Abstract
A lot of Japanese people are generally known for having a healthy diet, and consume a variety of mushrooms daily. Many studies have reported anti-obesity effects of mushrooms, but few have investigated the effects of consuming a variety of edible mushroom types together in realistic quantities. In this study, we investigated whether supplementation with a variety of mushroom types affects visceral fat accumulation and gut microbiota in mice. The most popular mushroom varieties in Japan were lyophilized and mixed according to their local production ratios. C57BL/6J mice were fed a normal diet, high-fat (HF) diet, HF with 0.5% mushroom mixture (equivalent to 100 g mushrooms/day in humans) or HF with 3% mushroom mixture (equivalent to 600 g mushrooms/day in humans) for 4 weeks. The mice were then sacrificed, and blood samples, tissue samples and feces were collected. Our results show that mushroom intake suppressed visceral fat accumulation and increased the relative abundance of some short chain fatty acid- and lactic acid-producing gut bacteria. These findings suggest that mushroom intake is an effective strategy for obesity prevention.
1. Introduction
Japanese cuisine tends to include a greater diversity of ingredients, such as seafood, vegetables, soybeans and mushrooms, than European or American cuisine. Mushrooms are a particularly common ingredient in the Japanese cuisine, and have been used in cooking since about the 17th century [1]. Japanese people eat about 15 g of various kinds of mushrooms per day, which accounts for 0.68% of their total food intake [2]. Moreover, mushroom consumption is increasing in Japan following improvements in cultivation techniques that have stabilized mushroom supplies, and reports by many studies of the health effects of mushrooms [3,4]. The production volume of Japanese mushrooms was recently estimated at about 440,000 tons per year, with Flammulina velutipes (Enokitake) produced in the largest quantities, followed by Hypsizygus marmoreus (Bunashimeji), Lentinus edodes (Shiitake), Grifola frondosa (Maitake) and Pleurotus eryngii (Eringi or King oyster mushroom) [5]. These mushrooms contain many nutritional components such as dietary fiber, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, niacin, vitamin B6, vitamin D and folic acid [3], and are reported to have anti-obesity effects [6,7,8,9], immunomodulatory effects [10], anti-tumor effects [11], anti-atherosclerotic effects [12] and anti-diabetes effects [13]. However, these studies do not take into account the quantity of mushrooms realistically consumed as part of the diet.
Obesity is caused by an imbalance between the intake and expenditure of energy [14]. Compared with the American diet, the Japanese diet decreases the expression of stress responsive genes and increases that of metabolism-related genes, and thus has an anti-obesity effect [15,16]. However, the recent increase in animal fat in Japanese diets has led to a rapid increase in Japanese patients with lifestyle-related diseases [17,18]. To prevent or reduce obesity, the imbalance between energy intake and expenditure needs to be addressed by improving dietary habits and/or increasing physical activity, though this is difficult to achieve in modern society. Anti-obesity drugs, as an alternative option, have side effects and are expensive [19,20]. Conversely, the habitual consumption of foods with anti-obesity effects may be a cost-effective and manageable way to suppress obesity.
Gut bacteria are involved in host energy regulation and influence disease states such as obesity and diabetes [21,22]. The anti-obesity effects of improvements in gut microbiota have attracted attention following reports of obese mice and humans having a different gut microbiota to that of non-obese mice and humans [21,23]. Habitual diet is a major factor modulating the composition of gut microbiota [24]. Gut bacteria, which have beneficial effects for the host, proliferate using dietary fiber and oligosaccharides [25]. Some types of gut bacteria can produce lactic acid and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) (acetic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid), improve the intestinal environment and regulate host energy metabolism [26,27,28]. Increasing the numbers of these beneficial gut bacteria is suggested to have an anti-obesity effect.
Many studies have reported anti-obesity effects of mushrooms, but few have investigated the effects of consuming a variety of edible mushroom types together in realistic quantities. In this study, we investigated whether supplementation of a high-fat diet with a variety of mushroom types affects visceral fat accumulation and gut microbiota in mice.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Mushroom Mixture
Enokitake was obtained from Mashgarden Corp. (Miyagi, Japan). Bunashimeji, Shiitake, Maitake and Eringi were obtained from Hokuto Corp. (Nagano, Japan). The fresh fruiting bodies of the mushroom were boiled in water for 10 min, then the water and treated mushrooms were freeze-dried. The Japanese mushrooms export/import is very low, and domestic consumption of mushrooms is high in Japan [5]. For this reason, the Japanese mushrooms production and Japanese mushroom consumption are almost the same. The freeze-dried mushroom powders were mixed in accordance with the ratios of Japanese mushroom production, as reported by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan [5] (Table 1). The nutritional composition (protein, fat, carbohydrate, water-soluble dietary fiber, insoluble dietary fiber) of the mushroom mixture was measured at the Japan Functional Food Analysis and Research Center (Fukuoka, Japan) (Table 2).

Table 1.
Proportion of each mushroom species in the mushroom mixture.

Table 2.
Nutritional composition of the mushroom mixture and the mimic mushroom mixture.
