Stability, Continuity, and Bi-Directional Associations of Parental Feeding Practices and Standardized Child Body Mass Index in Children from 2 to 12 Years of Age
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedures
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Child Feeding Questionnaire (CFQ)
2.2.2. Child Characteristics
2.2.3. Socio-Economic Status (SES)
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Stability of Parental Feeding Practices and Standardized Child Body Mass Index
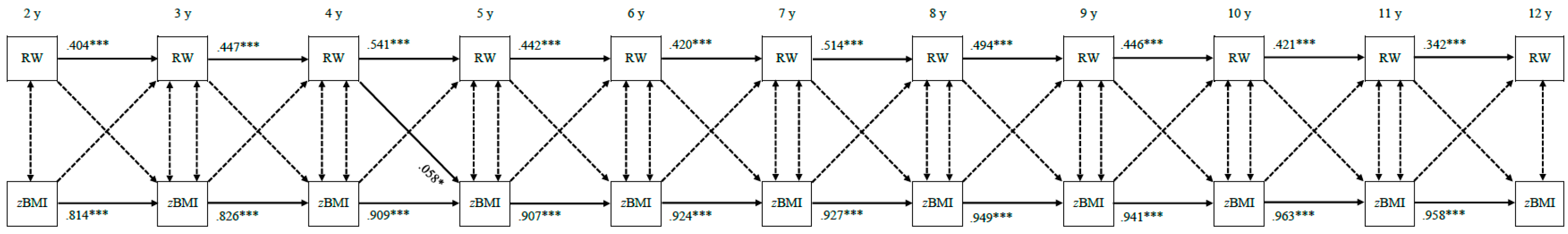
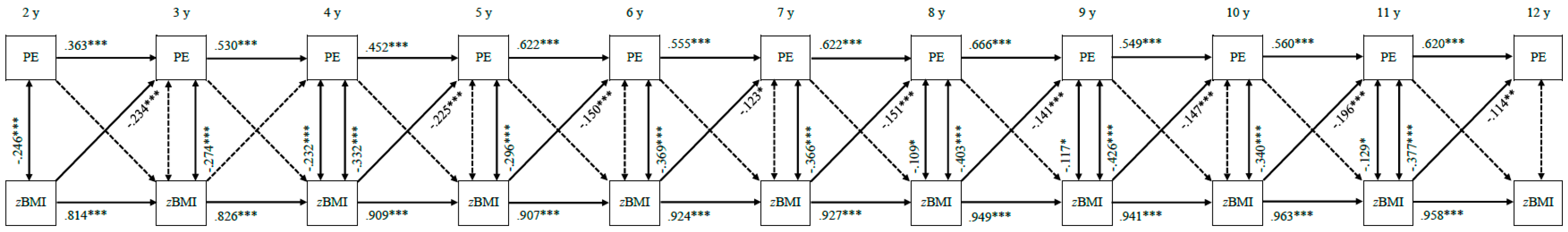
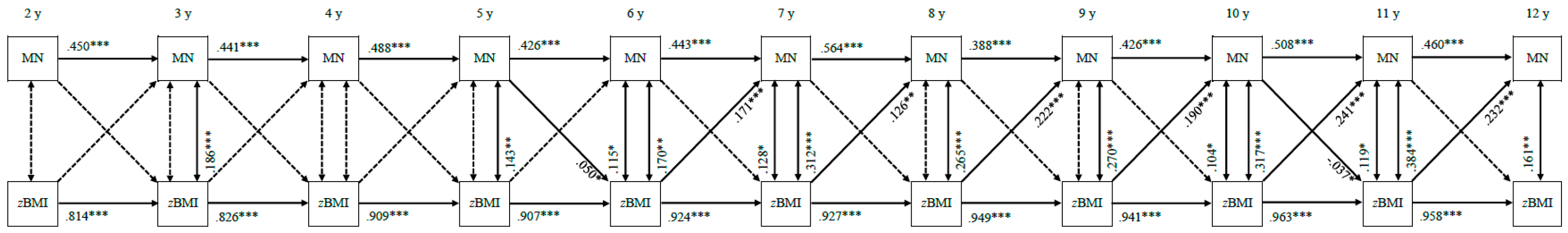
3.3. Continuity of Parental Feeding Practices and Standardized Child Body Mass Index
3.3.1. Restrictive Feeding
3.3.2. Food as Reward
3.3.3. Pressure to Eat
3.3.4. Monitoring
3.3.5. Standardized Child Body Mass Index
3.4. Bi-Directional Associations between Parental Feeding Practices and Standardized Child Body Mass Index
3.4.1. Restrictive Feeding
3.4.2. Food as Reward
3.4.3. Pressure to Eat
3.4.4. Monitoring
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | body mass index |
| CFQ | Child Feeding Questionnaire |
| LIFE | Leipzig Research Center for Civilization Diseases |
| MN | monitoring |
| PE | pressure to eat |
| RST | restrictive feeding |
| RW | food as reward |
| SEM | structural equation modeling |
| SES | socio-economic status |
| zBMI | standardized body mass index |
References
- Williams, E.P.; Mesidor, M.; Winters, K.; Dubbert, P.M.; Wyatt, S.B. Overweight and obesity: Prevalence, consequences, and causes of a growing public health problem. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnik, S.; Kanekar, A. Childhood obesity: A global public health crisis. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2012, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ebbeling, C.B.; Pawlak, D.B.; Ludwig, D.S. Childhood obesity: Public-health crisis, common sense cure. Lancet 2002, 360, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulgarón, E.R. Childhood obesity: A review of increased risk for physical and psychological comorbidities. Clin. Ther. 2013, 35, A18–A32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twig, G.; Reichman, B.; Afek, A.; Derazne, E.; Hamiel, U.; Furer, A.; Gershovitz, L.; Bader, T.; Cukierman-Yaffe, T.; Kark, J.D.; et al. Severe obesity and cardio-metabolic comorbidities: A nationwide study of 2.8 million adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 43, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutaria, S.; Devakumar, D.; Yasuda, S.S.; Das, S.; Saxena, S. Is obesity associated with depression in children? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2019, 104, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.O.; Wyatt, H.R.; Peters, J.C. Energy balance and obesity. Circulation 2012, 126, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihrauch-Blüher, S.; Wiegand, S. Risk factors and implications of childhood obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2018, 7, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, L.L. Child feeding practices and the etiology of obesity. Obesity 2006, 14, 343–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shloim, N.; Edelson, L.R.; Martin, N.; Hetherington, M.M. Parenting styles, feeding styles, feeding practices, and weight status in 4-12 year-old children: A systematic review of the literature. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, L.L.; Fisher, J.O.; Grimm-Thomas, K.; Markey, C.N.; Sawyer, R.; Johnson, S.L. Confirmatory factor analysis of the Child Feeding Questionnaire: A measure of parental attitudes, beliefs and practices about child feeding and obesity proneness. Appetite 2001, 36, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, J.S.; Fisher, J.O.; Birch, L.L. Parental influence on eating behavior: Conception to adolescence. J. Law Med. Ethics 2007, 35, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, S.; Golley, R.; Hendrie, G. Expanding the understanding of how parenting influences the dietary intake and weight status of children: A cross-sectional study. Nutr. Diet. 2011, 68, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubbels, J.S.; Kremers, S.P.J.; Stafleu, A.; de Vries, S.I.; Goldbohm, R.A.; Dagnelie, P.C.; de Vries, N.K.; van Buuren, S.; Thijs, C. Association between parenting practices and children’s dietary intake, activity behavior and development of body mass index: The KOALA Birth Cohort Study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, L.; Cooke, L.; Hill, C.; Wardle, J. Child adiposity and maternal feeding practices: A longitudinal analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.; Andrianopoulos, N.; Hesketh, K.; Ball, K.; Crawford, D.; Brennan, L.; Corsini, N.; Timperio, A. Parental use of restrictive feeding practices and child BMI z-score. A 3-year prospective cohort study. Appetite 2010, 55, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, R.F.; Paxton, S.J.; Massey, R.; Campbell, K.J.; Wertheim, E.H.; Skouteris, H.; Gibbons, K. Maternal feeding practices predict weight gain and obesogenic eating behaviors in young children: A prospective study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, M.S.; Berkowitz, R.I.; Stallings, V.A.; Kerns, J.; Storey, M.; Stunkard, A.J. Parental feeding attitudes and styles and child body mass index: Prospective analysis of a gene-environment interaction. Pediatrics 2004, 114, e429–e436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, C.V.; Blissett, J. Controlling feeding practices: Cause or consequence of early child weight? Pediatrics 2008, 121, e164–e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liszewska, N.; Scholz, U.; Radtke, T.; Horodyska, K.; Luszczynska, A. Bi-directional associations between parental feeding practices and children’s body mass in parent-child dyads. Appetite 2018, 129, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, K.E.; Coleman, S.M.; Appugliese, D.P.; Kaciroti, N.A.; Corwyn, R.F.; Davidson, N.S.; Bradley, R.H.; Lumeng, J.C. Maternal feeding practices become more controlling after and not before excessive rates of weight gain. Obesity 2009, 17, 1724–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, L.; Lopes, C.; Severo, M.; Santos, S.; Real, H.; Durão, C.; Moreira, P.; Oliveira, A. Bidirectional association between parental child-feeding practices and body mass index at 4 and 7 y of age. