U-Shaped Relationship between Serum Leptin Concentration and Cognitive Performance in Older Asian Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Circulating Leptin Concentration
2.3. Assessment of Cognitive Performance
2.4. Assessments of Potential Confounders
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffei, M.; Halaas, J.; Ravussin, E.; Pratley, R.E.; Lee, G.H.; Zhang, Y.; Fei, H.; Kim, S.; Lallone, R.; Ranganathan, S.; et al. Leptin levels in human and rodent: Measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tezapsidis, N.; Johnston, J.M.; Smith, M.A.; Ashford, J.W.; Casadesus, G.; Robakis, N.K.; Wolozin, B.; Perry, G.; Zhu, X.; Greco, S.J.; et al. Leptin: A novel therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2009, 16, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, J.; Pedrós, I.; Patraca, I.; Sureda, F.; Junyent, F.; Beas-Zarate, C.; Verdaguer, E.; Pallàs, M.; Auladell, C.; Camins, A. Neuroprotective and anti-ageing role of leptin. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 49, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalamaga, M.; Chou, S.H.; Shields, K.; Papageorgiou, P.; Polyzos, S.A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Leptin at the intersection of neuroendocrinology and metabolism: Current evidence and therapeutic perspectives. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.Q.; Zhang, J.; Hao, M.; Yang, J.; Han, Y.F.; Liu, X.J.; Shi, H.; Wu, M.N.; Liu, Q.S.; Qi, J.S. Leptin attenuates the detrimental effects of β-amyloid on spatial memory and hippocampal later-phase long term potentiation in rats. Horm. Behav. 2015, 73, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; He, Y.F.; Li, A.P. The Role of Leptin in Cognitive Development During Aging. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan 2015, 46, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Irving, A.J.; Harvey, J. Leptin regulation of hippocampal synaptic function in health and disease. Philos Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 369, 20130155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, K.; Kosaka, H.; Okazawa, H.; Murata, T.; Wada, Y. Relationship between plasma leptin level and brain structure in elderly: A voxel-based morphometric study. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 992–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.M.; Hu, W.T.; Fardo, D.W.; Greco, S.J.; Perry, G.; Montine, T.J.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Shaw, L.M.; Ashford, J.W.; Tezapsidis, N.; et al. Low plasma leptin in cognitively impaired ADNI subjects: Gender differences and diagnostic and therapeutic potential. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2014, 11, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albala, C.; Angel, B.; Lera, L.; Sanchez, H.; Marquez, C.; Fuentes, P. Low Leptin Availability as a Risk Factor for Dementia in Chilean Older People. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Dis. Extra 2016, 6, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beydoun, M.A.; Beydoun, H.A.; Shroff, M.R.; Kitner-Triolo, M.H.; Zonderman, A.B. Serum leptin, thyroxine and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels interact to affect cognitive function among US adults: Evidence from a large representative survey. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 1730–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, P.; Toga, A.W.; Jack, C.R.; Weiner, M.W.; Thompson, P.M. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Fat-mass-related hormone, plasma leptin, predicts brain volumes in the elderly. Neuroreport 2013, 24, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonda, D.J.; Stone, J.G.; Torres, S.L.; Siedlak, S.L.; Perry, G.; Kryscio, R.; Jicha, G.; Casadesus, G.; Smith, M.A.; Zhu, X. Dysregulation of leptin signaling in Alzheimer disease: Evidence for neuronal leptin resistance. J. Neurochem. 2014, 128, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; van der Flier, W.M.; Scheltens, P.; Duits, A.; Wijnstok, N.; Nijpels, G.; Dekker, J.M.; Blankenstein, R.M.; Heijboer, A.C. Serum leptin is not altered nor related to cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 44, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoropoulou, A.; Metallinos, I.C.; Psyrogiannis, A.; Vagenakis, G.A.; Kyriazopoulou, V. Ghrelin and leptin secretion in patients with moderate Alzheimer’s disease. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2012, 16, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.W.; Hynan, L.S.; Weiner, M.F. Lipids and adipokines as risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 29, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshasai, S.; Liao, J.; Toh, Q.C.; Cheng, C.Y.; Cheung, G.C.; Sethi, S.; Wong, T.Y.; Sabanayagam, C. Serum leptin and age-related macular degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 1880–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, A.W.; Saw, S.M.; Loo, J.L.; Shen, S.; Loon, S.C.; Rosman, M.; Aung, T.; Tan, D.T.; Tai, E.S.; Wong, T.Y. Rationale and methodology for a population-based study of eye diseases in Malay people: The Singapore Malay Eye Study (SiMES). Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2007, 14, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, R.; Jeganathan, V.S.; Zheng, Y.; Raju, P.; Cheung, N.; Tai, E.S.; Wang, J.J.; Lamoureux, E.; Mitchell, P.; Young, T.L.; et al. Methodology of the Singapore Indian Chinese Cohort (SICC) eye study: Quantifying ethnic variations in the epidemiology of eye diseases in Asians. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2009, 16, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodkinson, H.M. Evaluation of a mental test score for assessment of mental impairment in the elderly. Age Ageing 1972, 1, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.C.; Wong, Y.Y.; Woo, J. Reliability and validity of the abbreviated mental test (Hong Kong version) in residential care homes. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2010, 58, 2255–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaiuto, S.; Rocca, W.A.; Lippi, A.; Luciani, P.; Giannandrea, E.; Cavarzeran, F.; Amaducci, L. Study on the validity of the Hodkinson Abbreviated Mental Test Score (AMTS) in detecting dementia of elderly subjects in appignano (Macerata province), Italy. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 1992, 15, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochon, J.; Gondan, M.; Kieser, M. To test or not to test: Preliminary assessment of normality when comparing two independent samples. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2012, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Luo, W.; Eitzman, D.T. Leptin in thrombosis and atherosclerosis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Martínez, E.; Miana, M.; Jurado-López, R.; Bartolomé, M.V.; Souza Neto, F.V.; Salaices, M.; López-Andrés, N.; Cachofeiro, V. The potential role of leptin in the vascular remodeling associated with obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, J.P.; Oka, R.K. Does leptin cause vascular disease? Circulation 2002, 106, 1904–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, D.J.; Inam, Q.U.; Haider, S.; Perveen, T.; Haleem, M.A. Serum leptin and cortisol, related to acutely perceived academic examination stress and performance in female university students. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback 2015, 40, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letra, L.; Santana, I.; Seiça, R. Obesity as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: The role of adipocytokines. Metab. Brain Dis. 2014, 29, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fewlass, D.C.; Noboa, K.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Johnston, J.M.; Yan, S.D.; Tezapsidis, N. Obesity-related leptin regulates Alzheimer’s Abeta. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanley, L.J.; Irving, A.J.; Harvey, J. Leptin enhances NMDA receptor function and modulates hippocampal synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Jiang, H.; Xu, X.; Duan, W.; Mattson, M.P. Leptin-mediated cell survival signaling in hippocampal neurons mediated by JAK STAT3 and mitochondrial stabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragano, N.R.; Haddad-Tovolli, R.; Velloso, L.A. Leptin, Neuroinflammation and Obesity. Front. Horm. Res. 2017, 48, 84–96. [Google Scholar]
- Tana, C.; Ticinesi, A.; Prati, B.; Nouvenne, A.; Meschi, T. Uric Acid and Cognitive Function in Older Individuals. Nutrients 2018, 10, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ticinesi, A.; Tana, C.; Nouvenne, A.; Prati, B.; Lauretani, F.; Meschi, T. Gut microbiota, cognitive frailty and dementia in older individuals: A systematic review. Clin. Intervent. Aging 2018, 13, 1497–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
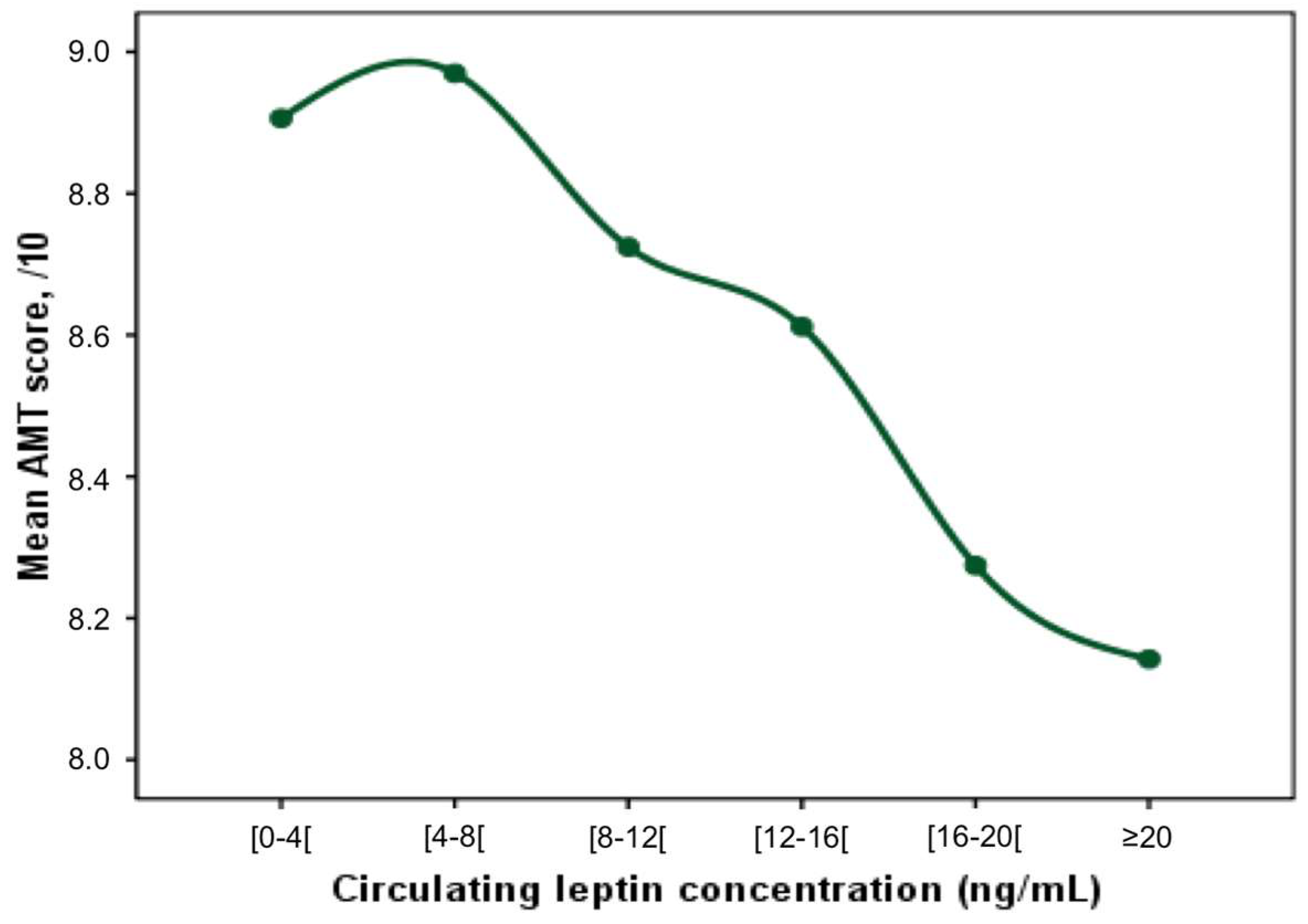

| Quintiles of Circulating Leptin Concentration, ng/mL | Overall p-Value * | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole Cohort (n = 1061) | Q1 (n = 212) ≤2.64 | Q2 (n = 206) 2.65–5.1 | Q3 (n = 222) 5.2–8.6 | Q4 (n = 212) 8.7–17.96 | Q5 (n = 209) ≥18 | ||