2.2. Preparation of the Test Diet
We prepared test diets of 0% (high fat, HF), 0.5% (mushroom low, ML) or 3% (mushroom high, MH) mushroom mixture in a high fat diet (D12079B, Research Diets, New Brunswick, NJ, USA). According to the National Health and Nutrition Survey of Japan [2], Japanese people eat about 15 g of various of mushrooms per day, which accounts for 0.68% of their total food intake. Therefore, consumption of 100 g of fresh mushrooms per day would account for about 5% of the Japanese daily intake. The dry weight of our mushroom mixture is 10% of fresh mushrooms. Thus, intake of test diets containing 0.5% or 3% mushroom mixture was assumed to be equivalent to an intake of about 100 g or 600 g, respectively, of fresh mushrooms per day in humans. To match the macronutrient balance and energy content of the test diets, a mimic mushroom mixture using casein as protein, soybean oil as lipid, cornstarch as carbohydrate, water-soluble dietary fiber as pectin powder, insoluble dietary fiber as cellulose powder and other as cellulose powder (Table 2) was added to the HF and ML diets as shown in Table 3. The energy content of the test diets was 460 kcal per 100 g. Finally, a low-fat diet containing 391 kcal per 100 g (98121701, Research Diets) was used as a control diet (control, CO).

Table 3.
Composition of the test diets.
2.3. Animals
All animal procedures were performed in accordance with the Animal Experiment Guidelines of Tohoku University, and the animal protocol was approved by the Animal Use Committee at Tohoku University (Registration ID No. 2016Noudou-009). Four-week-old male C57BL/6J mice (mean body weight: 18 g) were obtained from SLC, Inc. (Shizuoka, Japan). Mice were housed for the duration of the study under a 12 h/12 h light/dark cycle in a temperature and humidity controlled room, and fed a standard rodent chow (CE-2, CLEA Japan, Inc., Tokyo, Japan) for 1 week to acclimate. At 5 weeks old, the mice were randomly divided into four dietary groups (n = 8 in each group, 4 mice per cage), with each group receiving either CO, HF, ML or MH (Table 3) for four weeks with free access to food and water. At the end of the 4-week period, mice were weighed and blood samples were collected following decapitation under isoflurane anesthesia. Brain, heart, lung, liver, spleen, pancreas, kidney, small intestine, large intestine and white adipose tissues were removed and weighed. Serum samples and organs were stored at −80 °C until use.
2.4. Histological Analysis
Perinephric adipose tissue and liver were fixed in 10% formalin and embedded in paraffin [29]. Vertical sections (4 µm) were cut, mounted on a glass slide, stained with hematoxylin and eosin, and observed using a microscope (BZ-9000; Keyence, Osaka, Japan). The mean adipocyte area was calculated.
2.5. Biochemical Analyses in Serum and Liver
The lipid composition of liver and serum samples was measured as described previously [30]. Triacylglycerol (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) in serum and liver, and phospholipid (PL), glucose, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) in serum were measured using commercial enzyme kits (Wako Pure Chemical, Osaka, Japan). Insulin in serum was determined using an ELISA kit (Morinaga Institute of Biological Science, Kanagawa, Japan). Interleukin (IL)-6 in serum was determined using an ELISA kit (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Adiponectin in serum was determined using an ELISA kit (Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). PL in liver was determined using the method described by Rouser [31]. To examine oxidative stress caused by the diet, we measured the levels of thiobarbituric acid active substances (TBARS) in serum and liver as described previously [32].
2.6. mRNA Expression Analysis
For real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR, total RNA was isolated from perinephric adipose tissue using an RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) [33,34], eluted with 40 µL RNase-free water, and stored at −80 °C until use. To quantify gene expression levels, mRNA levels for adiponectin (Adipoq), fatty acid synthase (Fas), glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase X-linked (G6pdx), hormone-sensitive lipase (Hsl), malic enzyme (Me), peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (Pparγ), sterol regulatory element binding factor 1 c (Srebp-1c), and beta-actin (β-actin) in perinephric adipose tissue were determined with a Thermal Cycler Dice Real Time System (Takara Bio Inc., Otsu, Japan). In brief, cDNA was made using Prime Script RT Master Mix (Takara Bio Inc.) from total RNA in perinephric adipose tissue. This cDNA was subjected to PCR amplification using SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM (Takara Bio Inc.) and gene-specific primers for Adipoq, Fas, G6pdx, Hsl, PPARγ, Srebp-1c and β-actin (Table 4). PCR amplification was performed with an activation step of 95 °C for 10 s, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 5 s (denaturation) and 60 °C for 31 s (extension), and a dissociation stage of 95 °C for 15 s, 60 °C for 30 s and 95 °C for 15 s, for each gene. The β-actin content in test samples was used as the normalization factor.

Table 4.
Primer pairs used for the real-time quantitative PCR analysis.
