Catechin and Procyanidin B2 Modulate the Expression of Tight Junction Proteins but Do Not Protect from Inflammation-Induced Changes in Permeability in Human Intestinal Cell Monolayers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture and Experimental Treatments
2.3. Medium Conditioning by Raw264.7 Macrophages
2.4. TEER Measurement
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Immunofluorescence
2.7. Oxidative Stress
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
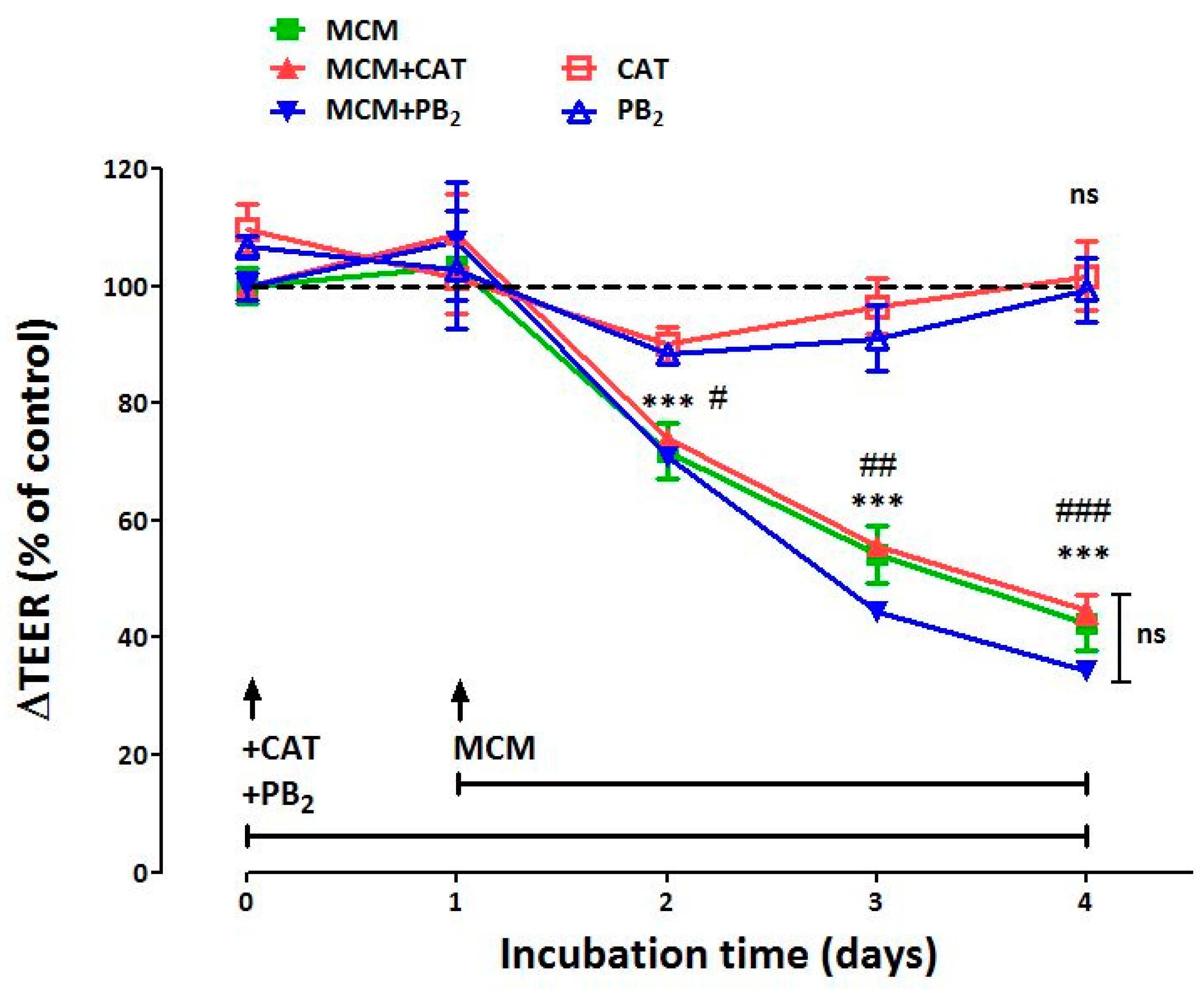
3.1. Neither CAT nor PB2 Prevent the Perturbation of Epithelial Barrier Function Induced by MCM
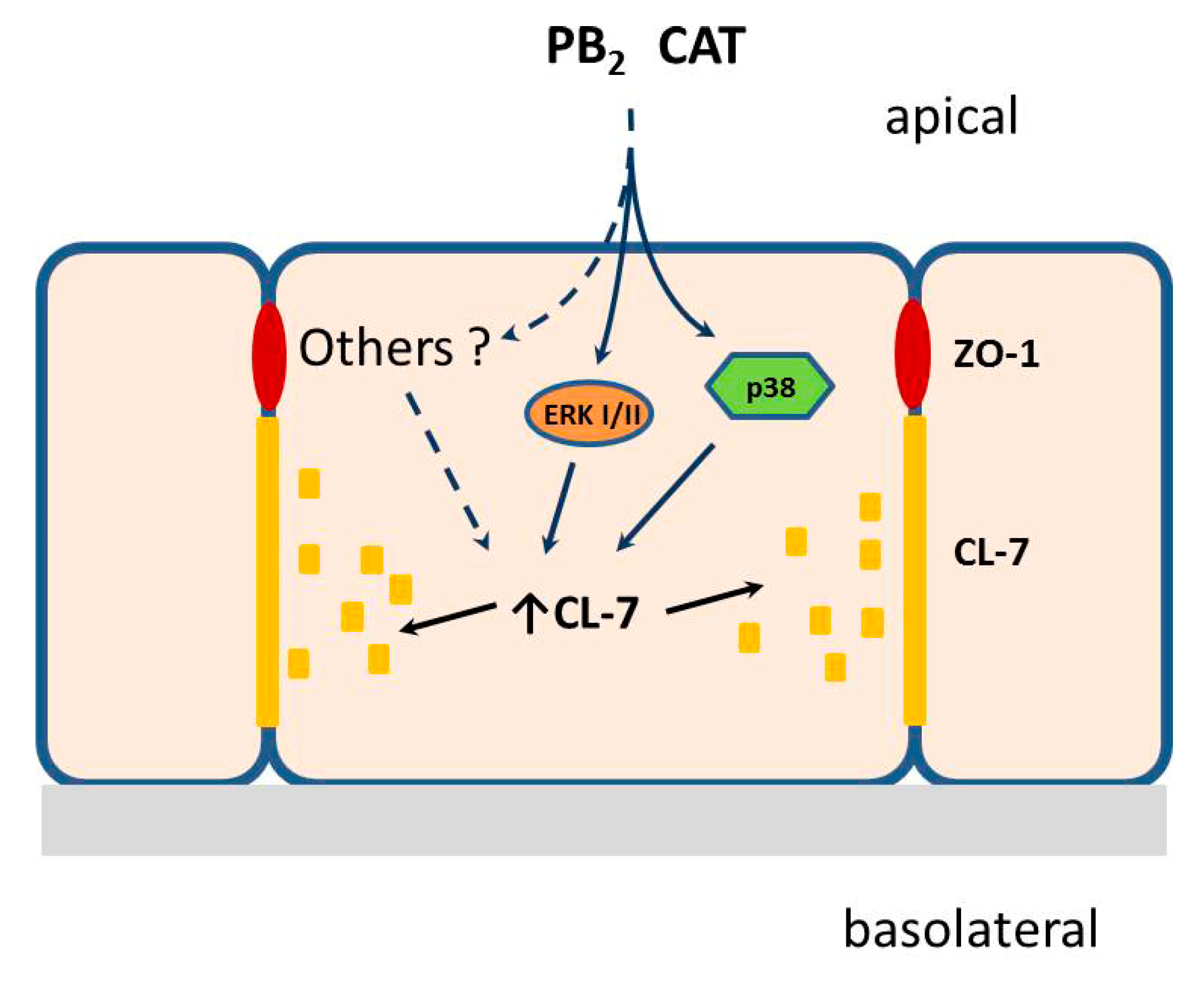
3.2. CAT and PB2 Differentially Affect TJ Protein Expression in MCM-Treated Monolayers
3.3. CAT and PB2 Partially Prevent the TJ Protein Redistribution Induced by MCM
3.4. CAT and PB2 Do Not Block the Transduction of Pro-Inflammatory Signaling
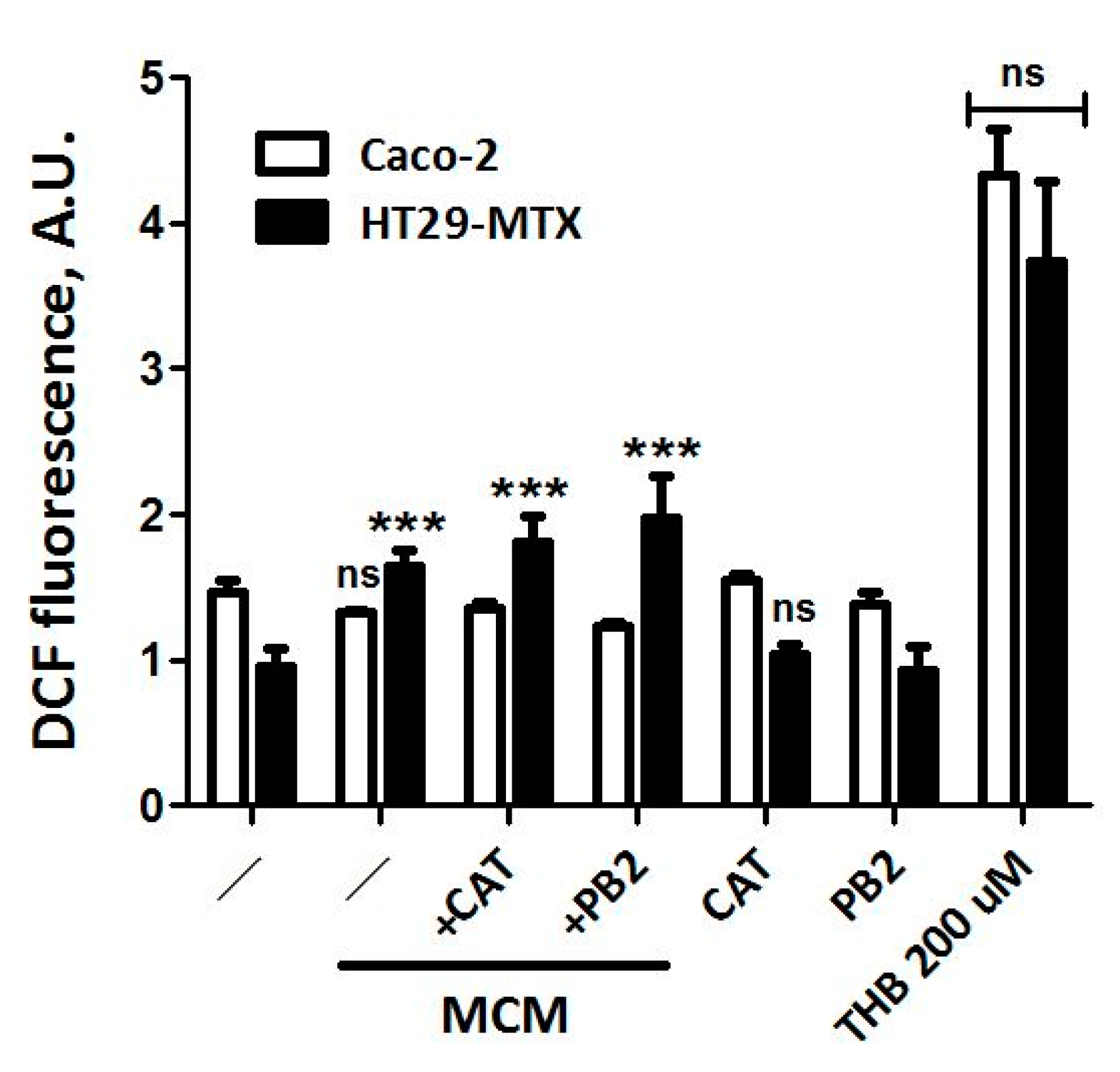
3.5. Neither CAT nor PB2 Prevent MCM Dependent Production of ROS in Caco-2 and HT29-MTX Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alican, I.; Kubes, P. A critical role for nitric oxide in intestinal barrier function and dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 270, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landy, J.; Ronde, E.; English, N.; Clark, S.K.; Hart, A.L.; Knight, S.C.; Ciclitira, P.J.; Al-Hassi, H.O. Tight junctions in inflammatory bowel diseases and inflammatory bowel disease associated colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3117–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michielan, A.; D’Inca, R. Intestinal Permeability in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pathogenesis, Clinical Evaluation, and Therapy of Leaky Gut. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 628157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suenaert, P.; Bulteel, V.; Lemmens, L.; Noman, M.; Geypens, B.; Van Assche, G.; Geboes, K.; Ceuppens, J.L.; Rutgeerts, P. Anti-Tumor necrosis factor treatment restores the gut barrier in Crohn’s disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 2000–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashukova, A.; Wald, F.A.; Salas, P.J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and inflammation disrupt the polarity complex in intestinal epithelial cells by a posttranslational mechanism. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Guo, S.; Ye, D.; Ma, T.Y. TNF-Alpha modulation of intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier is regulated by ERK1/2 activation of Elk-1. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1871–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, F.; Florian, P.; Bojarski, C.; Richter, J.; Christ, M.; Hillenbrand, B.; Mankertz, J.; Gitter, A.H.; Burgel, N.; Fromm, M.; et al. Interleukin-13 is the key effector Th2 cytokine in ulcerative colitis that affects epithelial tight junctions, apoptosis, and cell restitution. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharl, M.; Paul, G.; Barrett, K.E.; McCole, D.F. AMP-Activated protein kinase mediates the interferon-Gamma-Induced decrease in intestinal epithelial barrier function. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 27952–27963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Yoshinaga, N.; Tanabe, S. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) regulates claudin-2 expression and tight junction permeability in intestinal epithelium. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 31263–31271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, R.M.; Ma, T.Y. IL-1beta causes an increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 4641–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S.; Zhao, Z.; Satsu, H.; Totsuka, M.; Shimizu, M. Synergistic effect of tumor necrosis factor-Alpha and hydrogen peroxide on the induction of IL-8 production in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Inflammation 2011, 34, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.M.; Sun, B.W.; Sun, Z.W.; Jin, Q.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X. Suppression of inflammatory cytokine production and oxidative stress by CO-Releasing molecules-Liberated CO in the small intestine of thermally-Injured mice. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.X.; Wang, J.B.; Sun, B.; Zhao, J.; Li, L.; Xu, T.; Li, H.; Sun, J.Q.; Ren, J.; Liu, R.; et al. Suppression of TNF-Alpha and free radicals reduces systematic inflammatory and metabolic disorders: Radioprotective effects of ginseng oligopeptides on intestinal barrier function and antioxidant defense. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 40, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, T.C.; Ricciardi, E.; Cremonini, E.; Oteiza, P.I. (-)-Epicatechin in the prevention of tumor necrosis alpha-Induced loss of Caco-2 cell barrier integrity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 573, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.B.; Wang, P.Y.; Wang, X.; Wan, Y.L.; Liu, Y.C. Butyrate enhances intestinal epithelial barrier function via up-Regulation of tight junction protein Claudin-1 transcription. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, K.; Shirazi-Beechey, S.P. Microarray analysis of butyrate regulated genes in colonic epithelial cells. DNA Cell Biol. 2006, 25, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amasheh, M.; Andres, S.; Amasheh, S.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J.D. Barrier effects of nutritional factors. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1165, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canali, R.; Vignolini, F.; Nobili, F.; Mengheri, E. Reduction of oxidative stress and cytokine-Induced neutrophil chemoattractant (CINC) expression by red wine polyphenols in zinc deficiency induced intestinal damage of rat. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, D.; Almeida, L.M.; Dinis, T.C. Anti-Inflammatory protection afforded by cyanidin-3-Glucoside and resveratrol in human intestinal cells via Nrf2 and PPAR-gamma: Comparison with 5-Aminosalicylic acid. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 260, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaulmann, A.; Planchon, S.; Renaut, J.; Schneider, Y.J.; Hoffmann, L.; Bohn, T. Proteomic response of inflammatory stimulated intestinal epithelial cells to in vitro digested plums and cabbages rich in carotenoids and polyphenols. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 4388–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Ros, R.; Knaze, V.; Rothwell, J.A.; Hemon, B.; Moskal, A.; Overvad, K.; Tjonneland, A.; Kyro, C.; Fagherazzi, G.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; et al. Dietary polyphenol intake in Europe: The European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 55, 1359–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziauddeen, N.; Rosi, A.; Del Rio, D.; Amoutzopoulos, B.; Nicholson, S.; Page, P.; Scazzina, F.; Brighenti, F.; Ray, S.; Mena, P. Dietary intake of (poly)phenols in children and adults: Cross-sectional analysis of UK National Diet and Nutrition Survey Rolling Programme (2008-2014). Eur. J. Nutr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Vauzour, D.; Krueger, C.G.; Shanmuganayagam, D.; Reed, J.; Calani, L.; Mena, P.; Del Rio, D.; Crozier, A. Bioavailability, bioactivity and impact on health of dietary flavonoids and related compounds: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1803–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rio, D.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Spencer, J.P.; Tognolini, M.; Borges, G.; Crozier, A. Dietary (poly)phenolics in human health: Structures, bioavailability, and evidence of protective effects against chronic diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1818–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena, P.; Dominguez-Perles, R.; Girones-Vilaplana, A.; Baenas, N.; Garcia-Viguera, C.; Villano, D. Flavan-3-Ols, anthocyanins, and inflammation. Iubmb Life 2014, 66, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Ramiro, I.; Ramos, S.; Bravo, L.; Goya, L.; Martin, M.A. Procyanidin B2 and a cocoa polyphenolic extract inhibit acrylamide-Induced apoptosis in human Caco-2 cells by preventing oxidative stress and activation of JNK pathway. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.Y.; Sang, L.X.; Jiang, M. Catechins and Their Therapeutic Benefits to Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Molecules 2017, 22, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaulmann, A.; Andre, C.M.; Schneider, Y.J.; Hoffmann, L.; Bohn, T. Carotenoid and polyphenol bioaccessibility and cellular uptake from plum and cabbage varieties. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi Ekbatan, S.; Iskandar, M.M.; Sleno, L.; Sabally, K.; Khairallah, J.; Prakash, S.; Kubow, S. Absorption and Metabolism of Phenolics from Digests of Polyphenol-Rich Potato Extracts Using the Caco-2/HepG2 Co-Culture System. Foods 2018, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.F.; Lin, Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Fu, Y.; Gong, T.