A Calorie-Restricted Ketogenic Diet Reduces Cerebral Cortex Vascularization in Prepubertal Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Histology
2.3. Statistical Analysis
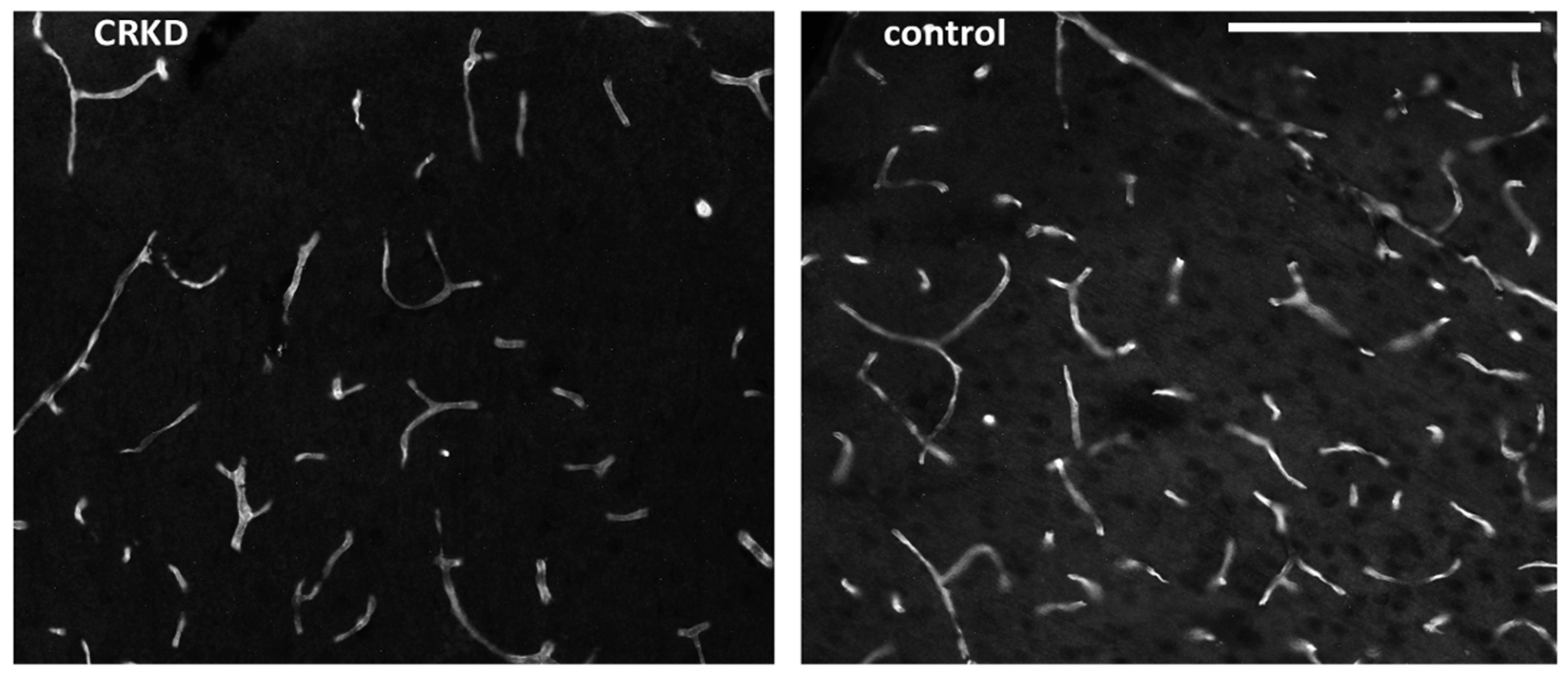
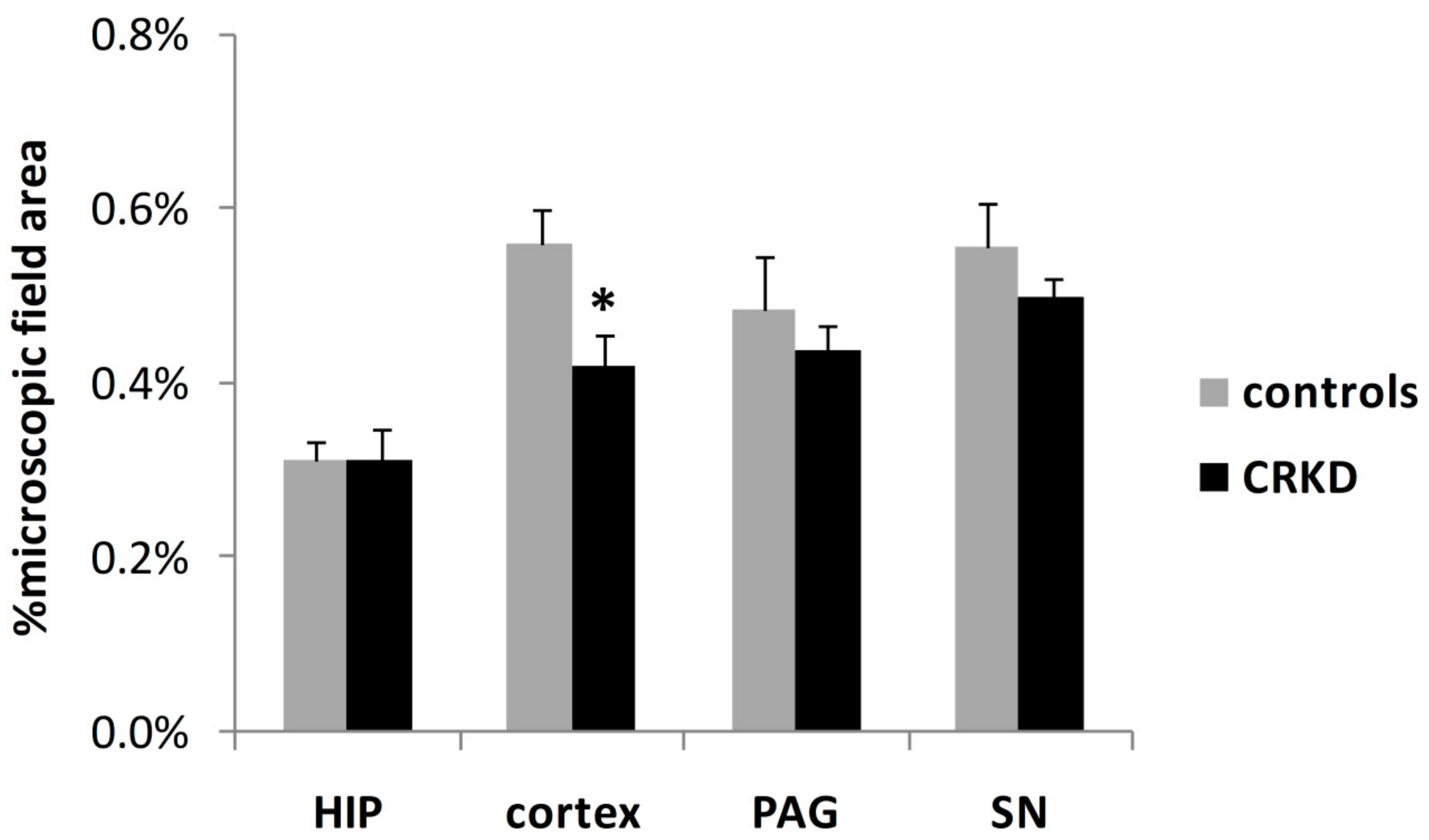
3. Results
3.1. Body Weight and Brain Dimensions
3.2. Capillary Density
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coppola, G.; Verrotti, A.; Ammendola, E.; Operto, F.F.; Della Corte, R.; Signoriello, G.; Pascotto, A. Ketogenic diet for the treatment of catastrophic epileptic encephalopathies in childhood. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2010, 14, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G.; D’Aniello, A.; Messana, T.; Di Pasquale, F.; Della Corte, R.; Pascotto, A.; Verrotti, A. Low glycemic index diet in children and young adults with refractory epilepsy: First Italian experience. Seizure 2011, 20, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veggiotti, P.; Burlina, A.; Coppola, G.; Cusmai, R.; De Giorgis, V.; Guerrini, R.; Tagliabue, A.; DallaBernardina, B. The ketogenic diet for Dravet syndrome and other epileptic encephalopathies: An Italian consensus. Epilepsia 2001, 52 (Suppl. 2), 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G. Malignant migrating partial seizures in infancy. Stroke 2013, 111, 605–609. [Google Scholar]
- Rogawski, M.A.; Löscher, W.; Rho, J.M. Mechanisms of action of antiseizuredrugs and the ketogenic diet. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a022780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, D.P.; Pilla, R.; Held, H.E.; Landon, C.S.; Puchowicz, M.; Brunengraber, H.; Ari, C.; Arnold, P.; Dean, J.B. Therapeutic ketosis with ketone ester delays central nervous system oxygen toxicity seizures in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 304, R829–R836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viggiano, A.; Pilla, R.; Arnold, P.; Monda, M.; D’Agostino, D.; Coppola, G. Anticonvulsant properties of an oral ketone ester in a pentylenetetrazole-model of seizure. Brain Res. 2015, 1618, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bough, K.J.; Valiyil, R.; Han, F.T.; Eagles, D. Seizure resistance is dependent upon age and calorie restriction in rats fed a ketogenic diet. Epilepsy Res. 1999, 35, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, A.W.; Sander, J.W. Rationale for using intermittent calorie restriction as a dietary treatment for drug resistant epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2014, 33, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viggiano, A.; Pilla, R.; Arnold, P.; Monda, M.; D’Agostino, D.; Zeppa, P.; Coppola, G. Different calorie restriction treatments have similar anti-seizure efficacy. Seizure 2016, 35, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viggiano, A.; Stoddard, M.; Pisano, S.; Operto, F.F.; Iovane, V.; Monda, M.; Coppola, G. Ketogenic diet prevents neuronal firing increase within the substantia nigra during pentylenetetrazole-induced seizure in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2016, 125, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groesbeck, D.K.; Bluml, R.M.; Kossoff, E.H. Long-term use of the ketogenic diet in the treatment of epilepsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2006, 48, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.T.; Kang, H.C.; Song, J.E.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, E.J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.D. Catch-up growth after long-term implementation and weaning from ketogenic diet in pediatric epileptic patients. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groleau, V.; Schall, J.I.; Stallings, V.A.; Bergqvist, C.A. Long-term impact of the ketogenic diet on growth and resting energy expenditure in children with intractable epilepsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woolf, E.C.; Curley, K.L.; Liu, Q.; Turner, G.H.; Charlton, J.A.; Preul, M.C.; Scheck, A.C. The Ketogenic Diet Alters the Hypoxic Response and Affects Expression of Proteins Associated with Angiogenesis, Invasive Potential and Vascular Permeability in a Mouse Glioma Model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Mukherjee, P.; Kiebish, M.A.; Markis, W.T.; Mantis, J.G.; Seyfried, T.N. The calorically restricted ketogenic diet, an effective alternative therapy for malignant brain cancer. Nutr. Metab. 2007, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benini, R.; Roth, R.; Khoja, Z.; Avoli, M.; Wintermark, P. Does angiogenesis play a role in the establishment of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy? Int. J. Dev.Neurosci. 