2.7. Gut Microbiota Analysis
Feces were collected at 0 weeks (start of test period), 2 weeks and 4 weeks just after routine cage changing. Collected feces were pooled into a single-tube for each group, and stored at −80 °C until use. Total genome DNA was extracted from feces using a DNasey Powersoil kit (Qiagen) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The V3-V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene was amplified using forward primer 341 F (5′-TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGCCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG-3′) and reverse primer 806 R (5′-GTCTCGTGGGCTCGGAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGGGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MI, USA). PCR cycling conditions consisted of an initial denaturation of 1 min at 94 °C, and 28 cycles of 10 s at 98 °C, 15 s at 30 °C and 15 s at 68 °C. The presence of the amplified 16S rRNA gene band was verified in an agarose gel. The PCR products were amplified in a second PCR employing Nextera XT Index primer (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). This PCR was run for 1 min at 94 °C, followed by 8 cycles of 10 s at 98 °C, 15 s at 60 °C and 15 s at 68 °C. Amplicon sequencing was performed on the Illumina MiSeq system (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
2.8. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using KaleidaGraph (HULINKS Inc., Tokyo, Japan). Results are expressed as mean ± standard error. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with a Dunnett test. A difference was considered to be significant at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Mushroom Intake on Growth Parameters
There were no significant differences in body weight or weight gain between groups (Table 5). Food intake was significantly greater in the CO group than in the HF, ML or MH groups, but there were no significant differences among groups in energy intake. The ML and MH groups showed a significant decrease in heart weight compared with the CO group. But, there is no significant difference in measured value of the heart (data not shown). The weight of the large intestine in the ML group was significantly greater than that in the HF group. Mushroom intake decreased the weight of white adipose tissue in a dose-dependent manner compared with the HF group, and the MH group showed significant decrease in perinephric adipose tissue weight compared with the HF group. There were no other significant differences in organ weights among the groups. Because there was a significant difference in the perinephric adipose tissue weight, histological analysis was performed by staining perinephric adipose tissue with hematoxylin-eosin. The average size of adipocytes in the MH group was significantly smaller than that in the HF group (Figure 1). These results indicate that mushroom intake suppressed visceral fat accumulation.

Table 5.
Body weights, food intake, tissue weights and large intestine lengths.
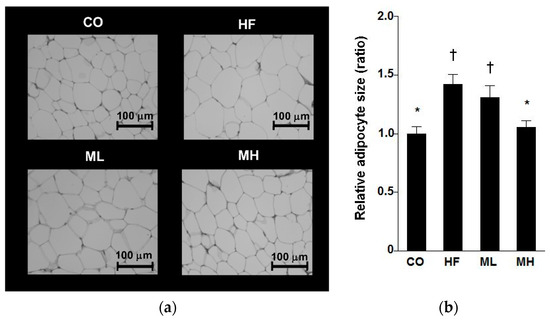
Figure 1.
Effect of mushroom intake on white adipose tissue in mice. (a) Perinephric adipose tissue sections from mice of each group (hematoxylin and eosin, scale bar = 100 µm); (b) Average size of adipocytes in perinephric adipose tissue. Values are mean ± standard error, n = 8. CO: control diet, HF: high fat diet, ML: mushroom low (0.5%) diet, MH: mushroom high (3%) diet. †: p < 0.05 (vs. CO group), *: p < 0.05 (vs. HF group).
3.2. Biochemical Parameters in Serum and Liver
We investigated the effect of mushroom intake on serum lipid metabolism (TC, TG and PL), lipid peroxidation (TBARS), glucose metabolism (glucose and insulin), liver injury (ALT and AST) and inflammation (IL-6) (Table 6). Serum TC levels were significantly higher in the HF, ML and MH groups than the CO group, and significantly higher in the ML group than the HF group. Serum PL levels were significantly higher in the ML and MH groups than the CO group, and significantly higher in the ML group than the HF group. Serum TBARS levels were significantly lower in the HF, ML and MH groups than the CO group, and significantly higher in the ML group than the HF group. The serum level of adiponectin was significantly higher in the MH group than the CO or HF groups. There were no significant differences in serum TG, glucose, insulin, ALT, AST or IL-6 levels among groups. We then examined the effect of mushroom intake on liver TC, TG, PL and TBARS (Table 6). Liver TC levels were significantly higher in the HF, ML and MH groups than the CO group, and significantly higher in the ML group than the HF group. Mushroom intake increased liver TG levels in a dose-dependent manner compared with the HF group, and the TG level was significantly higher in the MH group than the HF group. Liver TBARS levels were significantly lower in the HF and MH groups than the CO group, and significantly higher in the ML group than the HF group. There were no significant differences in liver PL levels among groups. Since the TG level in the liver increased in a dose-dependent manner with mushroom intake, a histological analysis was performed by staining liver with hematoxylin-eosin to observe lipid droplets. An increase in the number of lipid droplets in the liver was observed in the HF group compared with the CO group, but there were no differences among the HF, ML and MH groups (Figure 2). These results suggest that mushroom intake did not significantly affect lipid or glucose metabolism, but increased serum adiponectin levels.

Table 6.
Biochemical parameters of serum and liver.
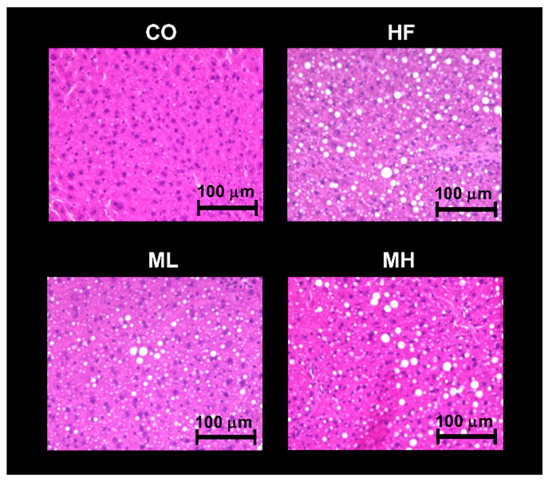
Figure 2.