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Z.R. Absorptive interactions of concurrent oral administration of (+)-Catechin and puerarin in rats and the underlying mechanisms. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaulmann, A.; Legay, S.; Schneider, Y.J.; Hoffmann, L.; Bohn, T. Inflammation related responses of intestinal cells to plum and cabbage digesta with differential carotenoid and polyphenol profiles following simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.W.; Zhu, J.; Zuo, S.; Zhang, J.L.; Chen, Z.Y.; Chen, G.W.; Wang, X.; Pan, Y.S.; Liu, Y.C.; Wang, P.Y. Protective effect of hydrogen sulfide on TNF-Alpha and IFN-Gamma-Induced injury of intestinal epithelial barrier function in Caco-2 monolayers. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Wu, Q.; Kuang, Z. Baicalin Protects against TNF-Alpha-Induced Injury by Down-Regulating miR-191a That Targets the Tight Junction Protein ZO-1 in IEC-6 Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, E.; Janich, S.; Roessler, B.J.; Hilfinger, J.M.; Amidon, G.L. HT29-MTX/Caco-2 cocultures as an in vitro model for the intestinal epithelium: In vitro-In vivo correlation with permeability data from rats and humans. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 85, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barilli, A.; Rotoli, B.M.; Visigalli, R.; Ingoglia, F.; Cirlini, M.; Prandi, B.; Dall’Asta, V. Gliadin-Mediated production of polyamines by RAW264.7 macrophages modulates intestinal epithelial permeability in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, L.B.; Bosquillon, C.; Dailey, L.A.; Delattre, L.; Martin, G.P.; Evrard, B.; Forbes, B. Sparing methylation of beta-Cyclodextrin mitigates cytotoxicity and permeability induction in respiratory epithelial cell layers in vitro. J. Controll. Release 2009, 136, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotoli, B.M.; Bussolati, O.; Barilli, A.; Zanello, P.P.; Bianchi, M.G.; Magrini, A.; Pietroiusti, A.; Bergamaschi, A.; Bergamaschi, E. Airway barrier dysfunction induced by exposure to carbon nanotubes in vitro: Which role for fiber length? Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2009, 28, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotoli, B.M.; Gatti, R.; Movia, D.; Bianchi, M.G.; Di Cristo, L.; Fenoglio, I.; Sonvico, F.; Bergamaschi, E.; Prina-Mello, A.; Bussolati, O. Identifying contact-Mediated, localized toxic effects of MWCNT aggregates on epithelial monolayers: A single-Cell monitoring toxicity assay. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.L.; Ge, Z.; Fox, J.G.; Schauer, D.B. Disruption of tight junctions and induction of proinflammatory cytokine responses in colonic epithelial cells by Campylobacter jejuni. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 6581–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmeyer, C.; Erko, I.; Awad, K.; Fromm, A.; Bojarski, C.; Meissner, S.; Loddenkemper, C.; Kerick, M.; Siegmund, B.; Fromm, M.; et al. Epithelial barrier dysfunction in lymphocytic colitis through cytokine-Dependent internalization of claudin-5 and-8. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, R.; Luettig, J.; Hering, N.A.; Krug, S.M.; Albrecht, U.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J.D. Myrrh exerts barrier-Stabilising and-Protective effects in HT-29/B6 and Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2017, 32, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakre-Nighot, M.; Blikslager, A.T. Indomethacin induces increase in gastric epithelial tight junction permeability via redistribution of occludin and activation of p38 MAPK in MKN-28 Cells. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4, e1187325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre, E.; Matheus, N.; Layunta, E.; Alcalde, A.I.; Mesonero, J.E. IL-10 counteracts proinflammatory mediator evoked oxidative stress in Caco-2 cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 982639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, B.; Xu, M.; Chen, D.; Xiong, Y.; Lian, M.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, C.; et al. 6-Gingerol protects intestinal barrier from ischemia/reperfusion-Induced damage via inhibition of p38 MAPK to NF-kappaB signalling. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 119, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cires, M.J.; Wong, X.; Carrasco-Pozo, C.; Gotteland, M. The Gastrointestinal Tract as a Key Target Organ for the Health-Promoting Effects of Dietary Proanthocyanidins. Front. Nutr. 2016, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, X.; Carrasco-Pozo, C.; Escobar, E.; Navarrete, P.; Blachier, F.; Andriamihaja, M.; Lan, A.; Tome, D.; Cires, M.J.; Pastene, E.; et al. Deleterious Effect of p-Cresol on Human Colonic Epithelial Cells Prevented by Proanthocyanidin-Containing Polyphenol Extracts from Fruits and Proanthocyanidin Bacterial Metabolites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3574–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andriamihaja, M.; Lan, A.; Beaumont, M.; Audebert, M.; Wong, X.; Yamada, K.; Yin, Y.; Tome, D.; Carrasco-Pozo, C.; Gotteland, M.; et al. The deleterious metabolic and genotoxic effects of the bacterial metabolite p-Cresol on colonic epithelial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 85, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Phuong Nguyen, T.; Fenyvesi, F.; Remenyik, J.; Homoki, J.R.; Gogolak, P.; Bacskay, I.; Feher, P.; Ujhelyi, Z.; Vasvari, G.; Vecsernyes, M.; et al. Protective Effect of Pure Sour Cherry Anthocyanin Extract on Cytokine-Induced Inflammatory Caco-2 Monolayers. Nutrients 2018, 10, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Guo, J.; Li, C.; Shih, D.Q.; Zhang, X. Protective role of 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 in the mucosal injury and epithelial barrier disruption in DSS-Induced acute colitis in mice. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.; Gluth, M.; Pape, U.F.; Wiedenmann, B.; Theuring, F.; Baumgart, D.C. Adalimumab prevents barrier dysfunction and antagonizes distinct effects of TNF-Alpha on tight junction proteins and signaling pathways in intestinal epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 304, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luescher, S.; Urmann, C.; Butterweck, V. Effect of Hops Derived Prenylated Phenols on TNF-Alpha Induced Barrier Dysfunction in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiewiet, M.B.G.; Gonzalez Rodriguez, M.I.; Dekkers, R.; Gros, M.; Ulfman, L.H.; Groeneveld, A.; de Vos, P.; Faas, M.M. The epithelial barrier-Protecting properties of a soy hydrolysate. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4164–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhouayek, M.; Rankin, L.; Gouveia-Figueira, S.; Fowler, C.J. Interferon gamma treatment increases endocannabinoid and related N-Acylethanolamine levels in T84 human colon carcinoma cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 176, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, B.P.; Pirzai, W.; Eaton, A.D.; Harper, M.; Roper, J.; Zimmermann, C.; Ladics, G.S.; Layton, R.J.; Delaney, B. An experimental platform using human intestinal epithelial cell lines to differentiate between hazardous and non-Hazardous proteins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 92, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, S.; Baum, M.; Eisenbrand, G.; Dietrich, H.; Will, F.; Janzowski, C. Polyphenolic apple juice extracts and their major constituents reduce oxidative damage in human colon cell lines. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, S.; Baum, M.; Eisenbrand, G.; Janzowski, C. Modulation of oxidative cell damage by reconstituted mixtures of phenolic apple juice extracts in human colon cell lines. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auger, C.; Mullen, W.; Hara, Y.; Crozier, A. Bioavailability of polyphenon E flavan-3-Ols in humans with an ileostomy. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1535S–1542S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalmach, A.; Mullen, W.; Steiling, H.; Williamson, G.; Lean, M.E.J.; Crozier, A. Absorption, metabolism, and excretion of green tea flavan-3-ols in humans with an ileostomy. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.A.; Pope, J.L.; Smith, J.J.; Ahmad, R.; Chen, X.; Washington, M.K.; Beauchamp, R.D.; Singh, A.B.; Dhawan, P. Claudin-7 expression induces mesenchymal to epithelial transformation (MET) to inhibit colon tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4570–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, T.; Xu, C.; Ding, Y.; Li, W.; Ding, L. Claudin-7 downregulation induces metastasis and invasion in colorectal cancer via the promotion of epithelial-Mesenchymal transition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 508, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, C.; Wang, K.; Ding, Y.; Ding, L. Non-Tight junction-Related function of claudin-7 in interacting with integrinbeta1 to suppress colorectal cancer cell proliferation and migration. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzano, M.C.; DiGuilio, K.; Mercado, J.; Teter, M.; To, J.; Ferraro, B.; Mixson, B.; Manley, I.; Baker, V.; Moore, B.A.; et al. Remodeling of Tight Junctions and Enhancement of Barrier Integrity of the CACO-2 Intestinal Epithelial Cell Layer by Micronutrients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Antibody | Host | Clonality | Dilution | Company |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| anti-ERK | Rabbit | polyclonal | 1:1000 (WB 1) | R&D Systems |
| anti-p-ERK | Rabbit | polyclonal | 1:1000 (WB) | R&D Systems |
| anti-Claudin7 | Rabbit | polyclonal | 1:1000 (WB); 1:400 (IF 2) | Cell Signaling |
| anti-Occludin | Rabbit | polyclonal | 1:1000 (WB) | Thermo Fischer |
| anti-p38 | Rabbit | polyclonal | 1:500 (WB) | R&D Systems |
| anti-p-p38 | Rabbit | polyclonal | 1:500 (WB) | R&D Systems |
| anti-p-p65 (NF B) | Rabbit | polyclonal | 1:1000 (WB) | Cell Signaling |
| anti-p65 (NF B) | Rabbit | polyclonal | 1:1000 (WB) | Cell Signaling |
| anti-β-Tubulin | Mouse | monoclonal | 1:1000 (WB) | Sigma |
| Anti-ZO-1 | Mouse | monoclonal | 1:1000 (WB); 1:400 (IF) | Thermo Fisher |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bianchi, M.G.; Chiu, M.; Taurino, G.; Brighenti, F.; Del Rio, D.; Mena, P.; Bussolati, O. Catechin and Procyanidin B2 Modulate the Expression of Tight Junction Proteins but Do Not Protect from Inflammation-Induced Changes in Permeability in Human Intestinal Cell Monolayers. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102271
Bianchi MG, Chiu M, Taurino G, Brighenti F, Del Rio D, Mena P, Bussolati O. Catechin and Procyanidin B2 Modulate the Expression of Tight Junction Proteins but Do Not Protect from Inflammation-Induced Changes in Permeability in Human Intestinal Cell Monolayers. Nutrients. 2019; 11(10):2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102271
Chicago/Turabian StyleBianchi, Massimiliano G., Martina Chiu, Giuseppe Taurino, Furio Brighenti, Daniele Del Rio, Pedro Mena, and Ovidio Bussolati. 2019. "Catechin and Procyanidin B2 Modulate the Expression of Tight Junction Proteins but Do Not Protect from Inflammation-Induced Changes in Permeability in Human Intestinal Cell Monolayers" Nutrients 11, no. 10: 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102271
APA StyleBianchi, M. G., Chiu, M., Taurino, G., Brighenti, F., Del Rio, D., Mena, P., & Bussolati, O. (2019). Catechin and Procyanidin B2 Modulate the Expression of Tight Junction Proteins but Do Not Protect from Inflammation-Induced Changes in Permeability in Human Intestinal Cell Monolayers. Nutrients, 11(10), 2271. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102271