2016, 49, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bough, K.J.; Eagles, D.A. A ketogenic diet increases the resistance to pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in the rat. Epilepsia 1999, 40, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchowicz, M.A.; Xu, K.; Sun, X.; Ivy, A.; Emancipator, D.; Lamanna, J.C. Diet-induced ketosis increases capillary density without altered blood flow in rat brain. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2007, 292, E1607–E1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krum, J.M.; More, N.S.; Rosenstein, J.M. Brain angiogenesis: Variations in vascular basement membrane glycoprotein immunoreactivity. Exp. Neurol. 1991, 111, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spulber, G.; Spulber, S.; Hagenäs, L.; Åmark, P.; Dahlin, M. Growth dependence on insulin-like growth factor-1 during the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbain, P.; Strom, L.; Morawski, L.; Wehrle, A.; Deibert, P.; Bertz, H. Impact of a 6-week non-energy-restricted ketogenic diet on physical fitness, body composition and biochemical parameters in healthy adults. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Amicis, R.; Leone, A.; Lessa, C.; Foppiani, A.; Ravella, S.; Ravasenghi, S.; Trentani, C.; Ferraris, C.; Veggiotti, P.; De Giorgis, V.; et al. Long-Term Effects of a Classic Ketogenic Diet on Ghrelin and Leptin Concentration: A 12-Month Prospective Study in a Cohort of Italian Children and Adults with GLUT1-Deficiency Syndrome and Drug Resistant Epilepsy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-López, C.; Leroith, D.; Torres-Aleman, I. Insulin-like growth factor I is required for vessel remodeling in the adult brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9833–9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Z. Cerebral insulin, insulin signaling pathway, and brain angiogenesis. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeller, K.; Vogel, J.; Kuschinsky, W. Postnatal distribution of Glut1 glucose transporter and relative capillary density in blood-brain barrier structures and circumventricular organs during development. Dev. Brain Res. 1996, 91, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, G.; Veggiotti, P.; Cusmai, R.; Bertoli, S.; Cardinali, S.