Effect of mushroom intake on liver histology in mice. Liver sections from mice of each group (hematoxylin and eosin, scale bar = 100 µm). CO: control diet, HF: high fat diet, ML: mushroom low (0.5%) diet, MH: mushroom high (3%) diet.
3.3. mRNA Expression in Perinephric Adipose Tissue
Mushroom intake decreased the weight of perinephric adipose tissue and suppressed adipocyte hypertrophy. To elucidate the mechanism underlying this effect, mRNA levels of lipid metabolism-related genes in perinephric adipose tissue were measured using real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR. As shown in Table 7, the fatty acid synthesis-related genes Fas, Me, G6pdx and Srebp-1c showed different responses. Me expression was significantly decreased in the HF and ML groups compared with the CO group. G6pdx expression increased with mushroom intake in a dose-dependent manner compared with the HF group, and was significantly higher in the MH group than the CO or HF groups. Srebp-1c expression was significantly higher in the HF and ML groups than the CO group, and decreased with mushroom intake in a dose-dependent manner compared with HF group so that Srebp-1c expression was significantly lower in the MH group than the HF group. The expression of Hsl, a lipolysis-related gene, increased with mushroom intake in a dose-dependent manner, and was significantly higher in the MH group than the CO or HF groups. The expression of Fas, a gene related to the synthesis of fatty acids, showed no significant differences among groups. The expression of Pparγ, a cell differentiation-related gene, increased with mushroom intake in a dose-dependent manner, and was significantly higher in the MH group than the CO group. These results indicate that dietary mushroom intake suppressed fatty acid synthesis, promoted lipolysis and promoted differentiation and increase of adipocytes, thereby inhibiting fat accumulation in white adipose tissue. As the MH group had increased serum adiponectin levels (Table 6), we measured Adipoq expression levels in adipocytes to determine whether mushroom intake regulates adipocyte adiponectin production. The results showed that adipocyte Adipoq expression increased with mushroom intake in a dose-dependent manner, and was significantly increased the MH group compared with the CO and HF groups (Table 7). These results indicate that dietary mushroom intake promoted adiponectin production in adipocytes.

Table 7.
mRNA expression levels in perinephric adipose tissue.
3.4. Effects of Mushroom Intake on Gut Microbiota
At the phylum level after 2 weeks, the relative abundance of Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria was lower in the HF, ML and MH groups than the CO group, and the relative abundance of Firmicutes and Proteobacteria was higher in the HF, ML and MH groups than the CO group (Figure 3). There were no significant changes at the phylum level after 2 weeks among the HF, ML and MH groups. At the phylum level after 4 weeks, the relative abundance of Bacteroidetes was lower in the HF, ML and MH groups than the CO group, and lower in the ML and MH groups than the HF group. The relative abundance of Firmicutes was higher in the HF, ML and MH groups than the CO group, and higher in the ML and MH groups than the HF group. The relative abundance of Proteobacteria was higher in the HF group than the CO group, and lower in the ML and MH groups than the HF group. The relative abundance of Actinobacteria was lower in the HF group than the CO group, and higher in the ML and MH groups than the HF group. The relative abundance of Deferribacteres and Verrucomicrobia was lower in the MH group than the HF group. There were no significant differences in the relative abundance of Tenericutes, TM7 or “Other” among the HF, ML and MH groups. The relative abundance of each bacterial phylum is given in Table S1. We focused on the gut bacterial genera whose relative abundance in the MH group after 4 weeks was more than 2-fold or less than half that of the HF group after 4 weeks. At the genus level after 2 weeks, there were significant differences in the gut microbiota between the HF and CO groups, but not among the HF, ML and MH groups. At the genus level after 4 weeks, the gut microbiota of the ML and MH groups was significantly different to that of the HF group. The ML and MH groups showed a tendency towards increased SCFA-producing bacteria (Allobaculum, Bifidobacterium and Ruminococcus) and lactic acid-producing bacteria (Lactobacillus, Lactococcus and Streptococcus) compared with the HF group. The MH group tended to have increased Adlercreutzia and Sutterella and decreased Bacteroides, Prevotella, Mucispirillum, Dorea, Roseburia, Anaerotruncus, Oscillospira, Escherichia and Akkermansia compared with the HF group. The relative abundance of each bacterial genus is given in Table S2. These results suggest that the gut microbiota composition changed over time with mushroom intake, leading to an increase in some SCFA- and lactic acid-producing bacteria at 4 weeks.
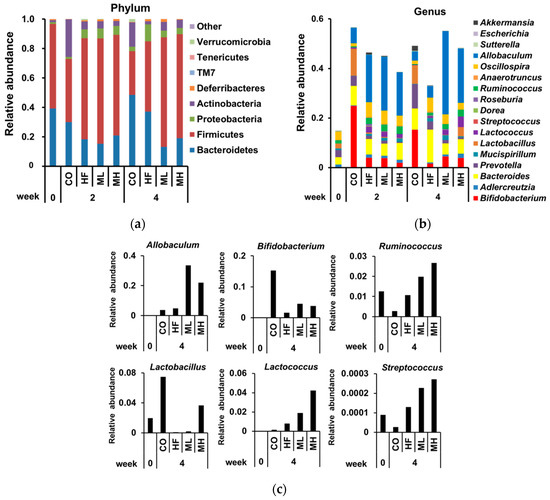
Figure 3.