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, P.W.; Tharner, A.; Van Der Ende, J.; Wake, M.; Raat, H.; Hofman, A.; Verhulst, F.C.; Van Ijzendoorn, M.H.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Tiemeier, H. Feeding practices and child weight: Is the association bidirectional in preschool children? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derks, I.P.; Tiemeier, H.; Sijbrands, E.J.; Nicholson, J.M.; Voortman, T.; Verhulst, F.C.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Jansen, P.W. Testing the direction of effects between child body composition and restrictive feeding practices: Results from a population-based cohort. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh-Taskar, P.; Nicklas, T.A.; Morales, M.; Yang, S.J.; Zakeri, I.; Berenson, G.S. Tracking of overweight status from childhood to young adulthood: The Bogalusa Heart Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 60, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, K.M.; Craig, C.L.; Gauvin, L.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Tracking of obesity and physical activity from childhood to adulthood: The Physical Activity Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2009, 4, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesketh, K.; Wake, M.; Waters, E.; Carlin, J.; Crawford, D. Stability of body mass index in Australian children: A prospective cohort study across the middle childhood years. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geserick, M.; Vogel, M.; Gausche, R.; Lipek, T.; Spielau, U.; Keller, E.; Pfäffle, R.; Kiess, W.; Körner, A. Acceleration of BMI in early childhood and risk of sustained obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, C.; Blissett, J. Stability and continuity of parentally reported child eating behaviours and feeding practices from 2 to 5 years of age. Appetite 2012, 58, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.E.; Paxton, S.J.; Brozovic, A.M. Maternal feeding practices, child eating behaviour and body mass index in preschool-aged children: A prospective analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2010, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blissett, J.; Farrow, C. Predictors of maternal control of feeding at 1 and 2 years of age. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 1520–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, F.; Farrow, C.; Meyer, C.; Haycraft, E. The stability and continuity of maternally reported and observed child eating behaviours and feeding practices across early childhood. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulain, T.; The LIFE Child Study Team; Baber, R.; Vogel, M.; Pietzner, D.; Kirsten, T.; Jurkutat, A.; Hiemisch, A.; Hilbert, A.; Kratzsch, J.; et al. The LIFE Child study: A population-based perinatal and pediatric cohort in Germany. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quante, M.; Hesse, M.; Döhnert, M.; Fuchs, M.; Hirsch, C.; Sergeyev, E.; Casprzig, N.; Geserick, M.; Naumann, S.; Koch, C.; et al. The LIFE child study: A life course approach to disease and health. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Richter, R.; Brauhardt, A.; Hiemisch, A.; Kiess, W.; Hilbert, A. Parental feeding practices in families with children aged 2-13 years: Psychometric properties and child age-specific norms of the German version of the Child Feeding Questionnaire (CFQ). Appetite 2017, 109, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, A.; Vijayasiri, G.; Fitzgibbon, M.L.; Schiffer, L.A.; Campbell, R.T. Confirmatory factor analysis and measurement invariance of the Child Feeding Questionnaire in low-income Hispanic and African-American mothers with preschool-age children. Appetite 2015, 90, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-H.; Mallan, K.M.; Mihrshahi, S.; Daniels, L.A. Feeding beliefs and practices of Chinese immigrant mothers. Validation of a modified version of the child feeding questionnaire. Appetite 2014, 80, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kromeyer-Hauschild, K.; Wabitsch, M.; Kunze, D.; Geller, F.; Geiß, H.C.; Hesse, V.; Von Hippel, A.; Jaeger, U.; Johnsen, D.; Korte, W.; et al. Perzentile für den Body-mass-Index für das Kindes- und Jugendalter unter Heranziehung verschiedener deutscher Stichproben. Mon. Kinderheilkd. 2001, 149, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.; Stolzenberg, H. Der Sozialschichtindex im Bundes-Gesundheitssurvey. Gesundheitswesen 1999, 61, 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Lampert, T.; Kroll, L.E. Soziale Unterschiede in der Mortalität und Lebenserwartung. GBE Kompakt 5 (2). 2014. Available online: www.rki.de/gbe-kompakt (accessed on 19 June 2019).
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.-G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacobucci, D. Structural equations modeling: Fit indices, sample size, and advanced topics. J. Consum. Psychol. 2010, 20, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka, P.; Flodmark, C.-E.; Hales, D.; Faith, M.S. Assessment of parental overt and covert control of child’s food intake: A population-based validation study with mothers of preschoolers. Eat. Behav. 2014, 15, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, J.; Reynolds, R.; Smith, A. Expanding the concept of parental control: A role for overt and covert control in children’s snacking behaviour? Appetite 2006, 47, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschann, J.M.; Gregorich, S.E.; Penilla, C.; Pasch, L.A.; De Groat, C.L.; Flores, E.; Deardorff, J.; Greenspan, L.C.; Butte, N.F. Parental feeding practices in Mexican American families: Initial test of an expanded measure. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berridge, K.C. Food reward: Brain substrates of wanting and liking. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1996, 20, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliegman, R.; Nelson, W.E. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 18th ed.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, L.; Marx, J.M.; Musher-Eizenman, D.R. Using food as a reward: An examination of parental reward practices. Appetite 2018, 120, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnowski, A. Energy density, palatability, and satiety: Implications for weight control. Nutr. Rev. 1998, 56, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colak, H.; Dülgergil, C.T.; Dalli, M.; Hamidi, M.M. Early childhood caries update: A review of causes, diagnoses, and treatments. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2013, 4, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, C.J. An effect size primer: A guide for clinicians and researchers. Prof. Psychol. Res. Pract. 2009, 40, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Van Duijn, C.M.; Van Der Heijden, A.J.; MacKenbach, J.P.; Moll, H.A.; Steegers, E.A.P.; Tiemeier, H.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Verhulst, F.C.; Hofman, A. The Generation R Study: Design and cohort update 2010. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 823–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardel, M.; Willig, A.L.; Dulin-Keita, A.; Casazza, K.; Beasley, T.M.; Fernández, J.R. Parental feeding practices and socioeconomic status are associated with child adiposity in a multi-ethnic sample of children. Appetite 2012, 58, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumanyika, S.K. Environmental influences on childhood obesity: Ethnic and cultural influences in context. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 94, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loth, K.A.; MacLehose, R.F.; Fulkerson, J.A.; Crow, S.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Are food restriction and pressure-to-eat parenting practices associated with adolescent disordered eating behaviors? Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2014, 47, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolotarjova, J.; Velde, G.T.; Vreugdenhil, A.C.E. Effects of multidisciplinary interventions on weight loss and health outcomes in children and adolescents with morbid obesity. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 931–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleich, S.N.; Vercammen, K.A.; Zatz, L.Y.; Frelier, J.M.; Ebbeling, C.B.; Peeters, A. Interventions to prevent global childhood overweight and obesity: A systematic review. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Years of Age | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 to 3 (n = 328) | 3 to 4 (n = 366) | 4 to 5 (n = 299) | 5 to 6 (n = 358) | 6 to 7 (n = 307) | 7 to 8 (n = 401) | 8 to 9 (n = 372) | 9 to 10 (n = 416) | 10 to 11 (n = 360) | 11 to 12 (n = 363) | |||||||||||
| Children | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Sex % girls/boys | 49.1/50.9 | 48.6/51.4 | 48.2/51.8 | 48.0/52.0 | 50.2/49.8 | 49.1/50.9 | 44.9/55.1 | 44.0/56.0 | 43.6/56.4 | 46.0/54.0 | ||||||||||
| Age | 2.04 ± 0.16 | 3.05 ± 0.17 | 3.02 ± 0.21 | 4.03 ± 0.21 | 4.04 ± 0.26 | 5.04 ± 0.26 | 4.99 ± 0.27 | 5.99 ± 0.27 | 5.97 ± 0.28 | 6.98 ± 0.29 | 6.97 ± 0.29 | 7.97 ± 0.28 | 7.99 ± 0.28 | 9.00 ± 0.28 | 8.99 ± 0.27 | 10.00 ± 0.27 | 9.98 ± 0.28 | 10.99 ± 0.28 | 11.01 ± 0.29 | 12.02 ± 0.29 |
| zBMI | 0.24 ± 0.81 | 0.23 ± 0.74 | 0.20 ± 0.74 | 0.03 ± 0.73 | −0.01 ± 0.77 | −0.11 ± 0.79 | −0.12 ± 0.82 | −0.15 ± 0.87 | −0.14 ± 0.84 | −0.15 ± 0.85 | −0.14 ± 0.90 | −0.18 ± 0.91 | −0.07 ± 0.97 | −0.07 ± 1.01 | 0.01 ± 1.02 | 0.05 ± 1.02 | 0.08 ± 1.02 | 0.09 ± 1.05 | 0.18 ± 1.12 | 0.22 ± 1.14 |
