Modulation of T Regulatory and Dendritic Cell Phenotypes Following Ingestion of Bifidobacterium longum, AHCC® and Azithromycin in Healthy Individuals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Interventions
2.4. Blood Sampling and Immunological Assays
2.5. Randomisation, Blinding and Allocation Concealment
2.6. Sample Size Calculation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Ethics and Trial Registration
3. Results
3.1. Volunteer Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Effect of Prebiotic and Probiotic or Antibiotic on Serum Inflammatory Markers
3.3. In Vitro Cytokine Secretion by CD3+ T Cells in Response to PDB-Ionomycin
3.4. Th1:Th2 Class Cytokine Ratios
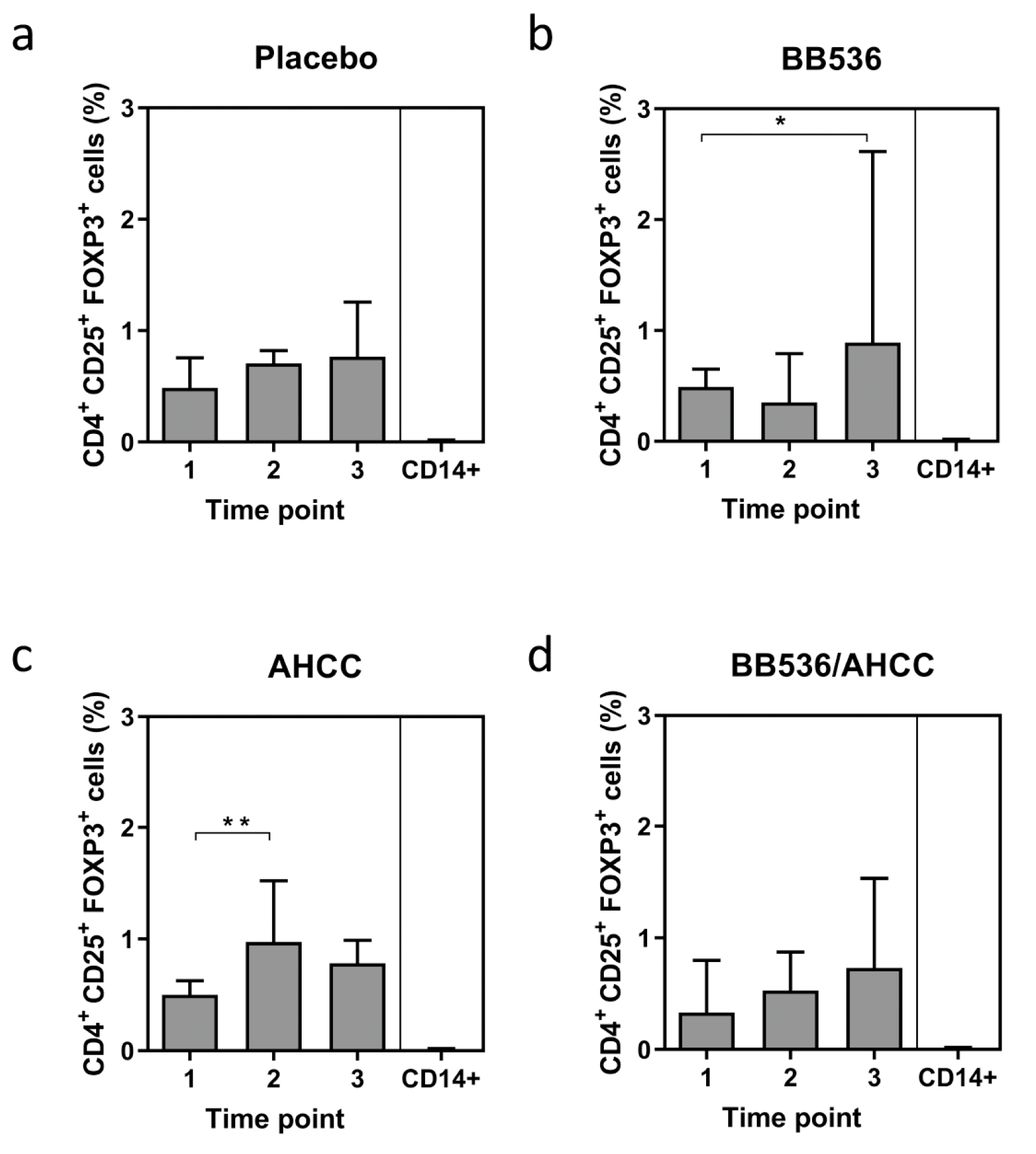
3.5. Foxp3 Expression as a Marker of T Regulatory CELL (Treg) Activity
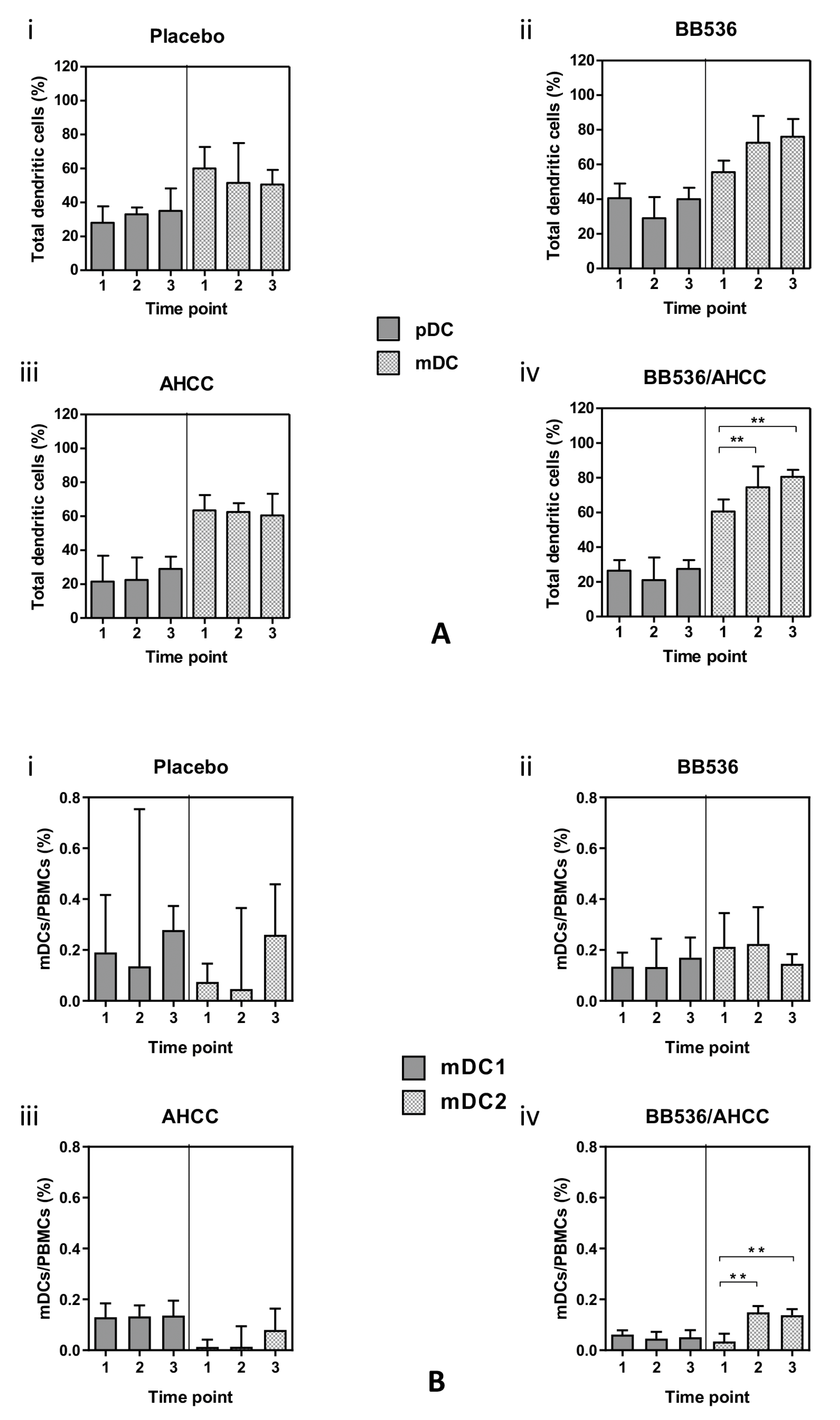
3.6. Plasmacytoid (pDC) and Myeloid (mDC) Dendritic Cells
3.7. Co-Stimulatory Molecule Expression in DC Subsets
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wright, J.; Paauw, D.S. Complications of antibiotic therapy. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 97, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larcombe, S.; Hutton, M.L.; Lyras, D. Involvement of Bacteria Other Than Clostridium difficile in Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhoea. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, G.L. The continuing crisis in antibiotic resistance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 36, S3–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabot, S.; Rafter, J.; Rijkers, G.T.; Watzl, B.; Antoine, J.M. Guidance for substantiating the evidence for beneficial effects of probiotics: Impact of probiotics on digestive system metabolism. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 677S–689S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO/FAO. Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria; Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Evaluation of health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria; World Health Organization, Ed.; Rome, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, World Health Organization: Rome, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bernaola Aponte, G.; Bada Mancilla, C.A.; Carreazo, N.Y.; Rojas Galarza, R.A. Probiotics for treating persistent diarrhoea in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 8, CD007401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.J.; Martinez, E.G.; Gregorio, G.V.; Dans, L.F. Probiotics for treating acute infectious diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 2, CD003048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, E.A.; Roy, T.; D’Adamo, C.R.; Wieland, L.S. Probiotics and gastrointestinal conditions: An overview of evidence from the Cochrane Collaboration. Nutrition 2018, 45, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, L.V. Meta-analysis of probiotics for the prevention of traveler’s diarrhea. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2007, 5, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, J.Z.; Lytvyn, L.; Steurich, J.; Parkin, P.; Mahant, S.; Johnston, B.C. Probiotics for the prevention of pediatric antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 12, CD004827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, B.C.; Supina, A.L.; Ospina, M.; Vohra, S. Probiotics for the prevention of pediatric antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, 2, CD004827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawrelak, J.A.; Whitten, D.L.; Myers, S.P. Is Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG effective in preventing the onset of antibiotic-associated diarrhoea: A systematic review. Digestion 2005, 72, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szajewska, H.; Mrukowicz, J. Meta-analysis: Non-pathogenic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii in the prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhoea. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempel, S.; Newberry, S.J.; Maher, A.R.; Wang, Z.; Miles, J.N.; Shanman, R.; Johnsen, B.; Shekelle, P.G. Probiotics for the prevention and treatment of antibiotic-associated diarrhea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2012, 307, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vrese, M.; Schrezenmeir, J. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2008, 111, 1–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, A. Immune-mediated mechanisms of action of probiotics and synbiotics in treating pediatric intestinal diseases. Nutrients 2018, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado Galdeano, C.; Cazorla, S.I.; Lemme Dumit, J.M.; Velez, E.; Perdigon, G. Beneficial effects of probiotic consumption on the immune system. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 74, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, A.; Foey, A. Probiotic modulation of innate cell pathogen sensing and signaling events. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.C.; Hart, A.L.; Kamm, M.A.; Stagg, A.J.; Knight, S.C. Mechanisms of action of probiotics: Recent advances. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2009, 15, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, W.A. Mechanisms of action of probiotics. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, S87–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.G.; Kayama, H.; Ueda, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Asahara, T.; Tsuji, H.; Tsuji, N.M.; Kiyono, H.; Ma, J.S.; Kusu, T.; et al. Probiotic Bifidobacterium breve induces IL-10-producing Tr1 cells in the colon. PLoS Pathog 2012, 8, e1002714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fatheree, N.Y.; Mangalat, N.; Rhoads, J.M. Lactobacillus reuteri strains reduce incidence and severity of experimental necrotizing enterocolitis via modulation of TLR4 and NF-kappaB signaling in the intestine. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G608–G617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grangette, C. Bifidobacteria and subsets of dendritic cells: Friendly players in immune regulation! Gut 2012, 61, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamadzadeh, M.; Olson, S.; Kalina, W.V.; Ruthel, G.; Demmin, G.L.; Warfield, K.L.; Bavari, S.; Klaenhammer, T.R. Lactobacilli activate human dendritic cells that skew T cells toward T helper 1 polarization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2880–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konieczna, P.; Groeger, D.; Ziegler, M.; Frei, R.; Ferstl, R.; Shanahan, F.; Quigley, E.M.; Kiely, B.; Akdis, C.A.; O’Mahony, L. Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 administration induces Foxp3 T regulatory cells in human peripheral blood: Potential role for myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Gut 2012, 61, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, A.L.; Lammers, K.; Brigidi, P.; Vitali, B.; Rizzello, F.; Gionchetti, P.; Campieri, M.; Kamm, M.A.; Knight, S.C.; Stagg, A.J. Modulation of human dendritic cell phenotype and function by probiotic bacteria. Gut 2004, 53, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, E.R.; Landy, J.D.; Bernardo, D.; Peake, S.T.; Hart, A.L.; Al-Hassi, H.O.; Knight, S.C. Intestinal dendritic cells: Their role in intestinal inflammation, manipulation by the gut microbiota and differences between mice and men. Immunol. Lett. 2013, 150, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy-Grand, D.; Azogui, O.; Celli, S.; Darche, S.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Kourilsky, P.; Vassalli, P. Extrathymic T cell lymphopoiesis: Ontogeny and contribution to gut intraepithelial lymphocytes in athymic and euthymic mice. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocon, B.; Anzola, A.; Ortega-Gonzalez, M.; Zarzuelo, A.; Suarez, M.D.; Sanchez de Medina, F.; Martinez-Augustin, O. Active hexose-correlated compound and Bifidobacterium longum BB536 exert symbiotic effects in experimental colitis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Backer, E.; Verhelst, R.; Verstraelen, H.; Claeys, G.; Verschraegen, G.; Temmerman, M.; Vaneechoutte, M. Antibiotic susceptibility of Atopobium vaginae. BMC Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, S.; Steinman, R.M. Dendritic cells as controllers of antigen-specific Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2009, 54, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.M.; Hall, J.A.; Blank, R.B.; Bouladoux, N.; Oukka, M.; Mora, J.R.; Belkaid, Y. Small intestine lamina propria dendritic cells promote de novo generation of Foxp3 T reg cells via retinoic acid. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.M. Immunomodulatory mechanisms of lactobacilli. Microb. Cell Fact. 2011, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shida, K.; Nanno, M.; Nagata, S. Flexible cytokine production by macrophages and T cells in response to probiotic bacteria: A possible mechanism by which probiotics exert multifunctional immune regulatory activities. Gut Microbes 2011, 2, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atarashi, K.; Umesaki, Y.; Honda, K. Microbiotal influence on T cell subset development. Semin. Immunol. 2011, 23, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, E.R.; Claesson, M.H.; Schmidt, E.G.; Jensen, S.S.; Ravn, P.; Olsen, J.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Kristensen, N.N. Consumption of probiotics increases the effect of regulatory T cells in transfer colitis. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2012, 18, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, A.; O’Mahony, D.; O’Brien, F.; MacSharry, J.; Sheil, B.; Ceddia, M.; Russell, W.M.; Forsythe, P.; Bienenstock, J.; Kiely, B.; et al. Bacterial strain-specific induction of Foxp3+ T regulatory cells is protective in murine allergy models. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braat, H.; van den Brande, J.; van Tol, E.; Hommes, D.; Peppelenbosch, M.; van Deventer, S. Lactobacillus rhamnosus induces peripheral hyporesponsiveness in stimulated CD4+ T cells via modulation of dendritic cell function. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1618–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roock, S.; van Elk, M.; van Dijk, M.E.; Timmerman, H.M.; Rijkers, G.T.; Prakken, B.J.; Hoekstra, M.O.; de Kleer, I.M. Lactic acid bacteria differ in their ability to induce functional regulatory T cells in humans. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Rowland, I.; Yaqoob, P. Comparative effects of six probiotic strains on immune function in vitro. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.K.; Lee, C.G.; So, J.S.; Chae, C.S.; Hwang, J.S.; Sahoo, A.; Nam, J.H.; Rhee, J.H.; Hwang, K.C.; Im, S.H. Generation of regulatory dendritic cells and CD4+Foxp3+ T cells by probiotics administration suppresses immune disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2159–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, C.; Scully, P.; O’Mahony, D.; Murphy, S.; O’Brien, F.; Lyons, A.; Sherlock, G.; MacSharry, J.; Kiely, B.; Shanahan, F.; et al. Commensal-induced regulatory T cells mediate protection against pathogen-stimulated NF-kappaB activation. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeuthen, L.H.; Fink, L.N.; Frokiaer, H. Toll-like receptor 2 and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-2 play divergent roles in the recognition of gut-derived lactobacilli and bifidobacteria in dendritic cells. Immunology 2008, 124, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, H.R.; Frokiaer, H.; Pestka, J.J. Lactobacilli differentially modulate expression of cytokines and maturation surface markers in murine dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redpath, S.A.; Heieis, G.A.; Reynolds, L.A.; Fonseca, N.M.; Kim, S.S.; Perona-Wright, G. Functional specialization of intestinal dendritic cell subsets during Th2 helminth infection in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 48, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, S.; Erturk-Hasdemir, D.; Ochoa-Reparaz, J.; Reinecker, H.C.; Kasper, D.L. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells mediate anti-inflammatory responses to a gut commensal molecule via both innate and adaptive mechanisms. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Lee, C.; Jeun, E.J.; Yi, J.; Kim, K.S.; Ghosh, A.; Byun, S.; Lee, C.G.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, G.C.; et al. Cell surface polysaccharides of Bifidobacterium bifidum induce the generation of Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaat6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Ba, Z.; Lee, Y.; Peng, J.; Lin, J.; Fleming, J.A.; Furumoto, E.J.; Roberts, R.F.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Rogers, C.J. Consumption of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 in yogurt reduced expression of TLR-2 on peripheral blood-derived monocytes and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion in young adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernini, L.J.; Simao, A.N.; Alfieri, D.F.; Lozovoy, M.A.; Mari, N.L.; de Souza, C.H.; Dichi, I.; Costa, G.N. Beneficial effects of Bifidobacterium lactis on lipid profile and cytokines in patients with metabolic syndrome: A randomized trial. Effects of probiotics on metabolic syndrome. Nutrition 2016, 32, 716–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Group | Treatment Length | Intervention |
|---|---|---|
| 1 (n = 10) Placebo arm | 7 days | Placebo prebiotic and placebo probiotic |
| 5 days | Azithromycin and placebo prebiotic and placebo probiotic | |
| 2 (n = 10) Probiotic arm | 7 days | Placebo prebiotic and BB536 |
| 5 days | Azithromycin, placebo prebiotic and BB536 | |
| 3 (n = 10) Prebiotic arm | 7 days | AHCC® and placebo probiotic |
| 5 days | Azithromycin, AHCC® and placebo probiotic | |
