Nutritional Composition Assessment of 3000 Individualized Parenteral Nutrition Bags in a Tertiary Referral Hospital: Current Prescribing Patterns
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
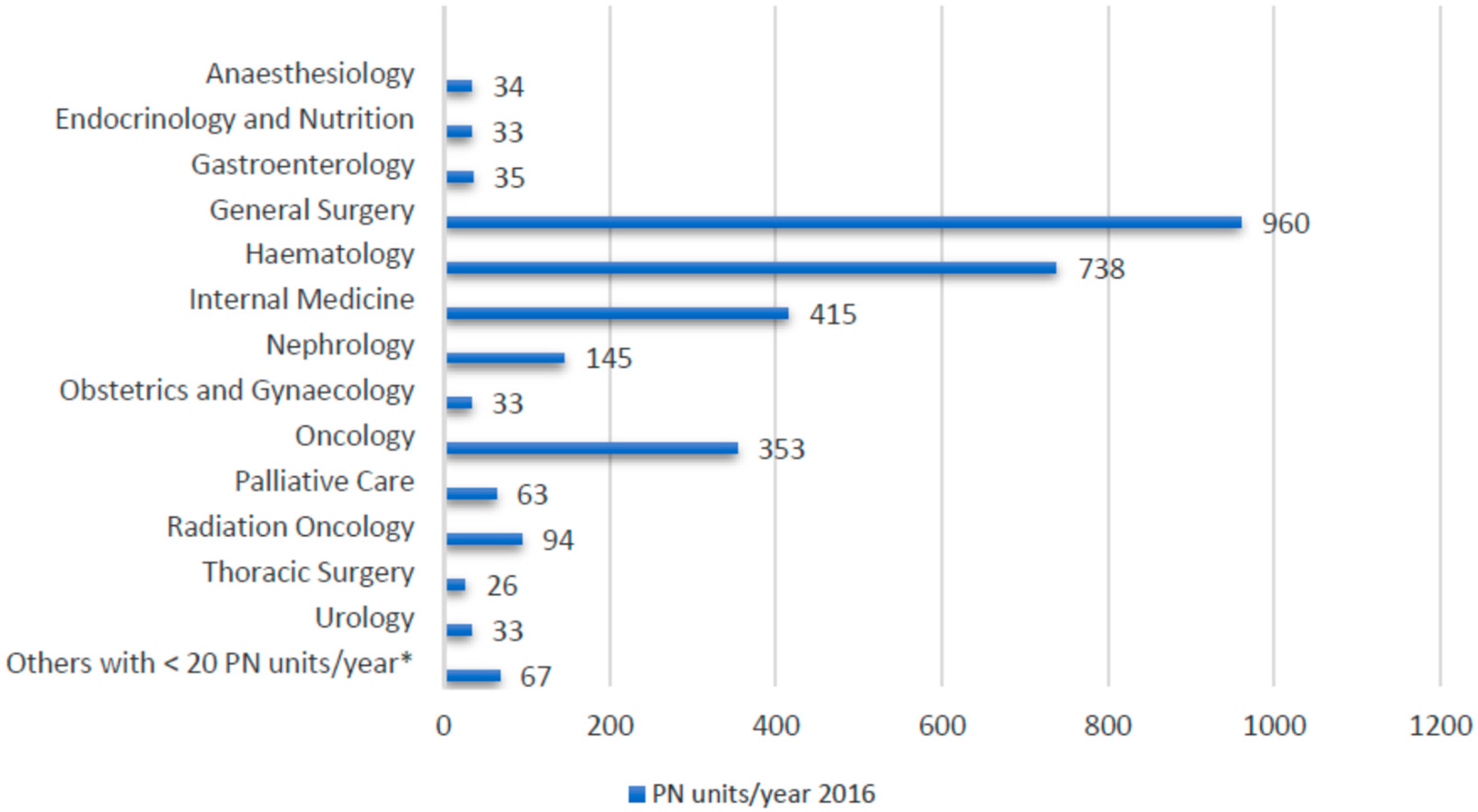
3. Results
3.1. Macronutrient Composition
3.2. Micronutrient Composition and Volume
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olveira, G.; García-Luna, P.P. Recommendations of the GARIN group for managing non-critically ill patients with diabetes or stress hyperglycaemia and artificial nutrition. Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 1837–1849. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, J.A.; Stanley, J.; Dudrick, M.D. A paradigm shift. Arch. Surg. 2010, 145, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Singer, P.; Hiesmayr, M.; Biolo, G.; Felbinger, T.W.; Berger, M.M.; Goeters, C.; Kondrup, J.; Wunder, C.; Pichard, C. Pragmatic approach to nutrition in the ICU: Expert opinion regarding which calorie protein target. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudrick, S.J.; Palesty, J.A. Historical highlights of the development of total parenteral nutrition. Surg. Clin. North. Am. 2011, 91, 693–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klek, S.; Forbes, A.; Gabe, S.; Holst, M.; Wanten, G.; Irtun, Ø.; Damink, S.O.; Panisic-Sekeljic, M.; Pelaez, R.B.; Pironi, L.; et al. Management of acute intestinal failure: A position paper from the European society for clinical nutrition and metabolism (ESPEN) special interest group. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fell, G.L.; Nandivada, P.; Gura, K.M.; Puder, M. Intravenous Lipid Emulsions in Parenteral Nutrition123. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, M.; Almutairdi, A.; Mulesa, L.; Alberda, C.; Beattie, C.; Gramlich, L. Parenteral nutrition and lipids. Nutrients 2017, 9, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurt, R.T.; McClave, S.A.; Martindale, R.G.; Ochoa Gautier, J.B.; Coss-Bu, J.A.; Dickerson, R.N.; Heyland, D.K.; Hoffer, L.J.; Moore, F.A.; Morris, C.R.; et al. Summary points and consensus recommendations from the international protein summit. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2017, 32, 142S–151S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClave, S.A.; Taylor, B.E.; Martindale, R.G.; Warren, M.M.; Johnson, D.R.; Braunschweig, C.; McCarthy, M.S.; Davanos, E.; Rice, T.W.; Cresci, G.A.; et al. Guidelines for the provision and assessment of nutrition support therapy in the adult critically ill patient. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2016, 40, 159–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, P.; Berger, M.M.; Van den Berghe, G.; Biolo, G.; Calder, P.; Forbes, A.; Griffiths, R.; Kreyman, G.; Leverve, X.; Pichard, C. ESPEN guidelines on parenteral nutrition: Intensive care. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, F.; Schuetz, P.; Bounoure, L.; Austin, P.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.; Cederholm, T.; Fletcher, J.; Laviano, A.; Norman, K.; Poulia, K.-A.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutritional support for polymorbid internal medicine patients. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arends, J.; Bachmann, P.; Baracos, V.; Barthelemy, N.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Fearon, K.; Hütterer, E.; Isenring, E.; Kaasa, S.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutrition in cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzetti, F.; Arends, J.; Lundholm, K.; Micklewright, A.; Zurcher, G.; Muscaritoli, M. ESPEN guidelines on parenteral nutrition: Non-surgical oncology. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arends, J.; Baracos, V.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Calder, P.C.; Deutz, N.E.P.; Erickson, N.; Laviano, A.; Lisanti, M.P.; Lobo, D.N.; et al. ESPEN expert group recommendations for action against cancer-related malnutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alp Ikizler, T.; Cano, N.J.; Franch, H.; Fouque, D.; Himmelfarb, J.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kuhlmann, M.K.; Stenvinkel, P.; TerWee, P.; Teta, D.; et al. Prevention and treatment of protein energy wasting in chronic kidney disease patients: A consensus statement by the international society of renal nutrition and metabolism. Kidney. Int. 2013, 84, 1096–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalobos-Gámez, J.L.; Lara-Ramos, C.; Domínguez-Rivas, Y.; Vallejo-Báez, A.; Cota-Delgado, F.; Márquez-Fernández, E.; García-Almeida, J.M.; López-Medina, J.A.; Rioja-Vázquez, R.; Santacreu-Regí, A.; et al. Nitrogenous content in parenteral nutrition: A four-year experience in a general hospital. critically-ill patient specificity. Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Martínez-Lozano Aranaga, F.; Palacio Vales, P.; Serrano Navarro, J.M.; Caballero Requejo, C.; Gómez Ramos, M.J.; Sánchez Álvarez, C. Estudio comparativo de la eficacia y seguridad de una nutrición parenteral formulada con dos lípidos distintos: SMOFlipid® frente a Clinoleic®. Estudio preliminar. Nutr. Hosp. 2016, 33, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klek, S.; Chambrier, C.; Singer, P.; Rubin, M.; Bowling, T.; Staun, M.; Joly, F.; Rasmussen, H.; Strauss, B.J.; Wanten, G.; et al. Four-week parenteral nutrition using a third generation lipid emulsion (SMOFlipid)—A double-blind, randomised, multicentre study in adults. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Yao, X.; Zeng, R.; Sun, R.; Tian, H.; Shi, C.; Li, L.; Tian, J.; Yang, K. Safety and efficacy of a new parenteral lipid emulsion (SMOF) for surgical patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobotka, L.; Schneider, S.M.; Berner, Y.N.; Cederholm, T.; Krznaric, Z.; Shenkin, A.; Stanga, Z.; Toigo, G.; Vandewoude, M.; Volkert, D. ESPEN guidelines on parenteral nutrition: Geriatrics. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plauth, M.; Cabré, E.; Campillo, B.; Kondrup, J.; Marchesini, G.; Schütz, T.; Shenkin, A.; Wendon, J. ESPEN guidelines on parenteral nutrition: Hepatology. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gossum, A.; Cabre, E.; Hébuterne, X.; Jeppesen, P.; Krznaric, Z.; Messing, B.; Powell-Tuck, J.; Staun, M.; Nightingale, J. ESPEN guidelines on parenteral nutrition: Gastroenterology. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianotti, L.; Meier, R.; Lobo, D.N.; Bassi, C.; Dejong, C.H.C.; Ockenga, J.; Irtun, O.; MacFie, J. ESPEN guidelines on parenteral nutrition: Pancreas. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, M.; Ljungqvist, O.; Soeters, P.; Fearon, K.; Weimann, A.; Bozzetti, F. ESPEN guidelines on parenteral nutrition: Surgery. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez Faedo, C.; Laborda González, L.; Virgili Casas, N.; Gómez Enterría, P. Complicaciones hepatobiliares asociadas a la Nutrición Parenteral Domiciliaria (NPD). Nutr. Hosp. 2011, 26, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weimann, A.; Braga, M.; Carli, F.; Higashiguchi, T.; Hübner, M.; Klek, S.; Laviano, A.; Ljungqvist, O.; Lobo, D.N.; Martindale, R.; et al. ESPEN guideline: Clinical nutrition in surgery. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 623–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, A.; Escher, J.; Hébuterne, X.; Kłęk, S.; Krznaric, Z.; Schneider, S.; Shamir, R.; Stardelova, K.; Wierdsma, N.; Wiskin, A.E.; et al. ESPEN guideline: Clinical nutrition in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 321–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, M.L.; Ayers, P.; Boullata, J.I.; Guenter, P.; Gura, K.M.; Holcombe, B.; Seres, D.S.; Sacks, G.S. Lipid injectable emulsion survey with gap analysis. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2017, 32, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beattie, C.; Allard, J.; Raman, M. Comparison between premixed and compounded parenteral nutrition solutions in hospitalized patients requiring parenteral nutrition. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2016, 31, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Candela, C. Intervención nutricional en el paciente oncohematológico. Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Nitrogen (g) | PN Units (%) | Nitrogen (g) | PN Units (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5.4 | 124 (4.09) | 13 | 38 (1.25) |
| 6 | 27 (0.89) | 13.4 | 875 (28.8) |