Modulation of gut microbiota by mushroom intake. Fecal microbiota composition of mice after 0 weeks, 2 weeks and 4 weeks on a control diet (CO), high fat diet (HF), mushroom low (0.5%) diet (ML), or mushroom high (3%) diet (MH). (a) Phylum level and (b) genus level taxonomic distributions of fecal microbial communities determined by next generation sequencing. (c) Relative abundance of short chain fatty acid-producing bacteria (Allobaculum, Bifidobacterium and Ruminococcus) and lactic acid-producing bacteria (Lactobacillus, Lactococcus and Streptococcus).
4. Discussion
Our study shows that dietary intake of a variety of mushrooms is effective in preventing obesity by suppressing visceral fat accumulation. Similarly, many studies have reported that the dietary fiber contained in mushrooms has an anti-obesity effect [8,35,36]. Mushrooms are known to contain a large amount of dietary fiber [37], and the mushroom mixture used in this study contained 5.20% water-soluble dietary fiber and 30.5% insoluble dietary fiber (Table 2). The dietary fiber contained in mushrooms is glucan, lignin, pectin and chitin [38,39]. Although water-soluble dietary fiber has a weaker anti-obesity effect than insoluble dietary fiber [40], pectin, which is water-soluble, has the effect of suppressing feeding [41]. Furthermore, water-soluble dietary fibers have been shown to prevent diabetes [42], improve serum cholesterol and increase SCFA concentrations in the body [43]. Insoluble dietary fibers, such as insoluble glucan, lignin and chitin, increase the amount of feces because of their hygroscopic properties, and promote lipid adsorption and discharge [40]. We hypothesized that the dietary fiber component of the mushrooms was likewise involved in the prevention of fat accumulation in our study. Pectin and cellulose were added to the HF diet to match the amount of dietary fiber in the MH diet; nevertheless, the anti-obesity effect of the MH diet was greater than that of the HF group. Thus, we suggest that intake of different types of dietary fiber from a variety of mushrooms suppresses fat accumulation. Furthermore, dietary fiber increases the weight and length of colon [44]. We hypothesized that the dietary fiber of mushrooms involved in the increase in weight and length of large intestine in our study.
SREBP-1c enhances the gene expression of fatty acid synthesis factors such as FAS, inducing the conversion of glucose to fatty acids and triacylglycerols for storage [45,46]. There have been reports that mushroom components [47,48] and 25-hydroxyvitamin D [49] suppress SREBP-1c and FAS, but no studies have examined the effects of edible mushroom intake in mice. The results of this study show that mushroom intake decreased Srebp-1c gene expression in a dose-dependent manner compared with the HF group. Thus, we show that mushrooms inhibited the synthesis of fatty acids even when ingested as part of a diet. Moreover, our results show that mushroom intake increased the gene expression of G6pdx, which is involved in fatty acid synthesis. G6PDH produces nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate [50], which suppresses oxidation along with antioxidant enzymes [51]; thus, G6pdx activation may have an antioxidant effect.
In this study, mushroom intake increased the gene expression levels of Pparγ and Adipoq. PPARγ regulates the differentiation from pre-adipocyte to adipocyte [52]. Obesity occurs through an increase in the number and size of adipocytes with the excessive accumulation of triacylglycerols; therefore, a PPARγ-mediated increase in adipocytes enhances obesity. Moreover, high levels of PPARγ expression increase the number of small adipocytes and decrease number of large ones [53]. Small adipocytes reduce the production of inflammatory cytokines that promote metabolic syndrome, and increase the production of adiponectin that prevents metabolic syndrome [54]. We hypothesized that mushroom intake suppressed adipocyte hypertrophy through activation of PPARγ, because mushroom intake suppressed the enlargement of adipocytes and promoted adiponectin production in the present rodent study.
Mushroom intake also affected the gut microbiota of our HF diet-fed mice. Gut microbiota has been shown to affect the progression of obesity in the host. Obese mice exhibit high Firmicutes and low Bacteroidetes at the phylum level compared with normal mice [19,21]. Intake of dietary fiber decreases Firmicutes and increases Bacteroidetes [55]. In this study, despite its suppression of obesity, mushroom intake increased Firmicutes and decreased Bacteroidetes compared with the HF group. This was the result of an increase in the Firmicutes genera Allobaculum, Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, Ruminococcus and Streptococcus. Some Firmicutes gut bacteria grow using dietary fiber and produce lactic acid and SCFAs [56]. This increase in intestinal lactic acid results in the proliferation of SCFA-producing bacteria, prevention of intestinal inflammation and suppression of obesity [25]. In the present study, an increase in lactic acid-producing bacteria (Lactobacillus, Lactococcus and Streptococcus) and SCFA-producing bacteria (Allobaculum, Bifidobacterium and Ruminococcus) was observed with mushroom intake. This could be because these bacteria thrived on the dietary fiber from the mushrooms [28,57,58,59]. SCFAs produced by these bacteria promote energy metabolism in the host [26]. Thus, we hypothesized that mushroom intake increased SCFA concentrations in the body, and that these played a role in suppressing fat accumulation.
