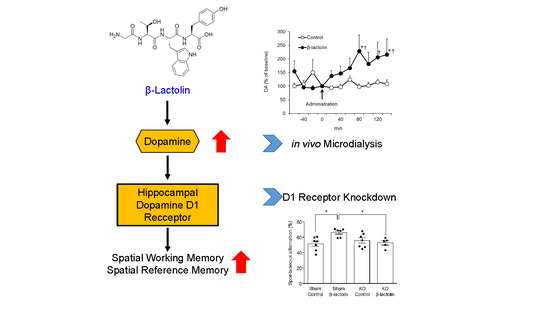
The Lacto-Tetrapeptide Gly–Thr–Trp–Tyr, β-Lactolin, Improves Spatial Memory Functions via Dopamine Release and D1 Receptor Activation in the Hippocampus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals
2.3. In Vivo Microdialysis
2.4. Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.5. Adeno-Associated Virus (AAV) Injection
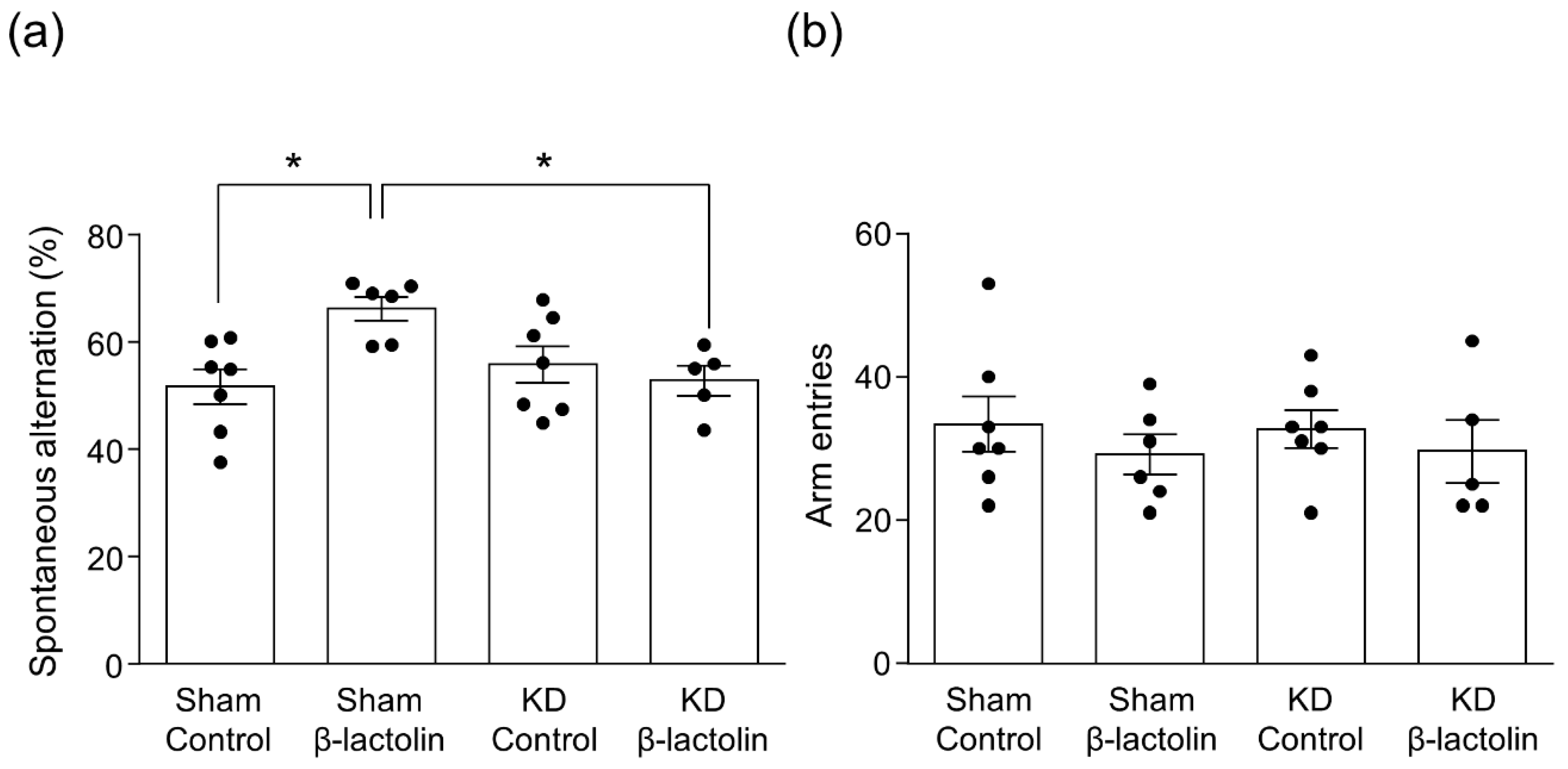
2.6. Y-Maze Test
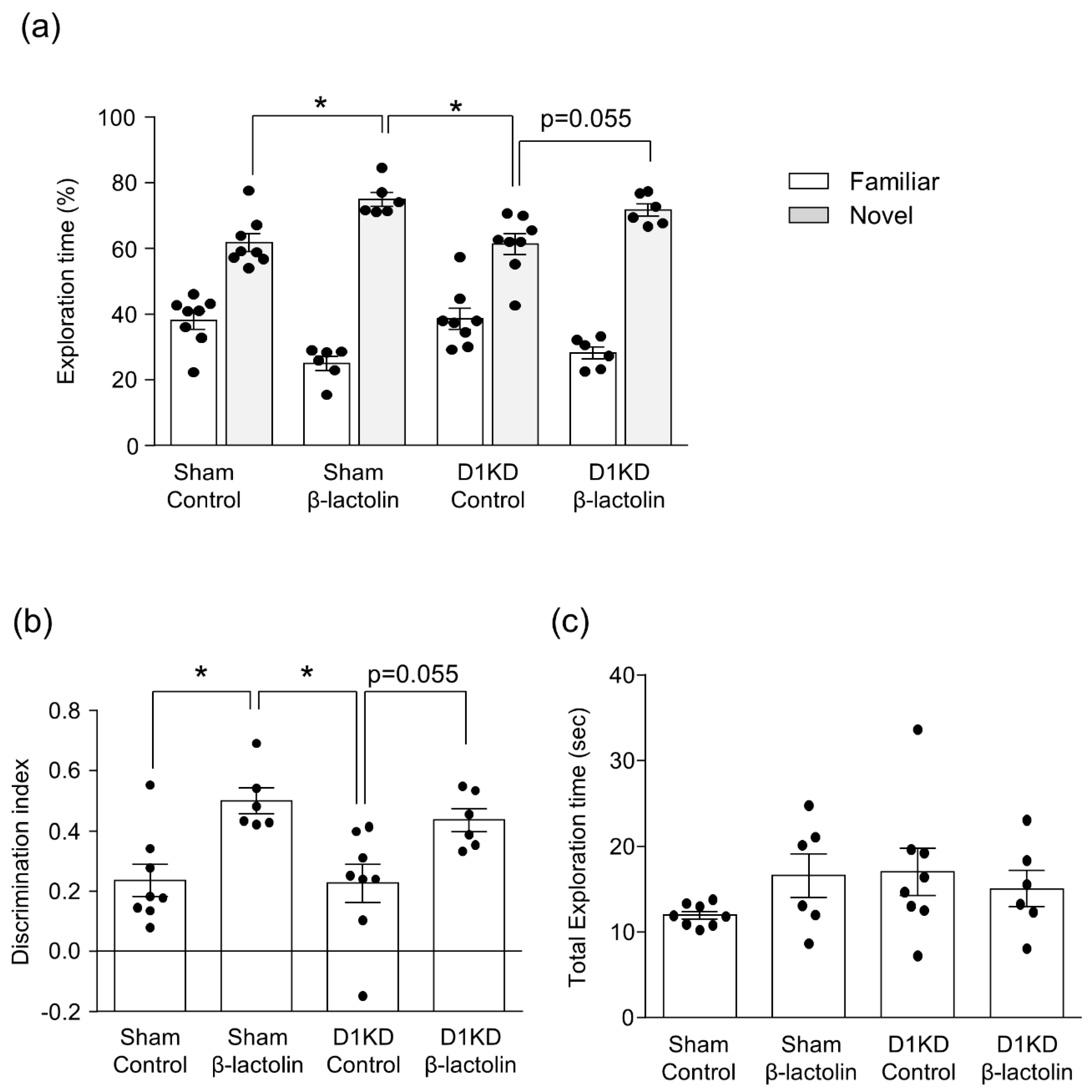
2.7. Novel Object Recognition Test (NORT)
2.8. Novel Object Location Test (NOLT)
2.9. Dosage Information
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. β-Lactolin Increases the Extracellular Concentration of Dopamine in the Hippocampus
3.2. β-Lactolin Improves Spatial Working Memory via the Dopamine D1 Receptor in the Hippocampus
3.3. The Dopamine D1 Receptor in the Hippocampus Is Vital for the Enhancing Effect of β-Lactolin on Spatial Reference Memory
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAV | adeno-associated virus |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| GTWY | glycine–threonine–tryptophan–tyrosine |
| LTP | long-term synaptic potentiation |
| MAO | monoamine oxidase |
| MWM | Morris water maze |
| WY | tryptophan–tyrosine |
References
- Camfield, D.A.; Owen, L.; Scholey, A.B.; Pipingas, A.; Stough, C. Dairy constituents and neurocognitive health in ageing. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crichton, G.E.; Murphy, K.J.; Bryan, J. Dairy intake and cognitive health in middle-aged South Australians. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 19, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, M.; Ninomiya, T.; Ohara, T.; Doi, Y.; Uchida, K.; Shirota, T.; Yonemoto, K.; Kitazono, T.; Kiyohara, Y. Dietary patterns and risk of dementia in an elderly Japanese population: The Hisayama Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 97, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ano, Y.; Kutsukake, T.; Hoshi, A.; Yoshida, A.; Nakayama, H. Identification of a novel dehydroergosterol enhancing microglial anti-inflammatory activity in a dairy product fermented with Penicillium candidum. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ano, Y.; Ozawa, M.; Kutsukake, T.; Sugiyama, S.; Uchida, K.; Yoshida, A.; Nakayama, H. Preventive effects of a fermented dairy product against Alzheimer’s disease and identification of a novel oleamide with enhanced microglial phagocytosis and anti-inflammatory activity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ano, Y.; Kutsukake, T.; Sasaki, T.; Uchida, S.; Yamada, K.; Kondo, K. Identification of a Novel Peptide from beta-Casein That Enhances Spatial and Object Recognition Memory in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8160–8167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ano, Y.; Ayabe, T.; Kutsukake, T.; Ohya, R.; Takaichi, Y.; Uchida, S.; Yamada, K.; Uchida, K.; Takashima, A.; Nakayama, H. Novel lactopeptides in fermented dairy products improve memory function and cognitive decline. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 72, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ano, Y.; Ayabe, T.; Ohya, R.; Kondo, K.; Kitaoka, S.; Furuyashiki, T. Tryptophan-Tyrosine Dipeptide, the Core Sequence of beta-Lactolin, Improves Memory by Modulating the Dopamine System. Nutrients 2019, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, W.C.; Kohler, C.C.; Radiske, A.; Cammarota, M. D1/D5 dopamine receptors modulate spatial memory formation. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2012, 97, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bundel, D.; Femenia, T.; DuPont, C.M.; Konradsson-Geuken, A.; Feltmann, K.; Schilstrom, B.; Lindskog, M. Hippocampal and prefrontal dopamine D1/5 receptor involvement in the memory-enhancing effect of reboxetine. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.R.; Sun, N.; Lei, L.; Li, X.Y.; Yao, B.; Sun, K.; Hu, R.; Zhang, X.; Shi, X.D.; Gao, C. L-Stepholidine rescues memory deficit and synaptic plasticity in models of Alzheimer’s disease via activating dopamine D1 receptor/PKA signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan Xiang, P.; Janc, O.; Grochowska, K.M.; Kreutz, M.R.; Reymann, K.G. Dopamine agonists rescue Abeta-induced LTP impairment by Src-family tyrosine kinases. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 40, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, R.; Taniguchi, M.; Ehrlich, A.T.; Yokogawa, K.; Deguchi, Y.; Cherasse, Y.; Lazarus, M.; Urade, Y.; Ogawa, A.; Kitaoka, S.; et al. Dopamine D1 receptor subtype mediates acute stress-induced dendritic growth in excitatory neurons of the medial prefrontal cortex and contributes to suppression of stress susceptibility in mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayabe, T.; Ohya, R.; Taniguchi, Y.; Shindo, K.; Kondo, K.; Ano, Y. Matured Hop-Derived Bitter Components in Beer Improve Hippocampus-Dependent Memory Through Activation of the Vagus Nerve. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayabe, T.; Ohya, R.; Kondo, K.; Ano, Y. Iso-alpha-acids, bitter components of beer, prevent obesity-induced cognitive decline. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Am, O.; Amit, T.; Kupershmidt, L.; Aluf, Y.; Mechlovich, D.; Kabha, H.; Danovitch, L.; Zurawski, V.R.; Youdim, M.B.; Weinreb, O. Neuroprotective and neurorestorative activities of a novel iron chelator-brain selective monoamine oxidase-A/monoamine oxidase-B inhibitor in animal models of Parkinson’s disease and aging. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justo, L.A.; Duran, R.; Alfonso, M.; Fajardo, D.; Faro, L.R.F. Effects and mechanism of action of isatin, a MAO inhibitor, on in vivo striatal dopamine release. Neurochem. Int. 2016, 99, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, D.; Mirrione, M.M.; Henn, F.A. Cognitive aspects of congenital learned helplessness and its reversal by the monoamine oxidase (MAO)-B inhibitor deprenyl. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2010, 93, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangarossa, G.; Longueville, S.; De Bundel, D.; Perroy, J.; Herve, D.; Girault, J.A.; Valjent, E. Characterization of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor-expressing neurons in the mouse hippocampus. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 2199–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puighermanal, E.; Cutando, L.; Boubaker-Vitre, J.; Honore, E.; Longueville, S.; Herve, D.; Valjent, E. Anatomical and molecular characterization of dopamine D1 receptor-expressing neurons of the mouse CA1 dorsal hippocampus. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 1897–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wan, P.; Wang, W.; Xiao, B.; Jin, H.; Jin, Q. Dopamine in the hippocampal dentate gyrus modulates spatial learning via D1-like receptors. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 144, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulla, A.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Depotentiation in the dentate gyrus of freely moving rats is modulated by D1/D5 dopamine receptors. Cereb. Cortex 2000, 10, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.J.; Stackman, R.W., Jr. Assessing rodent hippocampal involvement in the novel object recognition task. A review. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 285, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morici, J.F.; Bekinschtein, P.; Weisstaub, N.V. Medial prefrontal cortex role in recognition memory in rodents. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 292, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, T.; Takuma, K.; Kamei, H.; Ito, Y.; Nakamichi, N.; Ibi, D.; Nakanishi, Y.; Murai, M.; Mizoguchi, H.; Nabeshima, T.; et al. Dopamine D1 receptors regulate protein synthesis-dependent long-term recognition memory via extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 in the prefrontal cortex. Learn. Mem. 2007, 14, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari-Serenjeh, F.; Rezayof, A.; Zarrindast, M.R. Functional correlation between GABAergic and dopaminergic systems of dorsal hippocampus and ventral tegmental area in passive avoidance learning in rats. Neuroscience 2011, 196, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Aimone, J.B.; Gage, F.H. New neurons and new memories: How does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.; Guo, J.; Meng, X.; Wei, S.G.; Li, S.B. The dopamine D1 