The Association of TMPRSS6 Gene Polymorphism and Iron Intake with Iron Status among Under-Two-Year-Old Children in Lombok, Indonesia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Dietary Iron Intake Assessment
2.3. Iron and Hemoglobin Measurements
2.4. Genotyping Procedure
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Global Database on Anaemia. Worldwide Prevalence of Anaemia 1993–2005; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- McLean, E.; Cogswell, M.; Egli, I.; Wojdyla, D.; de Benoist, B. Worldwide prevalence of anaemia, WHO vitamin and mineral nutrition information system, 1993–2005. Public Health Nutr. 2009, 12, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Roy, C.N.; Yao, W.; Matteini, A.; Semba, R.D.; Arking, D.; Walston, J.D.; Fried, L.P.; Singleton, A.; Guralnik, J.; et al. A genome-wide association analysis of serum iron concentrations. Blood J. 2010, 115, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gichohi-Wainaina, W.N.; Towers, G.W.; Swinkels, D.W.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Feskens, E.J.; Melse-Boonstra, A. Inter-ethnic differences in genetic variants within the transmembrane protease, serine 6 (TMPRSS6) gene associated with iron status indicators: A systematic review with meta-analyses. Genes Nutr. 2014, 10, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chambers, J.C.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Sehmi, J.; Wass, M.N.; Zabaneh, D.; Hoggart, C.; Bayele, H.; McCarthy, M.I.; Peltonen, L.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants in TMPRSS6 associated with hemoglobin levels. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1170–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatala, S.; Ndossi, G.; Ash, D. Impact of dietary iron intake on anaemia in Tanzanian schoolchildren. Sajcn 2004, 17, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurnham, D.I.; Mccabe, G.P. Influence of infection and inflammation on biomarkers of nutritional status with an emphasis on vitamin A and iron. In World Health Organization, Proceedings of the Priorities in the Assessment of Vitamin A and Iron Status in Populations, Panama City, Panama, 15–17 September 2010; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, J.D.; Skikne, B.; Baynes, R. The use of transferrin receptor for the assessment of iron status. In Iron Nutrition in Health and Disease; Hallberg, L.A., Asp, N.