TG in the liver accumulates following absorption of dietary lipids from the small intestine or synthesis in the liver [60]. The chitin/chitosan contained in mushrooms has been shown to suppress accumulation of liver TG by suppressing the absorption of diet-derived lipid [61,62]. However, in the present study, the TG level in the liver increased with mushroom intake. One explanation for this is that mushroom intake promoted Hsl expression in adipose tissues, which induces the breakdown of adipocyte TG into free fatty acids that are then released into the blood. When not consumed as energy, free fatty acids reach the liver where they are resynthesized as TG [63]. Therefore, liver TG in the MH group may have been elevated because of increased free fatty acids following the promotion of TG decomposition in adipocytes. Notably, there were no significant differences in serum ALT or AST or liver TBARS between the HF group and the ML and MH groups. Thus, we suggest that the liver TG accumulation resulting from mushroom intake did not cause inflammation and oxidative stress. In addition, histological analysis showed that there were no significant differences in the lipid droplets in the liver between the HF and MH groups, indicating that mushroom intake did not adversely affect the liver. It is known that liver TG and lipid droplets are increased by Shiitake, among the edible mushrooms [64,65], possibly as a result of the eritadenine content of Shiitake [65,66]. Eritadenine inhibits S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase activity in the liver and increases S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine concentration, suppressing phosphatidylcholine (PC) synthesis by methylation of phosphatidylamine (PE) and increasing PE concentration [66]. The PC/PE ratio affects cell membrane permeability of the liver [67]. Intake of Shiitake decreases the PC/PE ratio of the liver [65,66], which promotes fatty liver. Therefore, we suggest that the Shiitake contained in our test diet played a role in the increase in liver TG following mushroom intake. To compensate for this effect, it may be beneficial to eat foods that promote the metabolism of liver fat, such as the EPA and DHA contained in fish, at the same time as eating mushrooms [68]. Further studies are needed to elucidate the mechanisms underpinning the metabolic effects of mushroom intake.
5. Conclusions
Our results show that mushroom intake suppressed fat accumulation by inhibiting fatty acid synthesis and promoting lipolysis of visceral fat. Mushroom intake also suppressed adipocyte enlargement and promoted adiponectin production. Moreover, mushroom intake caused some lactic acid- and SCFA-producing bacteria to proliferate, possibly because of the dietary fiber content of the mushrooms. Thus, we speculate that mushroom intake increases the production of SCFAs, which promote energy metabolism in the host and play a role in suppressing fat accumulation. In conclusion, our findings suggest that mushroom intake is an effective strategy for the prevention of obesity.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/10/5/610/s1, Table S1: The relative abundance of gut bacterial phyla in mice. Table S2: The relative abundance of gut bacterial genera in mice.
Author Contributions
T.S., K.M., K.O. and T.T. conceived and designed the experiments; T.S. and M.K. performed the experiments; T.S. and T.T. analyzed the data; T.S., K.M. and T.T. wrote the paper.
Acknowledgments
We thank Alice Tait, from Edanz Group (www.edanzediting.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
Three of the authors (T.S., K.M. and K.O.) are salaried employees of the Hokuto Corporation, which cultivated some of the mushrooms used in this study. The remaining authors (M.K. and T.T.) have no conflicts of interest to disclose. All research funding for this study was provided by the Hokuto Corporation.
References
- Sugahara, T. Japanese people and mushrooms. J. Cook. Sci. Jpn. 2001, 34, 313–320. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- National Health and Nutrition Survey Report. 2015. Available online: http://www.mhlw.go.jp/bunya/kenkou/eiyou/h27-houkoku.html (accessed on 1 June 2016).
- Valverde, M.E.; Hernández-Pérez, T.; Paredes-López, O. Edible mushrooms: Improving human health and promoting quality life. Int. J. Microbiol. 2015, 2015, 376387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Nie, S. The structure of mushroom polysaccharides and their beneficial role in health. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3205–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Survey on Production Forest Products Production Statistics. 2014. Available online: https://www.e-stat.go.jp/stat-search/files?page=1&layout=datalist&lid=000001149816 (accessed on 1 June 2016).