but not D3 receptor plays a fundamental role in spatial working memory and BDNF expression in prefrontal cortex of mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 235, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarinana, J.; Kitamura, T.; Kunzler, P.; Sultzman, L.; Tonegawa, S. Differential roles of the dopamine 1-class receptors, D1R and D5R, in hippocampal dependent memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8245–8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, M.; Obara, K.; Kondo, S.; Umeda, S.; Ano, Y. Effect of Supplementation of a Whey Peptide Rich in Tryptophan-Tyrosine-Related Peptides on Cognitive Performance in Healthy Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Guitart-Masip, M.; Bunzeck, N.; Dolan, R.J.; Duzel, E. Dopamine modulates episodic memory persistence in old age. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 14193–14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.; Guitart-Masip, M.; Lambert, C.; Dayan, P.; Huys, Q.; Duzel, E.; Dolan, R.J. Dopamine restores reward prediction errors in old age. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Forward Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Gapdh | CATCACTGCCACCCAGAAGACTG | ATGCCAGTGAGCTTCCCGTTCAG |
| Drd1 | AGATGACTCCGAAGGCAGCCTT | GCCATGTAGGTTTTGCCTTGTGC |
| Drd2 | CCTGTCCTTCACCATCTCTTGC | TAGACCAGCAGGGTGACGATGA |
| Drd3 | ACCCTGGATGTCATGATGTG | GGCATGACCACTGCTGTGTA |
| Drd4 | CCTCTCTTTGTCTACTCCGAGGT | GCCATGAGCGTGTCACAG |
| Drd5 | TCCTGGTGTGCTTATGCTTTC | TCAGCTAAGAATCGTTTGGTTTC |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayabe, T.; Ano, Y.; Ohya, R.; Kitaoka, S.; Furuyashiki, T. The Lacto-Tetrapeptide Gly–Thr–Trp–Tyr, β-Lactolin, Improves Spatial Memory Functions via Dopamine Release and D1 Receptor Activation in the Hippocampus. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102469
Ayabe T, Ano Y, Ohya R, Kitaoka S, Furuyashiki T. The Lacto-Tetrapeptide Gly–Thr–Trp–Tyr, β-Lactolin, Improves Spatial Memory Functions via Dopamine Release and D1 Receptor Activation in the Hippocampus. Nutrients. 2019; 11(10):2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102469
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyabe, Tatsuhiro, Yasuhisa Ano, Rena Ohya, Shiho Kitaoka, and Tomoyuki Furuyashiki. 2019. "The Lacto-Tetrapeptide Gly–Thr–Trp–Tyr, β-Lactolin, Improves Spatial Memory Functions via Dopamine Release and D1 Receptor Activation in the Hippocampus" Nutrients 11, no. 10: 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102469
APA StyleAyabe, T., Ano, Y., Ohya, R., Kitaoka, S., & Furuyashiki, T. (2019). The Lacto-Tetrapeptide Gly–Thr–Trp–Tyr, β-Lactolin, Improves Spatial Memory Functions via Dopamine Release and D1 Receptor Activation in the Hippocampus. Nutrients, 11(10), 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102469