-G., Eds.; John Libbey& Co.: London, UK, 1996; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- James, W.H. The validity of Weinberg’s differential rule. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2007, 10, 771–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, O. A century of Hardy-weinberg equilibrium. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2008, 11, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, S.R. Principles of Nutritional Assesment, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; 446p. [Google Scholar]
- Thurnham, D.I.; Mburu, A.S.W.; Mwaniki, D.L.; Wagt, A.D. Micronutrients in childhood and the influence of subclinical inflammation. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2005, 64, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkesson, A.; Bjellerup, P.; Berglund, M.; Bremme, K.; Vahter, M. Serum transferrin receptor: A specific marker of iron deficiency in pregnancy. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, W.; Guan, Y.; Wu, Q.; An, P.; Zhu, J.; Lu, L.; Jing, L.; Yu, Y.; Ruan, S.; Xie, D.; et al. Association of TMPRSS6 polymorphisms with ferritin, hemoglobin, and type 2 diabetes risk in a Chinese Han population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gichohi-Wainaina, W.N.; Melse-Boonstra, A.; Swinkels, D.W.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Feskens, E.J.; Towers, G.W. Common variants and haplotypes in the TF, TNF-alpha, and TMPRSS6 genes are associated with iron status in a female black South. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumagalli, M.; Sironi, M.; Pozzoli, U.; Ferrer-Admettla, A.; Pattini, L.; Nielsen, R. Signatures of environmental genetic adaptation pinpoint pathogens as the main selective pressure through human evolution. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatala, S.; Svanberg, U.; Mduma, B. Low dietary iron availability a major cause of anaemia. A nutrition survey in Lindi District of Tanzania. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, M.B.; Hurrell, R.F. Nutritional iron deficiency. Lancet 2007, 370, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, D.; An, P.; Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, A.; Mu, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; et al. Associations between serum hepcidin, ferritin and Hb concentrations and type 2 diabetes risks in a Han Chinese population. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 110, 2180–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