| Demographical measures | |||||||
| Age, years | 70.6 ± 6.4 | 71.5 ± 6.5 | 69.9 ± 6.2 | 70.7 ± 6.3 | 70.6 ± 6.6 | 69.9 ± 6.4 | 0.067 |
| Female gender, n (%) | 441 (41.6) | 32 (15.1) | 35 (17.0) | 77 (34.7) | 122 (57.5) | 175 (83.7) | <0.001 b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j |
| Regular smoking, n (%) | 342 (32.2) | 98 (46.2) | 90 (43.7) | 91 (41.0) | 44 (20.8) | 19 (9.1) | <0.001 c,d,f,g,h,i,j |
| Regular alcohol consumption †, n (%) | 16 (1.5) | 6 (2.8) | 5 (2.4) | 2 (0.9) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (1.4) | 0.112 |
| High education level ‡, n (%) | 447 (42.1) | 90 (42.5) | 101 (49.0) | 102 (45.9) | 83 (39.2) | 71 (34.0) | 0.019 f,g,i |
| Clinical measures | |||||||
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 24.8 ± 4.6 | 21.2 ± 2.9 | 23.5 ± 2.7 | 24.1 ± 2.9 | 25.3 ± 3.2 | 29.8 ± 5.7 | <0.001 a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j |
| Mean arterial pressure, mmHg | 98.3 ± 11.0 | 98.5 ± 11.2 | 98.2 ± 10.8 | 98.6 ± 10.8 | 98.5 ± 11.1 | 97.5 ± 11.1 | 0.810 |
| Memory complaint, n (%) | 292 (48.6) | 69 (50.4) | 53 (49.5) | 59 (49.2) | 60 (50.8) | 51 (42.9) | 0.730 |
| Anxiodepressive disorders, n (%) | 282 (26.6) | 35 (16.5) | 39 (18.9) | 51 (23.0) | 68 (32.1) | 89 (42.6) | <0.001 c,d,f,g,h,i,j |
| Blood measures | |||||||
| Leptin, ng/mL | 12.1 ± 15.5 | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 3.7 ± 0.7 | 6.7 ± 1.0 | 12.6 ± 2.66 | 36.4 ± 20.3 | - |
| Glycosylated hemoglobin, % | 6.4 ± 1.1 | 6.2 ± 1.1 | 6.3 ± 1.1 | 6.4 ± 1.0 | 6.5 ± 1.1 | 6.5 ± 1.0 | 0.003 b,c,d,f |
| LDL cholesterol concentration, mmol/L | 3.0 ± 0.9 | 3.1 ± 0.9 | 2.9 ± 0.8 | 3.0 ± 1.0 | 3.0 ± 0.9 | 3.0 ± 0.8 | 0.249 |
| 25-hydroxyvitamin D, µg/L | 22.3 ± 11.2 | 30.1 ± 10.3 | 27.8 ± 11.1 | 25.1 ± 10.4 | 23.1 ± 11.5 | 20.2 ± 9.8 | <0.001 a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate, mL/min | 69.2 ± 20.3 | 73.5 ± 17.4 | 72.4 ± 19.1 | 69.2 ± 20.4 | 68.3 ± 20.9 | 62.5 ± 21.7 | <0.001 b,c,d,f,g,i,j |
| Circulating Leptin Concentration, ng/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 (Lowest) | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 (Highest) | |||||
| β (95% CI) | p-Value | β (95% CI) | p-Value | β | β (95% CI) | p-Value | β (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| AMT score, /10 | |||||||||
| Unadjusted model | −0.10 (−0.40;0.19) | 0.489 | 0.24 (−0.02;0.51) | 0.071 | ref | −0.37 (−0.68;−0.06) | 0.021 | −0.71 (−1.05;−0.38) | <0.001 |
| Fully adjusted model * | −0.53 (−0.98;−0.09) | 0.018 | −0.08 (−0.45;0.30) | 0.697 | ref | −0.08 (−0.52;0.36) | 0.724 | −0.60 (−1.15;−0.04) | 0.036 |
| Anterograde episodic memory subscore, /1 | |||||||||
| Unadjusted model | −0.03 (−0.12;0.06) | 0.538 | 0.04 (−0.05;0.13) | 0.402 | ref | −0.06 (−0.16;0.03) | 0.192 | −0.17 (−0.26;−0.08) | <0.001 |
| Fully adjusted model * | −0.06 (−0.21;0.09) | 0.409 | −0.00 (−0.13;0.13) | 0.981 | ref | −0.28 (−0.16;0.10) | 0.677 | −0.19 (−0.35;−0.03) | 0.020 |
