Herbal Medicines Attenuate PD-L1 Expression to Induce Anti-Proliferation in Obesity-Related Cancers
Abstract
1. Background
2. Obesity, PD-L1, and Cancers
3. Thyroid Hormone and PD-L1
4. Steroid Hormone and PD-L1
5. Herbal Medicines, Obesity, and PD-L1
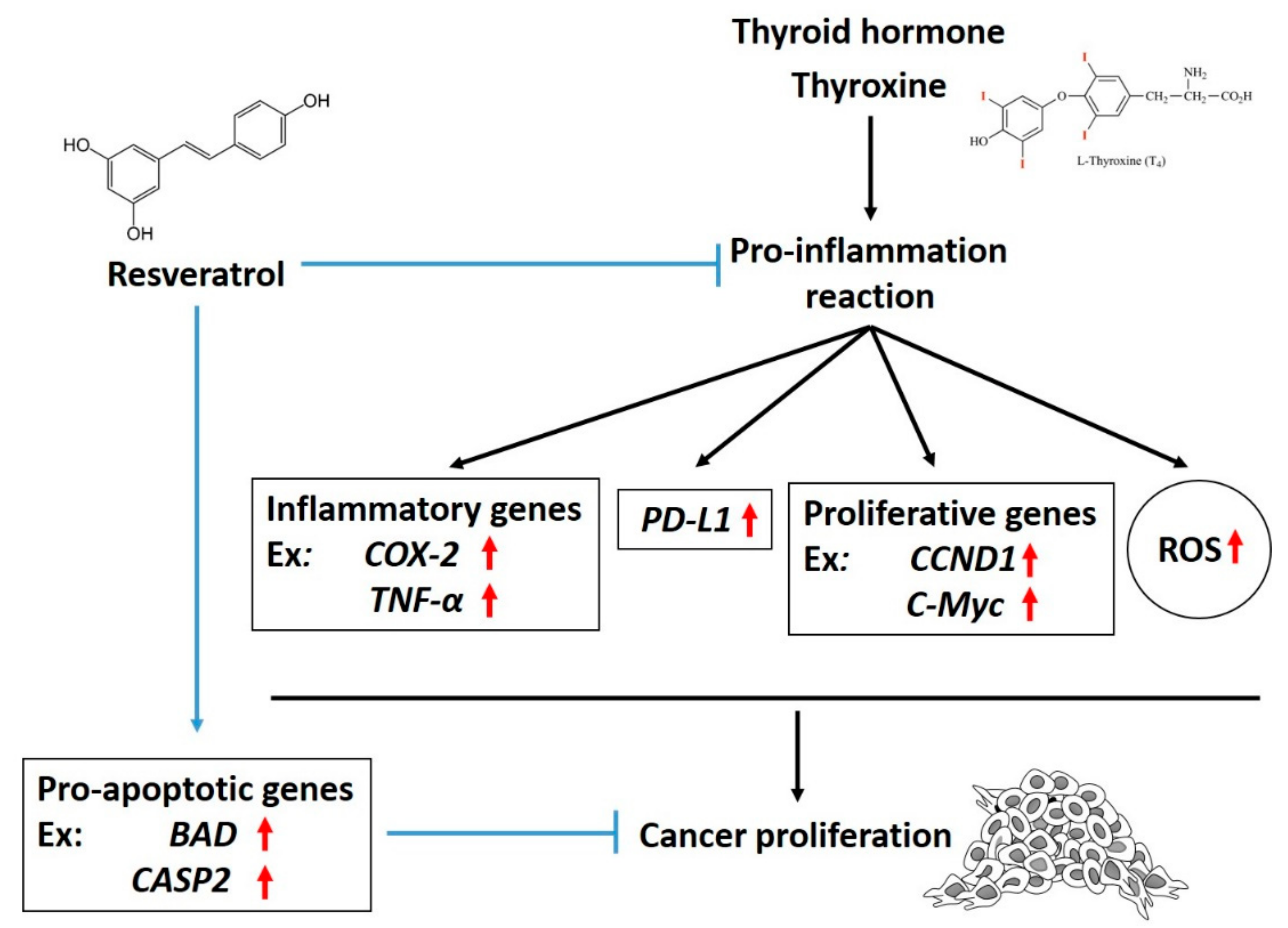
5.1. Resveratrol
5.2. Curcumin
6. Anoectochilus Formosanus Hayata
7. The Balance between Herbal Medicines and Hormones in PD-L1 Expression
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Aguilar, E.G.; Luna, J.I.; Dunai, C.; Khuat, L.T.; Le, C.T.; Mirsoian, A.; Minnar, C.M.; Stoffel, K.M.; Sturgill, I.R.; et al. Paradoxical effects of obesity on T cell function during tumor progression and PD-1 checkpoint blockade. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, A.; Di Segni, C.; Raimondo, S.; Olivieri, G.; Silvestrini, A.; Meucci, E.; Curro, D. Thyroid hormones, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 6757154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, E.A.; Sheridan, P.A.; Beck, M.A. Diet-induced obesity impairs the T cell memory response to influenza virus infection. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3127–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliakim, A.; Schwindt, C.; Zaldivar, F.; Casali, P.; Cooper, D.M. Reduced tetanus antibody titers in overweight children. Autoimmunity 2006, 39, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Corno, M.; D’Archivio, M.; Conti, L.; Scazzocchio, B.; Vari, R.; Donninelli, G.; Varano, B.; Giammarioli, S.; De Meo, S.; Silecchia, G.; et al. Visceral fat adipocytes from obese and colorectal cancer subjects exhibit distinct secretory and omega6 polyunsaturated fatty acid profiles and deliver immunosuppressive signals to innate immunity cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 63093–63105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, T.Y.; Park, J.; Scherer, P.E. Hyperglycemia as a risk factor for cancer progression. Diabetes Metab. J. 2014, 38, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Wang, L.H.; Hsu, K.Y.; Chin, Y.T.; Yang, Y.S.H.; Wang, S.H.; Chen, Y.R.; Shih, Y.J.; Liu, L.F.; et al. Inhibitory effect of anoectochilus formosanus extract on hyperglycemia-related PD-L1 expression and cancer proliferation. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortellini, A.; Bersanelli, M.; Buti, S.; Cannita, K.; Santini, D.; Perrone, F.; Giusti, R.; Tiseo, M.; Michiara, M.; Di Marino, P.; et al. A multicenter study of body mass index in cancer patients treated with anti-PD-1/ PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors: When overweight becomes favorable. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysaght, J. The ‘obesity paradox’ in action with cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 132–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calise, S.J.; Keppeke, G.D.; Andrade, L.E.; Chan, E.K. Anti-rods/rings: A human model of drug-induced autoantibody generation. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, J.A.; Otsuka, A.; Kabashima, K. Anti-PD-1 and anti-ctla-4 therapies in cancer: Mechanisms of action, efficacy, and limitations. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Desai, A. Ctla-4 and PD-1 pathways: Similarities, differences, and implications of their inhibition. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Zhang, R.; Peng, Z.; Dong, D.; Wei, G.; Wang, Y. Inhibition of il-18-mediated myeloid derived suppressor cell accumulation enhances anti-pd1 efficacy against osteosarcoma cancer. J. Bone Oncol. 2017, 9, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Flies, D.B. Molecular mechanisms of T cell co-stimulation and co-inhibition. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedy, J.; Bekiaris, V.; Ware, C.F. Tumor necrosis factor superfamily in innate immunity and inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 7, a016279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, M.W.; Cheung, T.C.; Ware, C.F. The signaling networks of the herpesvirus entry mediator (tnfrsf14) in immune regulation. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 244, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Li, S.; Gao, H.; Nanding, A.; Quan, L.; Yang, C.; Ding, S.; Xue, Y. Increased btla and hvem in gastric cancer are associated with progression and poor prognosis. Oncotargets Ther. 2017, 10, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Jin, H.; Huang, D. Overexpression of b7-h1 correlates with malignant cell proliferation in pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; Ma, L.; You, Z. Inflammatory cytokines il-17 and tnf-alpha up-regulate PD-L1 expression in human prostate and colon cancer cells. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 184, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Mi, Y.; Guo, N.; Xu, H.; Xu, L.; Gou, X.; Jin, W. Cytokine-induced killer cells as pharmacological tools for cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhuang, M.; Zong, Z.; Zou, J.; Li, G.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; et al. Cross-talk between tnf-alpha and ifn-gamma signaling in induction of b7-h1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowrishankar, K.; Gunatilake, D.; Gallagher, S.J.; Tiffen, J.; Rizos, H.; Hersey, P. Inducible but not constitutive expression of PD-L1 in human melanoma cells is dependent on activation of nf-kappab. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Qu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; Ning, W.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, N.; Du, W.; Chen, C.; et al. PD-L1 induced by ifn-gamma from tumor-associated macrophages via the jak/stat3 and pi3k/akt signaling pathways promoted progression of lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 22, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Li, C.; Liu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Hua, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Ge, C. A blockade of PD-L1 produced antitumor and antimetastatic effects in an orthotopic mouse pancreatic cancer model via the pi3k/akt/mtor signaling pathway. Oncotargets Ther. 2017, 10, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Okayama, T.; Oka, K.; Mizushima, K.; Yasuda, T.; Sakamoto, N.; Katada, K.; Kamada, K.; Uchiyama, K.; et al. The jak/stat pathway is involved in the upregulation of PD-L1 expression in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimura, K.; Teh, J.L.; Okayama, H.; Shiraishi, K.; Kua, L.F.; Koh, V.; Smoot, D.T.; Ashktorab, H.; Oike, T.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. PD-L1 expression is mainly regulated by interferon gamma associated with jak-stat pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Huang, F.; Mei, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Xi, M.; You, Z. Posttranscriptional control of PD-L1 expression by 17beta-estradiol via pi3k/akt signaling pathway in eralpha-positive cancer cell lines. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2017, 27, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Chin, Y.T.; Nana, A.W.; Shih, Y.J.; Lai, H.Y.; Tang, H.Y.; Leinung, M.; Mousa, S.A.; Davis, P.J. Actions of l-thyroxine and nano-diamino-tetrac (nanotetrac) on PD-L1 in cancer cells. Steroids 2016, 114, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.J.; Chin, Y.T.; Ho, Y.; Chou, S.Y.; Sh Yang, Y.C.; Nana, A.W.; Su, K.W.; Lim, Y.T.; Wang, K.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Nano-diamino-tetrac (NDAT) inhibits PD-L1 expression which is essential for proliferation in oral cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 120, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.R.; Chin, Y.T.; Li, Z.L.; Shih, Y.J.; Yang, Y.C.; ChangOu, C.A.; Su, P.Y.; Wang, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Liu, L.F.; et al. Expression of inflammatory genes by thyroid hormone interferes with resveratrol-induced anti-proliferation in oral cancer cells via stat3 signal transduction pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, S.M.; Fallahi, P.; Galetta, F.; Citi, E.; Benvenga, S.; Antonelli, A. Thyroid disorders induced by checkpoint inhibitors. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2018, 19, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-C.; Chin, Y.-T.; Shih, Y.