- Mizutani, T.; Inatomi, S.; Inazu, A.; Kawahara, E. Hypolipidemic effect of Pleurotus eryngii extract in fat-loaded mice. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2010, 56, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handayani, D.; Chen, J.; Meyer, B.J.; Huang, X.-F. Dietary shiitake mushroom (Lentinus edodes) prevents fat deposition and lowers triglyceride in rats fed a high-fat diet. J. Obes. 2011, 2011, 258051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, M.-Y.; Ko, W.-C.; Lin, L.-Y. Hypolipidemic and antioxidant activity of enoki mushrooms (Flammulina velutipes). BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 352385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iuchi, T.; Hosaka, T.; Shiroishi, M.; Ono, H.; Inukai, K.; Sumita, T.; Sakai, G.; Katayama, S.; Awata, T. Influence of treatment with extracts of Hypsyzigus marmoreus mushroom on body composition during obesity development in kk-ay mice. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2015, 61, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetvicka, V.; Vetvickova, J. Immune-enhancing effects of maitake (Grifola frondosa) and shiitake (Lentinula edodes) extracts. Ann. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Masuda, Y.; Inoue, H.; Ohta, H.; Miyake, A.; Konishi, M.; Nanba, H. Oral administration of soluble β-glucans extracted from Grifola frondosa induces systemic antitumor immune response and decreases immunosuppression in tumor-bearing mice. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Kobayashi, C.; Tomita, T.; Inatomi, S.; Ikeda, M. Antiatherosclerotic effect of the edible mushrooms Pleurotus eryngii (eringi), Grifola frondosa (maitake), and Hypsizygus marmoreus (bunashimeji) in apolipoprotein e-deficient mice. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.; Xun, M.; Wutong, W. Anti-diabetic effect of an α-glucan from fruit body of maitake (Grifola frondosa) on kk-ay mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofbauer, K. Molecular pathways to obesity. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuduki, T.; Takeshika, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Igarashi, M.; Miyazawa, T. DNA microarray analysis of rat liver after ingestion of japanese and american food. J. Jpn. Soc. Nutr. Food Sci. 2008, 61, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, M.; Ohuo, H.; Oki, K. Westernization of Lifestyle Causes Obesity-Associated Metabolic Disorders in the Japanese Population. J. Obes. Eat. Disord. 2016, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kitano, Y.; Honma, T.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Jibu, Y.; Kawakami, Y.; Tsuduki, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Miyazawa, T. Effects of historical differences in components of the japanese diet on the risk of obesity in mice. J. Jpn. Soc. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 67, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egusa, G.; Watanabe, H.; Ohshita, K.; Fujikawa, R.; Yamane, K.; Okubo, M.; Kohno, N. Influence of the extent of westernization of lifestyle on the progression of preclinical atherosclerosis in Japanese subjects. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2002, 9, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enzi, G.; Baritussio, A.; Marchiori, E.; Crepaldi, G. Short-term and long-term clinical evaluation of a non-amphetaminic anorexiant (mazindol) in the treatment of obesity. J. Int. Med. Res. 1976, 4, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.G.; Park, C.Y. Anti-obesity drugs: A review about their effects and safety. Diabetes Metab. J. 2012, 36, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Bibiloni, R.; Knauf, C.; Waget, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Bäckhed, F.; Turnbaugh, P.; Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R.D.; Gordon, J.I. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11070–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, M.A.; Bird, A.R. The impact of diet and lifestyle on gut microbiota and human health. Nutrients 2014, 7, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremaroli, V.; Bäckhed, F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 2012, 489, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Besten, G.; Van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.-T.; Cheng, P.-C.; Pan, T.-M. Anti-obesity effects of gut microbiota are associated with lactic acid bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasaki, M.; Honma, T.; Yanaka, M.; Sato, K.; Shinohara, N.; Ito, J.; Tanaka, Y.; Tsuduki, T.; Ikeda, I. Continuous intake of a high-fat diet beyond one generation promotes lipid accumulation in liver and white adipose tissue of female mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuduki, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Sakamoto, Y. High dietary fat intake during lactation promotes the development of social stress-induced obesity in the offspring of mice. Nutrients 2015, 7, 5916–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouser, G.; Fleischer, S.; Yamamoto, A. Two dimensional thin layer chromatographic separation of polar lipids and determination of phospholipids by phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids 1970, 5, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuzuki, T.; Tokuyama, Y.; Igarashi, M.; Miyazawa, T. Tumor growth suppression by α-eleostearic acid, a linolenic acid isomer with a conjugated triene system, via lipid peroxidation. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuduki, T.; Kikuchi, I.; Kimura, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Miyazawa, T. Intake of mulberry 1-deoxynojirimycin prevents diet-induced obesity through increases in adiponectin in mice. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuduki, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Sakamoto, Y. High dietary cholesterol intake during lactation promotes development of fatty liver in offspring of mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, M.; Ohashi, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Sonoyama, K.; Nakano, M. Cholesterol-lowering effects of maitake (Grifola frondosa) fiber, shiitake (Lentinus edodes) fiber, and enokitake (Flammulina velutipes) fiber in rats. Exp. Biol. Med. 2001, 226, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caz, V.; Gil-Ramírez, A.; Largo, C.; Tabernero, M.; Santamaría, M.N.; Martin-Hernandez, R.; Marín, F.R.; Reglero, G.; Soler-Rivas, C. Modulation of cholesterol-related gene expression by dietary fiber fractions from edible mushrooms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7371–7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nile, S.H.; Park, S.W. Total, soluble, and insoluble dietary fibre contents of wild growing edible mushrooms. Czech J. Food Sci. 2014, 32, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurasawa, S.; Sugahara, T.; Hayashi, J. Proximate and dietary fibre analysis of mushrooms. Nippon Shokuhin Kogyo Gakkaishi 1982, 29, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzi, P.; Pizzoferrato, L. Beta-glucans in edible mushrooms. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isken, F.; Klaus, S.; Osterhoff, M.; Pfeiffer, A.F.; Weickert, M.O. Effects of long-term soluble vs. Insoluble dietary fiber intake on high-fat diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6J mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, C.L.; Thomson, L.M.; Williams, P.A.; Ross, A.W. Soluble fermentable dietary fibre (pectin) decreases caloric intake, adiposity and lipidaemia in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannan, J.; Ali, L.; Rokeya, B.; Khaleque, J.; Akhter, M.; Flatt, P.; Abdel-Wahab, Y. Soluble dietary fibre fraction of Trigonella foenum-graecum (fenugreek) seed improves glucose homeostasis in animal models of type 1 and type 2 diabetes by delaying carbohydrate digestion and absorption, and enhancing insulin action. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 97, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzano, L.A. Effects of soluble dietary fiber on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and coronary heart disease risk. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2008, 10, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Jørgensen, H.; Eggum, B.O. The influence of dietary fibre on body composition, visceral organ weight, digestibility and energy balance in rats housed in different thermal environments. Br. J. Nutr. 1995, 73, 687–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. The srebp pathway: Regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell 1997, 89, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.D.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Srebps: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.; Kim, J.; Ryoo, I.; Kim, Y.; Choo, S.; Yoo, I.; Min, B.; Na, M.; Hattori, M.; Bae, K. Lanostane triterpenes from Ganoderma lucidum suppress the adipogenesis in 3T3-l1 cells through down-regulation of SREBP-1c. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 5577–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanagasabapathy, G.; Malek, S.; Mahmood, A.; Chua, K.; Vikineswary, S.; Kuppusamy, U. Beta-glucan-rich extract from Pleurotus sajor-caju (Fr.) singer prevents obesity and oxidative stress in C57BL/6J mice fed on a high-fat diet. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 185259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, L.; Watanabe, M.; Ryoden, Y.; Usuda, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Khambu, B.; Takashima, M.; Sato, S.; Sakai, J.; Nagasawa, K. Vitamin D metabolite, 25-hydroxyvitamin d, regulates lipid metabolism by inducing degradation of SREBP/SCAP. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupte, S.A.; Levine, R.J.; Gupte, R.S.; Young, M.E.; Lionetti, V.; Labinskyy, V.; Floyd, B.C.; Ojaimi, C.; Bellomo, M.; Wolin, M.S. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-derived nadph fuels superoxide production in the failing heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2006, 41, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecker, P.A.; Lionetti, V.; Ribeiro, R.F.; Rastogi, S.; Brown, B.H.; O’Connell, K.A.; Cox, J.W.; Shekar, K.C.; Gamble, D.; Sabbah, H.N. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency increases redox stress and moderately accelerates the development of heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2012, 112, 969576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.D.; Spiegelman, B.M. PPARγ: A nuclear regulator of metabolism, differentiation, and cell growth. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 37731–37734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuno, A.; Tamemoto, H.; Tobe, K.; Ueki, K.; Mori, Y.; Iwamoto, K.; Umesono, K.; Akanuma, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Horikoshi, H. Troglitazone increases the number of small adipocytes without the change of white adipose tissue mass in obese zucker rats. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, J.; Richards, A.; Hickman, I.; Macdonald, G.; Prins, J. Adiponectin—A key adipokine in the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2006, 8, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trompette, A.; Gollwitzer, E.S.; Yadava, K.; Sichelstiel, A.K.; Sprenger, N.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Blanchard, C.; Junt, T.; Nicod, L.P.; Harris, N.L. Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, H.J.; Duncan, S.H.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P. Links between diet, gut microbiota composition and gut metabolism. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2015, 74, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douillard, F.P.; De Vos, W.M. Functional genomics of lactic acid bacteria: From food to health. Microb. Cell Fact. 2014, 13, S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Pang, X.; Xu, J.; Kang, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Structural changes of gut microbiota during berberine-mediated prevention of obesity and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-fed rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, S.; Toh, H.; Hase, K.; Oshima, K.; Nakanishi, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Tobe, T.; Clarke, J.M.; Topping, D.L.; Suzuki, T. Bifidobacteria can protect from enteropathogenic infection through production of acetate. Nature 2011, 469, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Hsieh, J.; Adeli, K.; Lewis, G.F. Gut-liver interaction in triglyceride-rich lipoprotein metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 301, E429–E446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacour, A.C.; Silva, M.E.; Cecon, P.R.; Bambirra, E.A.; Vieira, E.C. Effect of dietary chitin on cholesterol absorption and metabolism in rats. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 1992, 38, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyrinck, A.M.; Bindels, L.B.; De Backer, F.; Pachikian, B.D.; Cani, P.D.; Delzenne, N.M. Dietary supplementation with chitosan derived from mushrooms changes adipocytokine profile in diet-induced obese mice, a phenomenon linked to its lipid-lowering action. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, D.; Karpe, F.; Lafontan, M.; Frayn, K. Physical activity and exercise in the regulation of human adipose tissue physiology. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 157–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, L.C.; Smith, B.J.; Clarke, S.L.; Marlow, D.; D’Offay, J.M.; Kuvibidila, S.R. Differential effects of shiitake-and white button mushroom-supplemented diets on hepatic steatosis in C57BL/6 mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 3074–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handayani, D.; Meyer, B.J.; Chen, J.; Brown, S.H.; Mitchell, T.W.; Huang, X.-F. A high-dose shiitake mushroom increases hepatic accumulation of triacylglycerol in rats fed a high-fat diet: Underlying mechanism. Nutrients 2014, 6, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, K.; Yamakawa, A. Dietary eritadenine-induced alteration of molecular species composition of phospholipids in rats. Lipids 1996, 31, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Agellon, L.B.; Allen, T.M.; Umeda, M.; Jewell, L.; Mason, A.; Vance, D.E. The ratio of phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylethanolamine influences membrane integrity and steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudyal, H.; Panchal, S.K.; Ward, L.C.; Brown, L. Effects of ALA, EPA and DHA in high-carbohydrate, high-fat diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).