070400000 | 6.54 | |
| P02787 | Serotransferrin | TRFE | 2035550000 | 6.43 | |
| P02647 | Apolipoprotein A-I | APOA1 | 1639730000 | 5.18 | |
| P02765 | Fetuin-A | FETUA | 1446420000 | 4.57 | |
| P01019 | Angiotensinogen | ANGT | 1050527500 | 3.32 | |
| P19823 | Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H2 | ITIH2 | 986895000 | 3.12 | |
| P02768 | Serum albumin | ALBU | 876332500 | 2.77 | |
| P01011 | Alpha-1-antichymotrypsin | AACT | 859190000 | 2.71 | |
| P01024 | Complement C3 | CO3 | 813957500 | 2.57 | |
| P02649 | Apolipoprotein E | APOE | 679975000 | 2.15 | |
| P36955 | Pigment epithelium-derived factor | PEDF | 672652500 | 2.12 | |
| P01034 | Cystatin-C | CYTC | 653532500 | 2.06 | |
| P02760 | Protein AMBP | AMBP | 627792500 | 1.98 | |
| P02749 | Beta-2-glycoprotein 1 | APOH | 560445000 | 1.77 | |
| P01023 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin | A2MG | 526075000 | 1.66 | |
| P61626 | Lysozyme C | LYSC | 498212500 | 1.57 | |
| P0C0L5 | Complement C4-B | CO4B | 496745000 | 1.57 | |
| P51654 | Glypican-3 | GPC3 | 382685000 | 1.21 | |
| P02753 | Retinol-binding protein 4 | RET4 | 363022500 | 1.15 | |
| P02763 | Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1 | A1AG1 | 331710000 | 1.05 | |
| Q08830 | Fibrinogen-like protein 1 | FGL1 | 243105000 | 0.77 | |
| P16870 | Carboxypeptidase E | CBPE | 236250000 | 0.75 | |
| P05121 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 | PAI1 | 214605000 | 0.68 | |
| Q08380 | Galectin-3-binding protein | LG3BP | 195722250 | 0.62 | |
| P08697 | Alpha-2-antiplasmin | A2AP | 193182750 | 0.61 | |
| O95445 | Apolipoprotein M | APOM | 170078750 | 0.54 | |
| P05546 | Heparin cofactor 2 | HEP2 | 169633750 | 0.54 | |
| P05154 | Plasma serine protease inhibitor | IPSP | 167712250 | 0.53 | |
| P07858 | Cathepsin B | CATB | 167710250 | 0.53 | |
| P02652 | Apolipoprotein A-II | APOA2 | 159891350 | 0.50 | |
| P06396 | Gelsolin | GELS | 157569250 | 0.50 | |
| P10646 | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor | TFPI1 | 156584750 | 0.49 | |
| P30086 | Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1 | PEBP1 | 153822500 | 0.49 | |
| P61769 | Beta-2-microglobulin | B2MG | 150395750 | 0.47 | |
| P00738 | Haptoglobin | HPT | 147916750 | 0.47 | |
| P11021 | Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP | BIP | x | 139597250 | 0.44 |
| P23284 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase B | PPIB | 134877500 | 0.43 | |
| P10909 | Clusterin | CLUS | 134223250 | 0.42 | |
| P20142 | Gastricsin | PEPC | 131868250 | 0.42 | |
| P10451 | Osteopontin | OSTP | 129970500 | 0.41 | |
| P00734 | Prothrombin | THRB | 127123250 | 0.40 | |
| P02751 | Fibronectin | FINC | 120668000 | 0.38 | |
| P00450 | Ceruloplasmin | CERU | 117001250 | 0.37 | |
| P19652 | Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 2 | A1AG2 | 111402750 | 0.35 | |
| P00751 | Complement factor B | CFAB | 108606250 | 0.34 | |
| P07339 | Cathepsin D | CATD | 104733250 | 0.33 | |
| P01031 | Complement C5 | CO5 | 100732500 | 0.32 | |
| Q15582 | Transforming growth factor-beta-induced protein ig-h3 | BGH3 | 95466000 | 0.30 |
| PHH 691 prot. | HepG2 745 prot. | ||
| Term ID | Term Name | adj. p-value | adj. p-value |
| KEGG:04979 | Cholesterol metabolism | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| KEGG:04610 | Complement and coagulation cascades | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| KEGG:04141 | Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| KEGG:00280 | Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation | <0.0001 | 0.0020 |
| KEGG:00603 | Glycosphingolipid biosynthesis-globo and isoglobo series | - | 0.0216 |
| KEGG:00520 | Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | 0.0176 | - |
| KEGG:00330 | Arginine and proline metabolism | 0.0185 | - |
| KEGG:00410 | Beta-alanine metabolism | 0.0183 | - |
| KEGG:00071 | Fatty acid degradation | 0.0107 | - |
| PHH 64 prot. | HepG2 101 prot. | ||
| Term ID | Term Name | adj. p-value | adj. p-value |
| KEGG:00472 | D-Arginine and D-ornithine metabolism | 0.0489 | - |
| KEGG:00340 | Histidine metabolism | 0.0489 | - |
| KEGG:00072 | Synthesis and degradation of ketone bodies | 0.0202 | - |
| KEGG:00601 | Glycosphingolipid biosynthesis-lacto and neolacto series | - | 0.0010 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franko, A.; Hartwig, S.; Kotzka, J.; Ruoß, M.; Nüssler, A.K.; Königsrainer, A.; Häring, H.-U.; Lehr, S.; Peter, A. Identification of the Secreted Proteins Originated from Primary Human Hepatocytes and HepG2 Cells. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081795
Franko A, Hartwig S, Kotzka J, Ruoß M, Nüssler AK, Königsrainer A, Häring H-U, Lehr S, Peter A. Identification of the Secreted Proteins Originated from Primary Human Hepatocytes and HepG2 Cells. Nutrients. 2019; 11(8):1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081795
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranko, Andras, Sonja Hartwig, Jörg Kotzka, Marc Ruoß, Andreas K. Nüssler, Alfred Königsrainer, Hans-Ulrich Häring, Stefan Lehr, and Andreas Peter. 2019. "Identification of the Secreted Proteins Originated from Primary Human Hepatocytes and HepG2 Cells" Nutrients 11, no. 8: 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081795
APA StyleFranko, A., Hartwig, S., Kotzka, J., Ruoß, M., Nüssler, A. K., Königsrainer, A., Häring, H.-U., Lehr, S., & Peter, A. (2019). Identification of the Secreted Proteins Originated from Primary Human Hepatocytes and HepG2 Cells. Nutrients, 11(8), 1795. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081795