-J.; Chen, Y.-R.; Chung, Y.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Hsiung, C.-N.; Whang-Peng, J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lin, H.-Y.; et al. Resveratrol antagonizes thyroid hormone-induced expression of checkpoint and proliferative genes in oral cancer cells. J. Dent. Sci. 2019, 14, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, Y.T.; Wei, P.L.; Ho, Y.; Nana, A.W.; Changou, C.A.; Chen, Y.R.; Yang, Y.S.; Hsieh, M.T.; Hercbergs, A.; Davis, P.J.; et al. Thyroxine inhibits resveratrol-caused apoptosis by PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nana, A.W.; Wu, S.Y.; Yang, Y.S.; Chin, Y.T.; Cheng, T.M.; Ho, Y.; Li, W.S.; Liao, Y.M.; Chen, Y.R.; Shih, Y.J.; et al. Nano-diamino-tetrac (NDAT) enhances resveratrol-induced antiproliferation by action on the rrm2 pathway in colorectal cancers. Horm. Cancer 2018, 9, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Chin, Y.T.; Yang, Y.C.; Lai, H.Y.; Wang-Peng, J.; Liu, L.F.; Tang, H.Y.; Davis, P.J. Thyroid hormone, cancer, and apoptosis. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 1221–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.R.; Chen, Y.S.; Chin, Y.T.; Li, Z.L.; Shih, Y.J.; Yang, Y.S.H.; ChangOu, C.A.; Su, P.Y.; Wang, S.H.; Wu, Y.H.; et al. Thyroid hormone-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines interfere with resveratrol-induced anti-proliferation of oral cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 132, 110693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.T.; Wang, L.M.; Changou, C.A.; Chin, Y.T.; Yang, Y.S.H.; Lai, H.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Yang, Y.N.; Whang-Peng, J.; Liu, L.F.; et al. Crosstalk between integrin alphavbeta3 and eralpha contributes to thyroid hormone-induced proliferation of ovarian cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 24237–24249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Tang, H.Y.; Westfall, J.; London, D.; Cao, J.H.; Mousa, S.A.; Luidens, M.; Hercbergs, A.; Davis, F.B.; Davis, P.J.; et al. Crosstalk between integrin alphavbeta3 and estrogen receptor-alpha is involved in thyroid hormone-induced proliferation in human lung carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnakish, M.T.; Ahmed, A.A.; Mohler, P.J.; Janssen, P.M. Role of oxidative stress in thyroid hormone-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and associated cardiac dysfunction: An undisclosed story. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 854265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcocci, C.; Leo, M.; Altea, M.A. Oxidative stress in graves’ disease. Eur. Thyroid J. 2012, 1, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, I.; Alva-Sanchez, C.; Pacheco-Rosado, J. The role of thyroid hormones as inductors of oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 218145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, P.J.; Glinsky, G.V.; Lin, H.Y.; Leith, J.T.; Hercbergs, A.; Tang, H.Y.; Ashur-Fabian, O.; Incerpi, S.; Mousa, S.A. Cancer cell gene expression modulated from plasma membrane integrin alphavbeta3 by thyroid hormone and nanoparticulate tetrac. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 240. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov, V.; Bouttier, M.; Boukhaled, G.; Salehi-Tabar, R.; Avramescu, R.G.; Memari, B.; Hasaj, B.; Lukacs, G.L.; Krawczyk, C.M.; White, J.H. Hormonal vitamin d up-regulates tissue-specific PD-L1 and pd-l2 surface glycoprotein expression in humans but not mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 20657–20668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Mishra, A.P.; Nigam, M.; Sener, B.; Kilic, M.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Martins, N.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Resveratrol: A double-edged sword in health benefits. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancon, A.; Frazzi, R.; Latruffe, N. Anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic properties of resveratrol in ocular diseases. Molecules 2016, 21, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradamante, S.; Barenghi, L.; Villa, A. Cardiovascular protective effects of resveratrol. Cardiovasc. Drug Rev. 2004, 22, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Hsieh, M.T.; Cheng, G.Y.; Lai, H.Y.; Chin, Y.T.; Shih, Y.J.; Nana, A.W.; Lin, S.Y.; Yang, Y.S.H.; Tang, H.Y.; et al. Mechanisms of action of nonpeptide hormones on resveratrol-induced antiproliferation of cancer cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1403, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.H.; Sethi, G.; Um, J.Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Arfuso, F.; Kumar, A.P.; Bishayee, A.; Ahn, K.S. The role of resveratrol in cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyenihi, O.R.; Oyenihi, A.B.; Adeyanju, A.A.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Antidiabetic effects of resveratrol: The way forward in its clinical utility. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 9737483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Schueller, K.; Schaefer, L.M.; Pignitter, M.; Esefelder, L.; Somoza, V. Resveratrol and its metabolites inhibit pro-inflammatory effects of lipopolysaccharides in u-937 macrophages in plasma-representative concentrations. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, Q.; Bai, J.; Shi, Y.; Le, G. Resveratrol prevents suppression of regulatory T-cell production, oxidative stress, and inflammation of mice prone or resistant to high-fat diet-induced obesity. Nutr. Res. 2013, 33, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Sun, J.; Li, L.; Zheng, J.; Shi, Y.; Le, G. Regulatory effects of resveratrol on glucose metabolism and t-lymphocyte subsets in the development of high-fat diet-induced obesity in c57bl/6 mice. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1452–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousef, M.; Vlachogiannis, I.A.; Tsiani, E. Effects of resveratrol against lung cancer: In vitro and in vivo studies. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Korner, H.; Zhang, L.; Wei, W. Molecular mechanisms of T cells activation by dendritic cells in autoimmune diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, G. Intercellular interplay between sirt1 signalling and cell metabolism in immune cell biology. Immunology 2015, 145, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Yang, Y.; Xia, F.; Huang, A.; Gao, X.; Fang, D.; Xiong, S.; Zhang, J. Resveratrol inhibits cd4+ T cell activation by enhancing the expression and activity of sirt1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.L.; Yu, L.; Jiao, X.Y.; Meng, K.W.; Pan, C.E. The suppressive effect of resveratrol on protein kinase c theta in peripheral blood t lymphocytes in a rat liver transplantation model. Transplant. Proc. 2006, 38, 3052–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, L. Influence of resveratrol on the immune response. Nutrients 2019, 11, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xue, J.; Shen, T.; Ba, G.; Yu, D.; Fu, Q. Curcumin alleviates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis by protecting osteoblasts from apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2016, 43, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Bordoloi, D.; Padmavathi, G.; Monisha, J.; Roy, N.K.; Prasad, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, the golden nutraceutical: Multitargeting for multiple chronic diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1325–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Jiang, Y.; Gupta, S.; Younus, M.; Ramzan, M. Anti-inflammatory potency of nano-formulated puerarin and curcumin in rats subjected to the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation. J. Med. Food 2013, 16, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Thiagarajan, R.; Rastrelli, L.; Daglia, M.; Sobarzo-Sanchez, E.; Alinezhad, H.; Nabavi, S.M. Curcumin: A natural product for diabetes and its complications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 2445–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Panda, A.