Altered Processing of Visual Food Stimuli in Adolescents with Loss of Control Eating
Abstract
1. Introduction
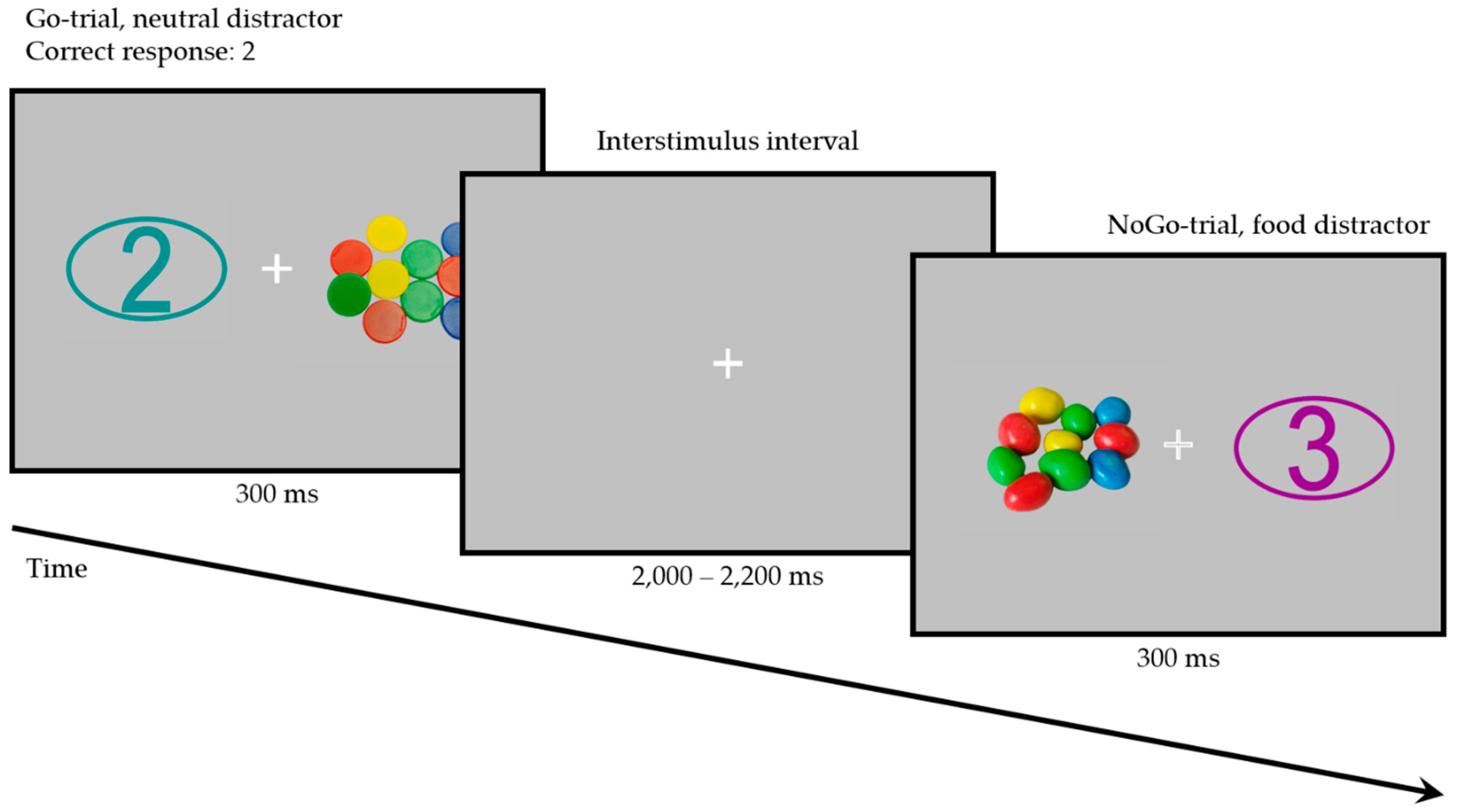
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Data and Stimulus Ratings
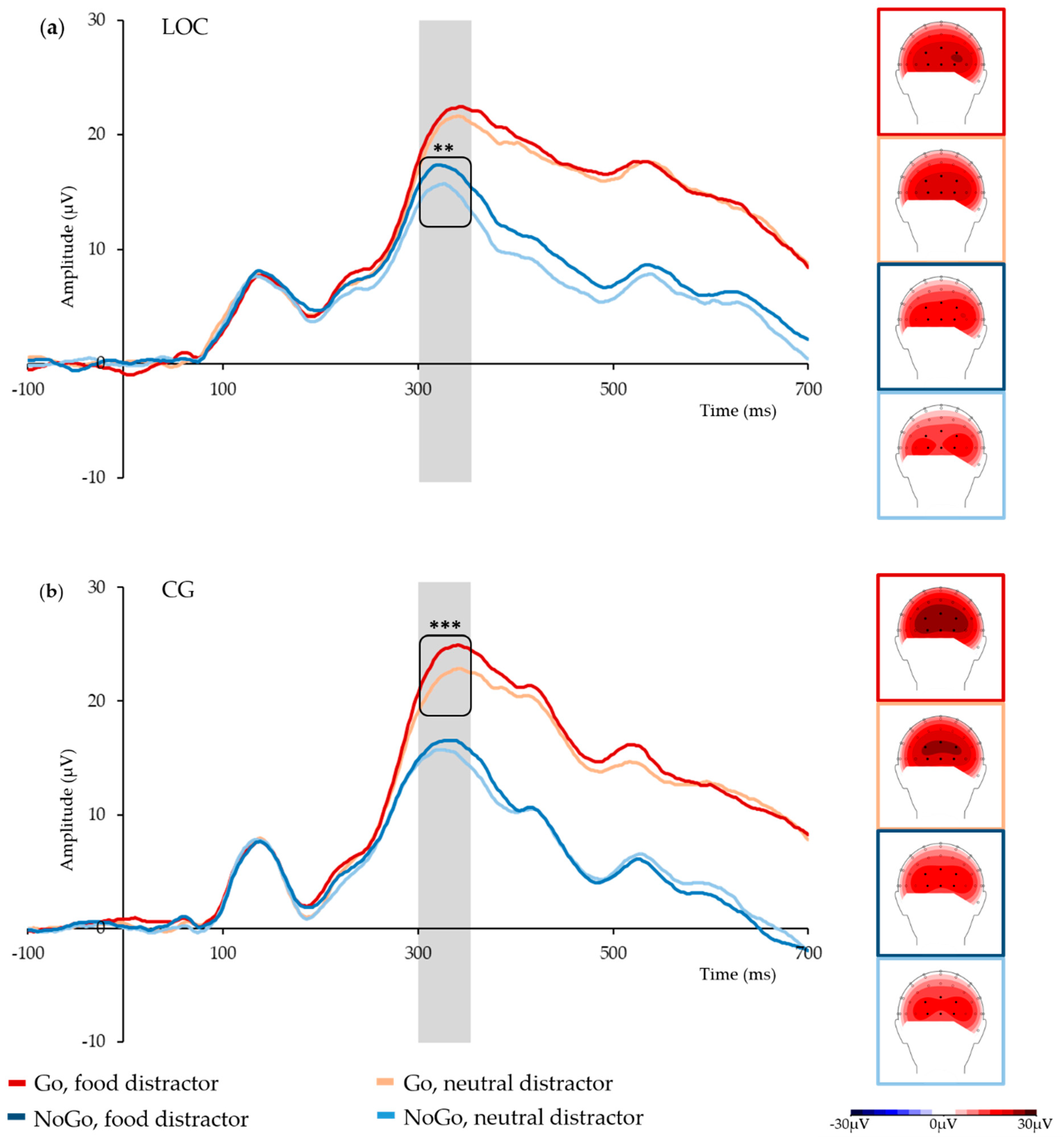
3.2. Electroencephalographic Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kelly, N.R.; Shank, L.M.; Bakalar, L.; Tanofsky-Kraff, M. Pediatric feeding and eating disorders: Current state of diagnosis and treatment. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2014, 16, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamerz, A.; Kuepper-Nybelen, J.; Bruning, N.; Wehle, C.; Trost-Brinkhues, G.; Brenner, H.; Hebebrand, J.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B. Prevalence of obesity, binge eating, and night eating in a cross-sectional field survey of 6-year-old children and their parents in a German urban population. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2005, 46, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smink, F.R.E.; van Hoeken, D.; Oldehinkel, A.J.; Hoek, H.W. Prevalence and severity of DSM-5 eating disorders in a community cohort of adolescents. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2014, 47, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association (APA). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Arlington, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Marcus, M.D.; Yanovski, S.Z.; Yanovski, J.A. Loss of control eating disorder in children age 12 years and younger: Proposed research criteria. Eat. Behav. 2008, 9, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, C.M.; Yanovski, S.Z.; Nguyen, T.T.; McDuffie, J.; Sebring, N.G.; Jorge, M.R.; Keil, M.; Yanovski, J.A. Loss of control over eating, adiposity, and psychopathology in overweight children. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2002, 31, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decaluwe, V.; Braet, C. Prevalence of binge-eating disorder in obese children and adolescents seeking weight-loss treatment. Int. J. Obes. 2003, 27, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shomaker, L.B.; Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Elliott, C.; Wolkoff, L.E.; Columbo, K.M.; Ranzenhofer, L.M.; Roza, C.A.; Yanovski, S.Z.; Yanovski, J.A. Salience of loss of control for pediatric binge episodes: Does size really matter? Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2010, 43, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafran, R.; Lee, M.; Cooper, Z.; Palmer, R.L.; Fairburn, C.G. Attentional bias in eating disorders. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2007, 40, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, F.; Naumann, E.; Trentowska, M.; Svaldi, J. Attentional bias for food cues in binge eating disorder. Appetite 2014, 80, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svaldi, J.; Naumann, E.; Trentowska, M.; Schmitz, F. General and food-specific inhibitory deficits in binge eating disorder. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2014, 47, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svaldi, J.; Schmitz, F.; Trentowska, M.; Tuschen-Caffier, B.; Berking, M.; Naumann, E. Cognitive interference and a food-related memory bias in binge eating disorder. Appetite 2014, 72, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, F.; Naumannm, E.; Biehlm, S.; Svaldi, J. Gating of attention towards food stimuli in binge eating disorder. Appetite 2015, 95, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.; Lüthold, P.; Kittel, R.; Tetzlaff, A.; Hilbert, A. Visual attentional bias for food in adolescents with binge-eating disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 80, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shank, L.M.; Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Nelson, E.E.; Shomaker, L.B.; Ranzenhofer, L.M.; Hannallah, L.M.; Field, S.E.; Vannucci, A.; Bongiorno, D.M.; Brady, S.M.; et al. Attentional bias to food cues in youth with loss of control eating. Appetite 2015, 87, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, S.L.; Kisbu-Sakarya, Y.; Reynolds, K.D.; Boyle, S.; Cappelli, C.; Cox, M.G.; Dust, M.; Grenard, J.L.; Mackinnon, D.P.; Stacy, A.W. Inhibitory control effects in adolescent binge eating and consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages and snacks. Appetite 2014, 81, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nederkoorn, C.; Braet, C.; Van Eijs, Y.; Tanghe, A.; Jansen, A. Why obese children cannot resist food: The role of impulsivity. Eat. Behav. 2006, 7, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picton, T.W. The P300 wave of the human event-related potential. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1992, 9, 456–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polich, J. Updating P300: An integrative theory of P3a and P3b. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 2128–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, M.J.; Weijers, H.G.; Wiesbeck, G.A.; Böning, J.; Fallgatter, A.J. Alcohol cue-reactivity in heavy and light social drinkers as revealed by event-related potentials. Alcohol Alcohol. 2001, 36, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Wu, J.; Crowley, M.J.; Fearon, P. Restrictive feeding practices and adiposity are differentially related to P3b cortical responses to food stimuli in children. Appetite 2013, 63, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupp, H.T.; Stockburger, J.; Codispoti, M.; Junghöfer, M.; Weike, A.I.; Hamm, A.O. Selective visual attention to emotion. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijs, I.M.T.; Franken, I.H.A.; Muris, P. Food cue-elicited brain potentials in obese and healthy-weight individuals. Eat. Behav. 2008, 9, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, J.; Ardelt-Gattinger, E.; Paulmichl, K.; Weghuber, D.; Blechert, J. Dietary restraint and impulsivity modulate neural responses to food in adolescents with obesity and healthy adolescents. Obesity 2015, 23, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoon, H.F.A.; Ohla, K.; de Graaf, C.; Boesveldt, S. Modulation of event-related potentials to food cues upon sensory-specific satiety. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 196, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blechert, J.; Feige, B.; Hajcak, G.; Tuschen-Caffier, B. To eat or not to eat? Availability of food modulates the electrocortical response to food pictures in restrained eaters. Appetite 2010, 54, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijs, I.M.T.; Muris, P.; Euser, A.S.; Franken, I.H. Differences in attention to food and food intake between overweight/obese and normal-weight females under conditions of hunger and satiety. Appetite 2010, 54, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justus, A.N.; Finn, P.R.; Steinmetz, J.E. P300, disinhibited personality, and early-onset alcohol problems. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijs, I.M.T.; Franken, I.H.A.; Smulders, F.T.Y. BIS/BAS sensitivity and the P300 event-related brain potential. J. Psychophysiol. 2007, 21, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. Bull. World Health Organ. 2001, 79, 373–374. [Google Scholar]
- Blechert, J.; Feige, B.; Joos, A.; Zeeck, A.; Tuschen-Caffier, B. Electrocortical processing of food and emotional pictures in anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. Psychosom. Med. 2011, 73, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Unnewehr, S.; Margraf, J. Diagnostisches Interview Bei Psychischen Störungen im Kindes- und Jugendalter (Kinder-DIPS); Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hilbert, A.; Hartmann, A.S.; Czaja, J. Child Eating Disorder Examination-Questionnaire: Psychometrische Eigenschaften der deutschsprachigen Übersetzung. Klinische Diagnostik Evaluation 2008, 1, 447–463. [Google Scholar]
- Meule, A.; Hermann, T.; Kuebler, A. A short version of the Food Cravings Questionnaire - Trait: The FCQ-T-reduced. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kromeyer-Hauschild, K.; Wabitsch, M.; Kunze, D.; Geller, F.; Geiß, H.C.; Hesse, V.; von Hippel, A.; Jaeger, U.; Johnsen, D.; Korte, W.; et al. Perzentile für den Body-mass-Index für das Kindes-und Jugendalter unter Heranziehung verschiedener deutscher Stichproben. Monatsschrift Kinderheilkunde 2001, 149, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willenbockel, V.; Sadr, J.; Fiset, D.; Horne, G.O.; Gosselin, F.; Tanaka, J.W. Controlling low-level image properties: The SHINE toolbox. Behav. Res. Methods 2010, 42, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, M.M.; Lang, P.J. Measuring emotion–the self-assessment mannequin and the semantic differential. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 1994, 25, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvers, J.A.; Insel, C.; Powers, A.; Franz, P.; Weber, J.; Mischel, W.; Casey, B.J.; Ochsner, K.N. Curbing craving: Behavioral and brain evidence that children regulate craving when instructed to do so but have higher baseline craving than adults. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 25, 1932–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratton, G.; Coles, M.G.; Donchin, E. A new method for off-line removal of ocular artifact. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1983, 55, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Willner, C.J.; Hill, C.; Fearon, P.; Mayes, L.C.; Crowley, M.J. Emotional eating and instructed food-cue processing in adolescents: An ERP study. Biol. Psychol. 2017, 132, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corr, P.J. Reinforcement sensitivity theory and personality. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2004, 28, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.A. The neuropsychology of anxiety-an inquiry into the functions of the septo-hippocampal system. Behav. Brain Sci. 1982, 5, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, N.; Gray, J.A. Anxiolytic action on the behavioural inhibition system implies multiple types of arousal contribute to anxiety. J. Affect. Disord. 2000, 61, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, J.; Hartmann, A.S.; Rief, W.; Hilbert, A. Mealtime family interactions in home environments of children with loss of control eating. Appetite 2011, 56, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wacker, J.; Chavanon, M.-L.; Leue, A.; Stemmler, G. Trait BIS predicts alpha asymmetry and P300 in a go/no-go task. Eur. J. Pers. 2010, 24, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiloni, C.; Del Percio, C.; Valenzano, A.; Marzano, N.; De Rosas, M.; Petito, A.; Bellomo, A.; Rossi, G.; Lecce, B.; Mundi, C.; et al. Frontal attentional responses to food size are abnormal in obese subjects: An electroencephalographic study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toepel, U.; Knebel, J.F.; Hudry, J.; le Coutre, J.; Murray, M.M. The brain tracks the energetic value in food images. Neuroimage 2009, 44, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, A.S.; Rief, W.; Hilbert, A. Impulsivity and negative mood in adolescents with loss of control eating and ADHD symptoms: An experimental study. Eat. Weight Disord. 2013, 18, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; McDuffie, J.R.; Yanovski, S.Z.; Kozlosky, M.; Schvey, N.A.; Shomaker, L.B.; Salaita, C.; Yanovski, J.A. Laboratory assessment of the food intake of children and adolescents with loss of control eating. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, L.; Van Malderen, E.; Van Durme, K.; Braet, C. Loss of control eating in adolescents: Associations with adaptive and maladaptive emotion regulation strategies. Eat. Behav. 2016, 22, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matherne, C.E.; Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Altschul, A.M.; Shank, L.M.; Schvey, N.A.; Brady, S.M.; Galescu, O.; Demidowich, A.P.; Yanovski, S.Z.; Yanovski, J.A. A preliminary examination of Loss of Control Eating Disorder (LOC-ED) in middle childhood. Eat. Behav. 2015, 18, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, S.; Peirano, P.; Peigneux, P.; Lozoff, B.; Algarin, C. Inhibitory control in otherwise healthy overweight 10-year-old children. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, T.D.; Garvey, K.T. Neurocognitive correlates of processing food-related stimuli in a Go/No-go paradigm. Appetite 2013, 71, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polich, J.; Kok, A. Cognitive and biological determinants of P300—An integrative review. Biol. Psychol. 