| 4 (n = 10) Synbiotic arm | 7 days | AHCC® and BB536 |
| 5 days | Azithromycin, AHCC® and BB536 |
| Normal Range | Placebo | BB536 | AHCC® | BB536/AHCC® | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 20.3 (0.2) | 21.1 (0.2) | 20.9 (0.3) | 22.5 (0.3) | |
| Height (m) | 1.82 (0.02) | 1.77 (0.02) | 1.78 (0.02) | 1.80 (0.02) | |
| Weight (kg) | 63.1 (0.3) | 65.4 (0.2) | 77.2 (0.3) | 68.9 (0.2) | |
| Haemoglobin (g/dL) | 130–180 g/L | 14.1 (0.2) | 15.0 (0.2) | 13.9 (0.2) | 14.8 (0.2) |
| White cell count (×109/L) | 4.0–11.0 × 109/L | 6.9 (0.7) | 8.7 (0.5) | 6.8 (0.7) | 8.1 (0.5) |
| Platelet count (×109/L) | 140–400 × 109/L | 302 (8) | 323 (7) | 298 (7) | 335 (8) |
| Serum bilirubin (μmol/L) | <21 μmol/L | 10 (2) | 8 (1) | 14 (2) | 6 (1) |
| Serum alanine amino transferase (IU/L) | 2–53 iu/L | 25 (4) | 27 (3) | 30 (4) | 19 (3) |
| Serum alkaline phosphatase (IU/L) | 30–130 iu/L | 58 (5) | 77 (6) | 63 (5) | 71 (5) |
| Serum albumin (g/L) | 35–50 g/L | 38 (0.4) | 39 (0.4) | 36 (0.4) | 41 (0.4) |
| Serum sodium (mmol/L) | 133–146mmol/L | 134 (0.5) | 134 (0.4) | 135 (0.4) | 133 (0.5) |
| Serum potassium (mmol/L) | 3.3–5.3mmol/L | 4.8 (0.2) | 4.2 (0.2) | 4.2 (0.2) | 4.5 (0.2) |
| Blood urea (mmol/L) | 2.5–7.8 mmol/L | 5.2 (0.2) | 4.5(0.2) | 3.6 (0.2) | 4.3 (0.2) |
| Serum creatinine (mmol/L) | 60–120μmol/L | 98 (3) | 77 (3) | 64 (2) | 74 (3) |
| Serum C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 0–10 mg/L | 8.1 (0.5) | 8 (0.4) | 7 (0.4) | 5 (0.4) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chowdhury, A.H.; Cámara, M.; Verma, C.; Eremin, O.; Kulkarni, A.D.; Lobo, D.N. Modulation of T Regulatory and Dendritic Cell Phenotypes Following Ingestion of Bifidobacterium longum, AHCC® and Azithromycin in Healthy Individuals. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102470
Chowdhury AH, Cámara M, Verma C, Eremin O, Kulkarni AD, Lobo DN. Modulation of T Regulatory and Dendritic Cell Phenotypes Following Ingestion of Bifidobacterium longum, AHCC® and Azithromycin in Healthy Individuals. Nutrients. 2019; 11(10):2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102470
Chicago/Turabian StyleChowdhury, Abeed H., Miguel Cámara, Chandan Verma, Oleg Eremin, Anil D. Kulkarni, and Dileep N. Lobo. 2019. "Modulation of T Regulatory and Dendritic Cell Phenotypes Following Ingestion of Bifidobacterium longum, AHCC® and Azithromycin in Healthy Individuals" Nutrients 11, no. 10: 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102470
APA StyleChowdhury, A. H., Cámara, M., Verma, C., Eremin, O., Kulkarni, A. D., & Lobo, D. N. (2019). Modulation of T Regulatory and Dendritic Cell Phenotypes Following Ingestion of Bifidobacterium longum, AHCC® and Azithromycin in Healthy Individuals. Nutrients, 11(10), 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102470