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Sa, G. Curcumin and tumor immune-editing: Resurrecting the immune system. Cell Div. 2015, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.O.; Li, C.W.; Xia, W.; Cha, J.H.; Chan, L.C.; Wu, Y.; Chang, S.S.; Lin, W.C.; Hsu, J.M.; Hsu, Y.H.; et al. Deubiquitination and stabilization of PD-L1 by csn5. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, F.; Liu, L.; Luo, E.; Hu, J. Curcumin enhances anti-tumor immune response in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Arch. Oral Biol. 2018, 92, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Zhu, W.; Da, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z. Bisdemethoxycurcumin in combination with alpha-PD-L1 antibody boosts immune response against bladder cancer. Oncotargets Ther. 2017, 10, 2675–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, K.; Chen, X.; Zhang, R.; Mu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Liu, F.; et al. Apigenin suppresses PD-L1 expression in melanoma and host dendritic cells to elicit synergistic therapeutic effects. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Chin, Y.T.; Shih, Y.J.; Nana, A.W.; Chen, Y.R.; Wu, H.C.; Yang, Y.S.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Davis, P.J. Thyroid hormone promotes beta-catenin activation and cell proliferation in colorectal cancer. Horm. Cancer 2018, 9, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nana, A.W.; Chin, Y.T.; Lin, C.Y.; Ho, Y.; Bennett, J.A.; Shih, Y.J.; Chen, Y.R.; Changou, C.A.; Pedersen, J.Z.; Incerpi, S.; et al. Tetrac downregulates beta-catenin and hmga2 to promote the effect of resveratrol in colon cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papiez, M.A.; Kaja, M.; Gebarowska, A. Age-dependent different action of curcumin in thyroid of rat. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2008, 46, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Belcaro, G.; Dugall, M.; Peterzan, P.; Hosoi, M.; Ledda, A.; Riva, A.; Giacomelli, L.; Togni, S.; Eggenhoffner, R.; et al. Interaction study between antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, thyroid replacement therapy and a bioavailable formulation of curcumin (Meriva®). Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 5042–5046. [Google Scholar]
- Jena, S.; Dandapat, J.; Chainy, G.B. Curcumin differentially regulates the expression of superoxide dismutase in cerebral cortex and cerebellum of l-thyroxine (T4)-induced hyperthyroid rat brain. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.H.; Lee, G.; Choi, H.Y. Effect of curcumin on the interaction between androgen receptor and wnt/beta-catenin in lncap xenografts. Korean J. Urol. 2015, 56, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ige, A.O.; Chidi, R.N.; Egbeluya, E.E.; Jubreel, R.O.; Adele, B.O.; Adewoye, E.O. Amelioration of thyroid dysfunction by magnesium in experimental diabetes may also prevent diabetes-induced renal impairment. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.-C.S.H.; Li, Z.-L.; Shih, Y.-J.; Bennett, J.A.; Whang-Peng, J.; Lin, H.-Y.; Davis, P.J.; Wang, K. Herbal Medicines Attenuate PD-L1 Expression to Induce Anti-Proliferation in Obesity-Related Cancers. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2979. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122979
Yang Y-CSH, Li Z-L, Shih Y-J, Bennett JA, Whang-Peng J, Lin H-Y, Davis PJ, Wang K. Herbal Medicines Attenuate PD-L1 Expression to Induce Anti-Proliferation in Obesity-Related Cancers. Nutrients. 2019; 11(12):2979. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122979
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yu-Chen S.H., Zi-Lin Li, Ya-Jung Shih, James A. Bennett, Jaqueline Whang-Peng, Hung-Yun Lin, Paul J. Davis, and Kuan Wang. 2019. "Herbal Medicines Attenuate PD-L1 Expression to Induce Anti-Proliferation in Obesity-Related Cancers" Nutrients 11, no. 12: 2979. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122979
APA StyleYang, Y.-C. S. H., Li, Z.-L., Shih, Y.-J., Bennett, J. A., Whang-Peng, J., Lin, H.-Y., Davis, P. J., & Wang, K. (2019). Herbal Medicines Attenuate PD-L1 Expression to Induce Anti-Proliferation in Obesity-Related Cancers. Nutrients, 11(12), 2979. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122979