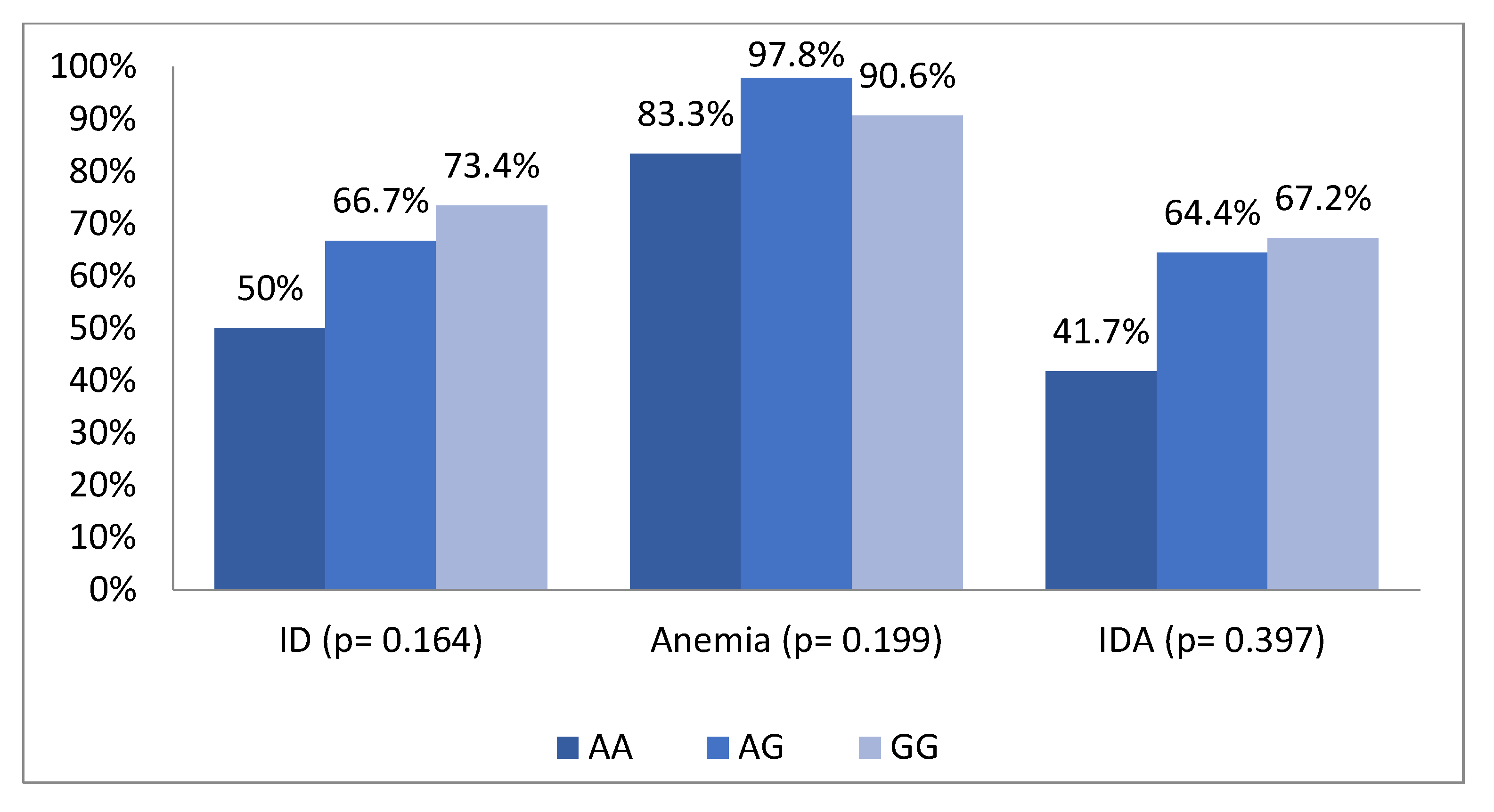
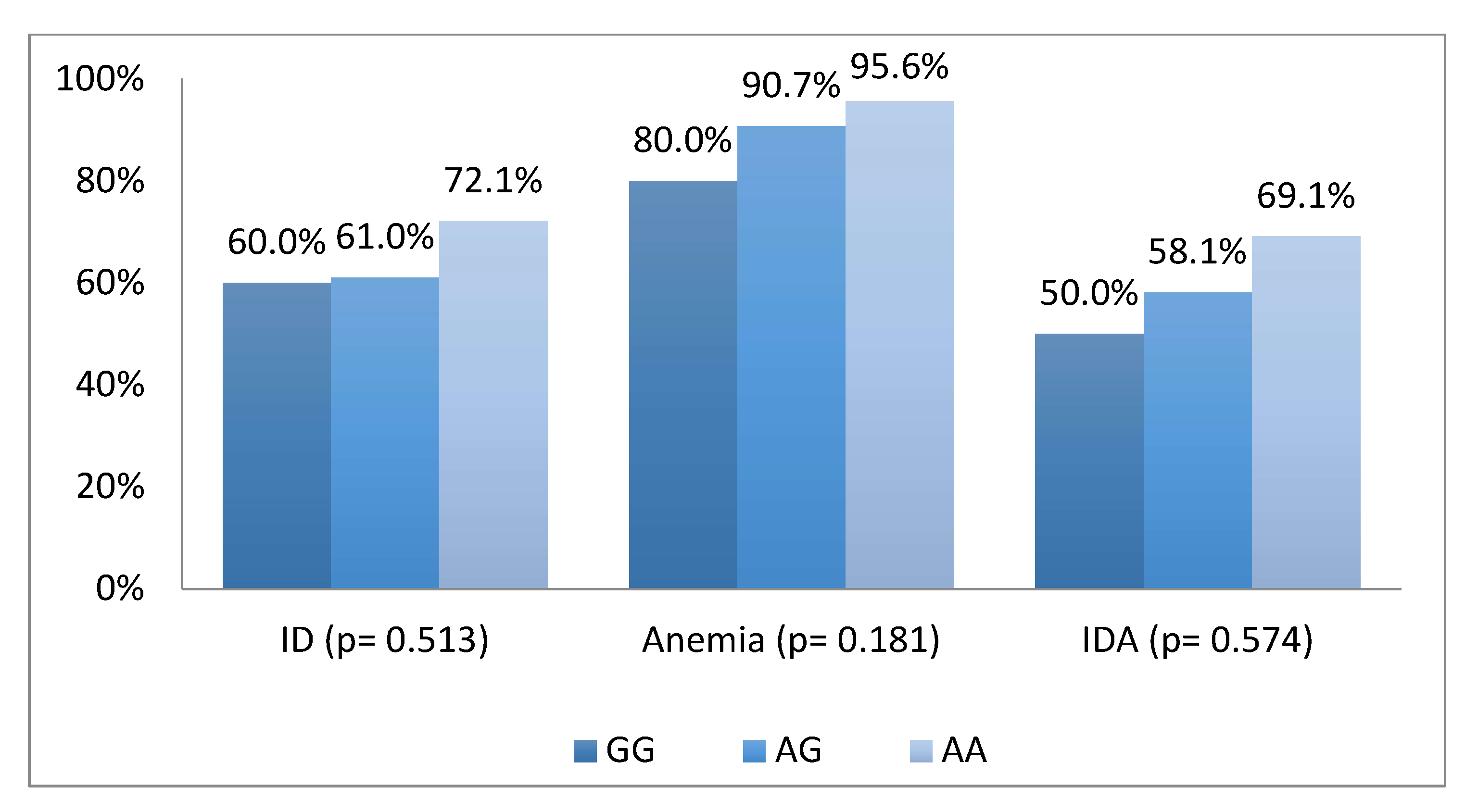
| Factors | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Demographic | |
| Age of children * [month] | 14.12 ± 1.39 |
| Sex of children | |
| Boy | 58 (47.9) |
| Girl | 63 (52.1) |
| Maternal Education | |
| Primary school | 81 (67.0) |
| Secondary school | 40 (37.0) |
| Maternal Occupation | |
| Not working | 88 (72.7) |
| Working | 33 (27.3) |
| Genotype Distribution | |
| Polymorphism of rs855791 | |
| GG homozygote | 10 (8.30) |
| GA heterozygote | 43 (35.50) |
| AA homozygote | 68 (56.20) |
| Polymorphism of rs4820268 | |
| AA homozygote | 12 (9.90) |
| AG heterozygote | 45 (37.20) |
| GG heterozygote | 64 (52.90) |
| Minor Allele Frequency (MAF) | |
| SNP rs855791 [A/G] | 179 (73.90) |
| SNP rs4820268 [G/A] | 173 (71.40) |
| Intake | |
| Iron [mg/day] * | 4.5 ± 3.01 |
| Iron indicator | |
| Serum ferritin [μg/L] *,† | 14.7 ± 18.00 |
| Serum transferrin receptor [mg/L] * | 8.7 ± 3.03 |
| Hemoglobin [g/dL] * | 9.51 ± 1.03 |
| Body iron store [mg/kg] * | −0.9 ± 3.8 |
| Anemia | 112 (92.6) |
| Iron deficiency | 84 (69.4) |
| Iron Deficiency Anemia | 77 (63.6) |
| SNP rs855791 | SNP rs420268 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GG (n = 10) | GA (n = 43) | AA (n = 68) | p | AA (n = 12) | AG (n = 45) | GG (n = 64) | p | |
| Age [mo] | 14.08 ± 1.4 | 14.19 ± 1.3 | 14.1 ± 1.5 | 0.945 | 14.3 ±1.3 | 14.1 ± 1.2 | 14.1 ± 1.5 | 0.875 |
| Sex [boy] * | 6 (5) | 18 (14.9) | 34 (28.1) | 0.823 | 5 (4.1) | 21 (17.4) | 32 (26.4) | 0.812 |
| Iron intake [mg] | 4.26 ± 3.17 | 4.7 ±3.62 | 4.49 ± 2.57 | 0.877 | 3.8 ± 2.9 | 4.7 ± 3.5 | 4.5 ± 2.5 | 0.638 |
| CRP [mg/L] | 5.7 ± 7.3 | 4.4 ± 8.4 | 3.4 ± 5.8 | 0.568 | 6.7 ± 10.1 | 3.9 ± 7.2 | 3.5 ± 5.9 | 0.351 |
| AGP [mg/L] | 1 ± 0.3 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.072 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 0.049 |
| Serum ferritin [μg/L] † | 11.4 ± 7.7 | 13.9 ± 14.9 | 10.5 ± 9.7 | 0.314 | 12.1 ± 8 | 14.1 ± 6 | 10 ± 7.7 | 0.197 |