| Retrograde episodic memory subscore, /2 | |||||||||
| Unadjusted model | −0.01 (−0.09;0.07) | 0.770 | 0.06 (−0.01;0.13) | 0.094 | ref | −0.11 (−0.20;−0.02) | 0.018 | −0.19 (−0.28;−0.09) | <0.001 |
| Fully adjusted model * | −0.11 (−0.25;0.02) | 0.101 | −0.01 (−0.12;0.10) | 0.824 | ref | −0.06 (−0.20;0.08) | 0.401 | −0.18 (−0.35;−0.09) | 0.039 |
| Semantic memory subscore, /2 | |||||||||
| Unadjusted model | −0.008 (−0.09;0.08) | 0.852 | 0.04 (−0.05;0.12) | 0.404 | ref | −0.12 (−0.21;−0.03) | 0.012 | −0.12 (−0.22;−0.03) | 0.012 |
| Fully adjusted model * | −0.05 (−0.18;0.09) | 0.504 | −0.03 (−0.16;0.10) | 0.629 | ref | −0.05 (−0.19;0.09) | 0.450 | −0.16 (−0.34;0.01) | 0.068 |
| Working memory subscore, /1 | |||||||||
| Unadjusted model | −0.05 (−0.12;0.02) | 0.127 | 0.03 (−0.03;0.09) | 0.357 | ref | −0.10 (−0.17;−0.03) | 0.006 | −0.10 (−0.17;−0.03) | 0.007 |
| Fully adjusted model * | −0.10 (−0.21;0.01) | 0.074 | −0.04 (−0.13;0.06) | 0.476 | ref | −0.06 (−0.16;0.05) | 0.279 | −0.07 (−0.20;0.06) | 0.281 |
| Orientation in space subscore, /1 | |||||||||
| Unadjusted model | −0.006 (−0.04;0.02) | 0.703 | 0.01 (−0.01;0.04) | 0.297 | ref | 0.01 (−0.02;0.03) | 0.518 | 0.00 (−0.02;0.03) | 0.807 |
| Fully adjusted model* | −0.05 (−0.11;−0.00) | 0.048 | −0.00 (−0.05;0.04) | 0.882 | ref | 0.04 (0.00;0.08) | 0.043 | 0.03 (−0.03;0.09) | 0.287 |
| Orientation in time subscore, /2 | |||||||||
| Unadjusted model | 0.003 (−0.06;0.07) | 0.922 | 0.06 (0.01;0.12) | 0.031 | ref | −0.00 (−0.07;0.07) | 0.966 | −0.11 (−0.19;−0.04) | 0.004 |
| Fully adjusted model * | −0.09 (−0.20;0.02) | 0.116 | 0.02 (−0.07;0.11) | 0.700 | ref | 0.07 (−0.03;0.17) | 0.186 | −0.01 (−0.14;0.13) | 0.922 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Annweiler, C.; Duval, G.T.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Wong, T.-Y.; Lamoureux, E.L.; Milea, D.; Sabanayagam, C. U-Shaped Relationship between Serum Leptin Concentration and Cognitive Performance in Older Asian Adults. Nutrients 2019, 11, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030660
Annweiler C, Duval GT, Cheng C-Y, Wong T-Y, Lamoureux EL, Milea D, Sabanayagam C. U-Shaped Relationship between Serum Leptin Concentration and Cognitive Performance in Older Asian Adults. Nutrients. 2019; 11(3):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030660
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnnweiler, Cedric, Guillaume T. Duval, Ching-Yu Cheng, Tien-Yin Wong, Ecosse L. Lamoureux, Dan Milea, and Charumathi Sabanayagam. 2019. "U-Shaped Relationship between Serum Leptin Concentration and Cognitive Performance in Older Asian Adults" Nutrients 11, no. 3: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030660
APA StyleAnnweiler, C., Duval, G. T., Cheng, C.-Y., Wong, T.-Y., Lamoureux, E. L., Milea, D., & Sabanayagam, C. (2019). U-Shaped Relationship between Serum Leptin Concentration and Cognitive Performance in Older Asian Adults. Nutrients, 11(3), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11030660






