β-glucan Salecan Improves Exercise Performance and Displays Anti-Fatigue Effects through Regulating Energy Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
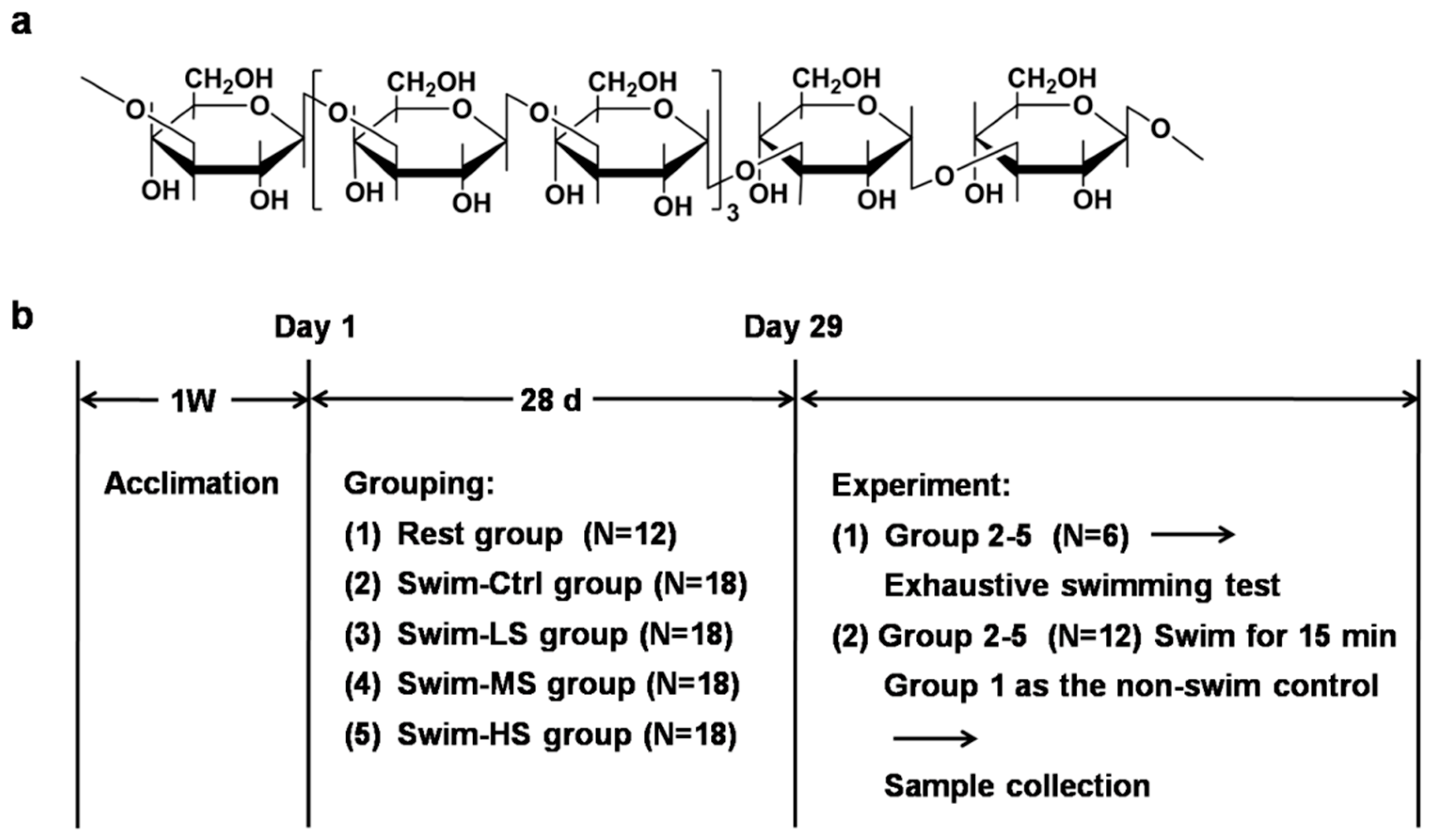
2.1. Preparation of Salecan
2.2. Mice and Treatment
2.3. Forced Swimming Test
2.4. Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Tissue Glycogen Examination and Oxidative Stress-Related Parameters Analysis
2.6. Tissue Energy Metabolic Enzymes Analysis
2.7. RNA Isolation and Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Analysis
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
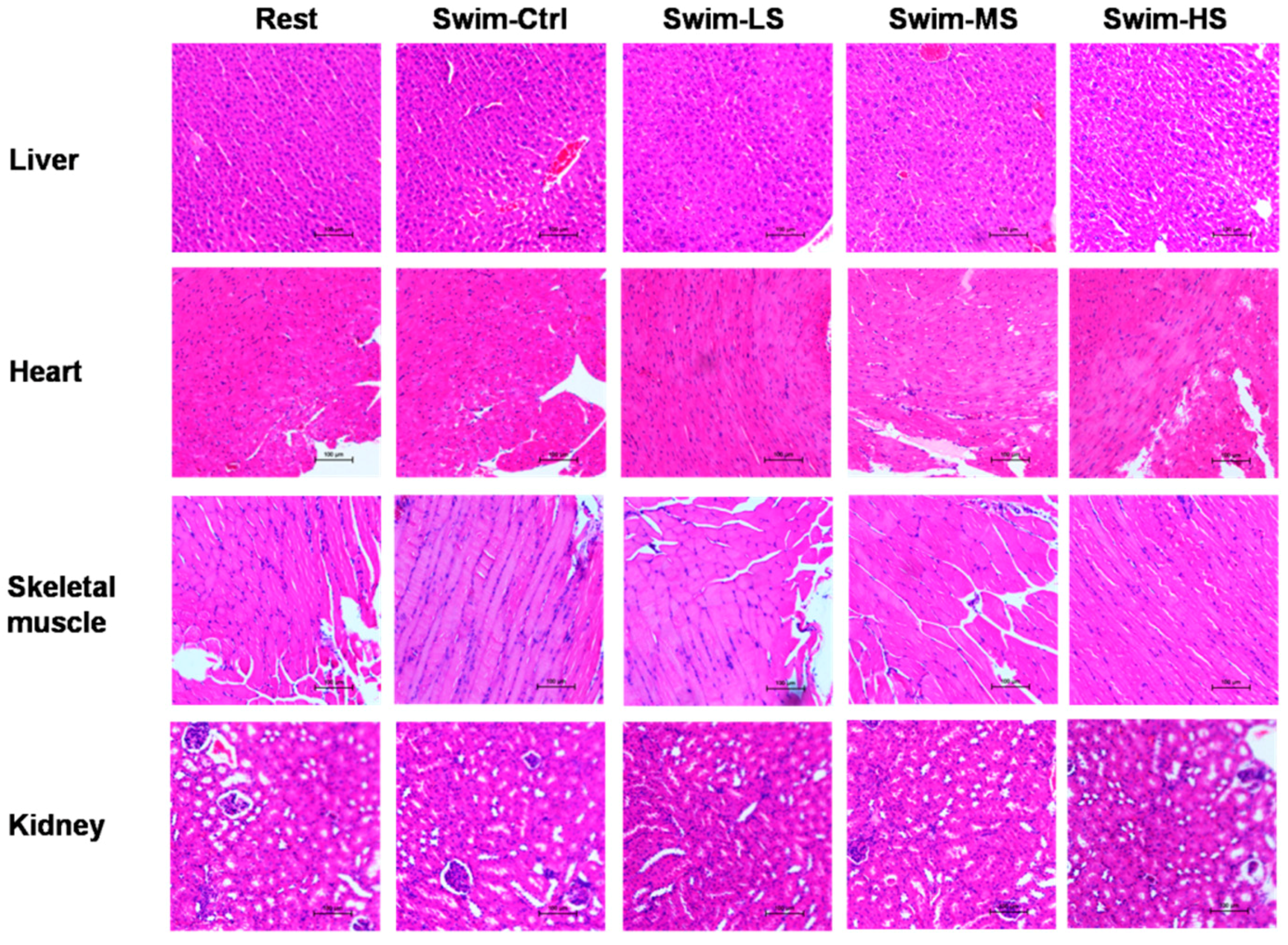
3.1. Effects of Salecan on the Body Weight and Histopathology of Mice
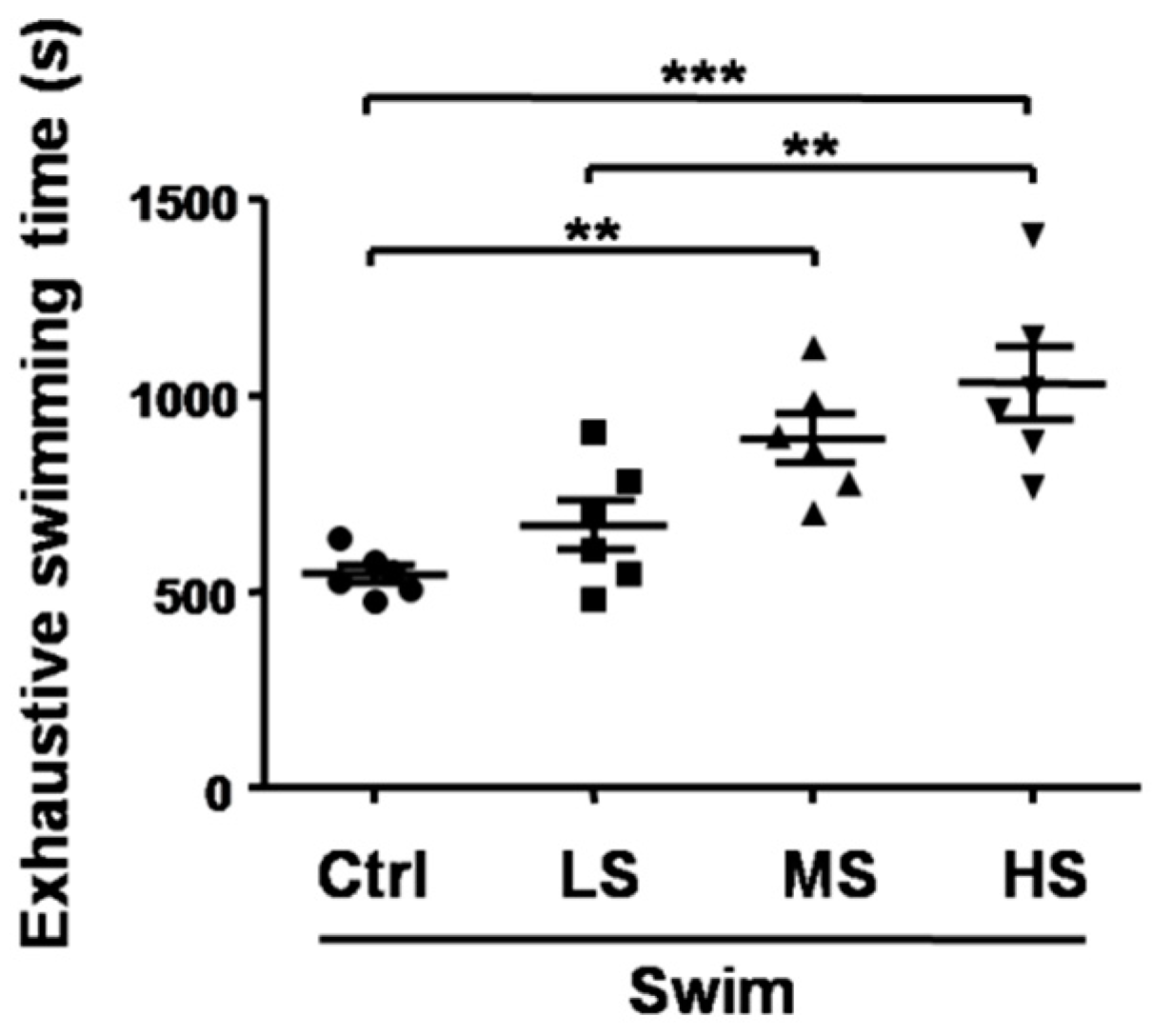
3.2. Salecan Prolonged the Exhaustive Swimming Time in the Forced Swimming Test
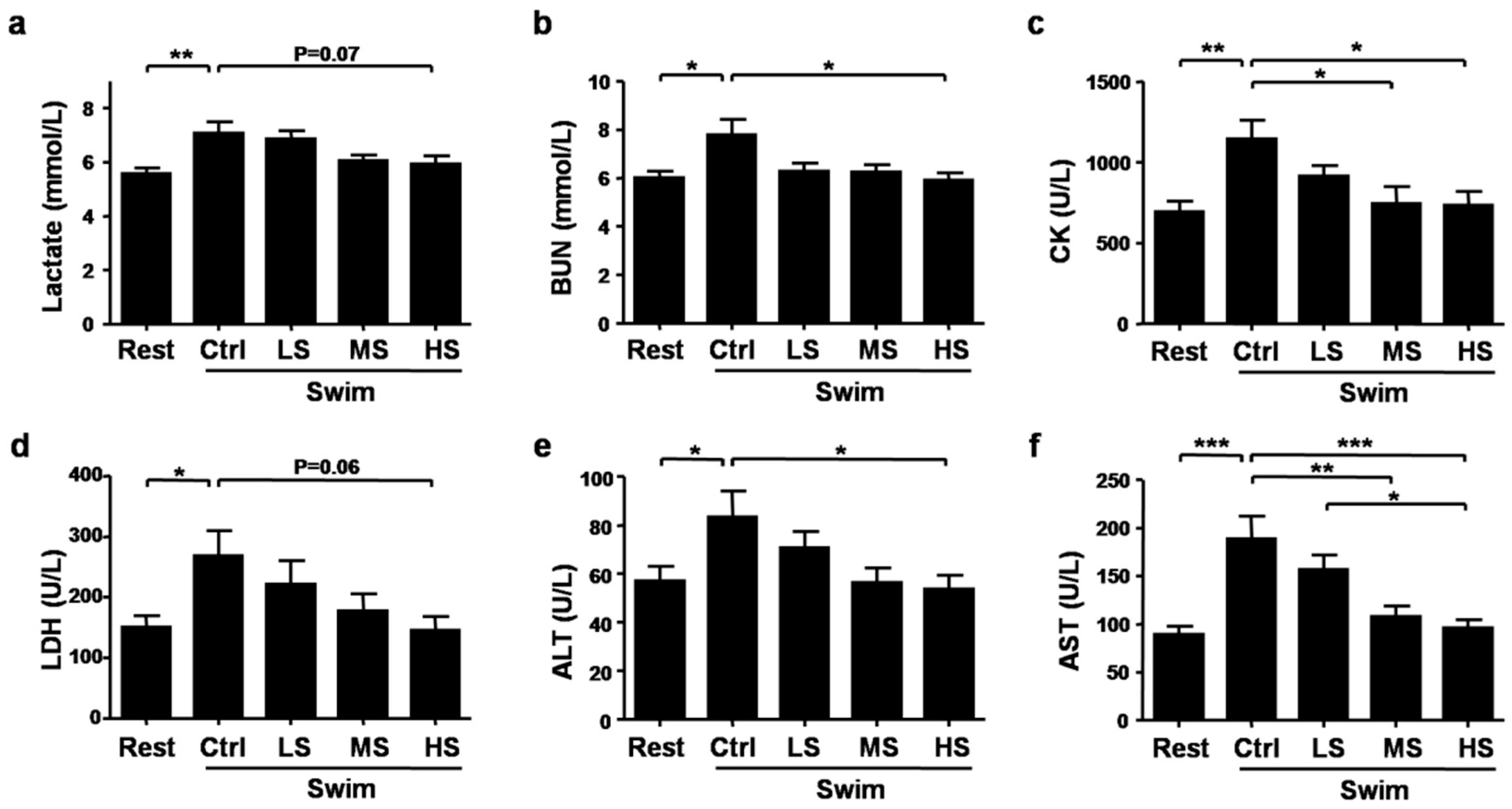
3.3. Salecan Ameliorated Exercise Fatigue and Injury-Related Biochemical Parameters after Strenuous Exercise
3.4. The Regulatory Effect of Salecan on Energy Metabolism
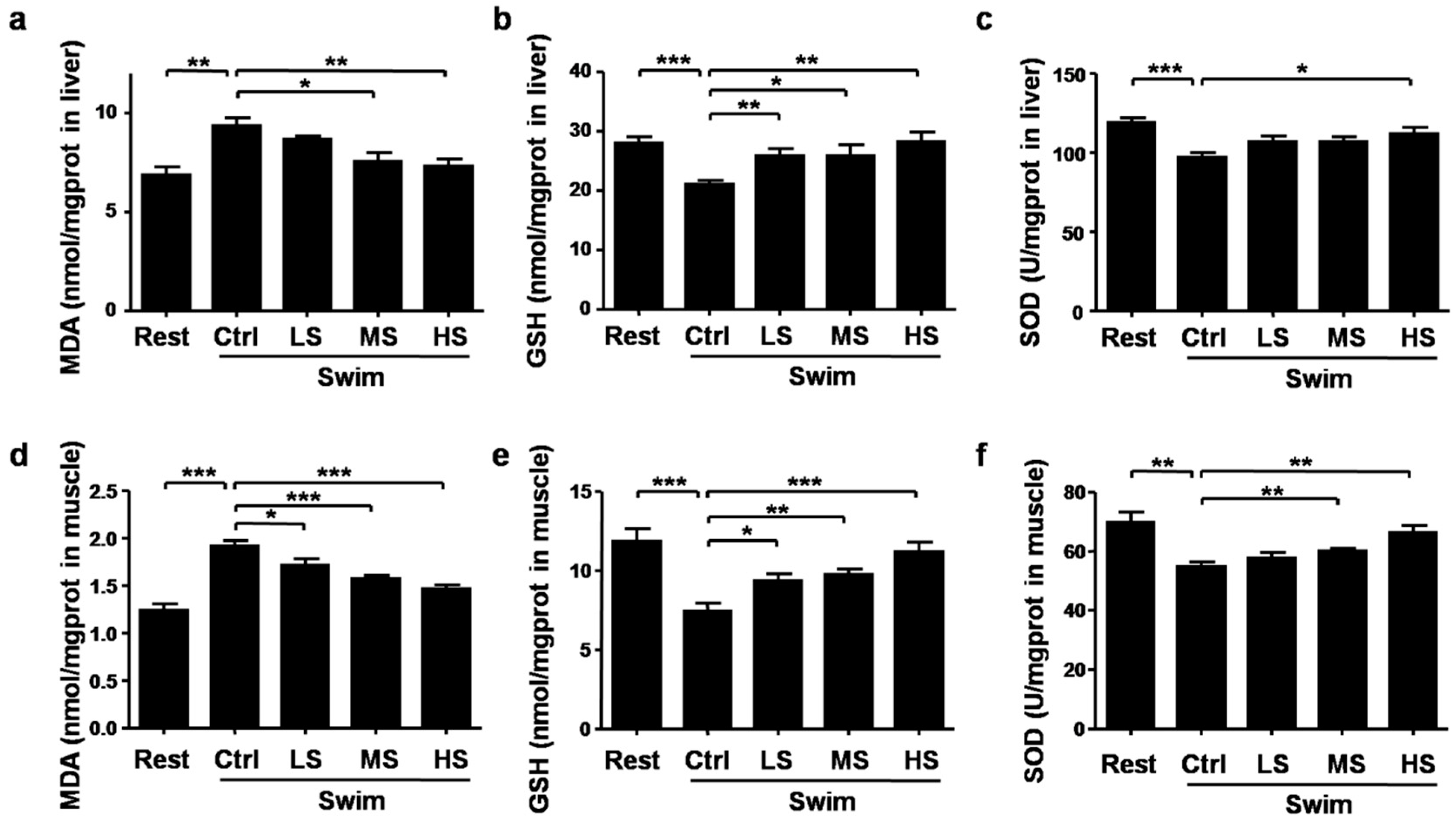
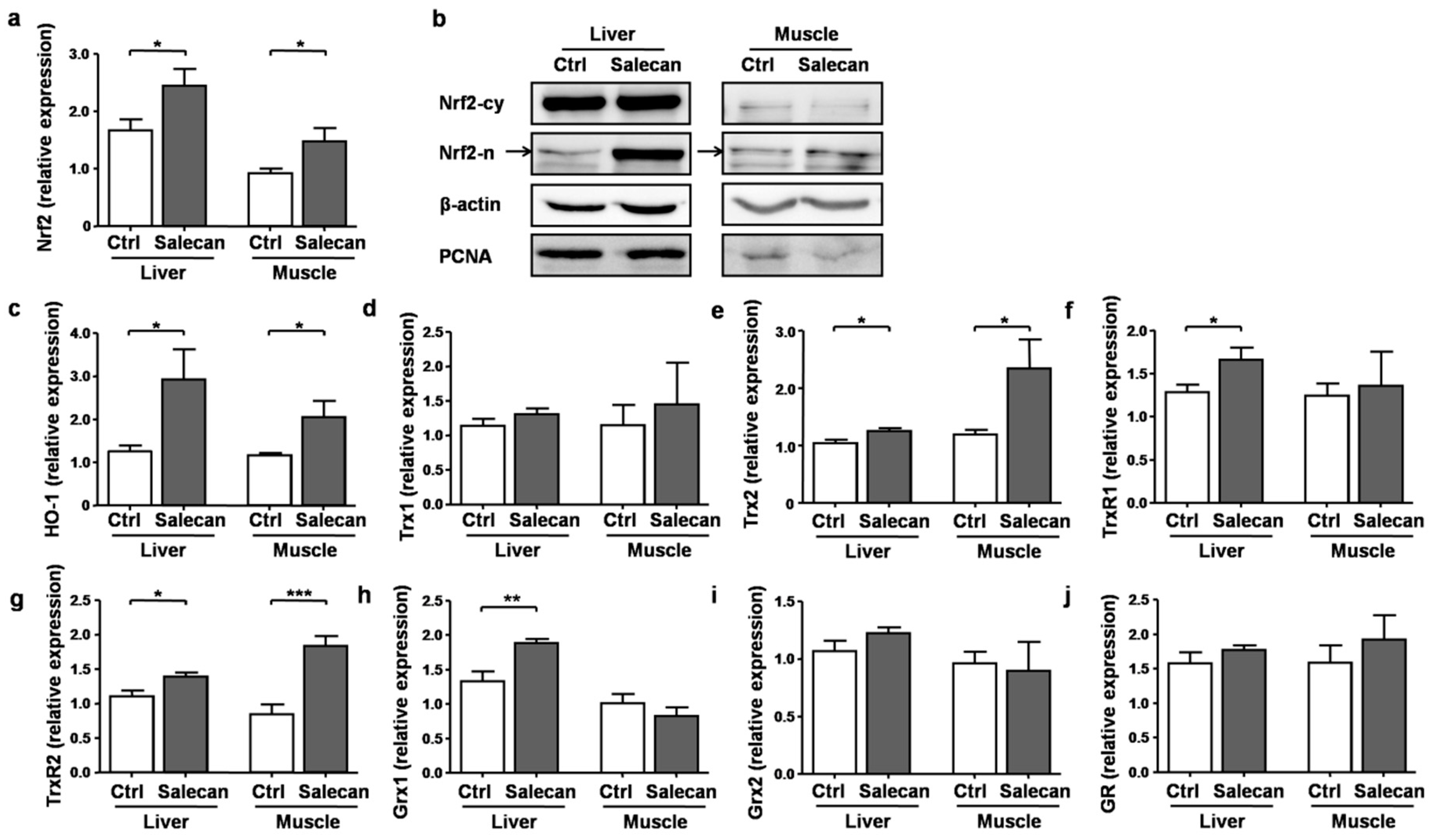
3.5. Salecan Alleviated the Oxidative Stress in Mice after Acute Exercise
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ament, W.; Verkerke, G.J. Exercise and fatigue. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 389–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pageaux, B.; Lepers, R. Fatigue Induced by Physical and Mental Exertion Increases Perception of Effort and Impairs Subsequent Endurance Performance. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoka, R.M.; Duchateau, J. Muscle fatigue: What, why and how it influences muscle function. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jason, L.A.; Evans, M.; Brown, M.; Porter, N. What is fatigue? Pathological and nonpathological fatigue. PM&R 2010, 2, 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Boksem, M.A.; Tops, M. Mental fatigue: Costs and benefits. Brain Res. Rev. 2008, 59, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, D.G.; Lamb, G.D.; Westerblad, H. Skeletal muscle fatigue: Cellular mechanisms. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 287–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent-Braun, J.A.; Fitts, R.H.; Christie, A. Skeletal muscle fatigue. Compr. Physiol. 2012, 2, 997–1044. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Margonis, K.; Fatouros, I.G.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Douroudos, I.; Chatzinikolaou, A.; Mitrakou, A.; Mastorakos, G.; Papassotiriou, I.; Taxildaris, K.; et al. Oxidative stress biomarkers responses to physical overtraining: Implications for diagnosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, S.; Tsukamoto, H.; Yoshimura, S.; Tamaki, T. Relationship between oxidative stress in muscle tissue and weight-lifting-induced muscle damage. Pflugers Arch. 2006, 452, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finsterer, J.; Drory, V.E. Wet, volatile, and dry biomarkers of exercise-induced muscle fatigue. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finsterer, J. Biomarkers of peripheral muscle fatigue during exercise. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2012, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancaccio, P.; Lippi, G.; Maffulli, N. Biochemical markers of muscular damage. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2010, 48, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Dong, W.; Jia, A.; Cai, C.; Zhang, J. A novel soluble beta-glucan salecan protects against acute alcohol-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 1990–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, J. Bacterial glucans: Production, properties, and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 9023–9036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, C.; Vigor, K.; Scott, R.; Jones, P.; Lentfer, H.; Bax, H.J.; Josephs, D.H.; Karagiannis, S.N.; Spicer, J.F. Beta-glucan contamination of pharmaceutical products: How much should we accept? Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2016, 65, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, R.A.; Moghadasian, M.H.; Jones, P.J. Cholesterol-lowering effects of oat beta-glucan. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, A.H.; Kong, Y.; Zhou, M.Y.; Zhu, B.; Wang, S.M.; Zhang, J.F. The chemical and digestive properties of a soluble glucan from Agrobacterium sp. ZX09. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, A.; Zhan, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, B.; Wang, S.; Jia, A.; Dong, W.; Cai, C.; Zhang, J. Results of a 90-day safety assessment study in mice fed a glucan produced by Agrobacterium sp. ZX09. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, L.; Wang, S.; Dong, W.; Jia, A.; Cai, C.; Zhang, J. Protective effects of salecan against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Weng, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Salecan protected against concanavalin A-induced acute liver injury by modulating T cell immune responses and NMR-based metabolic profiles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 317, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Jia, P.; Chen, J.; Xiu, A.; Zhao, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, J. Laxative effects of Salecan on normal and two models of experimental constipated mice. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, T.; Xia, L.; Wang, S.; Hua, Z.; Zhang, J. Supplementation of the diet with Salecan attenuates the symptoms of colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium in mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 1822–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, A.H.; Zhou, M.Y.; Zhu, B.; Wang, S.M.; Zhang, J.F. Rheological properties of Salecan as a new source of thickening agent. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1719–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Duan, Y.; Fang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Polysaccharides from fruit calyx of Physalis alkekengi var. francheti: Isolation, purification, structural features and antioxidant activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Ren, F.; Huang, W.; Ding, R.T.; Zhou, Q.S.; Liu, X.W. Anti-fatigue activity of extracts of stem bark from Acanthopanax senticosus. Molecules 2010, 16, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; Valentino, R.J.; Lucki, I. Assessing substrates underlying the behavioral effects of antidepressants using the modified rat forced swimming test. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Yu, K.Q.; Liu, Y.Y.; Ouyang, M.Z.; Yan, M.H.; Luo, R.; Zhao, X.S. Anti-fatigue activity of polysaccharides extract from Radix Rehmanniae Preparata. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Du, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z. Anti-fatigue activities of polysaccharides extracted from Hericium erinaceus. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortenblad, N.; Westerblad, H.; Nielsen, J. Muscle glycogen stores and fatigue. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 4405–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petri, S.; Korner, S.; Kiaei, M. Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway: Key Mediator in Oxidative Stress and Potential Therapeutic Target in ALS. Neurol. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 878030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Davies, K.J.A.; Forman, H.J. Oxidative stress response and Nrf2 signaling in aging. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 314–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthusamy, V.R.; Kannan, S.; Sadhaasivam, K.; Gounder, S.S.; Davidson, C.J.; Boeheme, C.; Hoidal, J.R.; Wang, L.; Rajasekaran, N.S. Acute exercise stress activates Nrf2/ARE signaling and promotes antioxidant mechanisms in the myocardium. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narasimhan, M.; Rajasekaran, N.S. Exercise, Nrf2 and Antioxidant Signaling in Cardiac Aging. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosker, H.R.; Schols, A.M. Fatigued muscles in COPD but no finishing line in sight. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 693–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, Y. Clinical significance of serum creatine phosphokinase activity levels following exercise. Isr. J. Med. Sci. 1995, 31, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peake, J.M.; Suzuki, K.; Coombes, J.S. The influence of antioxidant supplementation on markers of inflammation and the relationship to oxidative stress after exercise. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomer, R.J.; Goldfarb, A.H.; Wideman, L.; McKenzie, M.J.; Consitt, L.A. Effects of acute aerobic and anaerobic exercise on blood markers of oxidative stress. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- King, D.S.; Baldus, P.J.; Sharp, R.L.; Kesl, L.D.; Feltmeyer, T.L.; Riddle, M.S. Time course for exercise-induced alterations in insulin action and glucose tolerance in middle-aged people. J. Appl. Physiol. 1995, 78, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostojic, S.M. Exercise-induced mitochondrial dysfunction: A myth or reality? Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2016, 130, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Correlation Coefficient | Salecan | Exhaustive Swimming Time |
|---|---|---|
| Lactate | −0.41 ** | −0.23 |
| BUN | −0.32 * | −0.10 |
| CK | −0.44 ** | −0.49 * |
| LDH | −0.33 * | −0.13 |
| ALT | −0.40 ** | −0.32 |
| AST | −0.59 *** | −0.44 * |
| Glucose | 0.49 ** | 0.49 * |
| Muscle glycogen | 0.52 ** | 0.48 * |
| Muscle MDA | −0.71 *** | −0.46 * |
| Muscle GSH | 0.52 ** | 0.41 * |
| Correlation Coefficient | CK | AST | MDA |
|---|---|---|---|
| PK-muscle | 0.58 * | 0.73 ** | 0.27 |