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Elia, M.; Lispi, M.L.; Sarnelli, C.; Tagliabue, A.; et al. The ketogenic diet in children, adolescents and young adults with refractory epilepsy: An Italian multicentric experience. Epilepsy Res. 2002, 48, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadarola, M.; Gale, K. Substantia nigra: Site of anticonvulsant activity mediated by gamma-aminobutyric acid. Science 1982, 218, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, J.O.; Galloway, M.T.; Rigsbee, L.C.; Shin, C. Evidence implicatingsubstantianigra in regulation of kindled seizure threshold. J. Neurosci. 1984, 4, 2410–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, K. Role of the substantia nigra in GABA-mediated anticonvulsant actions. Adv. Neurol. 1986, 44, 343–364. [Google Scholar]
- Depaulis, A.; Vergnes, M.; Marescaux, C. Endogenous control of epilepsy: The nigral inhibitory system. Prog. Neurobiol. 1994, 42, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Berg, J.; Yellen, G. Ketogenic diet metabolites reduce firing in central neurons by opening K(ATP) channels. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 3618–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viggiano, A.; Meccariello, R.; Santoro, A.; Secondulfo, C.; Operto, F.F.; Monda, M.; Coppola, G. A Calorie-Restricted Ketogenic Diet Reduces Cerebral Cortex Vascularization in Prepubertal Rats. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112681
Viggiano A, Meccariello R, Santoro A, Secondulfo C, Operto FF, Monda M, Coppola G. A Calorie-Restricted Ketogenic Diet Reduces Cerebral Cortex Vascularization in Prepubertal Rats. Nutrients. 2019; 11(11):2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112681
Chicago/Turabian StyleViggiano, Andrea, Rosaria Meccariello, Antonietta Santoro, Carmine Secondulfo, Francesca Felicia Operto, Marcellino Monda, and Giangennaro Coppola. 2019. "A Calorie-Restricted Ketogenic Diet Reduces Cerebral Cortex Vascularization in Prepubertal Rats" Nutrients 11, no. 11: 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112681
APA StyleViggiano, A., Meccariello, R., Santoro, A., Secondulfo, C., Operto, F. F., Monda, M., & Coppola, G. (2019). A Calorie-Restricted Ketogenic Diet Reduces Cerebral Cortex Vascularization in Prepubertal Rats. Nutrients, 11(11), 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11112681