| zBMI % | ||||||||||||||||||||
| underweight | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.7 | 0.8 | 2.2 | 1.7 | 1.1 |
| normal weight | 89.9 | 92.1 | 92.3 | 94.5 | 95.3 | 94.7 | 92.7 | 92.2 | 93.8 | 92.5 | 92.3 | 92.3 | 90.9 | 88.4 | 86.8 | 85.8 | 86.7 | 83.3 | 80.7 | 81.0 |
| overweight | 6.7 | 6.4 | 6.3 | 4.4 | 3.7 | 4.7 | 5.3 | 3.6 | 2.9 | 4.6 | 3.0 | 2.7 | 3.2 | 4.3 | 4.6 | 5.5 | 4.7 | 6.4 | 7.4 | 7.4 |
| obesity | 2.1 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 3.1 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 3.7 | 4.0 | 5.6 | 6.2 | 7.5 | 7.0 | 7.8 | 8.1 | 10.2 | 10.5 |
| SES | 13.79 ± 3.02 | 13.89 ± 3.13 | 14.24 ± 3.12 | 14.08 ± 3.13 | 13.96 ± 3.18 | 13.83 ± 3.28 | 13.62 ± 3.21 | 13.68 ± 3.39 | 13.42 ± 3.23 | 13.63 ± 3.32 | ||||||||||
| SES % | ||||||||||||||||||||
| low | 4.6 | 7.1 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 5.2 | 7.5 | 8.3 | 6.7 | 6.7 | 8.8 | ||||||||||
| medium | 51.8 | 44.0 | 40.5 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 42.9 | 45.2 | 48.3 | 51.9 | 47.4 | ||||||||||
| high | 43.6 | 48.9 | 54.5 | 49.7 | 49.8 | 49.6 | 46.5 | 45.0 | 41.4 | 43.8 | ||||||||||
| CFQ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| RST | 2.67 ± 0.84 | 2.70 ± 0.79 | 2.70 ± 0.82 | 2.60 ± 0.83 | 2.54 ± 0.80 | 2.49 ± 0.80 | 2.51 ± 0.83 | 2.42 ± 0.82 | 2.35 ± 0.82 | 2.33 ± 0.84 | 2.31 ± 0.85 | 2.23 ± 0.85 | 2.32 ± 0.85 | 2.31 ± 0.84 | 2.35 ± 0.89 | 2.29 ± 0.93 | 2.32 ± 0.90 | 2.29 ± 0.89 | 2.31 ± 0.88 | 2.28 ± 0.87 |
| RW | 2.05 ± 1.06 | 2.25 ± 1.08 | 2.17 ± 1.05 | 2.10 ± 1.10 | 2.07 ± 1.06 | 1.99 ± 1.04 | 2.05 ± 1.07 | 1.84 ± 0.97 | 1.78 ± 0.91 | 1.78 ± 0.92 | 1.76 ± 0.89 | 1.66 ± 0.87 | 1.71 ± 0.92 | 1.60 ± 0.86 | 1.64 ± 0.87 | 1.56 ± 0.86 | 1.63 ± 0.85 | 1.54 ± 0.79 | 1.51 ± 0.76 | 1.37 ± 0.65 |
| PE | 1.83 ± 0.82 | 1.85 ± 0.85 | 1.83 ± 0.82 | 1.96 ± 0.88 | 1.99 ± 0.87 | 1.92 ± 0.90 | 2.00 ± 0.93 | 1.99 ± 0.96 | 1.95 ± 0.95 | 1.95 ± 0.91 | 1.97 ± 0.95 | 1.93 ± 0.94 | 1.94 ± 0.96 | 1.90 ± 0.97 | 1.87 ± 0.93 | 1.76 ± 0.88 | 1.75 ± 0.85 | 1.75 ± 0.88 | 1.74 ± 0.86 | 1.60 ± 0.81 |
| MN | 4.01 ± 1.00 | 3.89 ± 0.97 | 3.92 ± 0.97 | 3.86 ± 1.01 | 3.78 ± 1.02 | 3.66 ± 0.98 | 3.67 ± 1.01 | 3.63 ± 1.02 | 3.72 ± 1.03 | 3.56 ± 1.06 | 3.61 ± 1.06 | 3.48 ± 1.05 | 3.59 ± 1.03 | 3.43 ± 1.04 | 3.52 ± 1.02 | 3.37 ± 1.10 | 3.44 ± 1.08 | 3.35 ± 1.05 | 3.43 ± 1.02 | 3.34 ± 1.01 |
| Years of Age | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | 2 to 3 | 3 to 4 | 4 to 5 | 5 to 6 | 6 to 7 | 7 to 8 | 8 to 9 | 9 to 10 | 10 to 11 | 11 to 12 |
| CFQ | ||||||||||
| RST | 0.431 | 0.520 | 0.593 | 0.613 | 0.638 | 0.629 | 0.655 | 0.684 | 0.672 | 0.695 |
| RW | 0.416 | 0.476 | 0.552 | 0.429 | 0.445 | 0.557 | 0.482 | 0.424 | 0.403 | 0.365 |
| PE | 0.391 | 0.563 | 0.490 | 0.637 | 0.570 | 0.656 | 0.683 | 0.559 | 0.569 | 0.592 |
| MN | 0.458 | 0.491 | 0.481 | 0.417 | 0.448 | 0.576 | 0.473 | 0.483 | 0.584 | 0.542 |
| zBMI | 0.818 | 0.821 | 0.914 | 0.890 | 0.916 | 0.912 | 0.934 | 0.948 | 0.940 | 0.951 |
| Years of Age | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | 2 to 3 | 3 to 4 | 4 to 5 | 5 to 6 | 6 to 7 | 7 to 8 | 8 to 9 | 9 to 10 | 10 to 11 | 11 to 12 |
| CFQ | ||||||||||