| 7 | 36 (1.18) | 14.5 | 55 (1.81) |
| 8 | 168 (5.54) | 15 | 30 (0.99) |
| 8.4 | 115 (3.79) | 15.7 | 592 (19.54) |
| 9 | 84 (2.77) | 17.9 | 539 (17.79) |
| 10 | 144 (4.75) | 20 | 45 (1.48) |
| 11 | 61 (2.01) | Others with <10 units 1 | 40 (1.32) |
| 12 | 56 (1.84) |
| Nitrogen (g) | Carbohydrates (g) | Lipids (g) | CH/Lipid Ratio | NPC:N | PN (Units (%)) | Total Energy Intake (kcal) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.4 | 140 | 55 | 53.08/46.92 | 78:1 | 505 (16.67) | 1447.49 |
| 13.4 | 170 | 70 | 51.90/48.1 | 97:1 | 215 (7.09) | 1716.01 |
| 15.7 | 160 | 60 | 54.23/45.77 | 75:1 | 354 (11.68) | 1632.51 |
| 15.7 | 200 | 80 | 52.63/47.37 | 96:1 | 195 (6.43) | 1992.51 |
| 17.9 | 180 | 70 | 53.33/46.67 | 75:1 | 379 (12.51) | 1867.5 |
| 17.9 | 225 | 90 | 52.63/47.37 | 95:1 | 106 (3.49) | 2247.5 |
| N (g) | Na (mEq) | K (mEq) | Cl (mEq) | Mg (mEq) | Ca (mEq) | P (mEq) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.4 | 97.01 ± 25.19 | 67.97 ± 26.66 | 80.16 ± 24.21 | 15.13 ± 3.66 | 13.99 ± 4.03 | 22.52 ± 8.24 |
| 15.7 | 84.84 ± 34.13 | 72.38 ± 25.09 | 80.01 ± 25.18 | 14.74 ± 4.39 | 14.35 ± 4.01 | 22.76 ± 7.94 |
| 17.9 | 102.87 ± 17.24 | 71.31 ± 19.29 | 84.77 ± 14.80 | 14.70 ± 4.30 | 14.96 ± 2.08 | 23.45 ± 8.55 |
| N (g) | Volume (mL) |
|---|---|
| 13.4 | 1891.92 ± 251.71 |
| 15.7 | 2109.71 ± 297.89 |
| 17.9 | 2443.91 ± 392.19 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pelegrina-Cortés, B.; Bermejo, L.M.; López-Plaza, B.; Palma-Milla, S.; García-Vázquez, N.; Gómez-Candela, C. Nutritional Composition Assessment of 3000 Individualized Parenteral Nutrition Bags in a Tertiary Referral Hospital: Current Prescribing Patterns. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10081079
Pelegrina-Cortés B, Bermejo LM, López-Plaza B, Palma-Milla S, García-Vázquez N, Gómez-Candela C. Nutritional Composition Assessment of 3000 Individualized Parenteral Nutrition Bags in a Tertiary Referral Hospital: Current Prescribing Patterns. Nutrients. 2018; 10(8):1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10081079
Chicago/Turabian StylePelegrina-Cortés, Beatriz, Laura M Bermejo, Bricia López-Plaza, Samara Palma-Milla, Natalia García-Vázquez, and Carmen Gómez-Candela. 2018. "Nutritional Composition Assessment of 3000 Individualized Parenteral Nutrition Bags in a Tertiary Referral Hospital: Current Prescribing Patterns" Nutrients 10, no. 8: 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10081079
APA StylePelegrina-Cortés, B., Bermejo, L. M., López-Plaza, B., Palma-Milla, S., García-Vázquez, N., & Gómez-Candela, C. (2018). Nutritional Composition Assessment of 3000 Individualized Parenteral Nutrition Bags in a Tertiary Referral Hospital: Current Prescribing Patterns. Nutrients, 10(8), 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10081079