| SDH-liver | −0.50 | −0.65 * | −0.48 |
| SDH-muscle | −0.47 | −0.61 * | −0.53 |
| Na+-K+-ATPase-muscle | 0.49 | 0.66 * | 0.00 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. β-glucan Salecan Improves Exercise Performance and Displays Anti-Fatigue Effects through Regulating Energy Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070858
Xu X, Ding Y, Yang Y, Gao Y, Sun Q, Liu J, Yang X, Wang J, Zhang J. β-glucan Salecan Improves Exercise Performance and Displays Anti-Fatigue Effects through Regulating Energy Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in Mice. Nutrients. 2018; 10(7):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070858
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xi, Yijian Ding, Yunxia Yang, Yan Gao, Qi Sun, Junhao Liu, Xiao Yang, Junsong Wang, and Jianfa Zhang. 2018. "β-glucan Salecan Improves Exercise Performance and Displays Anti-Fatigue Effects through Regulating Energy Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in Mice" Nutrients 10, no. 7: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070858
APA StyleXu, X., Ding, Y., Yang, Y., Gao, Y., Sun, Q., Liu, J., Yang, X., Wang, J., & Zhang, J. (2018). β-glucan Salecan Improves Exercise Performance and Displays Anti-Fatigue Effects through Regulating Energy Metabolism and Oxidative Stress in Mice. Nutrients, 10(7), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070858