| RST | 0.68 (327) | 2.12 (365) * | 0.85 (298) | 1.03 (357) | 0.53 (306) | 1.76 (400) | −0.56 (371) | 1.24 (415) | 0.28 (359) | −0.15 (362) |
| RW | −3.13 (327) ** | 1.32 (365) | 1.46 (298) | 3.71 (357) *** | 0.15 (306) | 2.34 (400) * | 2.32 (371) * | 1.76 (415) | 1.90 (359) | 3.27 (362) ** |
| PE | −0.34 (327) | −3.18 (365) ** | 1.34 (298) | 0.09 (357) | −0.15 (306) | 1.11 (400) | 1.25 (371) | 2.84 (415) ** | 0.00 (359) | 3.72 (362) *** |
| MN | 2.14 (327) * | 1.12 (365) | 2.10 (298) * | 0.70 (357) | 2.58 (306) ** | 2.83 (400) ** | 2.78 (371) ** | 2.87 (415) ** | 1.78 (359) | 1.74 (362) |
| zBMI | 0.33 (327) | 7.32 (365) *** | 5.61 (298) *** | 1.43 (357) | 0.74 (306) | 2.29 (400) * | 0.07 (371) | −2.66 (415) ** | −0.95 (359) | −2.44 (362) * |
| n | χ2(df) | RMSEA (p Close) | RMSEA 95% CI | CFI | TLI | CMIN/df | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Years of Age | Lower | Upper | ||||||
| 2 to 3 | 328 | 24.272 (23) | 0.013 (0.962) | 0.000 | 0.048 | 0.998 | 0.996 | 1.055 |
| 3 to 4 | 366 | 48.002 (23) ** | 0.055 (0.337) | 0.033 | 0.076 | 0.978 | 0.936 | 2.087 |
| 4 to 5 | 299 | 25.104 (23) | 0.018 (0.936) | 0.000 | 0.052 | 0.998 | 0.995 | 1.091 |
| 5 to 6 | 358 | 41.822 (23) * | 0.048 (0.529) | 0.023 | 0.071 | 0.987 | 0.963 | 1.818 |
| 6 to 7 | 307 | 44.900 (23) ** | 0.056 (0.321) | 0.031 | 0.080 | 0.984 | 0.953 | 1.952 |
| 7 to 8 | 401 | 40.227 (23) * | 0.043 (0.668) | 0.019 | 0.065 | 0.992 | 0.976 | 1.749 |
| 8 to 9 | 372 | 24.075 (23) | 0.011 (0.978) | 0.000 | 0.045 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 1.047 |
| 9 to 10 | 416 | 44.411 (23) ** | 0.047 (0.553) | 0.026 | 0.068 | 0.990 | 0.972 | 1.931 |
| 10 to 11 | 360 | 37.133 (23) * | 0.041 (0.699) | 0.013 | 0.065 | 0.993 | 0.979 | 1.614 |
| 11 to 12 | 363 | 43.443 (23) ** | 0.050 (0.482) | 0.026 | 0.072 | 0.990 | 0.972 | 1.889 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eichler, J.; Schmidt, R.; Poulain, T.; Hiemisch, A.; Kiess, W.; Hilbert, A. Stability, Continuity, and Bi-Directional Associations of Parental Feeding Practices and Standardized Child Body Mass Index in Children from 2 to 12 Years of Age. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081751
Eichler J, Schmidt R, Poulain T, Hiemisch A, Kiess W, Hilbert A. Stability, Continuity, and Bi-Directional Associations of Parental Feeding Practices and Standardized Child Body Mass Index in Children from 2 to 12 Years of Age. Nutrients. 2019; 11(8):1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081751
Chicago/Turabian StyleEichler, Janina, Ricarda Schmidt, Tanja Poulain, Andreas Hiemisch, Wieland Kiess, and Anja Hilbert. 2019. "Stability, Continuity, and Bi-Directional Associations of Parental Feeding Practices and Standardized Child Body Mass Index in Children from 2 to 12 Years of Age" Nutrients 11, no. 8: 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081751
APA StyleEichler, J., Schmidt, R., Poulain, T., Hiemisch, A., Kiess, W., & Hilbert, A. (2019). Stability, Continuity, and Bi-Directional Associations of Parental Feeding Practices and Standardized Child Body Mass Index in Children from 2 to 12 Years of Age. Nutrients, 11(8), 1751. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081751