1995, 41, 103–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carver, C.S.; White, T.L. Behavioral inhibition, behavioral activation, and affective responses to impending reward and punishment: The BIS/BAS scales. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1994, 67, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbert, A.; Brauhardt, A. Childhood loss of control eating over five-year follow-up. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2014, 47, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Descriptive and Behavioral Data | LOC | CG |
|---|---|---|
| n (girls) | 15 (9) | 19 (9) |
| Age | 12.9 | 12.3 |
| BMI percentile | 75.8 (29.8) | 60.5 (35.9) |
| ChEDE-Q | 1.8 (1.3) ** | 0.5 (0.6) ** |
| FCQ-T-r | 35.2 (13.2) ** | 21.9 (5.1) ** |
| Energy intake | ||
| Total intake (kcal) | 661 (264) | 558 (249) |
| Fat (%) | 18.2 (3.8) | 16.7 (4.7) |
| Carbohydrates (%) | 49.9 (4.5) | 51.2 (3.1) |
| Protein (%) | 6.3 (1.2) # | 5.5 (1.2) # |
| Reaction time (ms) | ||
| High-calorie food distractor | 733 (106) | 784 (152) |
| Neutral distractor | 754 (133) | 780 (144) |
| % Incorrect responses | ||
| High-calorie food distractor | 5.1 (6.4) | 5.5 (8.7) |
| Neutral distractor | 3.7 (6.2) | 5.8 (8.6) |
| % Misses | ||
| High-calorie food distractor | 0.06 (0.09) | 0.06 (0.11) |
| Neutral distractor | 0.06 (0.09) | 0.06 (0.13) |
| False alarms | ||
| High-calorie food distractor | 0.3 (0.7) | 0.7 (1.2) |
| Neutral distractor | 0.5 (0.9) | 0.9 (1.9) |
| Valence | ||
| High-calorie food * | 6.3 (1.3) | 6.0 (1.2) |
| Neutral * | 5.9 (1.7) | 5.2 (1.1) |
| Arousal | ||
| High-calorie food * | 3.1 (1.9) | 3.4 (1.9) |
| Neutral * | 2.6 (1.5) | 2.9 (1.6) |
| Palatability | 5.7 (1.5) | 5.8 (1.2) |
| Condition | LOC | CG |
|---|---|---|
| Go, food distractor | 21.3 (12.7) | 23.9 (7.0) *** |
| Go, neutral distractor | 20.4 (12.3) | 21.9 (7.1) *** |
| NoGo, food distractor | 16.6 (11.4) ** | 16.0 (8.0) |
| NoGo, neutral distractor | 14.8 (11.3) ** | 15.1 (6.5) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biehl, S.C.; Ansorge, U.; Naumann, E.; Svaldi, J. Altered Processing of Visual Food Stimuli in Adolescents with Loss of Control Eating. Nutrients 2019, 11, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020210
Biehl SC, Ansorge U, Naumann E, Svaldi J. Altered Processing of Visual Food Stimuli in Adolescents with Loss of Control Eating. Nutrients. 2019; 11(2):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020210
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiehl, Stefanie C., Ulrich Ansorge, Eva Naumann, and Jennifer Svaldi. 2019. "Altered Processing of Visual Food Stimuli in Adolescents with Loss of Control Eating" Nutrients 11, no. 2: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020210
APA StyleBiehl, S. C., Ansorge, U., Naumann, E., & Svaldi, J. (2019). Altered Processing of Visual Food Stimuli in Adolescents with Loss of Control Eating. Nutrients, 11(2), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11020210