| Serum transferrin receptor [mg/L] | 7.4 ± 2.5 | 8.8 ± 2.9 | 8.8 ± 3.1 | 0.839 | 7.4 ± 2.3 | 8.7 ± 2.8 | 8.9 ± 3.2 | 0.290 |
| Body iron store [mg/Kg] | 0.5 ± 3.5 | −0.4 ± 4.0 | −1.4 ± 3.8 | 0.180 | −1.5 ± 3.6 | −0.4 ± 4.1 | −0.7 ± 3.5 | 0.123 |
| Hemoglobin [g/dL] | 10.04 ± 1.07 | 9.53 ± 1.08 | 9.41 ± 0.97 | 0.195 | 10.08 ± 1.05 | 9.37 ± 0.90 | 9.50 ± 1.08 | 0.103 |
| Factors | Serum Ferritin (μg/L) * | Serum Transferrin Receptor (mg/L) | Hemoglobin (g/dL) | Body Iron Store (mg/Kg Body Weight) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | SE | p | β | SE | p | β | SE | p | β | SE | p | |
| Model I | ||||||||||||
| rs855791 (G/A) ** | −4.495 | 2.548 | 0.080 | 0.378 | 0.428 | 0.379 | −0.232 | 0.146 | 0.133 | −0.213 | 0.543 | 0.064 |
| Iron Intake (mg) | 1.476 | 0.551 | 0.009 | −0.109 | 0.093 | 0.241 | −0.018 | 0.031 | 0.565 | 0.059 | 0.104 | 0.518 |
| Model II | ||||||||||||
| rs4820268 (A/G) † | −5.003 | 2.453 | 0.044 | 0.567 | 0.412 | 0.171 | −0.137 | 0.142 | 0.335 | −0.067 | 0.104 | 0.458 |
| Iron Intake (mg) | 1.518 | 0.549 | 0.007 | −0.114 | 0.092 | 0.221 | −0.017 | 0.032 | 0.598 | −0.192 | −1.111 | 0.745 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shinta, D.; Asmarinah; Adhiyanto, C.; Htet, M.K.; Fahmida, U. The Association of TMPRSS6 Gene Polymorphism and Iron Intake with Iron Status among Under-Two-Year-Old Children in Lombok, Indonesia. Nutrients 2019, 11, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040878
Shinta D, Asmarinah, Adhiyanto C, Htet MK, Fahmida U. The Association of TMPRSS6 Gene Polymorphism and Iron Intake with Iron Status among Under-Two-Year-Old Children in Lombok, Indonesia. Nutrients. 2019; 11(4):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040878
Chicago/Turabian StyleShinta, Dewi, Asmarinah, Chris Adhiyanto, Min Kyaw Htet, and Umi Fahmida. 2019. "The Association of TMPRSS6 Gene Polymorphism and Iron Intake with Iron Status among Under-Two-Year-Old Children in Lombok, Indonesia" Nutrients 11, no. 4: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040878
APA StyleShinta, D., Asmarinah, Adhiyanto, C., Htet, M. K., & Fahmida, U. (2019). The Association of TMPRSS6 Gene Polymorphism and Iron Intake with Iron Status among Under-Two-Year-Old Children in Lombok, Indonesia. Nutrients, 11(4), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040878





